Deck 12: Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/151
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets
1
The price a perfectly competitive firm receives for its output
A)is determined by the interaction of the firm and all of the consumers who buy from the firm.
B)is determined by the interaction of all sellers and all buyers in the firm's market.
C)will not change in response to changes in market demand and supply because the firm is a price taker.
D)will be lowered by the firm in order to sell more output.
A)is determined by the interaction of the firm and all of the consumers who buy from the firm.
B)is determined by the interaction of all sellers and all buyers in the firm's market.
C)will not change in response to changes in market demand and supply because the firm is a price taker.
D)will be lowered by the firm in order to sell more output.
is determined by the interaction of all sellers and all buyers in the firm's market.
2
Perfectly competitive industries tend to produce low-priced,low-technology products.
False
3
Which of the following is not an assumption of perfectly competitive markets?
A)There are many sellers and many buyers,all of which are small relative to the market.
B)Each firm produces a similar but not identical product.
C)There are no barriers to new firms entering the market.
D)The products sold by all firms in the market are identical.
A)There are many sellers and many buyers,all of which are small relative to the market.
B)Each firm produces a similar but not identical product.
C)There are no barriers to new firms entering the market.
D)The products sold by all firms in the market are identical.
Each firm produces a similar but not identical product.
4
Which of the following describes the difference between the market demand curve for a perfectly competitive industry and the demand curve for a firm in this industry?
A)The market demand curve is a horizontal line; the firm's demand curve is downward-sloping.
B)The market demand curve is downward-sloping; the firm's demand curve is a vertical line.
C)The market demand curve can not have a constant slope; the firm's demand curve has a slope equal to zero.
D)The market demand curve is downward-sloping; the firm's demand curve is a horizontal line.
A)The market demand curve is a horizontal line; the firm's demand curve is downward-sloping.
B)The market demand curve is downward-sloping; the firm's demand curve is a vertical line.
C)The market demand curve can not have a constant slope; the firm's demand curve has a slope equal to zero.
D)The market demand curve is downward-sloping; the firm's demand curve is a horizontal line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a perfectly competitive market the term "price taker" applies to
A)sellers and buyers.
B)firms but not buyers.
C)buyers but not sellers.
D)only the smallest sellers and buyers.
A)sellers and buyers.
B)firms but not buyers.
C)buyers but not sellers.
D)only the smallest sellers and buyers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following arguments could be made as evidence that the market for produce sold at a farmers' market is perfectly competitive?
A)The U.S.Department of Agriculture has established standards for the labeling of organic produce sold at farmers' markets.
B)Sales of organically grown food have increased at a rate of 20 percent per year.
C)As more farmers began selling their products at farmers' markets,the increase in supply has driven down prices to the point where they just cover the cost of production.
D)The profits earned by farmers who sell their products at farmers' markets have continued to grow,despite the increasing number of farmers entering this market.
A)The U.S.Department of Agriculture has established standards for the labeling of organic produce sold at farmers' markets.
B)Sales of organically grown food have increased at a rate of 20 percent per year.
C)As more farmers began selling their products at farmers' markets,the increase in supply has driven down prices to the point where they just cover the cost of production.
D)The profits earned by farmers who sell their products at farmers' markets have continued to grow,despite the increasing number of farmers entering this market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is the best example of a perfectly competitive firm?
A)a corn farmer in Illinois
B)a Taco Bell restaurant
C)the Ford Motor Company
D)the United Parcel Service (UPS)
A)a corn farmer in Illinois
B)a Taco Bell restaurant
C)the Ford Motor Company
D)the United Parcel Service (UPS)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A perfectly competitive firm faces a demand curve that is
A)horizontal.
B)vertical.
C)perpendicular to the quantity axis.
D)perfectly inelastic.
A)horizontal.
B)vertical.
C)perpendicular to the quantity axis.
D)perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following offers the best reason why restaurants are not considered to be perfectly competitive firms?
A)Restaurants do not sell identical products.
B)Restaurants compete in small market areas - neighborhoods and cities - rather than in regional or national markets.Therefore,restaurants are not small relative to their market size.
C)Restaurants usually have entry barriers in the form of zoning restrictions and health regulations.
D)Restaurants have significant liability costs that perfectly competitive firms do not have; for example,customers may sue if they suffer from food poisoning.
A)Restaurants do not sell identical products.
B)Restaurants compete in small market areas - neighborhoods and cities - rather than in regional or national markets.Therefore,restaurants are not small relative to their market size.
C)Restaurants usually have entry barriers in the form of zoning restrictions and health regulations.
D)Restaurants have significant liability costs that perfectly competitive firms do not have; for example,customers may sue if they suffer from food poisoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The delivery of first-class mail by the U.S.Postal Service is an example of
A)a monopoly.
B)perfect competition because consumers have access to other methods of written communication; for example,email and text messaging.
C)monopolistic competition,because mail delivery is a differentiated product provided by many firms.
D)an oligopoly because a few other firms provide delivery of letters and packages.
A)a monopoly.
B)perfect competition because consumers have access to other methods of written communication; for example,email and text messaging.
C)monopolistic competition,because mail delivery is a differentiated product provided by many firms.
