Deck 6: Intercompany Profit Transactions Plant Assets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Intercompany Profit Transactions Plant Assets
1
Pied Imperial Corporation acquired a 90% interest in Somest Corporation in 2012 when Somest's book values were equivalent to fair values. Somest sold equipment with a book value of $80,000 to Pied for $130,000 on January 1, 2014. Pied is fully depreciating the equipment over a 4-year period by using the straight-line method. Somest reported net income for 2014 was $320,000. Pied's 2014 income from Somest was
A) $249,250.
B) $250,500.
C) $254,250.
D) $288,000.
A) $249,250.
B) $250,500.
C) $254,250.
D) $288,000.
C
2
Parrot Corporation acquired a 70% interest in Swifti Corp. on January 1, 2013, when Swifti's book values and fair values were equivalent. On January 1, 2014, Swifti sold a building with a book value of $60,000 to Parrot for $80,000. The building had a remaining life of five years, no salvage value, and was depreciated by the straight-line method. Swifti reported net income of $200,000 for 2014. What was the noncontrolling interest share for 2014?
A) $54,000
B) $55,200
C) $60,000
D) $128,800
A) $54,000
B) $55,200
C) $60,000
D) $128,800
B
3
Peregrine Corporation acquired an 80% interest in Serine Corporation in 2011 at a time when Serine's book values and fair values were equal to one another. On January 1, 2014, Serine sold a truck with a $55,000 book value to Peregrine for $100,000. Peregrine is depreciating the truck over 10 years using the straight-line method. The truck has no salvage value. Separate incomes for Peregrine and Serine for 2014 were as follows: 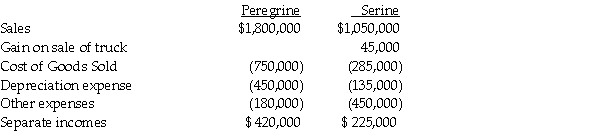 Peregrine's investment income from Serine for 2014 was
Peregrine's investment income from Serine for 2014 was
A) $108,000.
B) $144,000.
C) $147,600.
D) $180,000.
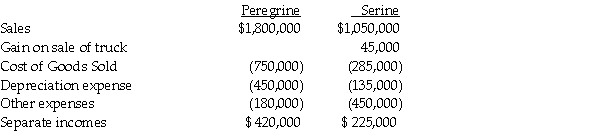 Peregrine's investment income from Serine for 2014 was
Peregrine's investment income from Serine for 2014 wasA) $108,000.
B) $144,000.
C) $147,600.
D) $180,000.
C
4
Use the following information to answer the question(s) below.
On January 1, 2012, Shrimp Corporation purchased a delivery truck with an expected useful life of five years, and a salvage value of $8,000. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp sold the truck to Pacet Corporation. Pacet assumed the same salvage value and remaining life of three years used by Shrimp. Straight-line depreciation is used by both companies. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp recorded the following journal entry:
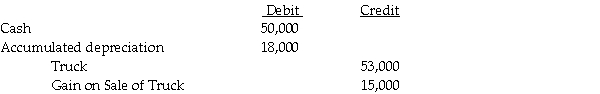 Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
In preparing the consolidated financial statements for 2014, the elimination entry for depreciation expense was a
A) debit for $5,000.
B) credit for $5,000.
C) debit for $15,000.
D) credit for $15,000.
On January 1, 2012, Shrimp Corporation purchased a delivery truck with an expected useful life of five years, and a salvage value of $8,000. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp sold the truck to Pacet Corporation. Pacet assumed the same salvage value and remaining life of three years used by Shrimp. Straight-line depreciation is used by both companies. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp recorded the following journal entry:
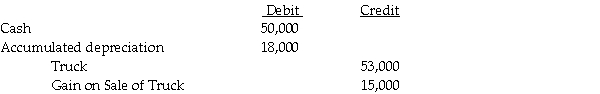 Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.In preparing the consolidated financial statements for 2014, the elimination entry for depreciation expense was a
A) debit for $5,000.
B) credit for $5,000.
C) debit for $15,000.
D) credit for $15,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An elimination entry at December 31, 2014 for the intercompany sale will include a
A) credit of $6,000 to Depreciation Expense.
B) credit of $6,000 to Accumulated Depreciation.
C) credit of $6,000 to Equipment.
D) credit of $6,000 to Gain on Sale of Equipment.
A) credit of $6,000 to Depreciation Expense.
B) credit of $6,000 to Accumulated Depreciation.
C) credit of $6,000 to Equipment.
D) credit of $6,000 to Gain on Sale of Equipment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is correct?
A) No consolidation working paper entry is required for this transaction in 2014.
B) A consolidation working paper entry is required only if the subsidiary was less than 100% owned in 2014.
C) A consolidation working paper entry is required each year that Sidd has the land.
D) A consolidated working paper entry was required only if the land was held for resale in 2014.
A) No consolidation working paper entry is required for this transaction in 2014.
B) A consolidation working paper entry is required only if the subsidiary was less than 100% owned in 2014.
C) A consolidation working paper entry is required each year that Sidd has the land.
D) A consolidated working paper entry was required only if the land was held for resale in 2014.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Parrot Company owns all the outstanding voting stock of Southern Manufacturing. On January 1, 2014, Parrot sold machinery to Southern at its book value of $24,000. Parrot had the machinery three years before selling it and used an eight-year straight-line depreciation method, with zero salvage value. Southern will use the straight-line depreciation method, and assumes the machine has five years remaining and no salvage value. In the 2014 consolidating working papers, the depreciation expense
A) required no adjustment.
B) decreased by $4,800.
C) increased by $4,800
D) increased by $8,000.
A) required no adjustment.
B) decreased by $4,800.
C) increased by $4,800
D) increased by $8,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Pogo Corporation acquired a 75% interest in Sperry Corporation on January 1, 2011 at a cost equal to book value and fair value. In the same year Sperry sold land costing $25,000 to Pogo for $50,000. On July 1, 2014, Pogo sold the land to an unrelated party for $85,000. What was the gain on the sale of the land on the consolidated income statement for 2014?
