Deck 14: An Introduction to Derivative Markets and Securities
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/102
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: An Introduction to Derivative Markets and Securities
1
An option to sell an asset is referred to as a call, whereas an option to buy an asset is called a put.
False
2
The forward market has low liquidity relative to the futures market.
True
3
Investment costs are generally higher in the derivative markets than in the corresponding cash markets.
False
4
A futures contract is an agreement between a trader and the clearinghouse of the exchange for delivery of an asset in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If an investor wants to acquire the right to buy or sell an asset, but not the obligation to do it, the best instrument is an option rather than a futures contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Futures contracts are slower to absorb new information than forward contracts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The minimum value of an option is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The initial value of a future contract is the price agreed upon in the contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A primary function of futures markets is to allow investors to transfer risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
All features of a forward contract are standardized, except for price and number of contracts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Forward contracts are traded over-the-counter and are generally not standardized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A cash or spot contract is an agreement for the immediate delivery of an asset, such as the purchase of stock on the NYSE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The price at which the stock can be acquired or sold is the exercise price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Investors buy call options because they expect the price of the underlying stock to increase before the expiration of the option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A put option is in the money if the current market price is above the strike price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A call option is in the money if the current market price is above the strike price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A futures contract eliminates uncertainty about the future spot price that an individual can expect to pay for an asset at the time of delivery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Forward and future contracts, as well as options, are types of derivative securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An option buyer must exercise the option on or before the expiration date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The futures market is a dealer market in which all the details of the transactions are negotiated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The payoffs to both the long and short position in the forward contact are symmetric around the contract price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
There are a number of differences between forward and futures contracts. Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Futures have less liquidity risk than forward contracts.
B) Futures have less credit risk than forward contracts.
C) Futures have more default risk than forward contracts.
D) In futures, the exchange becomes the counterparty to all transactions.
E) Futures have standardized terms of agreement.
A) Futures have less liquidity risk than forward contracts.
B) Futures have less credit risk than forward contracts.
C) Futures have more default risk than forward contracts.
D) In futures, the exchange becomes the counterparty to all transactions.
E) Futures have standardized terms of agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Derivative instruments exist because
A) they help shift risk from risk-averse investors to risk-takers.
B) they help in forming prices.
C) they have lower investment costs.
D) allow investors to hedge portfolio risk.
E) All of these are correct.
A) they help shift risk from risk-averse investors to risk-takers.
B) they help in forming prices.
C) they have lower investment costs.
D) allow investors to hedge portfolio risk.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A forward contract gives its holder the option to conduct a transaction involving another security or commodity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The payoffs diagrams to both long and short positions in a forward contract are asymmetrical around the contract price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The option premium is the price the call buyer will pay to the option seller if the option is exercised

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Forward contracts do not require an upfront premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Derivatives help shift risk from risk-adverse investors to risk-takers.
B) Derivatives assist in forming cash prices.
C) Derivatives provide additional information to the market.
D) In many cases, the investment in derivatives (both commissions and required investment) is more than in the cash market.
E) Some derivatives trade hypothetical underlying assets.
A) Derivatives help shift risk from risk-adverse investors to risk-takers.
B) Derivatives assist in forming cash prices.
C) Derivatives provide additional information to the market.
D) In many cases, the investment in derivatives (both commissions and required investment) is more than in the cash market.
E) Some derivatives trade hypothetical underlying assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is NOT a factor needed to calculate the value of an American call option?
A) price of the underlying stock
B) exercise price
C) price of an equivalent put option
D) volatility of the underlying stock
E) interest rate
A) price of the underlying stock
B) exercise price
C) price of an equivalent put option
D) volatility of the underlying stock
E) interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements is a true definition of an in-the-money option?
A) a call option in which the stock price exceeds the exercise price
B) a call option in which the exercise price exceeds the stock price
C) a put option in which the stock price exceeds the exercise price
D) an index option in which the exercise price exceeds the stock price
E) a call option in which the call premium exceeds the stock price
A) a call option in which the stock price exceeds the exercise price
B) a call option in which the exercise price exceeds the stock price
C) a put option in which the stock price exceeds the exercise price
D) an index option in which the exercise price exceeds the stock price
E) a call option in which the call premium exceeds the stock price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The minimum amount that must be maintained in an account is called the maintenance margin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the forward market, both parties are required to post collateral or margin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Forward contracts are much easier to unwind than futures contracts due to the standardization of the contracts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The value of a call option just prior to expiration is (where V is the underlying asset's market price and X is the option's exercise price)
A) max [0, V - X].