D)an oligopoly because a few other firms provide delivery of letters and packages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Firms that are price takers
A)must lower their prices to increase sales.
B)are able to sell a fixed quantity of output at the market price.
C)can raise their prices as a result of a successful advertising campaign.
D)are able to sell all their output at the market price.
A)must lower their prices to increase sales.
B)are able to sell a fixed quantity of output at the market price.
C)can raise their prices as a result of a successful advertising campaign.
D)are able to sell all their output at the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following characteristics of a farmers' market make it a good example of a perfectly competitive market?
A)Selling product at a farmers' market was very profitable for farmers in the early 2000s.As result,many farmers sold their farms to larger firms.
B)Farmers who sell product at a farmers' market are similar to other entrepreneurs who introduce products that earn short-run profits but invite competition that drives down prices and profits in the long run.
C)Farmers who sell product at a farmers' market are similar to other business owners who take advantage of the willingness of some consumers to pay high prices for new and different products.
D)Farmers selling product at a farmers' market provide a product that is a necessity,rather than a luxury.
A)Selling product at a farmers' market was very profitable for farmers in the early 2000s.As result,many farmers sold their farms to larger firms.
B)Farmers who sell product at a farmers' market are similar to other entrepreneurs who introduce products that earn short-run profits but invite competition that drives down prices and profits in the long run.
C)Farmers who sell product at a farmers' market are similar to other business owners who take advantage of the willingness of some consumers to pay high prices for new and different products.
D)Farmers selling product at a farmers' market provide a product that is a necessity,rather than a luxury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose the equilibrium price in a perfectly competitive industry is $10 and a firm in the industry charges $12.Which of the following will happen?
A)The firm will sell more output than its competitors.
B)The firm's revenue will increase.
C)The firm will not sell any output.
D)The firm's profits will increase.
A)The firm will sell more output than its competitors.
B)The firm's revenue will increase.
C)The firm will not sell any output.
D)The firm's profits will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A wheat farmer and a firm in a perfectly competitive market are similar in that
A)both face vertical demand curves.
B)both have to lower their prices if a rival firm lowers its price.
C)both face horizontal demand curves.
D)both will earn an economic profit if their total revenue equals their total cost.
A)both face vertical demand curves.
B)both have to lower their prices if a rival firm lowers its price.
C)both face horizontal demand curves.
D)both will earn an economic profit if their total revenue equals their total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A perfectly competitive firm has to charge the same price as every other firm in the market.Therefore,the firm
A)faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
B)is not able to make a profit in the short run.
C)is a price taker.
D)faces a perfectly elastic supply curve.
A)faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
B)is not able to make a profit in the short run.
C)is a price taker.
D)faces a perfectly elastic supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is a characteristic of a firm in a perfectly competitive market?
A)The firm cannot make a profit in the short run because it is too small a part of the total market.
B)The firm can make a profit in the long run but not in the short run.
C)The firm can sell as much as it wants without having to lower its price.
D)The firm must lower its price in order to increase quantity demanded.
A)The firm cannot make a profit in the short run because it is too small a part of the total market.
B)The firm can make a profit in the long run but not in the short run.
C)The firm can sell as much as it wants without having to lower its price.
D)The firm must lower its price in order to increase quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Firms in perfectly competitive industries are unable to control the prices of the products they sell and earn a profit in the long run.Which of the following is one reason for this?
A)Owners of perfectly competitive firms realize that their short-run profits are temporary.Therefore,they either sell their businesses or develop other products that will earn short-run profits.
B)Firms in perfectly competitive industries can use advertising in the short run to persuade consumers that their products are better than those of other firms.But eventually consumers realize that all of the firms sell virtually identical products.
C)Firms from other countries are able to produce similar products at lower costs.
D)Firms in these industries sell identical products.
A)Owners of perfectly competitive firms realize that their short-run profits are temporary.Therefore,they either sell their businesses or develop other products that will earn short-run profits.
B)Firms in perfectly competitive industries can use advertising in the short run to persuade consumers that their products are better than those of other firms.But eventually consumers realize that all of the firms sell virtually identical products.
C)Firms from other countries are able to produce similar products at lower costs.
D)Firms in these industries sell identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Some markets have many buyers and sellers but fall into the category of monopolistic competition rather than perfect competition.The most common reason for this is
A)there are high barriers to entering these markets.
B)firms in these markets sell identical products.
C)firms in these markets make high profits.
D)firms in these markets do not sell identical products.
A)there are high barriers to entering these markets.
B)firms in these markets sell identical products.
C)firms in these markets make high profits.
D)firms in these markets do not sell identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Firms in perfect competition are price takers because
A)one firm determines the price that all other firms in the industry will charge.
B)consumers have enough market power to set prices.
C)firms accept the price determined by the government.
D)each firm is too small relative to the market to be able to influence price.
A)one firm determines the price that all other firms in the industry will charge.
B)consumers have enough market power to set prices.
C)firms accept the price determined by the government.
D)each firm is too small relative to the market to be able to influence price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a perfectly competitive firm raises the price it charges to consumers,which of the following is the most likely outcome?
