Deck 16: Option Contracts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/122
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Option Contracts
1
It is always theoretically possible to use options as a perfect hedge against fluctuations in value of the underlying asset.
True
2
Risk management is the driving force behind the futures options market.
False
3
The owner of a call option on a futures contract has the obligation to buy the futures contract at a predetermined strike price during a specified time period.
False
4
The Chicago Board Options Exchange has the largest share of stock option trading.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The standardization of option contracts and the creation of the Options Clearing Corporation are two important results of the opening of the Chicago Board of Options Exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A portfolio containing a share of stock and a put option will have the same value as a portfolio containing a call option and the risk-free bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Stock options expire on the Sunday following the third Saturday of the designated month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Index options are settled by delivery of the stocks that make up the index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Index options can only be settled in cash.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The binomial model is a continuous method for valuing options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Investors should purchase market index put options if they anticipate an increase in the index value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In index options, the aggregate market takes the place of the individual stock issues being traded, as in stock options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The most important input the investor must provide in determining option values is the strike price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Options on futures expire at the same time the futures contract expires.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) acts as the guarantor of each Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) traded contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Risk management strategies involving interest rate agreements can be classified as forward-based or option-based.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The longer the time to expiration, the greater the value of a call option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Unlike stock options, futures options require the holder to enter into a futures contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
There is an inverse relationship between the market interest rate and the value of a call option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Credit risk in the options market is only a concern to the option seller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A price spread (or vertical spread) involves buying and selling an option for the same stock and expiration date but with different exercise prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The issuance of convertibles will ultimately lead to greater dilution than an initial issue of stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The binomial option pricing model and the Black and Scholes model are similar because they are both discrete models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The investment value of a convertible bond is the price that it would be expected to sell as a straight debt instrument.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A long-strip position indicates that an investor is bullish but conservative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Convertibles provide the upside potential of common stock and the downside protection of a bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a binomial option pricing model, the initial value of the call can be determined by working backward through the tree and solving for each of the remaining intermediate option values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The conversion parity price is equal to the par value of a convertible bond divided by the number of shares into which it can be converted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
European options can only be exercised on the expiration date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A credit default swap (CDS) is better regarded as an option-like arrangement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The delta in the Black-Scholes model is simply the slope of a line tangent to the call option price curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The underlying stock price and the value of the put option are factors that impact the value of an American call option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The binomial option pricing model approximates the price of an option obtained using the Black-Scholes option pricing model as the number of subintervals increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A currency call is like being ____ in the currency futures.
A) out-of-the-money
B) in-the-money
C) long
D) short
E) at-the-money
A) out-of-the-money
B) in-the-money
C) long
D) short
E) at-the-money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A strip is a call option on a stock that is written by someone who owns the stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The buyer of a straddle expects stock prices to move strongly in either direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The creation of the CBOE led to all the following innovations in options EXCEPT
A) the creation of a central marketplace.
B) the introduction of a clearing corporation.
C) the standardization of expiration dates.
D) the creation of a primary market.
E) the creation of a secondary market.
A) the creation of a central marketplace.
B) the introduction of a clearing corporation.
C) the standardization of expiration dates.
D) the creation of a primary market.
E) the creation of a secondary market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The entity that acts as the guarantor of each CBOE-traded contract is the
A) Federal Government.
B) Securities and Exchange Commission.
C) CBOE.
D) Options Clearing Corporation.
E) Federal Reserve Bank.
A) Federal Government.
B) Securities and Exchange Commission.
C) CBOE.
D) Options Clearing Corporation.
E) Federal Reserve Bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
It is a violation of the securities laws to combine option contracts to achieve a customized payoff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
By attaching a convertible feature to a bond issue, a firm can often get a lower rate of interest on its debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the Black-Scholes option pricing model, an increase in the risk-free rate (RFR) will cause
A) In the Black-Scholes option pricing model, an increase in the risk-free rate (RFR) will cause
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.
A) In the Black-Scholes option pricing model, an increase in the risk-free rate (RFR) will cause
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is not a variable required to determine an option's value in the Black-Scholes valuation model?
A) future security price
B) exercise price
C) time to expiration
D) risk-free rate
E) security price volatility
A) future security price
B) exercise price
C) time to expiration
D) risk-free rate
E) security price volatility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the Black-Scholes option pricing model, an increase in security price (S) will cause
A) an increase in call value and an increase in put value.
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.
A) an increase in call value and an increase in put value.
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
The following information is provided in the context of a two-period (two six-month periods) binomial option pricing model. A stock currently trades at $60 per share, and a call option on the stock has an exercise price of $65. The stock is equally likely to rise by 15 percent or fall by 15 percent during each six-month period. The one-year risk free rate is 3 percent.
Refer to Exhibit 16.2. Calculate the price of the call option after the stock price has already moved up in value once (Cu).
A) $7.77
B) $14.35
C) $0
D) $4.21
E) $6.44
The following information is provided in the context of a two-period (two six-month periods) binomial option pricing model. A stock currently trades at $60 per share, and a call option on the stock has an exercise price of $65. The stock is equally likely to rise by 15 percent or fall by 15 percent during each six-month period. The one-year risk free rate is 3 percent.
Refer to Exhibit 16.2. Calculate the price of the call option after the stock price has already moved up in value once (Cu).
A) $7.77
B) $14.35
C) $0
D) $4.21
E) $6.44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Options on futures contracts are very popular because
A) they require the holder to purchase at a future date.
B) of their ability to create leverage.
C) the seller of the futures contract is under no obligation.
D) the amount of the underlying commodity is negotiable.
E) None of these are correct.
A) they require the holder to purchase at a future date.
B) of their ability to create leverage.
C) the seller of the futures contract is under no obligation.
D) the amount of the underlying commodity is negotiable.
E) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
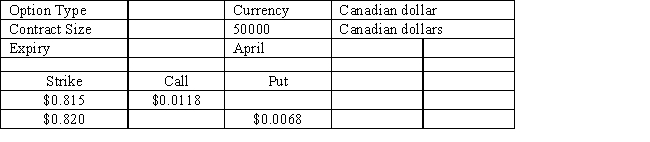
Refer to Exhibit 16.1. If the spot rate at expiration is $0.85 and the put option was purchased, what is the dollar gain or loss?
A) $340 loss
B) $125 gain
C) $750 gain
D) $750 loss
E) $200 loss

