Deck 5: Developmental Disorders
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Developmental Disorders
1
Which term describes a disorder present at and existing from the time of birth?
A)Anomaly
B)Inherited
C)Congenital
D)Developmental
A)Anomaly
B)Inherited
C)Congenital
D)Developmental
Congenital
2
What is the name of the pseudocyst filled with salivary gland tissue that may be an extension of the sublingual gland?
A)Ranula
B)Static bone cyst
C)Lymphoepithelial cyst
D)Traumatic bone cyst
A)Ranula
B)Static bone cyst
C)Lymphoepithelial cyst
D)Traumatic bone cyst
Static bone cyst
3
The body of the tongue develops from the:
A)frontal process.
B)first branchial arch.
C)second branchial arch.
D)third branchial arch.
A)frontal process.
B)first branchial arch.
C)second branchial arch.
D)third branchial arch.
first branchial arch.
4
This patient exhibits an extensive adhesion of the tongue to the floor of the mouth caused by the short lingual frenum. 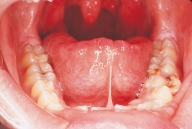 You suspect:
You suspect:
A)ankyloglossia.
B)frenectomy.
C)lingual thyroid.
D)total ankyloglossia.
 You suspect:
You suspect:A)ankyloglossia.
B)frenectomy.
C)lingual thyroid.
D)total ankyloglossia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which term describes partial anodontia or the lack of one or more teeth?
A)Anodontia
B)Ankylosed
C)Hypodontia
D)Gemination
A)Anodontia
B)Ankylosed
C)Hypodontia
D)Gemination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Total anodontia is often associated with a hereditary disturbance called:
A)taurodontism.
B)amelogenesis imperfecta.
C)ectodermal dysplasia.
D)cleidocranial dysplasia.
A)taurodontism.
B)amelogenesis imperfecta.
C)ectodermal dysplasia.
D)cleidocranial dysplasia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The _____ is characterized by its unique histologic appearance and its frequent recurrence rate.
A)radicular cyst
B)residual cyst
C)dentigerous cyst
D)odontogenic keratocyst
A)radicular cyst
B)residual cyst
C)dentigerous cyst
D)odontogenic keratocyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which term defines the joining of two adjacent teeth by cementum only?
A)Twinning
B)Concrescence
C)Cementogenesis
D)Fusion
A)Twinning
B)Concrescence
C)Cementogenesis
D)Fusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The lateral periodontal cyst occurs most often on the lateral aspect of a tooth root, which is usually the:
A)mandibular third molar.
B)maxillary premolars.
C)mandibular cuspid/premolars.
D)maxillary anteriors.
A)mandibular third molar.
B)maxillary premolars.
C)mandibular cuspid/premolars.
D)maxillary anteriors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The formation of dentin is called:
A)amelogenesis.
B)dentinogenesis.
C)dens in dente.
D)odontogenesis.
A)amelogenesis.
B)dentinogenesis.
C)dens in dente.
D)odontogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Clinically, the lingual thyroid nodule appears as a smooth nodular mass:
A)at the base of the tongue posterior to the circumvallate papillae.
B)on the anterior ventral tongue.
C)on the lateral borders of the middle third of the tongue.
D)anterior to the circumvallate papillae.
A)at the base of the tongue posterior to the circumvallate papillae.
B)on the anterior ventral tongue.
C)on the lateral borders of the middle third of the tongue.
D)anterior to the circumvallate papillae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Radiographically, this radiolucent cyst is often heart shaped, caused by the anatomic Y shape of the area. It is called the _____ cyst.
A)nasopalatine canal
B)median palatine
C)nasolabial
D)globulomaxillary
A)nasopalatine canal
B)median palatine
C)nasolabial
D)globulomaxillary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The most common cyst observed in the oral cavity is caused by pulpal inflammation and is called a(n) _____ cyst.
A)dentigerous
B)eruption
C)radicular
D)primordial
A)dentigerous
B)eruption
C)radicular
D)primordial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The first branchial arch divides into two maxillary processes and the _____ process.
A)mandibular
B)frontal
C)median nasal
D)globular
A)mandibular
B)frontal
C)median nasal
D)globular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which one of the following is not considered a pseudocyst?
A)Thyroglossal tract cyst
B)Static bone cyst
C)Simple bone cyst
D)Aneurysmal bone cyst
A)Thyroglossal tract cyst
B)Static bone cyst
C)Simple bone cyst
D)Aneurysmal bone cyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
This unilocular radiolucency around the crown of an unerupted second premolar is most likely a: 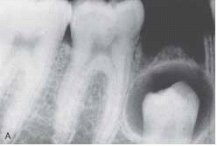
A)normal developmental sac.
B)dentigerous cyst.
C)primordial cyst.
D)lateral periodontal cyst.