A) $25,000
B) $35,000
C) $45,000
D) $60,000
A) $25,000
B) $35,000
C) $45,000
D) $60,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
After eliminating/adjusting entries are prepared, what was the intercompany sale impact on the consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2014? 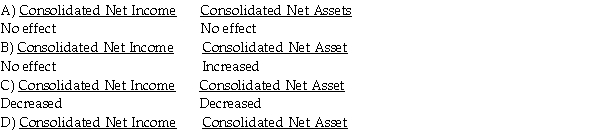 Decreased No effect
Decreased No effect
 Decreased No effect
Decreased No effect
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Assume an upstream sale of machinery occurs on January 1, 2014. The parent owns 70% of the subsidiary. There is a gain on the intercompany transfer and the machine has five remaining years of useful life and no salvage value. Straight-line depreciation is used. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Noncontrolling interest share for 2014 is equal to: subsidiary income for 2014 multiplied by 30%.
B) Noncontrolling interest share for 2014 is equal to: (subsidiary income for 2014 minus the gain on sale plus the excess depreciation expense) multiplied by 30%.
C) Noncontrolling interest share for 2014 is equal to: (subsidiary income for 2014 minus the gain on sale) multiplied by 30%.
D) Noncontrolling interest share for 2014 is equal to: (subsidiary income for 2014 plus the excess depreciation expense) multiplied by 30%.
A) Noncontrolling interest share for 2014 is equal to: subsidiary income for 2014 multiplied by 30%.
B) Noncontrolling interest share for 2014 is equal to: (subsidiary income for 2014 minus the gain on sale plus the excess depreciation expense) multiplied by 30%.
C) Noncontrolling interest share for 2014 is equal to: (subsidiary income for 2014 minus the gain on sale) multiplied by 30%.
D) Noncontrolling interest share for 2014 is equal to: (subsidiary income for 2014 plus the excess depreciation expense) multiplied by 30%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
On January 1, 2014 Saffron Co. recorded a $40,000 profit on the upstream sale of some equipment that had a remaining four-year life under the straight-line depreciation method. The equipment has no salvage value. Saffron had separate income of $100,000 in 2014. The parent company, Pommel Incorporated, owns 90% of Saffron. Pommel would report investment income from Saffron in 2014 of
A) $54,000.
B) $63,000.
C) $90,000.
D) $126,000.
A) $54,000.
B) $63,000.
C) $90,000.
D) $126,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The 2014 unrealized gain from the intercompany sale
A) should be recognized in consolidation in 2014 by a working paper entry.
B) should be eliminated from consolidated net income by a working paper entry that credits land for $14,000.
C) should be eliminated from consolidated net income by a working paper entry that debits land for $14,000.
D) should be eliminated from consolidated net income by a working paper entry that credits gain on sale of land for $14,000.
A) should be recognized in consolidation in 2014 by a working paper entry.
B) should be eliminated from consolidated net income by a working paper entry that credits land for $14,000.
C) should be eliminated from consolidated net income by a working paper entry that debits land for $14,000.
D) should be eliminated from consolidated net income by a working paper entry that credits gain on sale of land for $14,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use the following information to answer the question(s) below.
On January 1, 2012, Shrimp Corporation purchased a delivery truck with an expected useful life of five years, and a salvage value of $8,000. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp sold the truck to Pacet Corporation. Pacet assumed the same salvage value and remaining life of three years used by Shrimp. Straight-line depreciation is used by both companies. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp recorded the following journal entry:
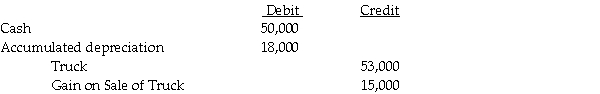 Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
Controlling interest share in consolidated net income for 2014 was
A) $121,000.
B) $125,000.
C) $131,000.
D) $143,000.
On January 1, 2012, Shrimp Corporation purchased a delivery truck with an expected useful life of five years, and a salvage value of $8,000. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp sold the truck to Pacet Corporation. Pacet assumed the same salvage value and remaining life of three years used by Shrimp. Straight-line depreciation is used by both companies. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp recorded the following journal entry:
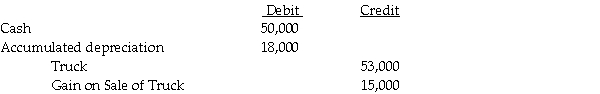 Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.Controlling interest share in consolidated net income for 2014 was
A) $121,000.
B) $125,000.
C) $131,000.
D) $143,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
On January 2, 2014, Paogo Company sold a truck with book value of $15,000 to Sanall Corporation, its wholly-owned subsidiary, for $20,000. The truck had a remaining useful life of five years with zero salvage value. Both firms use the straight-line depreciation method. If Paogo failed to make year-end adjustments/eliminations on the consolidated working papers in 2014, consolidated depreciation expense for 2014 would be
A) $5,000 too high.
B) $5,000 too low.
C) $1,000 too low.
D) $1,000 too high.
A) $5,000 too high.
B) $5,000 too low.
C) $1,000 too low.
D) $1,000 too high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Pigeon Corporation purchased land from its 60%-owned subsidiary, Seed Inc., in 2012 at a cost $50,000 greater than Seed's book value. In 2014, Pigeon sold the land to an outside entity for $20,000 more than Pigeon's book value. The 2014 consolidated income statement should report a gain on the sale of land of
A) $12,000.
B) $20,000.
C) $42,000.
D) $70,000.
A) $12,000.
B) $20,000.
C) $42,000.
D) $70,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Use the following information to answer the question(s) below.
On January 1, 2012, Shrimp Corporation purchased a delivery truck with an expected useful life of five years, and a salvage value of $8,000. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp sold the truck to Pacet Corporation. Pacet assumed the same salvage value and remaining life of three years used by Shrimp. Straight-line depreciation is used by both companies. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp recorded the following journal entry:
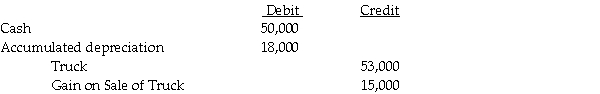 Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
In the eliminating/adjusting entries on consolidation working papers for 2014, the Truck account was
A) debited for $3,000.