Refer to Exhibit 16.1. If the spot rate at expiration is $0.85 and the put option was purchased, what is the dollar gain or loss?
A) $340 loss
B) $125 gain
C) $750 gain
D) $750 loss
E) $200 loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)

Refer to Exhibit 16.1. If the spot rate at expiration is $0.80 and the call option was purchased, what is the dollar gain or loss?
A) $123 gain
B) $590 loss
C) $312 gain
D) $237 gain
E) $0

Refer to Exhibit 16.1. If the spot rate at expiration is $0.80 and the call option was purchased, what is the dollar gain or loss?
A) $123 gain
B) $590 loss
C) $312 gain
D) $237 gain
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the Black-Scholes model N(d1) represents the
A) hedge ratio.
B) partial derivative of the call's value with respect to the stock price.
C) change in the option's value given a one dollar change in the underlying security's price.
D) option's delta.
E) All of these are correct.
A) hedge ratio.
B) partial derivative of the call's value with respect to the stock price.
C) change in the option's value given a one dollar change in the underlying security's price.
D) option's delta.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)

Refer to Exhibit 16.1. How much must an investor pay for one call option contract?
A) $680
B) $815
C) $625
D) $590
E) $340

Refer to Exhibit 16.1. How much must an investor pay for one call option contract?
A) $680
B) $815
C) $625
D) $590
E) $340

