Deck 11: Capital Budgeting
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/149
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Capital Budgeting
1
The minimum desired rate of return on an investment is sometimes referred to as ________.
A) the discount rate
B) the hurdle rate
C) the required rate of return
D) all of the above
A) the discount rate
B) the hurdle rate
C) the required rate of return
D) all of the above
D
2
The most widely used capital budgeting models are ________.
A) payback method
B) accounting rate of return
C) return on investment
D) discounted cash flow methods
A) payback method
B) accounting rate of return
C) return on investment
D) discounted cash flow methods
D
3
The net present value method computes the present value of all ________ using a minimum desired rate of return.
A) expected future cash inflows only
B) expected future cash outflows only
C) expected future cash inflows and expected future cash outflows
D) past cash inflows
A) expected future cash inflows only
B) expected future cash outflows only
C) expected future cash inflows and expected future cash outflows
D) past cash inflows
C
4
New Hampshire Company is considering two investments.The relevant data follows:
Ignore taxes.Using the net present value method,which project should be accepted?
A) Project A only
B) Project B only
C) both Project A and Project B
D) neither Project A nor Project B
Ignore taxes.Using the net present value method,which project should be accepted?
A) Project A only
B) Project B only
C) both Project A and Project B
D) neither Project A nor Project B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Arizona Company is considering two investments.The relevant data follows:
Ignore taxes.Using the internal rate of return method,which project should be accepted?
A) Project A only
B) Project B only
C) Project A and Project B
D) neither Project A nor Project B
Ignore taxes.Using the internal rate of return method,which project should be accepted?
A) Project A only
B) Project B only
C) Project A and Project B
D) neither Project A nor Project B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The higher the risk of an investment project,the ________ for the project.
A) lower the minimum desired rate of return
B) higher the minimum desired rate of return
C) lower the expected rate of return
D) higher the expected rate of return
A) lower the minimum desired rate of return
B) higher the minimum desired rate of return
C) lower the expected rate of return
D) higher the expected rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The internal rate of return method and the ________ method usually result in the same investment decisions.
A) payback period
B) accounting rate of return
C) net present value
D) return on investment
A) payback period
B) accounting rate of return
C) net present value
D) return on investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When using the Net Present Value model,which of the following assumptions is/are used?
A) We assume the predicted cash inflows and outflows are certain to occur at the times specified.
B) We assume perfect capital markets.
C) The Net Present Value model meets the cost-benefit criterion.
D) A and B
A) We assume the predicted cash inflows and outflows are certain to occur at the times specified.
B) We assume perfect capital markets.
C) The Net Present Value model meets the cost-benefit criterion.
D) A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Steps used in applying the net present value method to a proposed capital investment do NOT include ________.
A) identify the amount and timing of relevant expected cash inflows and outflows
B) find the present value of each expected future cash inflow and outflow
C) find the sum of the present values of each expected future cash inflow and outflow
D) find the future value of the cash outflow that occurs at the present time.
A) identify the amount and timing of relevant expected cash inflows and outflows
B) find the present value of each expected future cash inflow and outflow
C) find the sum of the present values of each expected future cash inflow and outflow
D) find the future value of the cash outflow that occurs at the present time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the capital budgeting process,accountants are NOT involved in ________.
A) follow-up monitoring of investments
B) choosing which investments to make
C) gathering data to aid the investment decision
D) identifying potential investments
A) follow-up monitoring of investments
B) choosing which investments to make
C) gathering data to aid the investment decision
D) identifying potential investments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In net present value analysis,the minimum desired rate of return for an investment project depends on the ________ of a proposed project.
A) expected return
B) desired return
C) risk
D) payback period
A) expected return
B) desired return
C) risk
D) payback period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Pennsylvania Company is considering two investments.The relevant data follows:
Ignoring taxes,the internal rate of return for Project A is approximately ________.
A) 6%
B) 7%
C) 8%
D) 10%
Ignoring taxes,the internal rate of return for Project A is approximately ________.
A) 6%
B) 7%
C) 8%
D) 10%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) The higher the minimum desired rate of return, the lower the present value of each future cash flow.
B) Higher required rates of return lead to lower net present values for capital investments.
C) Higher required rates of return lead to higher net present values for capital investments.
D) The net present value for a project can be negative or positive depending on the minimum desired rate of return used.
A) The higher the minimum desired rate of return, the lower the present value of each future cash flow.
B) Higher required rates of return lead to lower net present values for capital investments.
C) Higher required rates of return lead to higher net present values for capital investments.
D) The net present value for a project can be negative or positive depending on the minimum desired rate of return used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
California Company is considering two investments.The relevant data follows:
Ignoring taxes,the internal rate of return for Project B is approximately ________.
A) 5%
B) 6%
C) 7%
D) 8%
Ignoring taxes,the internal rate of return for Project B is approximately ________.
A) 5%
B) 6%
C) 7%
D) 8%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Dolly Madison Company is considering two investments.The relevant data follows:
Ignoring taxes,the internal rate of return for Project A is approximately ________.
A) 8%
B) 10%
C) 12%
D) 14%
Ignoring taxes,the internal rate of return for Project A is approximately ________.
A) 8%
B) 10%
C) 12%
D) 14%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
New Jersey Company is considering two investments.The relevant data follows:
Ignoring taxes,the internal rate of return for Project B is approximately ________.
A) 6%
B) 7%
C) 8%
D) 10%
Ignoring taxes,the internal rate of return for Project B is approximately ________.
A) 6%
B) 7%
C) 8%
D) 10%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A capital investment has a net present value of $1,000.00 at a required rate of return of 10%.At a 12% required rate of return,the net present value of the investment is $100.00.At a 14% required rate of return,the net present value of the investment is $0.The capital investment should be rejected if ________.
A) the required rate of return exceeds 14%
B) the required rate of return exceeds 12%
C) the required rate of return is less than 14%
D) the required rate of return is less than 12%
A) the required rate of return exceeds 14%
B) the required rate of return exceeds 12%
C) the required rate of return is less than 14%
D) the required rate of return is less than 12%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Discounted cash flow models focus on future cash inflows and outflows.
B) Discounted cash flow models consider the time value of money.
C) Discounted cash flow models focus on net income.
D) Discounted cash flow models compare cash outflows today to the present value of future cash flows.
A) Discounted cash flow models focus on future cash inflows and outflows.
B) Discounted cash flow models consider the time value of money.
C) Discounted cash flow models focus on net income.
D) Discounted cash flow models compare cash outflows today to the present value of future cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The phases of capital budgeting do NOT include ________.
A) a post-audit of the investment
B) gathering data to aid investment decisions
C) the identification of potential investments
D) sensitivity analysis of investment models
A) a post-audit of the investment
B) gathering data to aid investment decisions
C) the identification of potential investments
D) sensitivity analysis of investment models