B) max [0, X - V].
C) min [0, V - X].
D) min [0, X - V].
E) max [0, V > X].
A) max [0, V - X].
B) max [0, X - V].
C) min [0, V - X].
D) min [0, X - V].
E) max [0, V > X].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The CBOE brought numerous innovations to the option market. Which of the following is NOT such an innovation?
A) creation of a central marketplace
B) creation of a non-liquid secondary option market
C) introduction of a Clearing Corporation
D) standardization of all expiration dates
E) standardization of all exercise prices
A) creation of a central marketplace
B) creation of a non-liquid secondary option market
C) introduction of a Clearing Corporation
D) standardization of all expiration dates
E) standardization of all exercise prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
You own a stock that has risen from $10 per share to $32 per share. You wish to delay taking the profit, but you are troubled about the short-run behavior of the stock market. An effective action on your part would be to
A) buy a put option on the stock.
B) write a call option on the stock.
C) purchase an index option.
D) purchase an interest rate option.
E) write a put option on the stock.
A) buy a put option on the stock.
B) write a call option on the stock.
C) purchase an index option.
D) purchase an interest rate option.
E) write a put option on the stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following factors is NOTconsidered in the valuation of call and put options?
A) current stock price
B) exercise price
C) market interest rate
D) volatility of underlying stock price
E) the option trading market
A) current stock price
B) exercise price
C) market interest rate
D) volatility of underlying stock price
E) the option trading market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Futures differ from forward contracts because
A) futures have more liquidity risk.
B) futures have more credit risk.
C) futures have more maturity risk.
D) futures do not require collateral.
E) None of these are correct.
A) futures have more liquidity risk.
B) futures have more credit risk.
C) futures have more maturity risk.
D) futures do not require collateral.
E) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The price at which a futures contract is set at the end of the day is the
A) stock price.
B) strike price.
C) maintenance price.
D) settlement price.
E) parity price.
A) stock price.
B) strike price.
C) maintenance price.
D) settlement price.
E) parity price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) The buyer of a futures contract is said to be long futures.
B) The buyer of a futures contract is said to be long futures.
C) The seller of a futures contract is said to be long futures.
D) The buyer of a futures contract is said to be short futures.
E) The buyer of a futures contract is unwinding a long position.
A) The buyer of a futures contract is said to be long futures.
B) The buyer of a futures contract is said to be long futures.
C) The seller of a futures contract is said to be long futures.
D) The buyer of a futures contract is said to be short futures.
E) The buyer of a futures contract is unwinding a long position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A call option differs from a put option in that
A) a call option obliges the investor to purchase a given number of shares in a specific common stock at a set price; a put obliges the investor to sell a certain number of shares in a common stock at a set price.
B) both give the investor the opportunity to participate in stock market dealings without the risk of actual stock ownership.
C) a call option gives the investor the right to purchase a given number of shares of a specified stock at a set price; a put option gives the investor the right to sell a given number of shares of a stock at a set price.
D) a put option has risk because leverage is not as great as with a call.
E) All of these are correct.
A) a call option obliges the investor to purchase a given number of shares in a specific common stock at a set price; a put obliges the investor to sell a certain number of shares in a common stock at a set price.
B) both give the investor the opportunity to participate in stock market dealings without the risk of actual stock ownership.
C) a call option gives the investor the right to purchase a given number of shares of a specified stock at a set price; a put option gives the investor the right to sell a given number of shares of a stock at a set price.
D) a put option has risk because leverage is not as great as with a call.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
On the last day of October, Bruce Springsteen is considering the purchase of 100 shares of Olivia Corporation common stock selling at $37 1/2 per share and is considering an Olivia option.
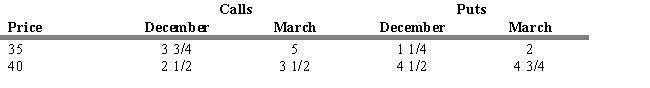
Refer to Exhibit 14.1. If Bruce decides to buy a March call option with an exercise price of 35, what is his dollar gain (loss) if he closes his position when the stock is selling at 43 1/2?
