Deck 8: Capital Gains and Losses
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/109
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Capital Gains and Losses
1
The first day a capital asset acquired on August 31, 2015 may be sold for long-term capital gain or loss treatment is September 1, 2016.
True
2
A taxpayer's personal automobile is a capital asset.
True
3
Which one of the following is a capital asset?
A)Accounts receivable
B)Copyright held by the author
C)Securities held for investment
D)Inventories
E)All of the above are capital assets
A)Accounts receivable
B)Copyright held by the author
C)Securities held for investment
D)Inventories
E)All of the above are capital assets
C
4
If a capital asset acquired August 5, 2015 is sold on February 6, 2016, any gain is a short-term capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If property is received from a decedent, the taxpayer who inherits the property has the same basis in the property as the decedent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the following are capital assets, mark with a "Yes." If they are not capital assets, mark with a "No."
a.A taxpayer's personal jet ski ______
b.Ford Motor Credit Company bond held by an investor ______
c.A baseball for sale at Sports.com ______
d.J.K.Rowling's personal copy of her original manuscript of
Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone ______
e.An antique grandfather clock inherited from the taxpayer's aunt ______
a.A taxpayer's personal jet ski ______
b.Ford Motor Credit Company bond held by an investor ______
c.A baseball for sale at Sports.com ______
d.J.K.Rowling's personal copy of her original manuscript of
Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone ______
e.An antique grandfather clock inherited from the taxpayer's aunt ______

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Sol purchased land as an investment on February 12, 2015 for $85,000. On January 31, 2016, Sol sold the land for $90,000 cash. What is the nature of the gain or loss?
A)Long-term capital loss
B)Long-term capital gain
C)Short-term capital gain
D)Short-term capital loss
E)None of the above
A)Long-term capital loss
B)Long-term capital gain
C)Short-term capital gain
D)Short-term capital loss
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The basis of property received as an inheritance is generally equal to the fair market value at the date of death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is a capital asset?
A)Inventory held by a manufacturer
B)Accounts receivable held by a dentist
C)All property owned by a taxpayer other than property specifically noted in the law as an exception
D)Depreciable property and real estate used in a trade or business
A)Inventory held by a manufacturer
B)Accounts receivable held by a dentist
C)All property owned by a taxpayer other than property specifically noted in the law as an exception
D)Depreciable property and real estate used in a trade or business

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An artist's painting is not a capital asset when held by the artist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Indicate whether a gain or loss realized in each of the following situations would be long-term or short-term by putting an "X" on the appropriate blank line:



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If a capital asset acquired on October 27, 2008 is sold on April 30, 2016 for a gain, the gain is a long-term capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The following are owned by Robert. Indicate which are capital assets.
a.Rental property at 123 Main Street ______
b.Tables and chairs sold in his furniture business ______
c.The cash register used in his furniture business ______
d.A 1972 Porsche 916 ______
e.The rights to Taylor Swift's song, "Blank Space" ______
a.Rental property at 123 Main Street ______
b.Tables and chairs sold in his furniture business ______
c.The cash register used in his furniture business ______
d.A 1972 Porsche 916 ______
e.The rights to Taylor Swift's song, "Blank Space" ______

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is a capital asset?
A)A literary work held by the author
B)Real estate held by a developer
C)A taxpayer's principle residence
D)A truck used in a taxpayer's business
E)None of the above
A)A literary work held by the author
B)Real estate held by a developer
C)A taxpayer's principle residence
D)A truck used in a taxpayer's business
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Sol purchased land as an investment on January 12, 2011 for $85,000. On January 31, 2016, Sol sold the land for $90,000 cash. What is the nature of the gain or loss?
A)Long-term capital loss
B)Long-term capital gain
C)Short-term capital gain
D)Short-term capital loss
E)None of the above
A)Long-term capital loss
B)Long-term capital gain
C)Short-term capital gain
D)Short-term capital loss
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is not true about capital assets?