B) credited for $3,000.
C) debited for $15,000.
D) credited for $15,000.
On January 1, 2012, Shrimp Corporation purchased a delivery truck with an expected useful life of five years, and a salvage value of $8,000. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp sold the truck to Pacet Corporation. Pacet assumed the same salvage value and remaining life of three years used by Shrimp. Straight-line depreciation is used by both companies. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp recorded the following journal entry:
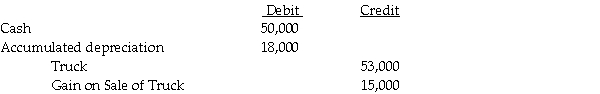 Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.In the eliminating/adjusting entries on consolidation working papers for 2014, the Truck account was
A) debited for $3,000.
B) credited for $3,000.
C) debited for $15,000.
D) credited for $15,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Plenny Corporation sold equipment to its 90%-owned subsidiary, Sourdough Corp., on January 1, 2014. Plenny sold the equipment for $100,000 when its book value was $75,000 and it had a 5-year remaining useful life with no expected salvage value. Straight-line depreciation is used by both companies. Separate balance sheets for Plenny and Sourdough included the following equipment and accumulated depreciation amounts on December 31, 2014:  Consolidated amounts for equipment and accumulated depreciation at December 31, 2014 were respectively
Consolidated amounts for equipment and accumulated depreciation at December 31, 2014 were respectively
A) $1,125,000 and $255,000.
B) $1,125,000 and $260,000.
C) $1,150,000 and $255,000.
D) $1,150,000 and $260,000.
 Consolidated amounts for equipment and accumulated depreciation at December 31, 2014 were respectively
Consolidated amounts for equipment and accumulated depreciation at December 31, 2014 were respectivelyA) $1,125,000 and $255,000.
B) $1,125,000 and $260,000.
C) $1,150,000 and $255,000.
D) $1,150,000 and $260,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Use the following information to answer the question(s) below.
On January 1, 2012, Shrimp Corporation purchased a delivery truck with an expected useful life of five years, and a salvage value of $8,000. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp sold the truck to Pacet Corporation. Pacet assumed the same salvage value and remaining life of three years used by Shrimp. Straight-line depreciation is used by both companies. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp recorded the following journal entry:
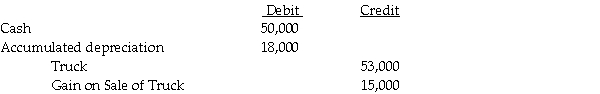 Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
The noncontrolling interest share for 2014 was
A) $18,000.
B) $22,000.
C) $23,000.
D) $27,000.
On January 1, 2012, Shrimp Corporation purchased a delivery truck with an expected useful life of five years, and a salvage value of $8,000. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp sold the truck to Pacet Corporation. Pacet assumed the same salvage value and remaining life of three years used by Shrimp. Straight-line depreciation is used by both companies. On January 1, 2014, Shrimp recorded the following journal entry:
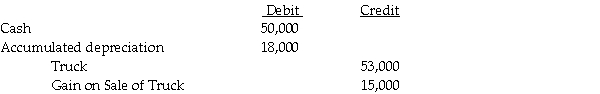 Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.
Pacet holds 60% of Shrimp. Shrimp reported net income of $55,000 in 2014 and Pacet's separate net income (excludes interest in Shrimp) for 2014 was $98,000.The noncontrolling interest share for 2014 was
A) $18,000.
B) $22,000.
C) $23,000.
D) $27,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Petrol Company acquired an 90% interest in Seadig Corporation on January 1, 2013. On January 1, 2014, Seadig sold a building with a book value of $120,000 to Petrol for $150,000. The building had a remaining useful life of ten years and no salvage value. Straight-line depreciation is used. The separate balance sheets of Petrol and Seadig on December 31, 2014 included the following balances: 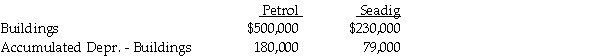 The consolidated amounts for Buildings and Accumulated Depreciation - Buildings that appeared, respectively, on the balance sheet at December 31, 2014, were
The consolidated amounts for Buildings and Accumulated Depreciation - Buildings that appeared, respectively, on the balance sheet at December 31, 2014, were
A) $700,000 and $256,000.
B) $700,000 and $259,000.
C) $730,000 and $256,000.
D) $730,000 and $259,000.
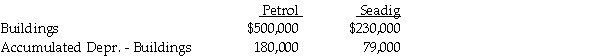 The consolidated amounts for Buildings and Accumulated Depreciation - Buildings that appeared, respectively, on the balance sheet at December 31, 2014, were
The consolidated amounts for Buildings and Accumulated Depreciation - Buildings that appeared, respectively, on the balance sheet at December 31, 2014, wereA) $700,000 and $256,000.
B) $700,000 and $259,000.
C) $730,000 and $256,000.
D) $730,000 and $259,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
On January 1, 2014, Bigg Corporation sold equipment with a book value of $20,000 and a 10-year remaining useful life to its wholly-owned subsidiary, Little Corporation, for $30,000. Both Bigg and Little use the straight-line depreciation method, assuming no salvage value. On December 31, 2014, the separate company financial statements held the following balances associated with the equipment: 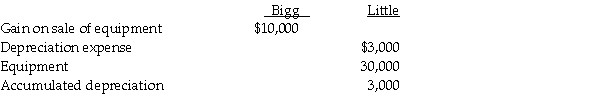 A working paper entry to consolidate the financial statements of Bigg and Little on December 31, 2014 included a
A working paper entry to consolidate the financial statements of Bigg and Little on December 31, 2014 included a
A) debit to equipment for $10,000.
B) credit to gain on sale of equipment for $10,000.
C) debit to accumulated depreciation for $1,000.
D) credit to depreciation expense for $3,000.