A) $225.00 loss
B) $350.00 loss
C) $225.00 gain
D) $350.00 gain
E) $850.00 gain
On the last day of October, Bruce Springsteen is considering the purchase of 100 shares of Olivia Corporation common stock selling at $37 1/2 per share and is considering an Olivia option.
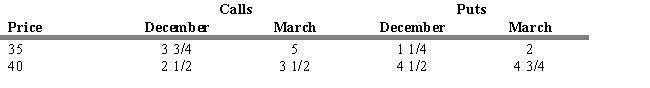
Refer to Exhibit 14.1. If Bruce decides to buy a March call option with an exercise price of 35, what is his dollar gain (loss) if he closes his position when the stock is selling at 43 1/2?
A) $225.00 loss
B) $350.00 loss
C) $225.00 gain
D) $350.00 gain
E) $850.00 gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The value of a put option at expiration is
A) max [0, S(T) - X].
B) max [0, X - S(T)].
C) min [0, X - S(T)].
D) X
A) max [0, S(T) - X].
B) max [0, X - S(T)].
C) min [0, X - S(T)].
D) X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The price paid for the option contract is referred to as the
A) forward price.
B) exercise price.
C) striking price.
D) option premium.
E) call price.
A) forward price.
B) exercise price.
C) striking price.
D) option premium.
E) call price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A call option in which the stock price is higher than the exercise price is said to be
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) before-the-money.
D) out-of-the-money.
E) above-the-money.
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) before-the-money.
D) out-of-the-money.
E) above-the-money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following statements is a true definition of an out-of-the-money option?
A) a call option in which the stock price exceeds the exercise price
B) a call option in which the exercise price exceeds the stock price
C) a call option in which the exercise price exceeds the stock price
D) a put option in which the exercise price exceeds the stock price
E) a call option in which the call premium exceeds the stock price
A) a call option in which the stock price exceeds the exercise price
B) a call option in which the exercise price exceeds the stock price
C) a call option in which the exercise price exceeds the stock price
D) a put option in which the exercise price exceeds the stock price
E) a call option in which the call premium exceeds the stock price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Futures contracts are similar to forward contracts in that they both
A) have volatile price movements and strong interest from buyers and sellers.
B) give the holder the option to make a transaction in the future.
C) have similar liquidity.
D) have similar credit risk.
E) trade on the same exchange.
A) have volatile price movements and strong interest from buyers and sellers.
B) give the holder the option to make a transaction in the future.
C) have similar liquidity.
D) have similar credit risk.
E) trade on the same exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An expiration date payoff and profit diagram for forward positions illustrates
A) gains and losses are usually small.
B) the payoffs to both long and short positions in the forward contract are asymmetrical around the contract price.
C) forward contracts are zero-sum games.
D) long positions benefit from falling prices.
E) short positions benefit from rising prices.
A) gains and losses are usually small.
B) the payoffs to both long and short positions in the forward contract are asymmetrical around the contract price.
C) forward contracts are zero-sum games.
D) long positions benefit from falling prices.
E) short positions benefit from rising prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
On the last day of October, Bruce Springsteen is considering the purchase of 100 shares of Olivia Corporation common stock selling at $37 1/2 per share and is considering an Olivia option.
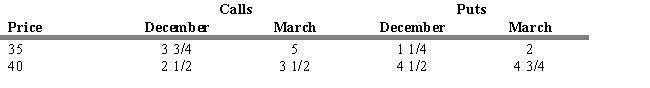
Refer to Exhibit 14.1. If Bruce buys a March put option with an exercise price of 40, what is his dollar gain (loss) if he closes his position when the stock is selling at 43 1/2?
A) $825.00 loss
B) $475.00 loss
C) $350.00 loss
D) $25.00 loss
E) $50.00 gain
On the last day of October, Bruce Springsteen is considering the purchase of 100 shares of Olivia Corporation common stock selling at $37 1/2 per share and is considering an Olivia option.
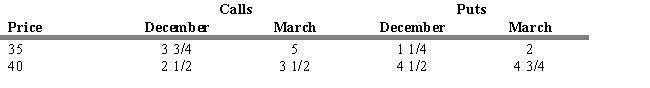
Refer to Exhibit 14.1. If Bruce buys a March put option with an exercise price of 40, what is his dollar gain (loss) if he closes his position when the stock is selling at 43 1/2?
A) $825.00 loss
B) $475.00 loss
C) $350.00 loss
D) $25.00 loss
E) $50.00 gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A stock currently sells for $15 per share. A put option on the stock with an exercise price of $20 currently sells for $6.50. The put option is
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) at breakeven.