A)The firm's revenue will not change because some consumers will refuse to pay the higher price.
B)The firm will not sell any output.
C)The firm's total revenue will increase only if the demand for its product is inelastic.
D)The firm's total revenue will increase only if the demand for its product is elastic.
A)The firm's revenue will not change because some consumers will refuse to pay the higher price.
B)The firm will not sell any output.
C)The firm's total revenue will increase only if the demand for its product is inelastic.
D)The firm's total revenue will increase only if the demand for its product is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
At the profit-maximizing level of output for a perfectly competitive firm,
A)price equals marginal cost.
B)average revenue equals average variable cost and price equals marginal cost.
C)marginal revenue equals marginal cost and average total cost equals average fixed cost.
D)price equals average revenue and marginal cost equals average variable cost.
A)price equals marginal cost.
B)average revenue equals average variable cost and price equals marginal cost.
C)marginal revenue equals marginal cost and average total cost equals average fixed cost.
D)price equals average revenue and marginal cost equals average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Table 12-1
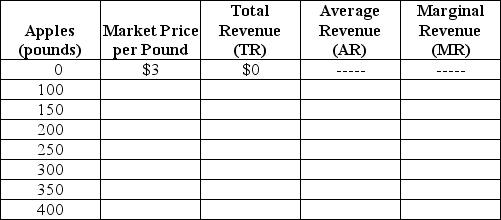 Table 12-1 lists the various pounds (lbs.)of apples that Margie Stattler can sell.Assume that Margie operates in a perfectly competitive market.
Table 12-1 lists the various pounds (lbs.)of apples that Margie Stattler can sell.Assume that Margie operates in a perfectly competitive market.
Refer to Table 12-1.What is Margie's total revenue if she sells 250 pounds of apples?
A)$250
B)$500
C)$750
D)There is not enough information in the table to determine Margie's total revenue.
 Table 12-1 lists the various pounds (lbs.)of apples that Margie Stattler can sell.Assume that Margie operates in a perfectly competitive market.
Table 12-1 lists the various pounds (lbs.)of apples that Margie Stattler can sell.Assume that Margie operates in a perfectly competitive market.Refer to Table 12-1.What is Margie's total revenue if she sells 250 pounds of apples?
A)$250
B)$500
C)$750
D)There is not enough information in the table to determine Margie's total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The market demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is downward-sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Table 12-1
 Table 12-1 lists the various pounds (lbs.)of apples that Margie Stattler can sell.Assume that Margie operates in a perfectly competitive market.
Table 12-1 lists the various pounds (lbs.)of apples that Margie Stattler can sell.Assume that Margie operates in a perfectly competitive market.
Refer to Table 12-1.How many pounds of apples should Margie sell to maximize her profit?
A)300 pounds
B)400 pounds
C)This cannot be determined without knowing Margie's total or marginal production costs.
D)This can be determined only when all of the values for market price,total revenue,average revenue and marginal revenue are given.
 Table 12-1 lists the various pounds (lbs.)of apples that Margie Stattler can sell.Assume that Margie operates in a perfectly competitive market.
Table 12-1 lists the various pounds (lbs.)of apples that Margie Stattler can sell.Assume that Margie operates in a perfectly competitive market.Refer to Table 12-1.How many pounds of apples should Margie sell to maximize her profit?
A)300 pounds
B)400 pounds
C)This cannot be determined without knowing Margie's total or marginal production costs.
D)This can be determined only when all of the values for market price,total revenue,average revenue and marginal revenue are given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
At the profit-maximizing level of output for a perfectly competitive firm,price equals marginal cost.Which of the following is also true?
A)The difference between total revenue and total cost is the greatest.
B)Total revenue equals total cost.
C)Average revenue equals average total cost.
D)Marginal profit equals marginal cost.
A)The difference between total revenue and total cost is the greatest.
B)Total revenue equals total cost.
C)Average revenue equals average total cost.
D)Marginal profit equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the relationship among the following variables in for a perfectly competitive firm: the market price,average revenue and marginal revenue?
A)Average revenue is equal to the market price; average revenue is greater than marginal revenue.
B)The market price is equal to both average revenue and marginal revenue.
C)Average revenue is equal to marginal revenue; average revenue is greater than the market price.
D)As a firm lowers the market price to sell more output,marginal revenue and average revenue will be less than the market price.
A)Average revenue is equal to the market price; average revenue is greater than marginal revenue.
B)The market price is equal to both average revenue and marginal revenue.
C)Average revenue is equal to marginal revenue; average revenue is greater than the market price.
D)As a firm lowers the market price to sell more output,marginal revenue and average revenue will be less than the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the market price is $40,the average revenue of selling five units is
A)$8.
B)$20.
C)$40.
D)$200.
A)$8.
B)$20.
C)$40.
D)$200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Of the following industries,which are perfectly competitive? For those that are not perfectly competitive,explain why.
a.Restaurants
b.Corn
c.College education
d.Local radio and television
a.Restaurants
b.Corn
c.College education
d.Local radio and television

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What assumptions are necessary for a market to be perfectly competitive? Explain why each of these assumptions is important.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In a graph that illustrates a perfectly competitive firm,marginal revenue is
A)a diagonal line that lies below the firm's demand curve.
