Deck 3: Taxation Planning
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Taxation Planning
1
Ms Barbara Phillips, 61 years of age, is employed as an editorial assistant by a large publishing firm. In addition to her base salary of $60,000 (including mandatory superannuation guarantee [SG] contributions) she receives the following non-cash benefits from her employer:
• Fully maintained BMW motor vehicle purchased by her employer at the commencement of the financial year for $50,000. During the year the vehicle travelled 22,000 kilometres of which 9,000 were for business use. The total running costs of the vehicle over the last financial year was $12,000.
• Employer superannuation contributions of $20,000 paid to a self-managed superannuation fund (SMSF) established by Barbara.
The company adopts the statutory formula method for calculating motor vehicle fringe benefits with the relevant taxation office rate of 20% applying to the kilometres travelled during the year by Barbara.
a) What is the total value of Barbara’s total salary package with her employer?
b) What amount of reportable fringe benefits and reportable employer superannuation contributions (RESC) would be reported on Barbara’s payment summary?
• Fully maintained BMW motor vehicle purchased by her employer at the commencement of the financial year for $50,000. During the year the vehicle travelled 22,000 kilometres of which 9,000 were for business use. The total running costs of the vehicle over the last financial year was $12,000.
• Employer superannuation contributions of $20,000 paid to a self-managed superannuation fund (SMSF) established by Barbara.
The company adopts the statutory formula method for calculating motor vehicle fringe benefits with the relevant taxation office rate of 20% applying to the kilometres travelled during the year by Barbara.
a) What is the total value of Barbara’s total salary package with her employer?
b) What amount of reportable fringe benefits and reportable employer superannuation contributions (RESC) would be reported on Barbara’s payment summary?
a)
b)
Hence the reportable fringe benefit included on Barbara's payment summary will be $18,692.
Reportable employer superannuation contributions (RESC) included on Barbara's payment summary would only be the additional $20,000 contributed by the employer for Barbara to her SMSF - it would not include the mandatory SG contributions.
b)
Hence the reportable fringe benefit included on Barbara's payment summary will be $18,692.
Reportable employer superannuation contributions (RESC) included on Barbara's payment summary would only be the additional $20,000 contributed by the employer for Barbara to her SMSF - it would not include the mandatory SG contributions.
2
The Commonwealth Government has exclusively levied income tax in Australia since:
A) 1912
B) 1936
C) 1942
D) 1997
A) 1912
B) 1936
C) 1942
D) 1997
C
3
Marginal income tax rates for individuals in Australia are best described as:
A) regressive.
B) progressive.
C) constant.
D) none of the above.
A) regressive.
B) progressive.
C) constant.
D) none of the above.
B
4
One of your taxation clients, Ms Carly Benicio, has brought in her taxation records for the current financial year. You have reconciled this information and have determined her taxable income to be $80,000, PAYG withholding from her salary during the year was $19,800 and no tax offsets were available. Prior to finalising these records you receive a telephone call from Carly saying that she is also entitled to an additional claim for an outgoing of $2,000 in the current financial year, however she is not sure whether this amount is to be included in her taxation return as an allowable deduction or a taxation offset.
Explain to Carly using the tax rates in the textbook, the incremental benefit in her current year taxation return of the amount being available as a taxation offset rather than as an allowable deduction.
Explain to Carly using the tax rates in the textbook, the incremental benefit in her current year taxation return of the amount being available as a taxation offset rather than as an allowable deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The taxable capital gain from the sale of an investment held for at least 12 months can potentially be calculated in which of the following ways?
A) Indexation method or discount method.
B) Sale price plus purchase price.
C) Purchase price less sale price.
D) None of the above.
A) Indexation method or discount method.
B) Sale price plus purchase price.
C) Purchase price less sale price.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
For negative gearing purposes:
A) the benefit of the tax loss created depends on the marginal tax rate of the lender.
B) the tax loss created by the investor can be offset against salary and other net investment income in the same financial year.
C) total allowable deductions excluding interest expense from the investment will always exceed net investment income.
D) all of the above.
A) the benefit of the tax loss created depends on the marginal tax rate of the lender.
B) the tax loss created by the investor can be offset against salary and other net investment income in the same financial year.
C) total allowable deductions excluding interest expense from the investment will always exceed net investment income.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The Australian company income tax rate is:
A) 10%
B) 15%
C) 30%
D) none of the above
A) 10%
B) 15%
C) 30%
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Where a shareholder is entitled to receive a dividend it will be included as part of their assessable income for the relevant financial year unless it is:
A) a fully franked dividend.
B) an unfranked dividend.
C) subject to a dividend reinvestment scheme.
D) none of the above.
A) a fully franked dividend.
B) an unfranked dividend.