E) above-the-money.
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) at breakeven.
E) above-the-money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A stock currently sells for $150 per share. A call option on the stock with an exercise price of $155 currently sells for $2.50. The call option is
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) at breakeven.
E) above-the-money.
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) at breakeven.
E) above-the-money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A stock currently sells for $15 per share. A put option on the stock with an exercise price of $15 currently sells for $1.50. The put option is
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) at breakeven.
E) above-the-money.
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) at breakeven.
E) above-the-money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Intrinsic value represents the value
A) the seller could extract from the option if they exercised it immediately.
B) the buyer could extract from the option if they exercised it immediately.
C) seller pays for the time premium.
D) buyer pays for time premium.
E) below zero.
A) the seller could extract from the option if they exercised it immediately.
B) the buyer could extract from the option if they exercised it immediately.
C) seller pays for the time premium.
D) buyer pays for time premium.
E) below zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A forward contract is similar to an option contract because they both
A) can provide insurance against the price of the underlying stock.
B) are paid for up front in the form of premiums.
C) are paid for at the end of the contract in the form of premiums.
D) require a future settlement payment.
E) trade on exchanges.
A) can provide insurance against the price of the underlying stock.
B) are paid for up front in the form of premiums.
C) are paid for at the end of the contract in the form of premiums.
D) require a future settlement payment.
E) trade on exchanges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements are TRUE?
A) Futures contracts have less liquidity risk and credit risk than forward contracts.
B) Futures contract prices are strongly linked to the prevailing level of the underlying spot index.
C) Futures contract decrease in price the further forward in time the delivery date is set.
D) Futures contracts have more liquidity risk and credit risk than forward contracts.
E) Futures contract prices are weakly linked to the prevailing level of the underlying spot index.
A) Futures contracts have less liquidity risk and credit risk than forward contracts.
B) Futures contract prices are strongly linked to the prevailing level of the underlying spot index.
C) Futures contract decrease in price the further forward in time the delivery date is set.
D) Futures contracts have more liquidity risk and credit risk than forward contracts.
E) Futures contract prices are weakly linked to the prevailing level of the underlying spot index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A stock currently sells for $75 per share. A call option on the stock with an exercise price of $70 currently sells for $5.50. The call option is
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) at breakeven.
E) above-the-money.
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) at breakeven.
E) above-the-money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An advantage of a forward contract over a futures contract is that
A) the terms of the contract are flexible.
B) it is more liquid.
C) it trades through a centralized market exchange.
D) it is easier to unwind due to contract homogeneity.
E) the counterparty is anonymous.
A) the terms of the contract are flexible.
B) it is more liquid.
C) it trades through a centralized market exchange.
D) it is easier to unwind due to contract homogeneity.
E) the counterparty is anonymous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A stock currently sells for $75 per share. A put option on the stock with an exercise price of $70 currently sells for $0.50. The put option is
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) at breakeven.
E) above-the-money.
A) at-the-money.
B) in-the-money.
C) out-of-the-money.
D) at breakeven.
E) above-the-money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A buyer of the call option is NOT speculating on the
A) direction of the price movement of the underlying investment.
B) timing of the price movement of the underlying investment.
C) leverage that a call option creates with respect to the underlying investment.
D) volatility of the price movement of the underlying investment.
E) liquidity of the underlying investment.
A) direction of the price movement of the underlying investment.
B) timing of the price movement of the underlying investment.
C) leverage that a call option creates with respect to the underlying investment.
D) volatility of the price movement of the underlying investment.
E) liquidity of the underlying investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following does NOT influence the option price?
A) past stock price
B) up and down factors u and d
C) risk free rate
D) exercise price
E) current stock price
A) past stock price
B) up and down factors u and d
C) risk free rate
D) exercise price
E) current stock price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Tom Gettback buys 100 shares of Johnson Walker stock for $87.00 per share and a three-month Johnson Walker put option with an exercise price of $105.00 for $20.00. What is Tom's dollar gain/loss if at expiration the stock is selling for $105.00 per share?
A) $1000 gain
B) $200 loss
C) $1000 loss
D) $200 gain
E) $500 gain
A) $1000 gain
B) $200 loss
C) $1000 loss
D) $200 gain
E) $500 gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Assume that you purchased shares of a stock at a price of $35 per share. At this time, you purchased a put option with a $35 strike price of $3. The stock currently trades at $40. Calculate the dollar return on this option strategy.