B)a line that intersects the firm's demand curve from below at its lowest point.
C)a line that intersects the firm's average total cost curve from below at its lowest point.
D)the same as the firm's demand curve.
A)a diagonal line that lies below the firm's demand curve.
B)a line that intersects the firm's demand curve from below at its lowest point.
C)a line that intersects the firm's average total cost curve from below at its lowest point.
D)the same as the firm's demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Producing where marginal revenue equals marginal cost is equivalent to producing where
A)average total cost equals average revenue.
B)average fixed cost is minimized.
C)total revenue is equal to total cost.
D)total profit is maximized.
A)average total cost equals average revenue.
B)average fixed cost is minimized.
C)total revenue is equal to total cost.
D)total profit is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Marginal revenue is
A)total revenue divided by the total quantity of output.
B)the change in profit divided by the change in the quantity of output.
C)the change in total revenue divided by the change in total cost.
D)the change in total revenue divided by the change in the quantity of output.
A)total revenue divided by the total quantity of output.
B)the change in profit divided by the change in the quantity of output.
C)the change in total revenue divided by the change in total cost.
D)the change in total revenue divided by the change in the quantity of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
For a perfectly competitive firm,average revenue is equal to
A)marginal cost.
B)the market price.
C)total revenue.
D)average fixed cost.
A)marginal cost.
B)the market price.
C)total revenue.
D)average fixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue
A)is greater than price.
B)is less than price because a firm must lower its price to sell more.
C)is equal to price.
D)may be either greater or less than price,depending on the quantity sold.
A)is greater than price.
B)is less than price because a firm must lower its price to sell more.
C)is equal to price.
D)may be either greater or less than price,depending on the quantity sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
To maximize profit,a perfectly competitive firm
A)should sell the quantity of output determined by the interaction between industry demand and supply.
B)should sell the quantity of output that results in a value for total revenue that is equal to total cost.
C)should produce the quantity of output that results in the greatest difference between total revenue and total cost.
D)should produce the quantity of output that results in the greatest difference between marginal revenue and marginal cost.
A)should sell the quantity of output determined by the interaction between industry demand and supply.
B)should sell the quantity of output that results in a value for total revenue that is equal to total cost.
C)should produce the quantity of output that results in the greatest difference between total revenue and total cost.
D)should produce the quantity of output that results in the greatest difference between marginal revenue and marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For a firm in a perfectly competitive market,price is
A)equal to both average revenue and marginal revenue.
B)equal to average revenue but greater than marginal revenue.
C)greater than marginal revenue but less than average revenue.
D)less than both average revenue and marginal revenue.
A)equal to both average revenue and marginal revenue.
B)equal to average revenue but greater than marginal revenue.
C)greater than marginal revenue but less than average revenue.
D)less than both average revenue and marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For a perfectly competitive firm,at profit maximization
A)market price exceeds marginal cost.
B)total revenue is maximized.
C)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D)production must occur where average cost is minimized.
A)market price exceeds marginal cost.
B)total revenue is maximized.
C)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D)production must occur where average cost is minimized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the market price is $40 in a perfectly competitive market,the marginal revenue from selling the fifth unit is
A)$8.
B)$20.
C)$40.
D)$200.
A)$8.
B)$20.
C)$40.
D)$200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The marginal revenue curve for a perfectly competitive firm
A)is downward-sloping.
B)is the same as its demand curve.
C)is perfectly inelastic.
D)is the same as its marginal cost curve.
A)is downward-sloping.
B)is the same as its demand curve.
C)is perfectly inelastic.
D)is the same as its marginal cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Mark Frost grows apples in a perfectly competitive market.If we drew a line in a graph that illustrates Mark's total revenue from selling apples,it would be
A)a straight,upward-sloping line.
B)a horizontal line.
C)a straight,downward-sloping line.
D)a curve that is negatively sloped at low levels of output and positively sloped at higher levels of output.
A)a straight,upward-sloping line.
B)a horizontal line.
C)a straight,downward-sloping line.
D)a curve that is negatively sloped at low levels of output and positively sloped at higher levels of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Explain two different ways to determine the profit-maximizing level of output for a firm in a perfectly competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A firm will make a profit when
A)P > AVC.
B)P > ATC.
C)P = ATC.
D)P = MC.
A)P > AVC.
B)P > ATC.
C)P = ATC.
D)P = MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Fill in the columns in the following table and use the values in the table to determine the profit-maximizing level of output.
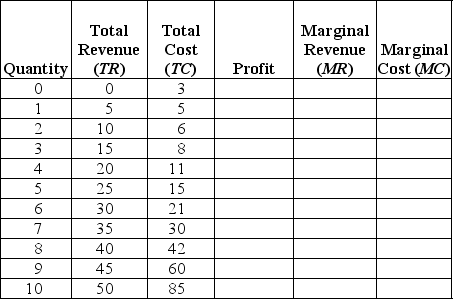


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Table 12-2
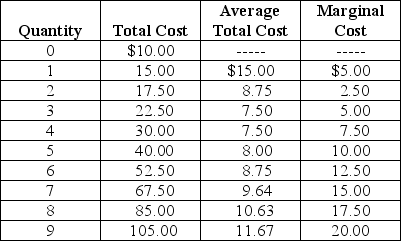 Arnie sells basketballs in a perfectly competitive market.Table 12-2 summarizes Arnie's output per day (Q),total cost (TC),average total cost (ATC)and marginal cost (MC).