A)Real property used in a trade or business is not a capital asset.
B)Capital losses may be carried back for 3 years to offset capital gains in those years.
C)For 2016, net long-term capital gains are granted preferential tax treatment.
D)Individual taxpayers may deduct net capital losses of up to $3,000 per year.
E)Shares of stock held for investment are capital assets.
A)Real property used in a trade or business is not a capital asset.
B)Capital losses may be carried back for 3 years to offset capital gains in those years.
C)For 2016, net long-term capital gains are granted preferential tax treatment.
D)Individual taxpayers may deduct net capital losses of up to $3,000 per year.
E)Shares of stock held for investment are capital assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following sales results in a short-term gain/loss?
A)A capital asset bought on June 30, 2015 and sold June 20, 2016.
B)A capital asset bought on July 25, 2015 and sold August 19, 2016.
C)A capital asset bought on September 12, 2009 and sold August 19, 2016.
D)A capital asset bought on August 15, 2015 and sold August 16, 2016.
E)All of the above are long-term gains/losses.
A)A capital asset bought on June 30, 2015 and sold June 20, 2016.
B)A capital asset bought on July 25, 2015 and sold August 19, 2016.
C)A capital asset bought on September 12, 2009 and sold August 19, 2016.
D)A capital asset bought on August 15, 2015 and sold August 16, 2016.
E)All of the above are long-term gains/losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Accounts receivable are capital assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Emily sold the following investments during the year:
For each stock, calculate the amount and the nature of the gain or loss.
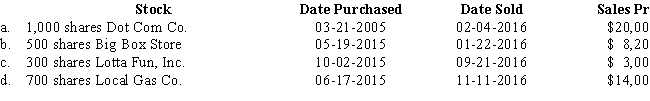
For each stock, calculate the amount and the nature of the gain or loss.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What are capital assets?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An asset has an original basis of $25,000 and depreciation has been claimed for the asset in the amount of $20,000. If the asset's adjusted basis is $15,000, what is the amount of capital improvements that have been made to the asset?
A)$5,000
B)$10,000
C)$20,000
D)$30,000
E)None of the above
A)$5,000
B)$10,000
C)$20,000
D)$30,000
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In December, 2016, Ben and Jeri (married filing jointly) have a long-term capital gain of $55,000 on the sale of stock held for 4 years. They have no other capital gains and losses for the year. After standard deduction and personal exemptions, their ordinary income for the year, before the capital gain, is $75,300, making their total income for the year $130,300, ($75,300 + $55,000). In 2016, married taxpayers who file jointly pay tax of $10,367.50 at 10 percent and 15 percent rates (from the tax rate schedules) on the first $75,300 of ordinary taxable income and 25 percent on ordinary taxable income up to $151,900. What is their total tax liability?
A)$10,367.50
B)$15.867.50
C)$18,617.50
D)$24,117.50
A)$10,367.50
B)$15.867.50
C)$18,617.50
D)$24,117.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
For purposes of determining the adjusted basis of a capital asset at the time of its sale,
A)Capital improvements are added to the basis.
B)Ordinary repairs reduce the adjusted basis.
C)Accumulated depreciation is added to the basis.
D)The basis does not include costs such as title insurance and escrow fees related to the initial purchase.
A)Capital improvements are added to the basis.
B)Ordinary repairs reduce the adjusted basis.
C)Accumulated depreciation is added to the basis.
D)The basis does not include costs such as title insurance and escrow fees related to the initial purchase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is true about capital gains?
A)Short-term capital gains are not netted with other capital gains and losses.
B)For 2016, long-term capital gains are subject to special tax treatment.
C)Long-term capital gains are never taxed.
D)Net short-term capital gains are not netted with net long-term capital losses.
E)None of the above.
A)Short-term capital gains are not netted with other capital gains and losses.