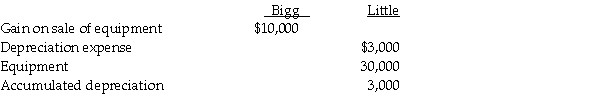 A working paper entry to consolidate the financial statements of Bigg and Little on December 31, 2014 included a
A working paper entry to consolidate the financial statements of Bigg and Little on December 31, 2014 included aA) debit to equipment for $10,000.
B) credit to gain on sale of equipment for $10,000.
C) debit to accumulated depreciation for $1,000.
D) credit to depreciation expense for $3,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
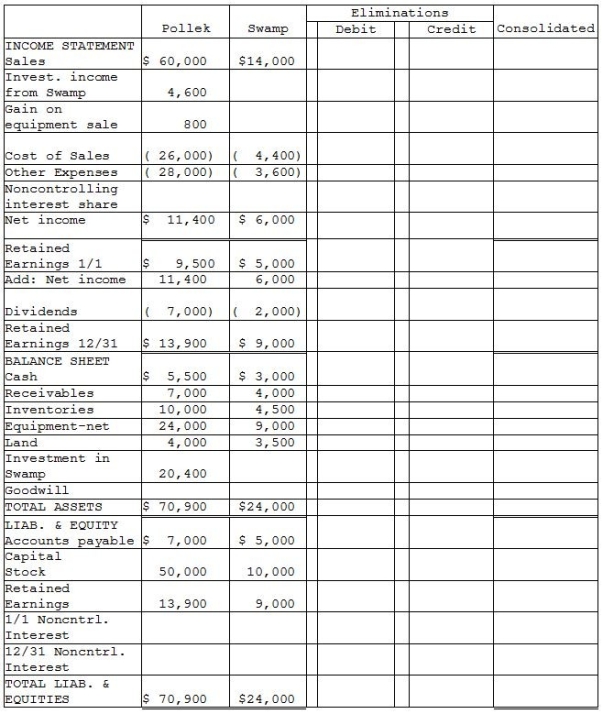
Pollek Corporation paid $16,200 for a 90% interest in Swamp Corporation on January 1, 2013, when Swamp stockholders' equity consisted of $10,000 Capital Stock and $3,000 of Retained Earnings. The excess cost over book value was attributable to goodwill.
Additional information:
1. Pollek sells merchandise to Swamp at 120% of Pollek's cost. During 2013, Pollek's sales to Swamp were $4,800, of which half of the merchandise remained in Swamp's inventory at December 31, 2013. (The 2013 ending inventory was sold in 2014.) During 2014, Pollek's sales to Swamp were $6,000 of which 60% remained in Swamp's inventory at December 31, 2014. At year-end 2014, Swamp owed Pollek $1,500 for the inventory purchased during 2014.
2. Pollek Corporation sold equipment with a book value of $2,000 and a remaining useful life of four years and no salvage value to Swamp Corporation on January 1, 2014 for $2,800. Straight-line depreciation is used.
3. Separate company financial statements for Pollek Corporation and Subsidiary at December 31, 2014 are summarized in the first two columns of the consolidation working papers.
4. The following information is available for 2013:
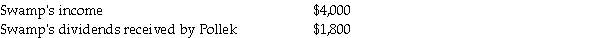 Required:
Required:
Complete the working papers to consolidate the financial statements of Pollek Corporation and subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Additional information:
1. Pollek sells merchandise to Swamp at 120% of Pollek's cost. During 2013, Pollek's sales to Swamp were $4,800, of which half of the merchandise remained in Swamp's inventory at December 31, 2013. (The 2013 ending inventory was sold in 2014.) During 2014, Pollek's sales to Swamp were $6,000 of which 60% remained in Swamp's inventory at December 31, 2014. At year-end 2014, Swamp owed Pollek $1,500 for the inventory purchased during 2014.
2. Pollek Corporation sold equipment with a book value of $2,000 and a remaining useful life of four years and no salvage value to Swamp Corporation on January 1, 2014 for $2,800. Straight-line depreciation is used.
3. Separate company financial statements for Pollek Corporation and Subsidiary at December 31, 2014 are summarized in the first two columns of the consolidation working papers.
4. The following information is available for 2013:
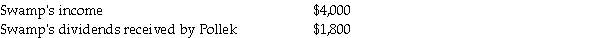 Required:
Required:Complete the working papers to consolidate the financial statements of Pollek Corporation and subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2014.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
On January 1, 2013, Pilgrim Imaging purchased 90% of the outstanding common stock of Snapshot Productions for $585,000 cash. The remaining 10% of Snapshot had an assessed fair value of $65,000 at that time. Snapshot had equipment that was undervalued on their books by $50,000, and an unrecorded patent with a fair value of $15,000. The equipment had five years remaining to its useful life, and the patent had 10 years remaining to its useful life.
On January 1, 2014, Pilgrim sold Snapshot a building for $100,000 that had originally cost $140,000. The book value was $60,000 at the date of transfer, and had a five-year remaining life at the date of transfer. Straight-line depreciation is used with no salvage value. Several line items from the companies' separate December 31, 2014 trial balances are shown below.
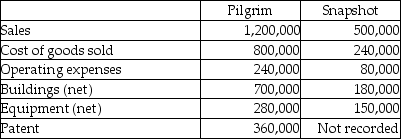 Required: Determine consolidated balances for each of the accounts listed as of December 31, 2014.
Required: Determine consolidated balances for each of the accounts listed as of December 31, 2014.
On January 1, 2014, Pilgrim sold Snapshot a building for $100,000 that had originally cost $140,000. The book value was $60,000 at the date of transfer, and had a five-year remaining life at the date of transfer. Straight-line depreciation is used with no salvage value. Several line items from the companies' separate December 31, 2014 trial balances are shown below.
 Required: Determine consolidated balances for each of the accounts listed as of December 31, 2014.
Required: Determine consolidated balances for each of the accounts listed as of December 31, 2014.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Plower Corporation acquired all of the outstanding voting common stock of the Squab Corporation several years ago when the book values and fair values of Squab's net assets were equal.