Arnie sells basketballs in a perfectly competitive market.Table 12-2 summarizes Arnie's output per day (Q),total cost (TC),average total cost (ATC)and marginal cost (MC).
Refer to Table 12-2.What price (P)will Arnie charge and how much profit will he earn if the market price of basketballs is $12.50?
A)Price and profit cannot be determined from the information given.
B)P = $12.50; profit = $52.50
C)P = $12.50; profit = $22.50
D)P = $20; profit = $75.00.
 Arnie sells basketballs in a perfectly competitive market.Table 12-2 summarizes Arnie's output per day (Q),total cost (TC),average total cost (ATC)and marginal cost (MC).
Arnie sells basketballs in a perfectly competitive market.Table 12-2 summarizes Arnie's output per day (Q),total cost (TC),average total cost (ATC)and marginal cost (MC).Refer to Table 12-2.What price (P)will Arnie charge and how much profit will he earn if the market price of basketballs is $12.50?
A)Price and profit cannot be determined from the information given.
B)P = $12.50; profit = $52.50
C)P = $12.50; profit = $22.50
D)P = $20; profit = $75.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 12-1 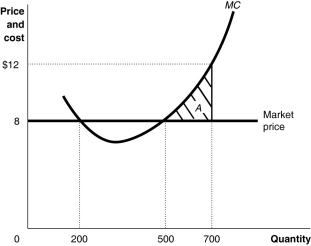
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the firm is producing 500 units,
A)it is making a profit.
B)it is making a loss.
C)it should maintain its output to maximize profit.
D)it should increase its output to maximize profit.

Refer to Figure 12-1.If the firm is producing 500 units,
A)it is making a profit.
B)it is making a loss.
C)it should maintain its output to maximize profit.
D)it should increase its output to maximize profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the early 2000s,some entrepreneurs took advantage of a reduction in the price of computed tomography (CT)scanning equipment by offering apparently healthy people preventive body scans to provide early detection of diseases.This effort failed to earn the entrepreneurs a profit.Which of the following is one reason for this failure?
A)Few people wanted to devote the time needed for an unnecessary medical procedure.
B)The Food and Drug Administration (FDA)published a warning to consumers that the procedure could cause negative side effects.
C)Since the CT scan was a voluntary procedure it was not covered under most medical insurance plans.
D)The American Medical Association (AMA)refused to endorse the procedure.
A)Few people wanted to devote the time needed for an unnecessary medical procedure.
B)The Food and Drug Administration (FDA)published a warning to consumers that the procedure could cause negative side effects.
C)Since the CT scan was a voluntary procedure it was not covered under most medical insurance plans.
D)The American Medical Association (AMA)refused to endorse the procedure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Figure 12-1 
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the firm is producing 500 units,what is the amount of its profit or loss?
A)profit of $280
B)loss equivalent to the area A
C)profit equivalent to the area A
D)There is insufficient information to answer the question.

Refer to Figure 12-1.If the firm is producing 500 units,what is the amount of its profit or loss?
A)profit of $280
B)loss equivalent to the area A
C)profit equivalent to the area A
D)There is insufficient information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If price = marginal cost at the output produced by a perfectly competitive firm and the firm is earning an economic profit,then
A)marginal revenue is less than price.
B)average total cost is at a minimum.
C)total revenue equals total cost.
D)price exceeds average total cost.
A)marginal revenue is less than price.
B)average total cost is at a minimum.
C)total revenue equals total cost.
D)price exceeds average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure 12-1 
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the firm is charging a price of $12 per unit
A)it breaks even.
B)it is making a profit.
C)it is selling 700 units.
D)it is not selling any output.

Refer to Figure 12-1.If the firm is charging a price of $12 per unit
A)it breaks even.
B)it is making a profit.
C)it is selling 700 units.
D)it is not selling any output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If,for the last bushel of apples produced and sold by an apple farm marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost,then in producing that bushel the farm
A)added more to total cost than it added to total revenue.
B)added an equal amount to both total revenue and total cost.
C)added more to total revenue than it added to total cost.
D)maximized its profits or minimized its losses.
A)added more to total cost than it added to total revenue.
B)added an equal amount to both total revenue and total cost.
C)added more to total revenue than it added to total cost.
D)maximized its profits or minimized its losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A perfectly competitive apple farm produces 1,000 bushels of apples at a total cost of $36,000.The price of each bushel is $50.Calculate the firm's short-run profit or loss.
A)loss of $14,000
B)profit of $14,000
C)profit of $50,000
D)There is insufficient information to answer the question.