B)For 2016, long-term capital gains are subject to special tax treatment.
C)Long-term capital gains are never taxed.
D)Net short-term capital gains are not netted with net long-term capital losses.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If property is inherited by a taxpayer,
A)To the recipient, the basis for the property is the same as the basis to the decedent.
B)At sale date, the basis of the property to the recipient differs depending on whether the property was sold at a gain or a loss.
C)At sale date, the recipient will not have a gain or loss even if the recipient has held the property for more than a year.
D)In general, the basis to the recipient is the fair market value at the decedent's date of death.
A)To the recipient, the basis for the property is the same as the basis to the decedent.
B)At sale date, the basis of the property to the recipient differs depending on whether the property was sold at a gain or a loss.
C)At sale date, the recipient will not have a gain or loss even if the recipient has held the property for more than a year.
D)In general, the basis to the recipient is the fair market value at the decedent's date of death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Carlos bought a building for $113,000 in 2012. He added an addition to the building for $26,000. In 2016, he sold it for $212,000. What was his long-term capital gain (ignore depreciation)?
A)$0
B)$47,000
C)$73,000
D)$99,000
E)$212,000
A)$0
B)$47,000
C)$73,000
D)$99,000
E)$212,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Net short-term capital gains may be offset by net long-term capital losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Taxpayers are allowed to offset net short-term capital losses with net long-term capital gains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Bennett purchased a tract of land for $20,000 in 2010 when he heard that a new highway was going to be constructed through the property and the land would soon be worth $200,000. The highway project was abandoned in 2016 and the value of the land fell to $15,000. Bennett can claim a loss in 2016 of:
A)$0
B)$5,000
C)$165,000
D)$180,000
E)None of the above
A)$0
B)$5,000
C)$165,000
D)$180,000
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Sol purchased land as an investment on January 12, 2011, for $85,000. On January 31, 2016, Sol sold the land for $25,000 cash. In addition, the purchaser assumed the mortgage of $70,000 on the land. What is the amount realized (not gain realized) on the sale of the land?
A)$10,000
B)$25,000
C)$70,000
D)$95,000
E)None of the above
A)$10,000
B)$25,000
C)$70,000
D)$95,000
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Bev owns an apartment complex she purchased 10 years ago for $480,000 with a $80,000 cash down payment accompanied by a $400,000 loan. Bev has made $70,000 of capital improvements on the complex and her depreciation claimed on the building to date is $100,000. Calculate Bev's adjusted basis in the building.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Currently, long-term capital gains are not afforded preferential tax treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Nick received a gift of stock from his father. Nick's father had purchased the stock 2 years earlier and his father's basis in the stock was $30,000. On the date of the gift, the stock had a fair market value of $25,000.
a.If Nick sells the stock for $33,000, calculate the amount of Nick's gain or loss on the transaction.
b.If Nick sells the stock for $22,000, calculate the amount of Nick's gain or loss on the transaction.
c.If Nick sells the stock for $27,000, calculate the amount of Nick's gain or loss on the transaction.
a.If Nick sells the stock for $33,000, calculate the amount of Nick's gain or loss on the transaction.
b.If Nick sells the stock for $22,000, calculate the amount of Nick's gain or loss on the transaction.
c.If Nick sells the stock for $27,000, calculate the amount of Nick's gain or loss on the transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
For the current year, Susan had salary income of $20,000. In addition she reported the following capital transactions during the year: There were no other items includable in her gross income. What is the amount of her adjusted gross income for the current year?
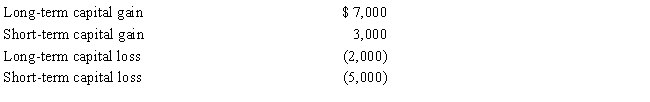
A)$19,000
B)$23,000
C)$24,000
D)$25,000
E)None of the above
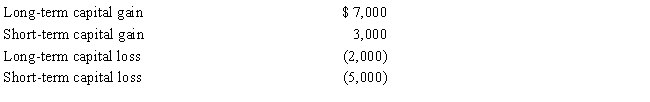
A)$19,000
B)$23,000
C)$24,000
D)$25,000
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The adjusted basis of an asset may be determined by the:
A)Selling price + gain realized.