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Investments of large amounts of cash in plant assets are called ________.
A) cash outflows
B) capital budgeting
C) capital projects
D) capital outlays
A) cash outflows
B) capital budgeting
C) capital projects
D) capital outlays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Using the net present value method,managers sum the present values of all expected future cash flows from the project and ________.
A) add the initial investment
B) subtract the initial investment
C) ignore the initial investment
D) add the depreciation expense
A) add the initial investment
B) subtract the initial investment
C) ignore the initial investment
D) add the depreciation expense

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When using the net present value method,if the net present value of a project is negative,then the ________.
A) the project should be rejected
B) the project should be accepted
C) the project should be recalculated for missing cash inflows
D) none of the above
A) the project should be rejected
B) the project should be accepted
C) the project should be recalculated for missing cash inflows
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The internal rate of return and the net present value methods usually result in the same investment decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Keisha Company is considering the following investment:
Assume straight-line depreciation is used.Ignore income taxes.The net present value of the investment is ________.
A) $12,234
B) $19,352
C) $22,234
D) $100,000
Assume straight-line depreciation is used.Ignore income taxes.The net present value of the investment is ________.
A) $12,234
B) $19,352
C) $22,234
D) $100,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Assume the net present value method is used to evaluate investment opportunities.A manager is faced with several investments,but only has funding for one investment.Which investment should be chosen?
A) the investment with the lowest net present value
B) the investment with a net present value equal to zero
C) the investment with a negative net present value
D) the investment with the largest net present value
A) the investment with the lowest net present value
B) the investment with a net present value equal to zero
C) the investment with a negative net present value
D) the investment with the largest net present value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Hewlett Company is considering the following investment:
Assume straight-line depreciation is used.Ignore income taxes.The net present value of the investment is ________.
A) $68,216
B) $75,334
C) $78,216
D) $150,229
Assume straight-line depreciation is used.Ignore income taxes.The net present value of the investment is ________.
A) $68,216
B) $75,334
C) $78,216
D) $150,229