A)loss of $14,000
B)profit of $14,000
C)profit of $50,000
D)There is insufficient information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For a perfectly competitive firm,at the profit-maximizing output average revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is always true at the quantity where a firm's average total cost equals average revenue?
A)The firm's revenue is maximized.
B)The firm's profit is maximized.
C)The firm breaks even.
D)Marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
A)The firm's revenue is maximized.
B)The firm's profit is maximized.
C)The firm breaks even.
D)Marginal cost equals marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Being a price-taker,a perfectly competitive firm cannot receive a producer surplus in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A firm will break even when
A)P = ATC.
B)P > ATC.
C)P < AVC.
D)P = AVC.
A)P = ATC.
B)P > ATC.
C)P < AVC.
D)P = AVC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If a perfectly competitive apple farm's marginal revenue exceeds the marginal cost of the last bushel of apples sold,what should the farm do to maximize its profit?
A)determine what the total revenue and total cost of production are
B)increase output
C)decrease output
D)lower its price to sell more
A)determine what the total revenue and total cost of production are
B)increase output
C)decrease output
D)lower its price to sell more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Letters are used to represent the terms used to answer this question: price (P),quantity of output (Q),total cost (TC)and average total cost (ATC).Which of the following equations is equal to a firm's profit?
A)P - ATC
B)(P × Q)- TC
C)(P × Q)- (P × ATC)
D)P - TC
A)P - ATC
B)(P × Q)- TC
C)(P × Q)- (P × ATC)
D)P - TC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Profit is the difference between
A)marginal revenue and marginal cost.
B)total revenue and variable cost.
C)total revenue and total explicit cost.
D)total revenue and total cost.
A)marginal revenue and marginal cost.
B)total revenue and variable cost.
C)total revenue and total explicit cost.
D)total revenue and total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Table 12-2
 Arnie sells basketballs in a perfectly competitive market.Table 12-2 summarizes Arnie's output per day (Q),total cost (TC),average total cost (ATC)and marginal cost (MC).
Arnie sells basketballs in a perfectly competitive market.Table 12-2 summarizes Arnie's output per day (Q),total cost (TC),average total cost (ATC)and marginal cost (MC).
Refer to Table 12-2.What will Arnie's output be and how much profit will he earn if the market price of basketballs is $5.00?
A)Q = 1; profit = -$10.
B)Q = 3; profit = -$7.50
C)Q = 0; profit = -$10.00
D)Price and profit cannot be determined from the information given.
 Arnie sells basketballs in a perfectly competitive market.Table 12-2 summarizes Arnie's output per day (Q),total cost (TC),average total cost (ATC)and marginal cost (MC).
Arnie sells basketballs in a perfectly competitive market.Table 12-2 summarizes Arnie's output per day (Q),total cost (TC),average total cost (ATC)and marginal cost (MC).Refer to Table 12-2.What will Arnie's output be and how much profit will he earn if the market price of basketballs is $5.00?
A)Q = 1; profit = -$10.
B)Q = 3; profit = -$7.50
C)Q = 0; profit = -$10.00
D)Price and profit cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Letters are used to represent the terms used to answer this question: price (P),quantity of output (Q),total cost (TC)and average total cost (ATC).Which of the following equations is equal to a firm's average profit?
A)P - ATC
B)(P - ATC)× Q
C)(P × Q)- TC
D)P - TC
A)P - ATC
B)(P - ATC)× Q
C)(P × Q)- TC
D)P - TC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Table 12-3
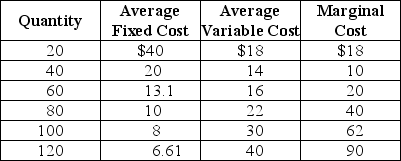 Table 12-3 shows the short-run cost data of a perfectly competitive firm.Assume that output can only be increased in batches of 20 units.
Table 12-3 shows the short-run cost data of a perfectly competitive firm.Assume that output can only be increased in batches of 20 units.
Refer to Table 12-3.If the market price is $45 the firm will produce
A)60 units.
B)80 units.
C)100 units
D)120 units
 Table 12-3 shows the short-run cost data of a perfectly competitive firm.Assume that output can only be increased in batches of 20 units.
Table 12-3 shows the short-run cost data of a perfectly competitive firm.Assume that output can only be increased in batches of 20 units.Refer to Table 12-3.If the market price is $45 the firm will produce
A)60 units.
B)80 units.
C)100 units
D)120 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Figure 12-2 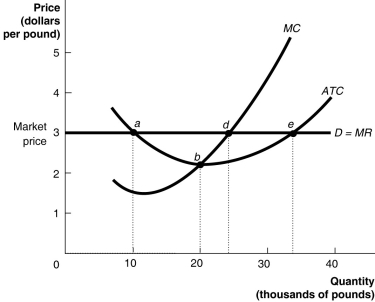 Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Refer to Figure 12-2.If Jason maximizes his profit he will produce the output rate indicated by point ________ and his average profit will equal ________.
A)d; $3 minus ATC at point d
B)b; $3 minus ATC at point b
C)e; $3 minus ATC at point e
D)a; $3
 Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.Refer to Figure 12-2.If Jason maximizes his profit he will produce the output rate indicated by point ________ and his average profit will equal ________.