B)Selling price - gain realized.
C)Selling price + capital improvements - accumulated depreciation.
D)Original basis + capital improvements - selling price.
E)None of the above.
A)Selling price + gain realized.
B)Selling price - gain realized.
C)Selling price + capital improvements - accumulated depreciation.
D)Original basis + capital improvements - selling price.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Sol purchased land as an investment on January 12, 2010 for $85,000. On January 31, 2016, Sol sold the land for $30,000 cash. In addition, the purchaser assumed the mortgage of $70,000 on the land. What is the amount of the realized gain or loss on the sale?
A)$65,000 loss
B)$15,000 gain
C)$5,000 gain
D)$90,000 gain
E)None of the above
A)$65,000 loss
B)$15,000 gain
C)$5,000 gain
D)$90,000 gain
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An asset's adjusted basis is computed as:
A)Original basis + capital improvements - accumulated depreciation.
B)Original basis - capital improvements + accumulated depreciation.
C)Original basis + capital improvements + accumulated depreciation.
D)Original basis + capital improvements + gain or loss realized.
E)None of the above.
A)Original basis + capital improvements - accumulated depreciation.
B)Original basis - capital improvements + accumulated depreciation.
C)Original basis + capital improvements + accumulated depreciation.
D)Original basis + capital improvements + gain or loss realized.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Robert and Becca are in the 25 percent tax bracket. They have a long-term capital gain of $28,000 and a long-term capital loss of $17,000 on sales of stock in the current year. What will their capital gains tax be in the current year?
A)$1,650
B)$2,200
C)$2,750
D)$11,000
E)None of the above is correct
A)$1,650
B)$2,200
C)$2,750
D)$11,000
E)None of the above is correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Karen received a stock portfolio upon the death of her grandmother. The stock originally cost her grandmother $32,000, but was worth $250,000 when she died. What is Karen's tax basis in the stock portfolio? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If a taxpayer is relieved of a liability on the disposition of property, the amount of the liability should be included in the amount realized on the sale or other disposition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
For the current tax year, Morgan had $25,000 of ordinary income. In addition, he had an $1,900 long-term capital loss and a $1,600 short-term capital loss. What will be the amount of Morgan's capital loss carryforward to the next year?
A)$0
B)$300
C)$500
D)$3,000
E)$3,500
A)$0
B)$300
C)$500
D)$3,000
E)$3,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Ben purchased an apartment building about 10 years ago, for $200,000. The building has been depreciated over the appropriate recovery period using the straight-line method. In the current year, the building was sold for $220,000, when the accumulated depreciation was $62,500. Ben is in the highest tax bracket; on his current year tax return, he should report:
A)Section 1231 gain of $20,000 and ordinary income of $62,500
B)Section 1231 gain of $62,500 and ordinary income of $20,000
C)Ordinary income of $82,500
D)Section 1231 gain of $20,000 and "unrecaptured depreciation" taxed at 25 percent of $62,500
E)None of the above
A)Section 1231 gain of $20,000 and ordinary income of $62,500
B)Section 1231 gain of $62,500 and ordinary income of $20,000
C)Ordinary income of $82,500
D)Section 1231 gain of $20,000 and "unrecaptured depreciation" taxed at 25 percent of $62,500
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following assets is not a Section 1231 asset?
A)Equipment used in a business
B)The unharvested crops of a farmer
C)Timber
D)Inventory
E)All of the above are Section 1231 assets
A)Equipment used in a business
B)The unharvested crops of a farmer
C)Timber
D)Inventory
E)All of the above are Section 1231 assets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Martha has a net capital loss of $17,000 and other ordinary taxable income of $45,000 for the current year. What is the amount of Martha's capital loss carryforward?