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the Black-Scholes option pricing model, an increase in exercise price (X) will cause
A) an increase in call value and an increase in put value.
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.
A) an increase in call value and an increase in put value.
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
The following information is provided in the context of a two-period (two six-month periods) binomial option pricing model. A stock currently trades at $60 per share, and a call option on the stock has an exercise price of $65. The stock is equally likely to rise by 15 percent or fall by 15 percent during each six-month period. The one-year risk free rate is 3 percent.
Refer to Exhibit 16.2. Calculate the price of the call option after the stock price has already moved down in value once (Cd).
A) $7.77
B) $14.35
C) $0
D) $4.21
E) $6.44
The following information is provided in the context of a two-period (two six-month periods) binomial option pricing model. A stock currently trades at $60 per share, and a call option on the stock has an exercise price of $65. The stock is equally likely to rise by 15 percent or fall by 15 percent during each six-month period. The one-year risk free rate is 3 percent.
Refer to Exhibit 16.2. Calculate the price of the call option after the stock price has already moved down in value once (Cd).
A) $7.77
B) $14.35
C) $0
D) $4.21
E) $6.44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the Black-Scholes option pricing model, an increase in security volatility ( ) will cause
A) an increase in call value and an increase in put value.
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.
A) an increase in call value and an increase in put value.
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the Black-Scholes option pricing model, an increase in time to expiration (T) will cause
A) an increase in call value and an increase in put value.
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.
A) an increase in call value and an increase in put value.
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A foreign currency option contract traded on U.S. exchanges allows for the sale or purchase of a set amount of
A) U.S. currency at a floating exchange rate.
B) U.S. currency at a fixed exchange rate.
C) foreign currency at a floating exchange rate.
D) foreign currency at a fixed exchange rate.
E) None of these are correct.
A) U.S. currency at a floating exchange rate.
B) U.S. currency at a fixed exchange rate.
C) foreign currency at a floating exchange rate.
D) foreign currency at a fixed exchange rate.
E) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
The following information is provided in the context of a two-period (two six-month periods) binomial option pricing model. A stock currently trades at $60 per share, and a call option on the stock has an exercise price of $65. The stock is equally likely to rise by 15 percent or fall by 15 percent during each six-month period. The one-year risk free rate is 3 percent.
Refer to Exhibit 16.2. Calculate the possible prices of the stock at the end of one year.
A) $69, $51, $79.35
B) $51, $79.35, $58.65
C) $79.35, $58.65, $43.35
D) $58.65, $43.35, $14.35
E) $72.65, $53.35, $17.25
The following information is provided in the context of a two-period (two six-month periods) binomial option pricing model. A stock currently trades at $60 per share, and a call option on the stock has an exercise price of $65. The stock is equally likely to rise by 15 percent or fall by 15 percent during each six-month period. The one-year risk free rate is 3 percent.
Refer to Exhibit 16.2. Calculate the possible prices of the stock at the end of one year.
A) $69, $51, $79.35
B) $51, $79.35, $58.65
C) $79.35, $58.65, $43.35
D) $58.65, $43.35, $14.35
E) $72.65, $53.35, $17.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The calculation of a weighted average of the implied volatility estimates from options on the Standard & Poor's 500 index using a wide range of exercise prices is known as
A) Spider.
B) QQQ.
C) VIX.
D) CIN.
E) VOL.
A) Spider.
B) QQQ.
C) VIX.
D) CIN.
E) VOL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)

Refer to Exhibit 16.1. If the spot rate at expiration is $0.75 and the put option was purchased, what is the dollar gain or loss?
A) $0
B) $200 loss
C) $200 gain
D) $3160 gain
E) $1187 loss

Refer to Exhibit 16.1. If the spot rate at expiration is $0.75 and the put option was purchased, what is the dollar gain or loss?
A) $0
B) $200 loss
C) $200 gain
D) $3160 gain
E) $1187 loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The Black-Scholes model assumes that stock price movements can be described by
A) geometric moving averages.
B) arithmetic moving averages.
C) regression towards the mean.
D) geometric Brownian motion.
E) stochastic time lags.
A) geometric moving averages.
B) arithmetic moving averages.
C) regression towards the mean.
D) geometric Brownian motion.
E) stochastic time lags.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)