A)d; $3 minus ATC at point d
B)b; $3 minus ATC at point b
C)e; $3 minus ATC at point e
D)a; $3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Figure 12-4 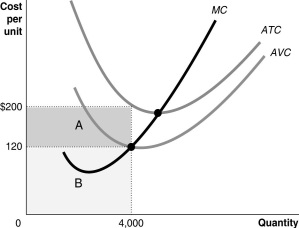
Refer to Figure 12-4.Suppose the firm produces 4,000 units.What does the shaded area labeled A represent?
A)total variable cost
B)profit
C)total fixed cost
D)total revenue

Refer to Figure 12-4.Suppose the firm produces 4,000 units.What does the shaded area labeled A represent?
A)total variable cost
B)profit
C)total fixed cost
D)total revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
To maximize profit,a firm will produce the level of output where MR = MC.If a firm actually makes a profit depends on the relationship of price to average total cost.What are the three possible relationships between price and average total cost that determine if a firm will make a profit,experience a loss,or break even?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the early 2000s,some entrepreneurs took advantage of a reduction in the price of computed tomography (CT)scanning equipment by offering apparently healthy people preventive body scans to provide early detection of diseases.Which of the following is one reason for the failure of this effort to be profitable?
A)Negative publicity from "false positives" that occurred from the CT tests reduced the demand for this service.
B)The federal government halted the CT body scans until further tests proved the procedure was safe and effective.
C)The U.S.Congress passed a law that restricted the ability of the entrepreneurs to offer the body scans.As a result,the industry was not able to reach minimum efficient scale.
D)A lack of publicity resulted in few consumers being aware that the procedure was available.
A)Negative publicity from "false positives" that occurred from the CT tests reduced the demand for this service.
B)The federal government halted the CT body scans until further tests proved the procedure was safe and effective.
C)The U.S.Congress passed a law that restricted the ability of the entrepreneurs to offer the body scans.As a result,the industry was not able to reach minimum efficient scale.
D)A lack of publicity resulted in few consumers being aware that the procedure was available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Figure 12-4 
Refer to Figure 12-4.Suppose the firm produces 4,000 units.What does the shaded area labeled B represent?
A)the firm's economic loss
B)total variable cost
C)average variable cost
D)total fixed cost

Refer to Figure 12-4.Suppose the firm produces 4,000 units.What does the shaded area labeled B represent?
A)the firm's economic loss
B)total variable cost
C)average variable cost
D)total fixed cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Table 12-3
 Table 12-3 shows the short-run cost data of a perfectly competitive firm.Assume that output can only be increased in batches of 20 units.
Table 12-3 shows the short-run cost data of a perfectly competitive firm.Assume that output can only be increased in batches of 20 units.
Refer to Table 12-3.If the market price is $45,the firm
A)earn a profit of $3,600.
B)will suffer a loss of $200.
C)will break even.
D)will earn profit of $1,040.
 Table 12-3 shows the short-run cost data of a perfectly competitive firm.Assume that output can only be increased in batches of 20 units.
Table 12-3 shows the short-run cost data of a perfectly competitive firm.Assume that output can only be increased in batches of 20 units.Refer to Table 12-3.If the market price is $45,the firm
A)earn a profit of $3,600.
B)will suffer a loss of $200.
C)will break even.
D)will earn profit of $1,040.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Figure 12-3 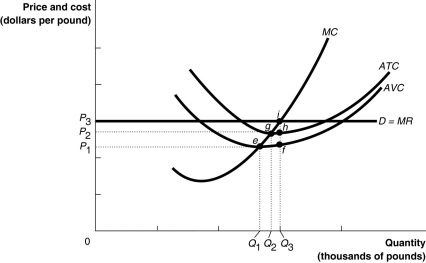 Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
Refer to Figure 12-3.If the market price is P1
A)The firm will experience a loss and raise its price to P2.The firm will then break even.
B)The firm will break even by producing a quantity of Q2.
C)The firm will experience a loss since price is less than ATC.
D)The firm may make a profit if it can increase the demand for its product.
 Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to Figure 12-3.If the market price is P1
A)The firm will experience a loss and raise its price to P2.The firm will then break even.
B)The firm will break even by producing a quantity of Q2.
C)The firm will experience a loss since price is less than ATC.
D)The firm may make a profit if it can increase the demand for its product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Figure 12-2  Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Refer to Figure 12-2.Jason is currently producing 20 thousand pounds of apples.To maximize his profit Jason should
A)keep production at 20 thousand pounds.
B)increase production to the output rate indicated by point d.
C)increase production to the output rate indicated by point e.
D)decrease production to the output rate indicated by point a.
 Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.Refer to Figure 12-2.Jason is currently producing 20 thousand pounds of apples.To maximize his profit Jason should
A)keep production at 20 thousand pounds.
B)increase production to the output rate indicated by point d.
C)increase production to the output rate indicated by point e.
D)decrease production to the output rate indicated by point a.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Figure 12-4 
Refer to Figure 12-4.Suppose the market price is $120.Which of the following is true?
A)The firm earns a profit equal to the area A.