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Accepting a project with a ________ NPV makes the firm worse off financially because the cost of the investment exceeds the ________.
A) positive; present value of future benefits
B) negative; present value of future cash flows
C) negative; present value of present cash flows
D) positive; present value of present cash flows
A) positive; present value of future benefits
B) negative; present value of future cash flows
C) negative; present value of present cash flows
D) positive; present value of present cash flows

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The net present value of a project is zero.The minimum desired rate of return used to obtain the net present value of zero is 8%.Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) The project is desirable if the minimum desired rate of return is 10%.
B) The project is desirable if the minimum desired rate of return is 6%.
C) The project is desirable if the minimum desired rate of return is 6% or 10%.
D) The project is undesirable if the minimum desired rate of return is 6%.
A) The project is desirable if the minimum desired rate of return is 10%.
B) The project is desirable if the minimum desired rate of return is 6%.
C) The project is desirable if the minimum desired rate of return is 6% or 10%.
D) The project is undesirable if the minimum desired rate of return is 6%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the first step in applying the net-present-value method to investment projects?
A) Identify the amount and timing of relevant future cash inflows.
B) Identify the amount and timing of relevant future cash inflows and outflows.
C) Find the present value of each expected cash flow.
D) Sum the individual present values of the cash flows.
A) Identify the amount and timing of relevant future cash inflows.
B) Identify the amount and timing of relevant future cash inflows and outflows.
C) Find the present value of each expected cash flow.
D) Sum the individual present values of the cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the net present value of an investment project is positive,then the project is ________.If the net present value of an investment project is negative,then the project is ________.
A) ignored; accepted
B) desirable; undesirable
C) unacceptable; acceptable
D) rejected; accepted
A) ignored; accepted
B) desirable; undesirable
C) unacceptable; acceptable
D) rejected; accepted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the IRR on a project is greater than the required rate of return,then the net present value of the project is ________.
A) equal to zero
B) less than zero
C) greater than zero
D) none of the above
A) equal to zero
B) less than zero
C) greater than zero
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Discounted-cash-flow models do not focus on net income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Discounted-cash-flow models focus on a project's cash inflows and cash outflows without regard to the time value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Brown Company is considering the following investment:
Assume straight-line depreciation is used.Ignore income taxes.The net present value of the investment is ________.
A) $68,216
B) $71,775
C) $73,216
D) $145,090
Assume straight-line depreciation is used.Ignore income taxes.The net present value of the investment is ________.
A) $68,216
B) $71,775
C) $73,216
D) $145,090

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
As the minimum required rate of return increases for an investment project,the net present value of the project ________.
A) increases
B) does not change
C) decreases
D) becomes positive
A) increases
B) does not change
C) decreases
D) becomes positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
You can receive $10,000 today or $3,000 per year at the end of each year for the next five years.If the required rate of return is 10%,what option should be selected? (The present value of an ordinary annuity of one at 10% for five periods is 3.7908.The present value of one at 10% for five periods is 0.6209.)
A) Receive $10,000 today.
B) Receive $3,000 per year for the next five years.
C) The results are the same for both options.
D) Neither option is desirable.
A) Receive $10,000 today.
B) Receive $3,000 per year for the next five years.
C) The results are the same for both options.
D) Neither option is desirable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The internal rate of return model determines the ________ at which the net present value of an investment project equals ________.
A) cost of capital; a positive number
B) hurdle rate; a positive number
C) interest rate; zero
D) discount rate; a positive number
A) cost of capital; a positive number
B) hurdle rate; a positive number
C) interest rate; zero
D) discount rate; a positive number