Refer to Exhibit 16.1. How much must an investor pay for one put option contract?
A) $680
B) $815
C) $340
D) $625
E) $590

Refer to Exhibit 16.1. How much must an investor pay for one put option contract?
A) $680
B) $815
C) $340
D) $625
E) $590

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)

Refer to Exhibit 16.1. If the spot rate at expiration is $0.90 and the call option was purchased, what is the dollar gain or loss?
A) $0
B) $3750 gain
C) $3660 gain
D) $4650 loss
E) $2680 loss

Refer to Exhibit 16.1. If the spot rate at expiration is $0.90 and the call option was purchased, what is the dollar gain or loss?
A) $0
B) $3750 gain
C) $3660 gain
D) $4650 loss
E) $2680 loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
The following information is provided in the context of a two-period (two six-month periods) binomial option pricing model. A stock currently trades at $60 per share, and a call option on the stock has an exercise price of $65. The stock is equally likely to rise by 15 percent or fall by 15 percent during each six-month period. The one-year risk free rate is 3 percent.
Refer to Exhibit 16.2. Calculate the price of the call option today (C0).
A) $7.77
B) $14.35
C) $0
D) $4.21
E) $6.44
The following information is provided in the context of a two-period (two six-month periods) binomial option pricing model. A stock currently trades at $60 per share, and a call option on the stock has an exercise price of $65. The stock is equally likely to rise by 15 percent or fall by 15 percent during each six-month period. The one-year risk free rate is 3 percent.
Refer to Exhibit 16.2. Calculate the price of the call option today (C0).
A) $7.77
B) $14.35
C) $0
D) $4.21
E) $6.44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
A stock currently trades for $130 per share. Options on the stock are available with a strike price of $125. The options expire in 10 days. The risk-free rate is 3 three over this time period, and the expected volatility is 0.35.
Refer to Exhibit 16.3. Calculate the price of the put option.
A) $1.086
B) $0.862
C) $6.234
D) $0.623
E) $2.317
A stock currently trades for $130 per share. Options on the stock are available with a strike price of $125. The options expire in 10 days. The risk-free rate is 3 three over this time period, and the expected volatility is 0.35.
Refer to Exhibit 16.3. Calculate the price of the put option.
A) $1.086
B) $0.862
C) $6.234
D) $0.623
E) $2.317