A) $3
B) -$2
C) $2
D) -$3
E) $0
A) $3
B) -$2
C) $2
D) -$3
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Consider a stock that is currently trading at $10. Calculate the intrinsic value for a call option that has an exercise price of $15.
A) $25
B) -$5
C) $0
D) $20
E) $5
A) $25
B) -$5
C) $0
D) $20
E) $5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Sarah Kling bought a six-month Peppy Cola put option with an exercise price of $55 for a premium of $8.25 when Peppy was selling for $48.00 per share.
Refer to Exhibit 14.3. What is Sarah's annualized gain/loss?
A) 11.51 percent gain
B) 115.15 percent gain
C) 11.51 percent loss
D) 115.15 percent loss
E) 0 percent
Sarah Kling bought a six-month Peppy Cola put option with an exercise price of $55 for a premium of $8.25 when Peppy was selling for $48.00 per share.
Refer to Exhibit 14.3. What is Sarah's annualized gain/loss?
A) 11.51 percent gain
B) 115.15 percent gain
C) 11.51 percent loss
D) 115.15 percent loss
E) 0 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Assume that you have purchased a call option with a strike price $60 for $5. At the same time, you purchase a put option on the same stock with a strike price of $60 for $4. If the stock is currently selling for $75 per share, calculate the dollar return on this option strategy.
A) $10
B) -$4
C) $5
D) $6
E) $15
A) $10
B) -$4
C) $5
D) $6
E) $15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A stock currently trades for $25. January call options with a strike price of $30 sell for $6. The appropriate risk-free bond has a price of $30. Calculate the price of the January put option.
A) $11
B) $24
C) $19
D) $30
E) $25
A) $11
B) $24
C) $19
D) $30
E) $25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Sarah Kling bought a six-month Peppy Cola put option with an exercise price of $55 for a premium of $8.25 when Peppy was selling for $48.00 per share.
Refer to Exhibit 14.3. If at expiration Peppy is selling for $42.00, what is Sarah's dollar gain or loss?
A) $420 gain
B) $420 loss
C) $475 loss
D) $475 gain
E) $525 gain
Sarah Kling bought a six-month Peppy Cola put option with an exercise price of $55 for a premium of $8.25 when Peppy was selling for $48.00 per share.
Refer to Exhibit 14.3. If at expiration Peppy is selling for $42.00, what is Sarah's dollar gain or loss?
A) $420 gain
B) $420 loss
C) $475 loss
D) $475 gain
E) $525 gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Datacorp stock currently trades at $50. August call options on the stock with a strike price of $55 are priced at $5.75. October call options with a strike price of $55 are priced at $6.25. Calculate the value of the time premium between the August and October options.
A) -$0.50
B) $0
C) $0.50
D) $5
E) -$5
A) -$0.50
B) $0
C) $0.50
D) $5
E) -$5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Consider a stock that is currently trading at $45. Calculate the intrinsic value for a call option that has an exercise price of $35.
A) $25
B) $35
C) $0
D) -$10
E) $10
A) $25
B) $35
C) $0
D) -$10
E) $10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Sarah Kling bought a six-month Peppy Cola put option with an exercise price of $55 for a premium of $8.25 when Peppy was selling for $48.00 per share.
Refer to Exhibit 14.3. If at expiration Peppy is selling for $47.00, what is Sarah's dollar gain or loss?
A) $25 loss
B) $250 loss
C) $25 gain
D) $250 gain
E) $0
Sarah Kling bought a six-month Peppy Cola put option with an exercise price of $55 for a premium of $8.25 when Peppy was selling for $48.00 per share.
Refer to Exhibit 14.3. If at expiration Peppy is selling for $47.00, what is Sarah's dollar gain or loss?
A) $25 loss
B) $250 loss
C) $25 gain
D) $250 gain
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Rick Thompson is considering the following alternatives for investing in Davis Industries, which is now selling for $44 per share:
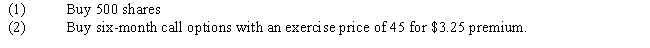
Refer to Exhibit 14.2. Assuming no commissions or taxes, what is the annualized percentage gain if the stock reaches $50 in four months and a call was purchased?