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Capital-budgeting decisions have significant financial effects beyond the current year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the internal rate of return on a project is ________ the required rate of return,then the project should be accepted.
A) higher than
B) lower than
C) the same as
D) none of the above
A) higher than
B) lower than
C) the same as
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Zebron Company is considering the following investment:
Assume straight-line depreciation is used.Ignore income taxes.The net present value of the investment is ________.
A) $48,690
B) $49,441
C) $49,690
D) $101,000
Assume straight-line depreciation is used.Ignore income taxes.The net present value of the investment is ________.
A) $48,690
B) $49,441
C) $49,690
D) $101,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Marvel Company is considering the acquisition of two machines.
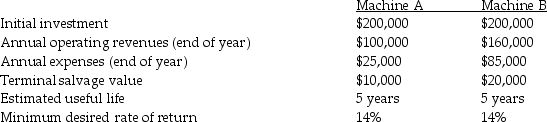
Assume straight-line depreciation.Ignore income taxes.The present value of an ordinary annuity of one at 14% and 5 periods is 3.4331.The present value of one at 14% and 5 periods is 0.5194.
Required:
A) Calculate the net present value for both machines.
B) Assume there are enough funds to purchase both machines. Should both machines be purchased?
C) Assume there are funds to purchase only one machine. Which machine should be purchased?
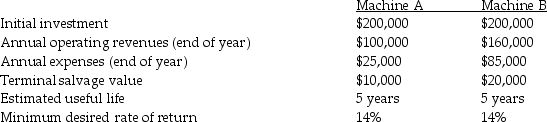
Assume straight-line depreciation.Ignore income taxes.The present value of an ordinary annuity of one at 14% and 5 periods is 3.4331.The present value of one at 14% and 5 periods is 0.5194.
Required:
A) Calculate the net present value for both machines.
B) Assume there are enough funds to purchase both machines. Should both machines be purchased?
C) Assume there are funds to purchase only one machine. Which machine should be purchased?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Jonathon Company is considering an investment in the project below:
Present value of ordinary annuity of one for
Ignoring taxes,what is the lowest level of annual cash operating savings that will result in a positive net present value?
A) $2,420
B) $2,638
C) $3,000
D) $3,120
Present value of ordinary annuity of one for
Ignoring taxes,what is the lowest level of annual cash operating savings that will result in a positive net present value?
A) $2,420
B) $2,638
C) $3,000
D) $3,120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Discounted-cash-flow models are not based on the theory of compound interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When comparing projects using the total project approach,a manager should choose the project with the ________.
A) smallest net present value
B) largest net present value
C) zero net present value
D) largest differential net present value
A) smallest net present value
B) largest net present value
C) zero net present value
D) largest differential net present value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Whitney Company is contemplating three different equipment investments.The relevant data follows:
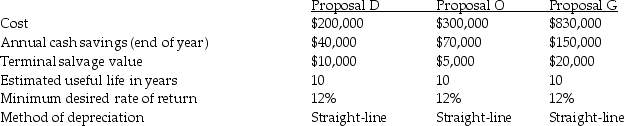
The present value factor of an ordinary annuity of one for 10 periods at 12% is 5.6502.
The present value factor of one for 10 periods at 12% is 0.322.
Required:
A) Compute the net present value of each investment. Ignore income taxes.
B) If only one investment can be acquired, which investment should be chosen?

The present value factor of an ordinary annuity of one for 10 periods at 12% is 5.6502.
The present value factor of one for 10 periods at 12% is 0.322.
Required:
A) Compute the net present value of each investment. Ignore income taxes.
B) If only one investment can be acquired, which investment should be chosen?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If a company accepts a project with a negative NPV,the project will increase the value of the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In capital budgeting decisions,the riskiness of a project may be shown by ________.
A) the size of the future cash inflows from the project
B) the size of the future cash outflows from the project
C) the timing of the cash flows from the project
D) the project's sensitivity to changes in predictions of cash flows
A) the size of the future cash inflows from the project
B) the size of the future cash outflows from the project
C) the timing of the cash flows from the project
D) the project's sensitivity to changes in predictions of cash flows