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If you were to purchase an October option with an exercise price of 50 for $8 and simultaneously sell an October option with an exercise price of 60 for $2, you would be
A) bullish and taking a high risk.
B) bullish and conservative.
C) bearish and taking a high risk.
D) bearish and conservative.
E) neutral.
A) bullish and taking a high risk.
B) bullish and conservative.
C) bearish and taking a high risk.
D) bearish and conservative.
E) neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A money spread involves buying and selling call options in the same stock with
A) the same time period and exercise price.
B) the same time period but different exercise price.
C) a different time period but same exercise price.
D) a different time period and different exercise price.
E) options in different markets.
A) the same time period and exercise price.
B) the same time period but different exercise price.
C) a different time period but same exercise price.
D) a different time period and different exercise price.
E) options in different markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Assume that you have just sold a stock for a loss at a price of $75 for tax purposes. You still wish to maintain exposure to the sold stock. Suppose that you buy a call with a strike price of $70 and a price of $6.75. Calculate the effective price paid to repurchase the stock if the price after 35 days is $65.
A) $71.75
B) $76.75
C) $58.25
D) $81.75
E) $85.25
A) $71.75
B) $76.75
C) $58.25
D) $81.75
E) $85.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Assume that you have just sold a stock for a loss at a price of $75 for tax purposes. You still wish to maintain exposure to the sold stock. Suppose that you buy a call with a strike price of $70 and a price of $6.75. Calculate the effective price paid to repurchase the stock if the price after 35 days is $80.
A) $81.75
B) $73.25
C) $86.75
D) $76.75
E) $85.25
A) $81.75
B) $73.25
C) $86.75
D) $76.75
E) $85.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Options can be used to
A) modify an equity portfolio's systematic risk.
B) modify an equity portfolio's unsystematic risk.
C) manage currency exposures in international equity portfolios.
D) change a portfolio's exposure to a particular asset.
E) All of these are correct.
A) modify an equity portfolio's systematic risk.
B) modify an equity portfolio's unsystematic risk.
C) manage currency exposures in international equity portfolios.
D) change a portfolio's exposure to a particular asset.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Consider the following information on put and call options for Citigroup
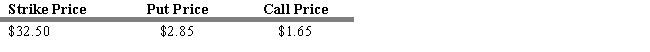
-Refer to Exhibit 16.4. Calculate the net value of a covered call position at a stock price at expiration of $20 and a stock price at expiration of $45.
A) $6.35, $18.85
B) $29.65, $42.15
C) $21.65, $34.15
D) $8, $8
E) -$8, -$8
Consider the following information on put and call options for Citigroup
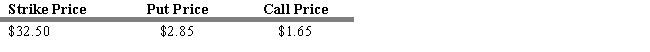
-Refer to Exhibit 16.4. Calculate the net value of a covered call position at a stock price at expiration of $20 and a stock price at expiration of $45.
A) $6.35, $18.85
B) $29.65, $42.15
C) $21.65, $34.15
D) $8, $8
E) -$8, -$8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Consider the following information on put and call options for Citigroup
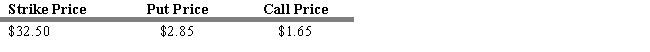
Refer to Exhibit 16.4. A protective put is an appropriate strategy if
A) an investor wishes to generate additional income.
B) an investor wished to insure against a decline in share values.
C) an investor expected share prices to be volatile.
D) an investor expected share prices to remain in a trading range.
E) an investor expected share prices to be volatile but was inclined to be bullish.
Consider the following information on put and call options for Citigroup
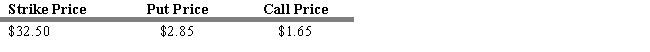
Refer to Exhibit 16.4. A protective put is an appropriate strategy if
A) an investor wishes to generate additional income.
B) an investor wished to insure against a decline in share values.
C) an investor expected share prices to be volatile.
D) an investor expected share prices to remain in a trading range.
E) an investor expected share prices to be volatile but was inclined to be bullish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Consider the following information on put and call options for Citigroup
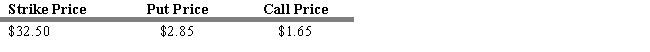
-Refer to Exhibit 16.4. Calculate the net value of a protective put position at a stock price at expiration of $20 and a stock price at expiration of $45.
A) $6.35, $18.85
B) $29.65, $42.15
C) $21.65, $34.15
D) $8, $8
E) -$8, -$8
Consider the following information on put and call options for Citigroup
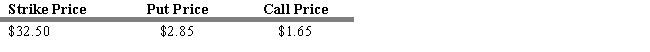
-Refer to Exhibit 16.4. Calculate the net value of a protective put position at a stock price at expiration of $20 and a stock price at expiration of $45.
A) $6.35, $18.85
B) $29.65, $42.15
C) $21.65, $34.15
D) $8, $8
E) -$8, -$8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
A stock currently trades for $130 per share. Options on the stock are available with a strike price of $125. The options expire in 10 days. The risk-free rate is 3 three over this time period, and the expected volatility is 0.35.
Refer to Exhibit 16.3. Use the Black-Scholes option pricing model to calculate the price of a call option.
A) $5.19
B) $4.35
C) $3.93
D) $6.19