B)The firm earns a profit equal to the area A + B.
C)The firm suffers a loss equal to the area A.
D)The firm will break even.

Refer to Figure 12-4.Suppose the market price is $120.Which of the following is true?
A)The firm earns a profit equal to the area A.
B)The firm earns a profit equal to the area A + B.
C)The firm suffers a loss equal to the area A.
D)The firm will break even.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Figure 12-2  Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Refer to Figure 12-2.Which of the following statements is true?
A)Jason should produce where MC equals $3 (point d)where he will minimize his losses.
B)Jason should produce where the distance between MC and his demand curve is greatest (point b).
C)Jason cannot earn a profit from selling any number of apples.
D)Jason should produce where MC equals $3 (point d)where he will maximize his profit.
 Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.Refer to Figure 12-2.Which of the following statements is true?
A)Jason should produce where MC equals $3 (point d)where he will minimize his losses.
B)Jason should produce where the distance between MC and his demand curve is greatest (point b).
C)Jason cannot earn a profit from selling any number of apples.
D)Jason should produce where MC equals $3 (point d)where he will maximize his profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Figure 12-3  Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
Refer to Figure 12-3.If the market price is P2 the firm
A)will break even and produce a quantity of Q2.
B)will make a profit and produce a quantity of Q2.
C)will make a profit and produce a quantity of Q1.
D)will make a profit and produce a quantity of Q3.
 Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to Figure 12-3.If the market price is P2 the firm
A)will break even and produce a quantity of Q2.
B)will make a profit and produce a quantity of Q2.
C)will make a profit and produce a quantity of Q1.
D)will make a profit and produce a quantity of Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For a given quantity,the total profit of a perfectly competitive firm is equal to the vertical distance between the firm's total revenue curve and its total cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose Veronica sells teapots in the perfectly competitive teapot market.Her output per day and her costs are as follows:
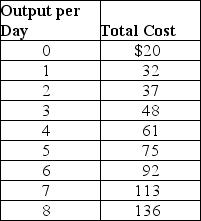 Suppose the current equilibrium price in the teapot market is $10.To maximize profit,how many teapots will Veronica produce,what price will she charge,and how much profit (or loss)will she make? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer.Your graph should include Veronica's demand,ATC,AVC,MC,and MR curves,the price she is charging,the quantity she is producing,and the area representing her profit (or loss).
Suppose the current equilibrium price in the teapot market is $10.To maximize profit,how many teapots will Veronica produce,what price will she charge,and how much profit (or loss)will she make? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer.Your graph should include Veronica's demand,ATC,AVC,MC,and MR curves,the price she is charging,the quantity she is producing,and the area representing her profit (or loss).
 Suppose the current equilibrium price in the teapot market is $10.To maximize profit,how many teapots will Veronica produce,what price will she charge,and how much profit (or loss)will she make? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer.Your graph should include Veronica's demand,ATC,AVC,MC,and MR curves,the price she is charging,the quantity she is producing,and the area representing her profit (or loss).
Suppose the current equilibrium price in the teapot market is $10.To maximize profit,how many teapots will Veronica produce,what price will she charge,and how much profit (or loss)will she make? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer.Your graph should include Veronica's demand,ATC,AVC,MC,and MR curves,the price she is charging,the quantity she is producing,and the area representing her profit (or loss).
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A perfectly competitive firm will maximize its profit at the rate of output where the vertical distance between its total revenue and total cost is the largest.This is the same rate of output where
A)average total cost equals marginal revenue.
B)marginal revenue equals marginal profit.
C)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue equals average revenue.
A)average total cost equals marginal revenue.
B)marginal revenue equals marginal profit.
C)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue equals average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Figure 12-2  Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Refer to Figure 12-2.To maximize his profit,Jason should produce the rate of output indicated by point
A)a.
B)b.
C)e.
D)d.
 Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.
Figure 12-2 shows the demand,marginal cost (MC)and average total cost (ATC)curves for Jason's House of Apples.Refer to Figure 12-2.To maximize his profit,Jason should produce the rate of output indicated by point
A)a.
B)b.
C)e.
D)d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In the short run,a firm that is operating at a loss has two options.These options are
A)to reduce output or reduce its variable costs.
B)to go out of business or declare bankruptcy.
C)to shut down temporarily or continue to produce.
D)to adopt new technology or change the size of its physical plant.
A)to reduce output or reduce its variable costs.
B)to go out of business or declare bankruptcy.
C)to shut down temporarily or continue to produce.
D)to adopt new technology or change the size of its physical plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If firms do not earn economic profits in a competitive equilibrium,why would the firms choose to stay in business?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure 12-3  Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
Refer to Figure 12-3.If the market price is P3 the firm
A)will break even.
B)will make a profit.
C)will earn enough revenue to cover its variable costs but not its fixed costs.
D)will produce a quantity of Q1.
 Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
Figure 12-3 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to Figure 12-3.If the market price is P3 the firm
A)will break even.
B)will make a profit.
C)will earn enough revenue to cover its variable costs but not its fixed costs.
D)will produce a quantity of Q1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If price is equal to average variable cost,a perfectly competitive firm breaks even.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