A)$0
B)$10,000
C)$14,000
D)$17,000
E)None of the above
A)$0
B)$10,000
C)$14,000
D)$17,000
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Elmer sold machinery used in his business for $20,000. The machinery originally cost $80,000 and had $45,000 of accumulated depreciation at the time of the sale. It is his only sale this year.
a.What is the gain or loss on the sale of the machinery?
b.Is the gain or loss treated as capital or ordinary? Explain.
a.What is the gain or loss on the sale of the machinery?
b.Is the gain or loss treated as capital or ordinary? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Martha has a net capital loss of $20,000 and other ordinary taxable income of $45,000 for the current tax year. What is the amount of Martha's taxable income after deducting the allowed capital loss?
A)$28,000
B)$38,000
C)$42,000
D)$45,000
E)None of the above
A)$28,000
B)$38,000
C)$42,000
D)$45,000
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
There is no limit on the amount of capital losses that an individual may deduct against ordinary income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
At the end of the current year, Falstaff sold for $4,800 General Martin stock that was purchased 5 months ago for $4,000. He also sold Cedar stock for $6,000 at the same time. The Cedar stock cost $4,000, 2 years ago. In addition, Falstaff has a short-term capital loss of $500 on the sale of silver.
a.Calculate the amount of Falstaff's net short-term and net long-term capital gain or loss.
b.If Falstaff has a net capital gain, what is the maximum rate at which the gain will be taxed?
a.Calculate the amount of Falstaff's net short-term and net long-term capital gain or loss.
b.If Falstaff has a net capital gain, what is the maximum rate at which the gain will be taxed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the current year, Henry, a sole proprietor, sold for $65,000 a machine that was used in his business. The machine had been purchased in a few years ago for $50,000, and when it was sold, it had accumulated depreciation of $20,000 and an adjusted basis of $30,000. For the current year, how should this gain be treated?
A)Ordinary income of $35,000
B)Section 1231 gain of $35,000
C)Section 1231 gain of $20,000 and ordinary income of $15,000
D)Section 1231 gain of $15,000 and ordinary income of $20,000
E)None of the above
A)Ordinary income of $35,000
B)Section 1231 gain of $35,000
C)Section 1231 gain of $20,000 and ordinary income of $15,000
D)Section 1231 gain of $15,000 and ordinary income of $20,000
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The depreciation recapture provisions are designed to prevent taxpayers from converting capital gains into ordinary income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which one of the following is true about Section 1231 assets?
A)Section 1231 assets are treated like capital assets when they produce losses on sale.
B)Business property held 1 year or less is considered a Section 1231 asset.
C)Section 1231 assets include company stock.
D)Section 1231 asset losses must be netted against 1231 asset gains before tax treatment is determined.
E)All of the above are false.
A)Section 1231 assets are treated like capital assets when they produce losses on sale.
B)Business property held 1 year or less is considered a Section 1231 asset.
C)Section 1231 assets include company stock.
D)Section 1231 asset losses must be netted against 1231 asset gains before tax treatment is determined.
E)All of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In October of the current year, Mike sold a share of Berkshire-Hathaway for $73,000. He had acquired it several years ago at a cost of $42,000. He also sold Microsoft stock he had held for 3 years at a gain of $17,000. He had a short-term $2,000 loss on the sale of stock of a start-up technology company. He has $85,000 in taxable income before capital transactions are taken into account.
Assuming Mike is single with no dependents, what is the amount of Mike's tax on the capital transactions?
Assuming Mike is single with no dependents, what is the amount of Mike's tax on the capital transactions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
During 2016, William sold the following capital assets:
Calculate the following:
a.Total short-term capital gain/loss realized for tax purposes
b.Total long-term capital gain/loss realized for tax purposes
c.Deductible capital gain/loss
d.The amount and nature (short-term or long-term) of his capital loss carryforward
e.Assuming that William has no capital gain or loss for 2017, how much can he deduct in 2017 and what is the amount and nature of any carryforward to 2018?