On April 1, 2012, Plower sold land that cost $25,000 to Squab for $40,000. Squab resold the land for $45,000 on December 1, 2014.
On July 1, 2014, Plower sold equipment with a book value of $10,000 to Squab for $26,000. Squab is depreciating the equipment over a four-year period using the straight-line method. The equipment has no salvage value.
Required:
The first two columns in the working papers presented below summarize income statement information from the separate company financial statements of Plower and Squab for the year ended December 31, 2014. Fill in the consolidated working paper columns to show how each of the items from the separate company reports will appear in the consolidated income statement for the year ended December 31, 2014.
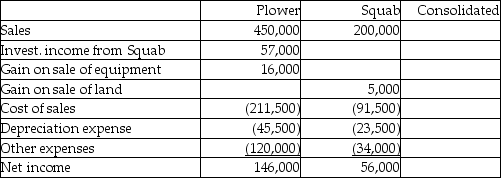
On April 1, 2012, Plower sold land that cost $25,000 to Squab for $40,000. Squab resold the land for $45,000 on December 1, 2014.
On July 1, 2014, Plower sold equipment with a book value of $10,000 to Squab for $26,000. Squab is depreciating the equipment over a four-year period using the straight-line method. The equipment has no salvage value.
Required:
The first two columns in the working papers presented below summarize income statement information from the separate company financial statements of Plower and Squab for the year ended December 31, 2014. Fill in the consolidated working paper columns to show how each of the items from the separate company reports will appear in the consolidated income statement for the year ended December 31, 2014.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Palmer Corporation purchased 75% of Stone Industries' common stock on January 2, 2012. On January 1, 2013, Stone sold equipment to Palmer that had a net book value of $16,000 and an original cost of $24,000 for $20,000. On January 1, 2013, Palmer sold a building to Stone that had a net book value of $200,000 and an original cost of $250,000 for $300,000. The equipment had a remaining useful life of 8 years, and the building had a remaining useful life of 20 years. Neither asset had salvage value. Both companies use straight-line depreciation.
Selected account balances are shown below for Palmer and Stone for the year ended December 31, 2013:
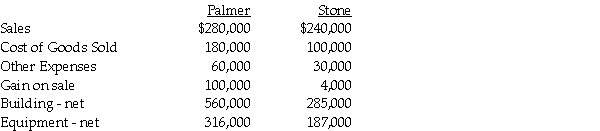 Required:
Required:
1. Prepare the consolidating working paper entries relating to the equipment and building for the year ended December 31, 2013.
2. Calculate the following balances for the year ended December 31, 2013:
A. Consolidated "Other Expenses"
B. Consolidated Buildings
C. Consolidated Equipment
D. Noncontrolling interest in Stone's net income
Selected account balances are shown below for Palmer and Stone for the year ended December 31, 2013:
 Required:
Required:1. Prepare the consolidating working paper entries relating to the equipment and building for the year ended December 31, 2013.
2. Calculate the following balances for the year ended December 31, 2013:
A. Consolidated "Other Expenses"
B. Consolidated Buildings
C. Consolidated Equipment
D. Noncontrolling interest in Stone's net income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
On January 2, 2014, Pal Corporation sold warehouse equipment to SimCo, a wholly-owned subsidiary. The equipment had an original cost of $130,000 and a net book value of $100,000 when it was sold to SimCo for $150,000. Both companies agreed that the equipment had a five-year remaining life and compute depreciation on the straight-line method. The equipment has no salvage value.
Pal reported $470,000 in net income in 2014 (prior to reporting any income from SimCo), and SimCo reported $160,000 in net income.
Required:
1. Calculate consolidated net income for 2014.
2. Determine the controlling share of net income for the year if Pal only owned 75% of SimCo.
3. Determine the controlling share of net income for the year if Pal only owned 75% of SimCo AND the equipment transfer was upstream.
Pal reported $470,000 in net income in 2014 (prior to reporting any income from SimCo), and SimCo reported $160,000 in net income.
Required:
1. Calculate consolidated net income for 2014.
2. Determine the controlling share of net income for the year if Pal only owned 75% of SimCo.
3. Determine the controlling share of net income for the year if Pal only owned 75% of SimCo AND the equipment transfer was upstream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Separate income statements of Plantation Corporation and its 90%-owned subsidiary, Savannah Corporation, for 2014 are as follows, prior to Plantation recording any income related to its subsidiary:
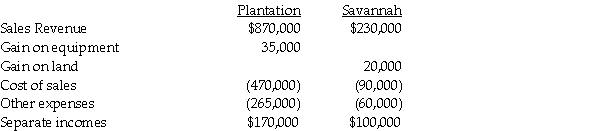 Additional information:
Additional information:
1. Plantation acquired its 90% interest in Savannah Corporation when the book values were equal to the fair values.
2. The gain on equipment relates to equipment with a book value of $95,000 and a 7-year remaining useful life that Plantation sold to Savannah for $130,000 on January 1, 2014. The straight-line depreciation method was used and the equipment has no salvage value.
3. On January 1, 2014, Savannah sold land to an outside entity for $90,000. The land was acquired from Plantation in 2009 for $70,000. The original cost of the land to Plantation was $45,000.
4. Savannah did not declare or distribute dividends in 2014.
Required:
1. Prepare elimination/adjusting entries on the consolidated worksheet for the year 2014.
2. Prepare the consolidated income statement for the year ended December 31, 2014.
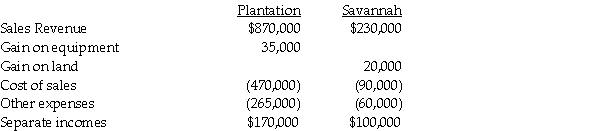 Additional information:
Additional information:1. Plantation acquired its 90% interest in Savannah Corporation when the book values were equal to the fair values.
2. The gain on equipment relates to equipment with a book value of $95,000 and a 7-year remaining useful life that Plantation sold to Savannah for $130,000 on January 1, 2014. The straight-line depreciation method was used and the equipment has no salvage value.