E) $8.17
A stock currently trades for $130 per share. Options on the stock are available with a strike price of $125. The options expire in 10 days. The risk-free rate is 3 three over this time period, and the expected volatility is 0.35.
Refer to Exhibit 16.3. Use the Black-Scholes option pricing model to calculate the price of a call option.
A) $5.19
B) $4.35
C) $3.93
D) $6.19
E) $8.17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In a money spread, an investor would
A) buy two in-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
B) buy two out-of-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
C) sell two in-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
D) sell an out-of-the-money call and purchase an in-the-money call on the same stock with the same exercise date.
E) sell two out-of-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
A) buy two in-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
B) buy two out-of-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
C) sell two in-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
D) sell an out-of-the-money call and purchase an in-the-money call on the same stock with the same exercise date.
E) sell two out-of-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the hedge ratio is 0.50, this indicates that the portfolio should hold
A) two shares of stock for every call option written.
B) one share of stock for every two call options written.
C) two shares of stock for every call option purchased.
D) one share of stock for every two call options purchased.
E) two call options for every put option written.
A) two shares of stock for every call option written.
B) one share of stock for every two call options written.
C) two shares of stock for every call option purchased.
D) one share of stock for every two call options purchased.
E) two call options for every put option written.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
You own a stock that has risen from $10 per share to $32 per share. You wish to delay taking the profit, but you are troubled about the short-run behavior of the stock market. An effective action on your part would be to
A) purchase a put.
B) purchase a call.
C) purchase an index option.
D) utilize a bearish spread.
E) utilize a bullish spread.
A) purchase a put.
B) purchase a call.
C) purchase an index option.
D) utilize a bearish spread.
E) utilize a bullish spread.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is NOT a factor needed to calculate the value of an American call option?
A) the stock price
B) the exercise price
C) the exchange on which the option is listed
D) the volatility of the underlying stock
E) the interest rate
A) the stock price
B) the exercise price
C) the exchange on which the option is listed
D) the volatility of the underlying stock
E) the interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Assume that you have just sold a stock for a loss at a price of $75 for tax purposes. You still wish to maintain exposure to the sold stock. Suppose that you sell a put with a strike price of $80 and a price of $7.25. Calculate the effective price paid to repurchase the stock if the price after 35 days is $70.
A) $77.75
B) $87.25
C) $82.25
D) $72.75
E) $85.25
A) $77.75
B) $87.25
C) $82.25
D) $72.75
E) $85.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If you were to purchase an October option with an exercise price of 50 for $8 and simultaneously sell an October option with an exercise price of 60 for $2, you would be
A) bullish and taking a high risk.
B) bullish and conservative.
C) bearish and taking a high risk.
D) bearish and conservative.
E) neutral.
A) bullish and taking a high risk.
B) bullish and conservative.
C) bearish and taking a high risk.
D) bearish and conservative.
E) neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A vertical spread involves buying and selling call options in the same stock with
A) the same time period and price.
B) the same time period but different price.
C) a different time period but same price.
D) a different time period and different price.
E) options in different markets.
A) the same time period and price.
B) the same time period but different price.
C) a different time period but same price.
D) a different time period and different price.
E) options in different markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Assume that you have just sold a stock for a loss at a price of $75 for tax purposes. You still wish to maintain exposure to the sold stock. Suppose that you sell a put with a strike price of $80 and a price of $7.25. Calculate the effective price paid to repurchase the stock if the price after 35 days is $85.
A) $77.75
B) $87.25
C) $82.25
D) $72.75
E) $85.25
A) $77.75
B) $87.25
C) $82.25
D) $72.75
E) $85.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A calendar spread requires the purchase and sale of two calls or two puts in the same stock with
A) the same expiration date but different exercise prices.
B) the same exercise price but different expiration dates.
C) different exercise prices and different expiration dates.
D) the same exercise price and the same expiration month.
E) traded in different markets.
A) the same expiration date but different exercise prices.
B) the same exercise price but different expiration dates.
C) different exercise prices and different expiration dates.
D) the same exercise price and the same expiration month.
E) traded in different markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