A) 161.54 percent gain
B) 53.85 percent gain
C) 161.54 percent loss
D) 11.11 percent gain
E) 53.85 percent loss
Rick Thompson is considering the following alternatives for investing in Davis Industries, which is now selling for $44 per share:
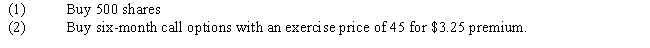
Refer to Exhibit 14.2. Assuming no commissions or taxes, what is the annualized percentage gain if the stock reaches $50 in four months and a call was purchased?
A) 161.54 percent gain
B) 53.85 percent gain
C) 161.54 percent loss
D) 11.11 percent gain
E) 53.85 percent loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A stock currently trades at $110. June put options on the stock with a strike price of $100 are priced at $5.25. Calculate the dollar return on one put contract.
A) -$525
B) $1000
C) $0
D) -$1000
E) $525
A) -$525
B) $1000
C) $0
D) -$1000
E) $525

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A stock currently trades at $110. June call options on the stock with a strike price of $120 are priced at $5.75. Calculate the dollar return on one call contract.
A) -$1000
B) $1000
C) $575
D) -$575
E) $0
A) -$1000
B) $1000
C) $575
D) -$575
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Consider a stock that is currently trading at $65. Calculate the intrinsic value for a put option that has an exercise price of $55.
A) $10
B) $50
C) $55
D) -$10
E) $0
A) $10
B) $50
C) $55
D) -$10
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Assume that you purchased shares of a stock at a price of $35 per share. At this time, you wrote a call option with a $35 strike and received a call price of $2. The stock currently trades at $70. Calculate the dollar return on this option strategy.
A) $25
B) -$2
C) $2
D) -$25
E) $0
A) $25
B) -$2
C) $2
D) -$25
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Consider a stock that is currently trading at $20. Calculate the intrinsic value for a put option that has an exercise price of $35.
A) $15
B) $55
C) $35
D) -$15
E) $0
A) $15
B) $55
C) $35
D) -$15
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Sarah Kling bought a six-month Peppy Cola put option with an exercise price of $55 for a premium of $8.25 when Peppy was selling for $48.00 per share.
Refer to Exhibit 14.3. What is Sarah's annualized gain/loss?
A) 60.60 percent gain
B) 6.06 percent loss
C) 60.60 percent loss
D) 6.06 percent gain
E) 0 percent
Sarah Kling bought a six-month Peppy Cola put option with an exercise price of $55 for a premium of $8.25 when Peppy was selling for $48.00 per share.
Refer to Exhibit 14.3. What is Sarah's annualized gain/loss?
A) 60.60 percent gain
B) 6.06 percent loss
C) 60.60 percent loss
D) 6.06 percent gain
E) 0 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Tom Gettback buys 100 shares of Johnson Walker stock for $87.00 per share and a three-month Johnson Walker put option with an exercise price of $105.00 for $20.00. What is his dollar gain if the stock is selling for $80.00 per share at expiration?
A) $200 loss
B) $700 loss
C) $200 gain
D) $700 gain
E) $900 gain
A) $200 loss
B) $700 loss
C) $200 gain
D) $700 gain
E) $900 gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Rick Thompson is considering the following alternatives for investing in Davis Industries, which is now selling for $44 per share:
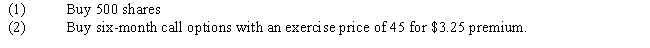
Refer to Exhibit 14.2. Assuming no commissions or taxes, what is the annualized percentage gain if the stock is at $30 in four months and the stock was purchased?
A) 9.54 percent loss
B) 95.45 percent loss
C) 0.9545 percent gain
D) 95.45 percent gain
E) 9.54 percent gain
Rick Thompson is considering the following alternatives for investing in Davis Industries, which is now selling for $44 per share:
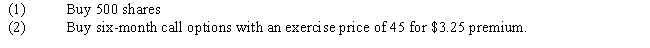
Refer to Exhibit 14.2. Assuming no commissions or taxes, what is the annualized percentage gain if the stock is at $30 in four months and the stock was purchased?
A) 9.54 percent loss
B) 95.45 percent loss
C) 0.9545 percent gain
D) 95.45 percent gain
E) 9.54 percent gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A stock currently trades at $110. June call options on the stock with a strike price of $105 are priced at $4. Calculate the arbitrage profit that you can earn.
A) $0
B) $1
C) $5
D) $4
E) $9
A) $0
B) $1
C) $5
D) $4
E) $9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