C) subject to a dividend reinvestment scheme.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
You have been approached by a new client, Ms Belinda Nguyen to prepare her 2014 income tax return. At the interview, Belinda provides you with the following information to assist with the completion of her tax return:
a) Calculate Belinda's 2014 taxable income.
b) Calculate Belinda's 2014 net tax payable / refund including the medicare levy and any low income tax offset.
c) After adjusting to remove the PAYG tax instalments deducted and the non-cash adjustment for franked dividends as part of assessable income, calculate the average tax rate payable by Belinda for the 2014 year. Note that Average tax rate = Adjusted tax payable / Adjusted taxable income.
a) Calculate Belinda's 2014 taxable income.
b) Calculate Belinda's 2014 net tax payable / refund including the medicare levy and any low income tax offset.
c) After adjusting to remove the PAYG tax instalments deducted and the non-cash adjustment for franked dividends as part of assessable income, calculate the average tax rate payable by Belinda for the 2014 year. Note that Average tax rate = Adjusted tax payable / Adjusted taxable income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Sources of taxation law includes:
A) Income Tax assessment Act 1997 (ITAA97).
B) case law.
C) both a and b
D) Corporations Act.
A) Income Tax assessment Act 1997 (ITAA97).
B) case law.
C) both a and b
D) Corporations Act.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How much tax would be payable by the Lee Superannuation Fund with all members in accumulation mode which provided the following details for the 2013 financial year: Sale of investments for a gross capital gain of $20,000 that were held for 9 months.
Sale of investments for a gross capital gain of $30,000 that were held for 3 years.
Other assessable income of $100,000.
Allowable deductions of $20,000.
A) $9,000
B) *$18,000
C) $19,500
D) $20,000
Sale of investments for a gross capital gain of $30,000 that were held for 3 years.
Other assessable income of $100,000.
Allowable deductions of $20,000.
A) $9,000
B) *$18,000
C) $19,500
D) $20,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In your opinion, why are relatively high marginal income tax rates and a low tax free threshold imposed on minors in relation to unearned income?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following items are generally exempt from the capital gains tax?
A) Main residence.
B) Passenger motor cars.
C) Gambling winnings.
D) All of the above.
A) Main residence.
B) Passenger motor cars.
C) Gambling winnings.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following are not tax deductible expenses?
A) Expenses of a domestic nature.
B) Expenses of a capital nature.
C) Expenses incurred in earning exempt income.
D) All of the above.
A) Expenses of a domestic nature.
B) Expenses of a capital nature.
C) Expenses incurred in earning exempt income.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The term(s) used to describe an employee taking a lower cash salary in lieu of other non- cash benefits include(s):
A) salary packaging.
B) salary sacrificing.
C) both a and b
D) none of the above.
A) salary packaging.
B) salary sacrificing.
C) both a and b
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Appropriate income splitting strategies for taxation purposes may include:
A) transferring personal services income (PSI) to another person.
B) transferring unearned income of at least $5,000 from an adult taxpayer on a marginal tax rate of 32.5% to a minor.
C) transferring assessable income from an adult taxpayer on a low marginal tax rate to an adult taxpayer on a high marginal tax rate.
D) none of the above.
A) transferring personal services income (PSI) to another person.
B) transferring unearned income of at least $5,000 from an adult taxpayer on a marginal tax rate of 32.5% to a minor.
C) transferring assessable income from an adult taxpayer on a low marginal tax rate to an adult taxpayer on a high marginal tax rate.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Where a company has paid no Australian company tax on profits from which a dividend is paid to shareholders, the dividend is said to be:
A) fully franked.
B) not taxable.
C) subject to the maximum marginal personal tax rate in the hands of the shareholder.
D) unfranked.
A) fully franked.
B) not taxable.
C) subject to the maximum marginal personal tax rate in the hands of the shareholder.
D) unfranked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Examples of income tax offsets in Australia include:
A) subscriptions to professional journals.
B) imputation or franked credits.
C) interest on loans used for investment purposes.
D) all of the above.
A) subscriptions to professional journals.
B) imputation or franked credits.
C) interest on loans used for investment purposes.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In Australia, the maximum marginal income tax rate imposed on unearned income by minors is:
A) less than that of adult individual taxpayers.
B) equal to that of adult individual taxpayers.
C) greater than that of adult individual taxpayers.
D) the same as that of that of adult individual taxpayers at all levels of taxable income.
A) less than that of adult individual taxpayers.
B) equal to that of adult individual taxpayers.
C) greater than that of adult individual taxpayers.
D) the same as that of that of adult individual taxpayers at all levels of taxable income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Income tax is imposed on a taxpayer's:
A) assessable income.
B) taxable income.
C) tax offsets.
D) taxable income less tax offsets.