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Using the total project approach to investment decisions,the following information is available:
Net present value of Alternative A is $12,000
Net present value of Alternative B is $14,000
If the differential approach is used to evaluate Alternatives A and B,what is the numerical result obtained?
A) $0
B) $2,000 advantage to Alternative B
C) $12,000
D) $14,000
Net present value of Alternative A is $12,000
Net present value of Alternative B is $14,000
If the differential approach is used to evaluate Alternatives A and B,what is the numerical result obtained?
A) $0
B) $2,000 advantage to Alternative B
C) $12,000
D) $14,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When using an NPV model,we assume predicted cash flows are certain to occur at the times specified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The " break-even" cash inflow for an investment project is the point at which ________.
A) the present value of the variable cost of future cash flows equals the present value of the fixed cost of future cash flows
B) the present value of the variable cost of future cash flows equals the present value of the variable cost of past cash flows
C) the net present value of the investment project is zero
D) the total cash revenues equal total cash expenses
A) the present value of the variable cost of future cash flows equals the present value of the fixed cost of future cash flows
B) the present value of the variable cost of future cash flows equals the present value of the variable cost of past cash flows
C) the net present value of the investment project is zero
D) the total cash revenues equal total cash expenses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The IRR model determines the interest rate at which the NPV of an investment equals zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What will happen to the net present value of a project if my predictions of cash flows change? I think the cash flows may be overestimated.What should be done to address this?
A) net present value analysis
B) internal rate of return
C) sensitivity analysis
D) payback period
A) net present value analysis
B) internal rate of return
C) sensitivity analysis
D) payback period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Spitzer Company is considering two investments.If the differential approach to investment decisions is used,which of the following steps is NOT used?
A) list the differences in cash flows for each investment for each year
B) calculate the net present value of the differential cash flows
C) identify the relevant cash flows
D) calculate the net present value of the cash flows for each investment
A) list the differences in cash flows for each investment for each year
B) calculate the net present value of the differential cash flows
C) identify the relevant cash flows
D) calculate the net present value of the cash flows for each investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the absence of taxes,depreciation expense on a long-term asset is a relevant cash flow for the NPV model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The minimum desired rate of return for an investment under the NPV method is based on the cost of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When choosing among several investments,managers should pick the project with the highest net present value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The ________ approach computes the differences in cash flows between two alternatives and then finds the present value of these differences.
A) differential
B) payback
C) total project
D) sensitivity
A) differential
B) payback
C) total project
D) sensitivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When using the NPV model,it is assumed that we can borrow or lend money at the same interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Valesano Company is considering a project with the following information:
Present value of ordinary annuity of one for
Ignoring taxes,what is the lowest level of annual cash operating savings that will result in a positive net present value?
A) $1,550
B) $1,600
C) $1,608
D) $2,000
Present value of ordinary annuity of one for
Ignoring taxes,what is the lowest level of annual cash operating savings that will result in a positive net present value?
A) $1,550
B) $1,600
C) $1,608
D) $2,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Ignoring taxes,the total project approach to investment decisions calculates the difference in the ________.Ignoring income taxes,the differential approach to investment decisions computes the net present value of the difference in ________.
A) depreciation expense; operating cost savings
B) tax savings due to depreciation expense; tax savings due to operating cost savings
C) cash flows between two projects; net present values between two projects
D) net present values between two projects; cash flows between two projects
A) depreciation expense; operating cost savings
B) tax savings due to depreciation expense; tax savings due to operating cost savings
C) cash flows between two projects; net present values between two projects
D) net present values between two projects; cash flows between two projects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Danworth Company is contemplating whether to use MACRS depreciation or straight-line depreciation for a plant asset.The following information is available:
Over the four years examined,how much did Danworth Company gain by using MACRS depreciation instead of straight-line depreciation for the plant asset? The tax rate is 40%.(Find the present value.)
A) $722
B) $1,806
C) $2,976
D) $9,178
Over the four years examined,how much did Danworth Company gain by using MACRS depreciation instead of straight-line depreciation for the plant asset? The tax rate is 40%.(Find the present value.)
A) $722
B) $1,806
C) $2,976
D) $9,178