3. On January 1, 2014, Savannah sold land to an outside entity for $90,000. The land was acquired from Plantation in 2009 for $70,000. The original cost of the land to Plantation was $45,000.
4. Savannah did not declare or distribute dividends in 2014.
Required:
1. Prepare elimination/adjusting entries on the consolidated worksheet for the year 2014.
2. Prepare the consolidated income statement for the year ended December 31, 2014.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Pigeon Company owns 80% of the outstanding stock of Spiniflex Corporation, which was purchased on January 1, 2008, when Spiniflex's book values were equal to its fair values. The amount paid by Pigeon included $16,000 for goodwill.
On January 1, 2009, Pigeon purchased a truck for $40,000 which had no salvage value with a useful life of 8 years, depreciated on a straight-line basis. On January 1, 2014, Pigeon sold the truck to Spiniflex Corporation for $18,000. The truck was estimated to have a three-year remaining life on this date and no salvage value. All affiliates use the straight-line depreciation method.
Required:
Prepare all relevant entries with respect to the truck.
1. Record the journal entries on Pigeon's books for 2014.
2. Record the journal entries on Spiniflex's books for 2014.
3. Prepare the consolidation entries required for Pigeon and subsidiary for 2014 as a result of this transaction.
On January 1, 2009, Pigeon purchased a truck for $40,000 which had no salvage value with a useful life of 8 years, depreciated on a straight-line basis. On January 1, 2014, Pigeon sold the truck to Spiniflex Corporation for $18,000. The truck was estimated to have a three-year remaining life on this date and no salvage value. All affiliates use the straight-line depreciation method.
Required:
Prepare all relevant entries with respect to the truck.
1. Record the journal entries on Pigeon's books for 2014.
2. Record the journal entries on Spiniflex's books for 2014.
3. Prepare the consolidation entries required for Pigeon and subsidiary for 2014 as a result of this transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Porter Corporation acquired 70% of the outstanding voting common stock of Sherman Inc. in 2008. On January 1, 2009, Sherman Inc. purchased a depreciable machine for $120,000 cash with an estimated useful life of 10 years that was depreciated on a straight-line basis. The machine has no estimated salvage value. Sherman used the machine until the end of 2011. On January 2, 2012, Sherman sold the machine to Porter who continued to use the same estimated life (seven years remaining), salvage value and depreciation method that was used by Sherman. At the end of 2012, Sherman reported a gain on sale of the machine of $14,000.
Required:
Answer the following questions concerning Porter and Sherman.
1. Prepare elimination/adjusting entries for the consolidated working papers for the year ended December 31, 2012.
2. How much depreciation expense relating to the transferred asset did Porter record in 2012 on the company's separate books?
3. How much depreciation expense relating to the transferred asset was reported on the consolidated income statement in 2012?
4. What amounts were reported for the Machine and the Accumulated Depreciation in the consolidated balance sheet on December 31, 2012?
Required:
Answer the following questions concerning Porter and Sherman.
1. Prepare elimination/adjusting entries for the consolidated working papers for the year ended December 31, 2012.
2. How much depreciation expense relating to the transferred asset did Porter record in 2012 on the company's separate books?
3. How much depreciation expense relating to the transferred asset was reported on the consolidated income statement in 2012?
4. What amounts were reported for the Machine and the Accumulated Depreciation in the consolidated balance sheet on December 31, 2012?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Several years ago, Pilot International purchased 70% of the outstanding stock of Skyway Incorporated, at a time when Skyway's book values were equal to its fair values. On January 1, 2011 Skyway purchased a truck for $80,000 which had no salvage value with a useful life of 8 years, depreciated on a straight-line basis. On January 1, 2014, Skyway sold the truck to Pilot Corporation for $28,000. The truck was estimated to have a five-year remaining life on this date, and no salvage value. All affiliates use the straight-line depreciation method.
Required:
Prepare all relevant entries with respect to the truck.
1. Record the journal entries on Pilot's books for 2014.
2. Record the journal entries on Skyway's books for 2014.
3. Prepare the consolidation entries required for Pilot and subsidiary for 2014 as a result of this transaction.
Required:
Prepare all relevant entries with respect to the truck.
1. Record the journal entries on Pilot's books for 2014.
2. Record the journal entries on Skyway's books for 2014.
3. Prepare the consolidation entries required for Pilot and subsidiary for 2014 as a result of this transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Passo Corporation acquired a 70% interest in Saun Corporation in 2009 at a time when Saun's book values and fair values were equal. In 2012, Saun sold land to Passo for $82,000 that cost $72,000. The land remained in Passo's possession until 2014 when Passo sold it outside the combined entity for $102,000.
After the books were closed in 2014, it was discovered that Passo had not considered the unrealized gain from its intercompany purchase of land in preparing the consolidated financial statements. The only entry on Passo's books was a debit to Land and a credit to Cash in 2012 for $82,000, and in 2014, a debit to Cash for $102,000 and credits to Land for $82,000 and Gain on sale of land for $20,000.
Before the discovery of the error, the consolidated financial statements disclosed the following amounts:
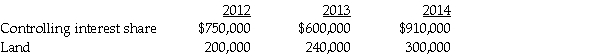 Required:
Required:
1. Prepare elimination/adjusting entries relating to the land on the consolidated working papers for December 31, 2012, December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2014.
2. Determine the correct amounts for Land in 2012, 2013, and 2014.
3. Calculate the amount at which the gain on the sale of land should have been reported in 2014.
After the books were closed in 2014, it was discovered that Passo had not considered the unrealized gain from its intercompany purchase of land in preparing the consolidated financial statements. The only entry on Passo's books was a debit to Land and a credit to Cash in 2012 for $82,000, and in 2014, a debit to Cash for $102,000 and credits to Land for $82,000 and Gain on sale of land for $20,000.
Before the discovery of the error, the consolidated financial statements disclosed the following amounts:
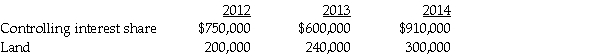 Required:
Required:1. Prepare elimination/adjusting entries relating to the land on the consolidated working papers for December 31, 2012, December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2014.