A) assessable income.
B) taxable income.
C) tax offsets.
D) taxable income less tax offsets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
As an experienced financial adviser with a medium-sized taxation and financial advisory practice, prepare some notes for your junior work colleagues in relation to issues they need to be aware of prior to them implementing income splitting strategies for the firm's tax clients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Mr Brady Chambers has approached you for advice as to which investment structure he should use to acquire some preference shares in Strikealite Ltd., a company that will list on the Australian Stock exchange on the 30th June 2014. Brady is 32 years old and seeks to purchase 200,000 shares at the listing price of $1 per share. The company has forecast fully franked annual preference dividends of 10 cents per share and analysts have forecast a price for the shares in 2 years of $1.60.
a) Assuming the dividend and price forecasts are realised, what would be the net investment return to Brady on the share acquisition over 2 years, expressing your return in the form of the net after-tax dollar amount received from the investment at the end of 2 years, where the shares were acquired in each of the following entities:
1-1Brady's own name assuming a marginal tax rate of 45% (ignore the medicare levy in your calculations).
1-2 A company name.
1-3 The name of a superannuation fund.
Show all calculations for each investment entity.
b) Based on your calculations in part (a), rank the alternatives from the most preferred to the least preferred investment entity.
c) Briefly outline other financial and non-financial issues in relation to the various investment entities that would be relevant to discuss with Brady prior to providing any recommendations.
a) Assuming the dividend and price forecasts are realised, what would be the net investment return to Brady on the share acquisition over 2 years, expressing your return in the form of the net after-tax dollar amount received from the investment at the end of 2 years, where the shares were acquired in each of the following entities:
1-1Brady's own name assuming a marginal tax rate of 45% (ignore the medicare levy in your calculations).
1-2 A company name.
1-3 The name of a superannuation fund.
Show all calculations for each investment entity.
b) Based on your calculations in part (a), rank the alternatives from the most preferred to the least preferred investment entity.
c) Briefly outline other financial and non-financial issues in relation to the various investment entities that would be relevant to discuss with Brady prior to providing any recommendations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Positive and negative gearing are alternative taxation strategies often recommended to investment clients for property-based investments. Outline the client characteristics that are likely to be different where they have been recommended to undertake positive / negative gearing taxation strategies in relation to property-based investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
As a taxation and financial expert, what taxation-related issues are relevant regarding investment returns in the form of income and / or capital gains when discussing the investment selection process with your clients? That is, how are income and capital gains taxed differently pursuant to the ITAA97? In addition, provide your clients with some general investment advice regarding the likelihood / risk of generating income / capital returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Companies are often used by taxpayers seeking to reduce their exposure to relatively high individual marginal tax rates. Would you recommend such practice to one of your financial planning clients who, in the current financial year, is likely to have a taxable income slightly above $90,000 and is also looking to acquire a personal residence and medium to long-term growth assets in the particular investment structure selected? Taxable income of the client in future years is also likely to remain slightly in excess of $90,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
From the previous question, Belinda omitted to advise you that she also has some capital gains tax information arising from shares she had sold in the 2014 financial year. In addition, Belinda also forgot to tell you that she has a carry forward capital loss as at the start of the 2014 financial year of $3,700. All the shares listed below were sold on the 19th March 2014 with the remaining relevant capital gains tax information as follows:
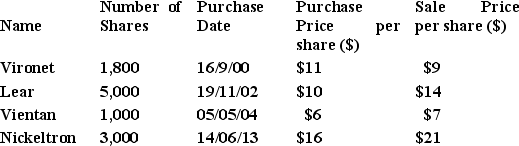 a) Calculate the 2014 net taxable capital gain / loss for Belinda.
a) Calculate the 2014 net taxable capital gain / loss for Belinda.
b) Calculate Belinda's adjusted 2014 taxable income.
c) Calculate Belinda's adjusted 2014 net tax payable / refund including the medicare levy and any low income tax offset.
d) Calculate the overall change in 2014 tax liability as a result of the additional information provided by Belinda.
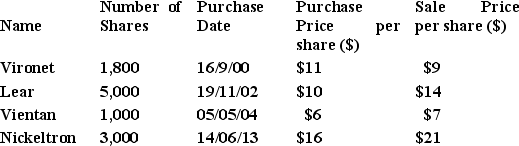 a) Calculate the 2014 net taxable capital gain / loss for Belinda.
a) Calculate the 2014 net taxable capital gain / loss for Belinda.b) Calculate Belinda's adjusted 2014 taxable income.
c) Calculate Belinda's adjusted 2014 net tax payable / refund including the medicare levy and any low income tax offset.
d) Calculate the overall change in 2014 tax liability as a result of the additional information provided by Belinda.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