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Generally,the most difficult part of capital budgeting decisions is predicting accurately the relevant cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following items does NOT affect the present value of the tax deduction for depreciation expense used in the net present value calculation of an investment?
A) recovery period
B) tax rates
C) discount rate
D) gain on disposal of investment
A) recovery period
B) tax rates
C) discount rate
D) gain on disposal of investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following items is NOT a relevant cash inflow or cash outflow when using the net present value method? (Ignore income taxes.)
A) acquisition cost of new equipment at time zero
B) future disposal value of a long-term plant asset
C) future operating cash inflows from a long-term plant
D) depreciation expense in future periods
A) acquisition cost of new equipment at time zero
B) future disposal value of a long-term plant asset
C) future operating cash inflows from a long-term plant
D) depreciation expense in future periods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The differential approach to investments can be used to compare any number of projects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The total project approach to investments can be used to compare any number of projects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Two common methods for comparing alternative investments are the total project approach and the conversion approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Haworth Company is considering the purchase of a labor saving piece of equipment with the following information:
Present value of ordinary annuity of one
What is the net present value of the equipment?
A) $(2,737)
B) $(174,442)
C) $70,851
D) $168,968
Present value of ordinary annuity of one
What is the net present value of the equipment?
A) $(2,737)
B) $(174,442)
C) $70,851
D) $168,968

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following approaches should be used to compare four investment alternatives?
A) total project approach
B) sensitivity analysis
C) payback method
D) differential approach
A) total project approach
B) sensitivity analysis
C) payback method
D) differential approach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A company is considering two investment projects.If they use the total project approach and the differential approach,both approaches produce ________.
A) different answers
B) similar answers
C) the same answer
D) not enough information is given to make an assessment
A) different answers
B) similar answers
C) the same answer
D) not enough information is given to make an assessment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is the benefit of depreciation expense on a plant asset when considering investment decisions with taxes?
A) increased future operating income
B) future tax deduction
C) increased cost of plant asset
D) decreased cost of plant asset
A) increased future operating income
B) future tax deduction
C) increased cost of plant asset
D) decreased cost of plant asset

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the NPV method,errors in forecasting terminal disposal values are usually not crucial because the present value of these cash flows is small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In net present value analysis,a reduction in a future cash outflow is treated as ________.
A) an irrelevant cash flow
B) a cash inflow
C) a disposal value of a long-term asset
D) an expense
A) an irrelevant cash flow
B) a cash inflow
C) a disposal value of a long-term asset
D) an expense

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The book value of an asset that is being replaced is a relevant cash flow in the net present value method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The present value of tax savings from depreciation deductions from an accelerated depreciation method will be ________ those from the straight-line method.
A) the same as
B) greater than
C) less than
D) none of the above
A) the same as
B) greater than
C) less than
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Danville Company is contemplating whether to use MACRS depreciation or straight-line depreciation for a plant asset.The following information is available:
Assume the tax rate is 40%.Over the four years examined,what is the present value of the difference in tax savings between MACRS depreciation and straight-line depreciation?
A) $722
B) $1,806
C) $2,976
D) $9,178
Assume the tax rate is 40%.Over the four years examined,what is the present value of the difference in tax savings between MACRS depreciation and straight-line depreciation?
A) $722
B) $1,806
C) $2,976
D) $9,178

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In the net present value method,the only relevant operating cash flows are the ones that differ among alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the net present value method,the disposal value of a long-term asset at the end of its useful life is considered to be a ________.
A) cash outflow at time zero
B) cash inflow at time zero
C) cash outflow in the year of disposal
D) cash inflow in the year of disposal
A) cash outflow at time zero
B) cash inflow at time zero
C) cash outflow in the year of disposal
D) cash inflow in the year of disposal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The first step in using the differential approach to investment analysis is to ________.
A) calculate the present value of the differential cash flows
B) sum the individual present values of each investment
C) estimate the difference in cash flows between two projects for each year
D) estimate the relevant cash inflows and cash outflows for each project
A) calculate the present value of the differential cash flows
B) sum the individual present values of each investment
C) estimate the difference in cash flows between two projects for each year
D) estimate the relevant cash inflows and cash outflows for each project

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A company is considering the acquisition of new equipment to replace old equipment.When using the net present value method,which of the following items is NOT relevant? Ignore taxes.
A) cash outflow for the purchase of new equipment
B) cash installation costs associated with the new equipment
C) disposal value of old equipment replaced with new equipment
D) fixed overhead costs that are the same under both alternatives
A) cash outflow for the purchase of new equipment
B) cash installation costs associated with the new equipment
C) disposal value of old equipment replaced with new equipment
D) fixed overhead costs that are the same under both alternatives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