Calculate the following:
a.Total short-term capital gain/loss realized for tax purposes
b.Total long-term capital gain/loss realized for tax purposes
c.Deductible capital gain/loss
d.The amount and nature (short-term or long-term) of his capital loss carryforward
e.Assuming that William has no capital gain or loss for 2017, how much can he deduct in 2017 and what is the amount and nature of any carryforward to 2018?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For purposes of taxation of capital gains:
A)Short-term capital gains are taxed at 5 percent.
B)Ordinary income tax rates are applied to gains on collectibles.
C)Gains on Section 1231 assets may be treated as long-term capital gains, while losses in some cases may be deducted as ordinary losses.
D)Under the provisions of Section 1245, any gain recognized on the disposition of a Section 1245 asset will be classified as a capital gain.
A)Short-term capital gains are taxed at 5 percent.
B)Ordinary income tax rates are applied to gains on collectibles.
C)Gains on Section 1231 assets may be treated as long-term capital gains, while losses in some cases may be deducted as ordinary losses.
D)Under the provisions of Section 1245, any gain recognized on the disposition of a Section 1245 asset will be classified as a capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the current year, Marc, a single taxpayer, has ordinary income of $35,000. In addition, he has $3,000 in short-term capital gains, short-term capital losses of $6,000, and long-term capital gains of $4,000. What is Marc's adjusted gross income (AGI) for the current year?
A)$32,000
B)$39,000
C)$36,000
D)$34,000
A)$32,000
B)$39,000
C)$36,000
D)$34,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In 2016, Paul, a single taxpayer, has taxable income of $30,000 exclusive of capital gains and losses. Paul incurred a $1,000 short-term capital loss and a $4,000 long-term capital loss. What is the amount of his long-term capital loss carryover to 2017?
A)$0
B)$2,000
C)$3,000
D)$5,000
E)None of the above
A)$0
B)$2,000
C)$3,000
D)$5,000
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Gain recognized on the sale of a Section 1245 asset is classified as ordinary income up to the amount of depreciation claimed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
After 4 years of life in the slow lane, Doug decided to give up his goat ranch and move back to the big city. He sold the goat milking machine for $1,000. The machine originally cost $1,200 and had $820 of accumulated depreciation at the time of sale.
a.What is the total gain or loss on the sale of the goat milking machine?
b.Is the gain or loss treated as capital or ordinary? Explain.
a.What is the total gain or loss on the sale of the goat milking machine?
b.Is the gain or loss treated as capital or ordinary? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the current year, Estes has net short-term capital losses of $3,000, a net long-term capital loss of $45,000, and taxable income from wages of $35,000.
a.Calculate the amount of Estes' deduction for capital losses for the current year.
b.Calculate the amount and nature (short-term or long-term) of his capital loss carryforward.
c.For how many years may Estes carry the unused loss forward?
a.Calculate the amount of Estes' deduction for capital losses for the current year.
b.Calculate the amount and nature (short-term or long-term) of his capital loss carryforward.
c.For how many years may Estes carry the unused loss forward?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Cows used in a farming business are Section 1231 property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the current year, Helen sold Section 1245 property for $6,000. The property cost $26,000 when it was purchased 5 years ago. The depreciation claimed on the property was $24,000.
a.Calculate the adjusted basis of the property.
b.Calculate the amount of ordinary income under Section 1245.
c.Calculate the Section 1231 gain.
a.Calculate the adjusted basis of the property.
b.Calculate the amount of ordinary income under Section 1245.
c.Calculate the Section 1231 gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Dan acquired rental property in June 2006 for $370,000 and sold it in October, 2016. $40,000 in straight-line depreciation has been taken on the house. A run-up in housing prices allowed him to sell the house for $575,000. In the year of sale, Dan received $175,000 when the buyer sold some investments, an additional $200,000 when the buyer closed a loan from the bank, and took a $200,000 note from the buyer, payable on the anniversary of the sale date in 10 installments of $20,000 each plus interest on the unpaid balance.