2. Determine the correct amounts for Land in 2012, 2013, and 2014.
3. Calculate the amount at which the gain on the sale of land should have been reported in 2014.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Separate income statements of Pingair Corporation and its 90%-owned subsidiary, Staunch Inc., for 2014 were as follows:
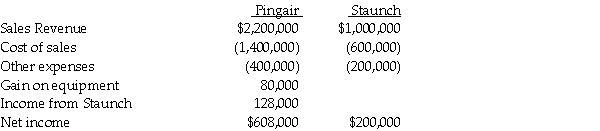 Additional information:
Additional information:
1. Pingair acquired its 90% interest in Staunch Inc. when the book values were equal to the fair values.
2. The gain on equipment relates to equipment with a book value of $120,000 and a 4-year remaining useful life that Pingair sold to Staunch for $200,000 on January 2, 2014. The straight-line depreciation method is used. The equipment has no salvage value.
3. Pingair sold inventory to Staunch in 2013 and 2014 as shown in the table below. (The 2013 ending inventory is sold in 2014.)
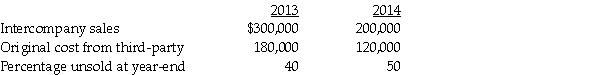 4. Staunch did not declare or pay dividends in 2013 and 2014.
4. Staunch did not declare or pay dividends in 2013 and 2014.
Required:
1. Prepare adjusting/eliminating entries for the consolidation worksheet at December 31, 2014.
2. Prepare a consolidated income statement for Pingair Corporation and Subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2014.
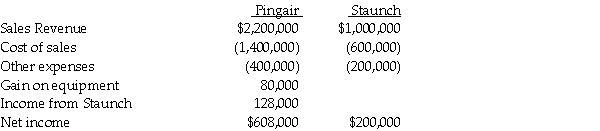 Additional information:
Additional information:1. Pingair acquired its 90% interest in Staunch Inc. when the book values were equal to the fair values.
2. The gain on equipment relates to equipment with a book value of $120,000 and a 4-year remaining useful life that Pingair sold to Staunch for $200,000 on January 2, 2014. The straight-line depreciation method is used. The equipment has no salvage value.
3. Pingair sold inventory to Staunch in 2013 and 2014 as shown in the table below. (The 2013 ending inventory is sold in 2014.)
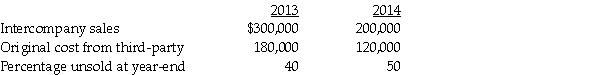 4. Staunch did not declare or pay dividends in 2013 and 2014.
4. Staunch did not declare or pay dividends in 2013 and 2014.Required:
1. Prepare adjusting/eliminating entries for the consolidation worksheet at December 31, 2014.
2. Prepare a consolidated income statement for Pingair Corporation and Subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2014.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Pierce Manufacturing owns all of the outstanding voting common stock of Sylvia Company, as acquired several years ago when the book values and fair values of Sylvia's net assets were equal.
In 2013, Pierce set out to re-structure the company, and in doing so, re-aligned the manufacturing processes to streamline the use of automated equipment. As a result, they set out to move certain equipment around between the facilities owned by both Pierce and Sylvia, and ultimately agreed on the following transfers and exchange prices. It was agreed that the exchange price would be paid in cash on January 1, 2014, the date the equipment was transferred. Straight-line depreciation is used and the different pieces of equipment have no salvage value.
 Required:
Required:
1. Prepare the journal entry that Pierce would record for each transfer listed.
2. Prepare the journal entry that Sylvia would record for each transfer listed.
3. Prepare the consolidation worksheet entries that would be required as a result of the above transactions for 2014.
In 2013, Pierce set out to re-structure the company, and in doing so, re-aligned the manufacturing processes to streamline the use of automated equipment. As a result, they set out to move certain equipment around between the facilities owned by both Pierce and Sylvia, and ultimately agreed on the following transfers and exchange prices. It was agreed that the exchange price would be paid in cash on January 1, 2014, the date the equipment was transferred. Straight-line depreciation is used and the different pieces of equipment have no salvage value.
 Required:
Required:1. Prepare the journal entry that Pierce would record for each transfer listed.
2. Prepare the journal entry that Sylvia would record for each transfer listed.
3. Prepare the consolidation worksheet entries that would be required as a result of the above transactions for 2014.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Snow Company is a wholly owned subsidiary of Penguin Corporation. On January 1, 2011, Penguin transferred equipment to Snow for $195,000. The equipment had originally cost $250,000, but at the time of transfer, had a $180,000 book value and a five year remaining life. Both companies use the straight-line method of depreciation and assume no salvage value for the equipment.
Required: Prepare the consolidation worksheet entries for this asset on the following dates:
1. December 31, 2011
2. December 31, 2012
3. December 31, 2013
Required: Prepare the consolidation worksheet entries for this asset on the following dates:
1. December 31, 2011
2. December 31, 2012
3. December 31, 2013

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Paula's Pizzas purchased 80% of their supplier, Sarah's Sauces. Sarah's book values equaled fair values at the time of the acquisition. Paula sold Sarah some packaging equipment on January 2, 2013 for $100,000. The equipment had a carrying value of $90,000, and original cost of $120,000, and had a remaining life of 10 years. Both Paula and Sarah depreciate their assets on the straight-line method. The equipment has no salvage value.