Using the installment method, calculate his taxable gain in the year of sale.
Using the installment method, calculate his taxable gain in the year of sale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Tim sells land to Brad for $90,000. Tim originally purchased the land for $50,000. Brad agrees to pay Tim six annual installments of $15,000 each. In year three, Brad makes his third installment of $15,000. How much taxable gain will Tim recognize in year three?
A)$5,000
B)$6,667
C)$13,333
D)$15,000
E)All the taxable gain should be recognized in year one.
A)$5,000
B)$6,667
C)$13,333
D)$15,000
E)All the taxable gain should be recognized in year one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Simon sold investment property 2 years ago for $750. Simon's basis in the property was $200. Simon is receiving $150 per year from the buyer. Simon reports this income on the installment method. If Simon collects $150 in principal during the current year, how much gain should he report from the sale for the year?
A)$0
B)$75
C)$90
D)$110
E)None of the above
A)$0
B)$75
C)$90
D)$110
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the treatment given to personal casualty gains and losses?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Robert acquired his rental property 10 years ago for $110,000 and sold it in the current year for $230,000. The accumulated straight-line depreciation on the property at the time of the sale was $35,000. Robert is in the 35 percent tax bracket for ordinary income.
a.What is Robert's gain on the sale of his rental property?
b.How is the gain taxed? (i.e., What tax bracket is the gain subject to)?
a.What is Robert's gain on the sale of his rental property?
b.How is the gain taxed? (i.e., What tax bracket is the gain subject to)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The exchange of inventory does not qualify for like-kind exchange treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Rod had the following personal casualty in 2016:
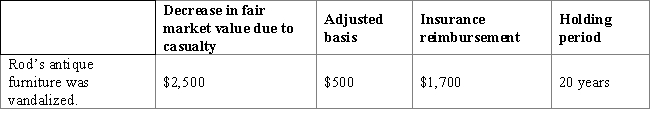
Calculate the amount and nature of Rod's gain or loss as a result of this casualty.

Calculate the amount and nature of Rod's gain or loss as a result of this casualty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the proceeds from the sale of property will be collected over a period of more than one year, a taxpayer is required to use the installment method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A taxpayer eligible to use the installment method for reporting gain on the sale of an asset must use the installment method unless he or she elects out of the provision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Assuming a taxpayer has no other gains or losses for the year, a loss from the theft of a Section 1231 asset is treated as a capital loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the current year, Tim sells Section 1245 property for $28,000 that he had purchased 6 years ago. Tim has claimed $7,000 in depreciation on the property and originally purchased it for $20,000. How much of the gain is taxable as ordinary income?
A)$7,000
B)$8,000
C)$13,000
D)$18,000
E)None of the above is correct
A)$7,000
B)$8,000
C)$13,000
D)$18,000
E)None of the above is correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Verlin sells a commercial building and receives $50,000 in cash and a note for $60,000 at 10 percent interest. Verlin's adjusted basis in the building on the date of sale is $45,000 and he collects only the $50,000 down payment in the year of the sale.
a.
If Verlin elects to recognize the total gain on the property in the year of sale, calculate the taxable gain.
b.
Assuming Verlin uses the installment sale method, calculate the taxable gain he must report for the year of the sale.
c.
Assuming Verlin collects $10,000 (not including interest) of the note principal in the year following the year of sale, calculate the amount of income recognized under the installment sale method.
a.
If Verlin elects to recognize the total gain on the property in the year of sale, calculate the taxable gain.
b.
Assuming Verlin uses the installment sale method, calculate the taxable gain he must report for the year of the sale.
c.