Required: Prepare the following entries:
1. Journal entries Paula and Sarah will prepare on their separate books in 2013.
2. Eliminating/adjusting entries on the consolidation worksheet at the end of 2013.
3. Eliminating/adjusting entries on the consolidation worksheet at the end of 2014.
Required: Prepare the following entries:
1. Journal entries Paula and Sarah will prepare on their separate books in 2013.
2. Eliminating/adjusting entries on the consolidation worksheet at the end of 2013.
3. Eliminating/adjusting entries on the consolidation worksheet at the end of 2014.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Piglet Incorporated purchased 90% of the outstanding stock of Sourgrape Company several years ago at book value. At January 1, 2012, Sourgrape sold land with a book value of $30,000 to Piglet at its fair market value of $40,000. At the same time, Sourgrape sold the building that was on the land to Piglet. The building had a book value of $80,000 and was sold at its fair value of $120,000. The building had a remaining useful life of 8 years and is depreciated using the straight-line method. The building has no salvage value. On January 1, 2014, Piglet sold the land and building to a third party. The sales price was allocated so that the land was sold for $50,000 and the building was sold for $150,000. Income statements for Piglet and Sourgrape for the year ended December 31, 2014 are summarized below:
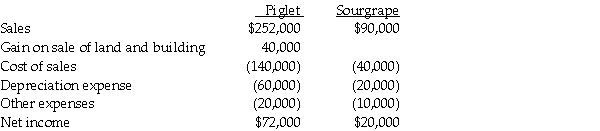 Required:
Required:
Prepare the eliminating/adjusting entries related to the land and building on the consolidated working papers on the following dates:
1. December 31, 2012
2. December 31, 2013
3. December 31, 2014
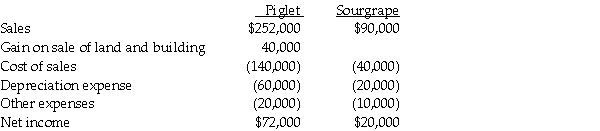 Required:
Required:Prepare the eliminating/adjusting entries related to the land and building on the consolidated working papers on the following dates:
1. December 31, 2012
2. December 31, 2013
3. December 31, 2014

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Plock Corporation, the 75% owner of Seraphim Company, reported net income of $400,000 in 2013, prior to recording any income from Seraphim. Seraphim reported net income for that same year of $80,000 on their stand-alone statements. During 2013, an intercompany sale of a vehicle resulted in a gain of $4,000, and the vehicle was assumed to have a four-year remaining useful life. The vehicle has no salvage value. Straight-line depreciation is used.
Required:
1. Assuming that the vehicle transfer was downstream, calculate Plock's consolidated net income for 2013, and controlling share of consolidated net income for 2013.
2. Assuming that the vehicle transfer was upstream, calculate Plock's consolidated net income for 2013, and controlling share of consolidated net income for 2013.
Required:
1. Assuming that the vehicle transfer was downstream, calculate Plock's consolidated net income for 2013, and controlling share of consolidated net income for 2013.
2. Assuming that the vehicle transfer was upstream, calculate Plock's consolidated net income for 2013, and controlling share of consolidated net income for 2013.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Several years ago, Peacock International purchased 80% of the outstanding stock of Strutt Incorporated, at a time when Strutt's book values were equal to its fair values. On January 1, 2009, Strutt purchased a truck for $160,000 which had no salvage value with a useful life of 8 years, depreciated on a straight-line basis. On January 1, 2012, Strutt sold the truck to Peacock Corporation for $56,000. The equipment was estimated to have a five-year remaining life on this date, with no salvage value. All affiliates use the straight-line depreciation method.
Required:
Prepare the consolidation entries required for Peacock and subsidiary at:
1. December 31, 2012
2. December 31, 2013
3. December 31, 2014
4. December 31, 2015
Required:
Prepare the consolidation entries required for Peacock and subsidiary at:
1. December 31, 2012
2. December 31, 2013
3. December 31, 2014
4. December 31, 2015

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Prey Corporation created a wholly owned subsidiary, Sage Corporation, on January 1, 2013, at which time Prey sold land with a book value of $90,000 to Sage at its fair market value of $140,000. Also, on January 1, 2013, Prey sold to Sage equipment with a book value of $130,000 and a selling price of $165,000. The equipment had a remaining useful life of 4 years and is being depreciated under the straight-line method. The equipment has no salvage value. On January 1, 2015, Sage resold the land to an outside entity for $150,000. Sage continues to use the equipment purchased from Prey. Income statements for Prey and Sage for the year ended December 31, 2015 are summarized below:
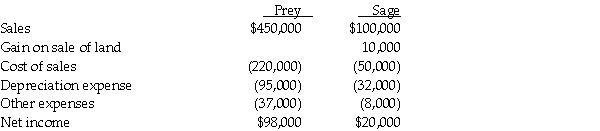 Required:
Required:
At what amounts did the following items appear on the consolidated income statement for Prey and Subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2015?
1. Gain on Sale of Land
2. Depreciation Expense
3. Consolidated net income
4. Controlling interest share of consolidated net income
 Required:
Required:At what amounts did the following items appear on the consolidated income statement for Prey and Subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2015?
1. Gain on Sale of Land
2. Depreciation Expense
3. Consolidated net income
4. Controlling interest share of consolidated net income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Park Incorporated purchased a 70% interest in Silk Company in 2012 at book value. On January 1, 2014, equipment having a historical cost of $100,000 and a net book value of $70,000 is sold in an intercompany transfer for $90,000. The equipment has a remaining useful life of five years and no salvage value. Straight-line depreciation is used by both companies. Silk reports net income of $180,000 in 2014 and $200,000 in 2015.
Required:
1. Assume Park sold the equipment to Silk.
A. Prepare the consolidating worksheet entries for the equipment for 2014 and 2015.
B. Calculate the noncontrolling interest share in Silk's income for 2014 and 2015.
2. Assume that Silk sold the equipment to Park.
A. Prepare the consolidating worksheet entries for the equipment for 2014 and 2015.
B. Calculate the noncontrolling interest share in Silk's income for 2014 and 2015.
Required:
1. Assume Park sold the equipment to Silk.
A. Prepare the consolidating worksheet entries for the equipment for 2014 and 2015.
B. Calculate the noncontrolling interest share in Silk's income for 2014 and 2015.
2. Assume that Silk sold the equipment to Park.
A. Prepare the consolidating worksheet entries for the equipment for 2014 and 2015.
B. Calculate the noncontrolling interest share in Silk's income for 2014 and 2015.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