Assuming Verlin collects $10,000 (not including interest) of the note principal in the year following the year of sale, calculate the amount of income recognized under the installment sale method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Perry acquired raw land as an investment 16 years ago. The land cost $60,000. In the current year, the land is sold for a total sales price of $120,000, consisting of $10,000 cash and the buyer's note for $110,000. If Perry elects to recognize the entire gain in the year of sale, what is his recognized gain in the current year?
A)$50,000
B)$60,000
C)$100,000
D)$110,000
E)None of the above
A)$50,000
B)$60,000
C)$100,000
D)$110,000
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A net long-term gain from the theft of a Section 1231 asset is treated as a Section 1231 gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Perry acquired raw land as an investment 16 years ago. The land cost $50,000. In the current year, the land is sold for a total sales price of $120,000, consisting of $10,000 cash and the buyer's note for $110,000. Assume that Perry uses the installment method to recognize the gain and receives only the $10,000 down payment in the year of sale. How much gain should Perry recognize in the current year?
A)$4,166
B)$5,833
C)$7,000
D)$9,000
E)None of the above
A)$4,166
B)$5,833
C)$7,000
D)$9,000
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Terry has a casualty gain of $1,000 and a casualty loss of $5,500, before the $100 floor and before the adjusted gross income limitation. The gain and loss were the result of two separate casualties occurring during the current year and both properties were personal-use assets. If Terry itemizes deductions on her current year return and has adjusted gross income of $25,000, what is Terry's gain or net itemized deduction as a result of these casualties?
A)$5,300 itemized deduction, $1,000 capital gain
B)$1,900 itemized deduction
C)$1,800 itemized deduction
D)$2,800 itemized deduction, $1,000 capital gain
E)None of the above
A)$5,300 itemized deduction, $1,000 capital gain
B)$1,900 itemized deduction
C)$1,800 itemized deduction
D)$2,800 itemized deduction, $1,000 capital gain
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Rod had the following loss on business-use property:
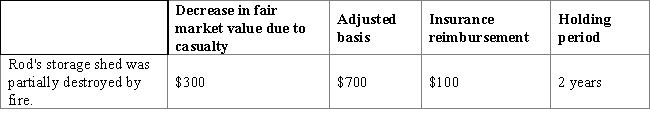
Calculate the amount and nature of Rod's gain or loss as a result of this casualty.

Calculate the amount and nature of Rod's gain or loss as a result of this casualty.
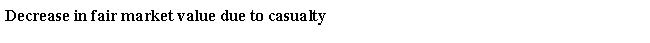
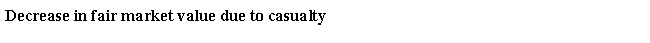
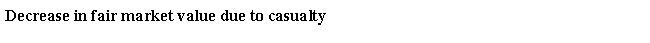

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Casualty gains and losses from business or investment property:
A)May be treated differently depending on whether the property has been held 1 year or less or has been held over 1 year.
B)Are treated the same as casualty gains and losses from personal property.
C)Are subject to the 10 percent of adjusted gross income limitation.
D)Are not subject to the depreciation recapture provisions.
A)May be treated differently depending on whether the property has been held 1 year or less or has been held over 1 year.
B)Are treated the same as casualty gains and losses from personal property.
C)Are subject to the 10 percent of adjusted gross income limitation.
D)Are not subject to the depreciation recapture provisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Sally acquired an apartment building 15 years ago for $150,000 and sold it for $410,000 in the current year. At the time of the sale, there is $65,000 of accumulated straight-line depreciation on the apartment building. Assuming Sally is in the 35 percent tax bracket for ordinary income, how much of her gain is taxed at 15 percent?
A)None
B)$65,000
C)$260,000
D)$325,000
E)$345,000
A)None
B)$65,000
C)$260,000
D)$325,000
E)$345,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