A)normal developmental sac.
B)dentigerous cyst.
C)primordial cyst.
D)lateral periodontal cyst.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which epithelium-lined tract is a developmental anomaly located in the corners of the mouth?
A)Commissural lip pit
B)Angular cheilitis
C)Fistula
D)Congenital lip pit
A)Commissural lip pit
B)Angular cheilitis
C)Fistula
D)Congenital lip pit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The _____ cyst has a strong predilection for females.
A)lateral periodontal
B)nasopalatine canal
C)nasolabial
D)gingival
A)lateral periodontal
B)nasopalatine canal
C)nasolabial
D)gingival

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which one of the following is not true about the thyroglossal tract cyst?
A)It is found in individuals younger than 20 years.
B)There is no sex predilection.
C)Clinically, it is located below the hyoid bone.
D)Conservative nonsurgical treatment is sufficient.
A)It is found in individuals younger than 20 years.
B)There is no sex predilection.
C)Clinically, it is located below the hyoid bone.
D)Conservative nonsurgical treatment is sufficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Odontogenesis in the human embryo occurs at:
A)three weeks.
B)five weeks.
C)five months.
D)one month.
A)three weeks.
B)five weeks.
C)five months.
D)one month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Impacted teeth cannot erupt because of:
A)lack of eruptive force.
B)physical obstruction.
C)ankylosis.
D)bone pathology.
A)lack of eruptive force.
B)physical obstruction.
C)ankylosis.
D)bone pathology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The pseudocyst seen in this radiograph is surrounded by salivary gland tissue. 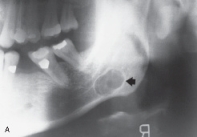 It is a(n) _____ bone cyst.
It is a(n) _____ bone cyst.
A)simple
B)Stafne
C)traumatic
D)aneurysmal
 It is a(n) _____ bone cyst.
It is a(n) _____ bone cyst.A)simple
B)Stafne
C)traumatic
D)aneurysmal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Multiple supernumerary teeth may be a component of which of the following?
A)Cleidocranial dysplasia
B)Dermoid cyst
C)Syphilis
D)Static bone cyst
A)Cleidocranial dysplasia
B)Dermoid cyst
C)Syphilis
D)Static bone cyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Regional odontodysplasia is:
A)a decrease in radiodensity seen on one or more unerupted teeth in a quadrant.
B)a genetic condition.
C)caused by systemic illness.
D)most often seen in the mandible.
A)a decrease in radiodensity seen on one or more unerupted teeth in a quadrant.
B)a genetic condition.
C)caused by systemic illness.
D)most often seen in the mandible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Regional odontodysplasia is also referred to as:
A)hypodontia.
B)ghost teeth.
C)taurodontism.
D)supernumerary teeth.
A)hypodontia.
B)ghost teeth.
C)taurodontism.
D)supernumerary teeth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Ingesting water with four times the amount of fluoride causes:
A)brown-to-black staining.
B)cusp fractures.
C)white spots on the middle third of smooth crowns.
D)increased dental caries.
A)brown-to-black staining.
B)cusp fractures.
C)white spots on the middle third of smooth crowns.
D)increased dental caries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The supernumerary tooth in this illustration is: 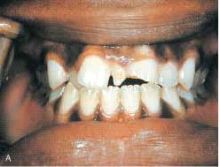
A)a mesiodens.
B)a dilaceration.
C)the result of twinning.
D)the result of gemination.

A)a mesiodens.
B)a dilaceration.
C)the result of twinning.
D)the result of gemination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Nonerupted supernumerary teeth should be extracted because of which of the following risks?
A)Malignant tumor development
B)Cysts around the crowns
C)Internal resorption
D)Condensing osteitis
A)Malignant tumor development
B)Cysts around the crowns
C)Internal resorption
D)Condensing osteitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which one of the following defines a disturbance of the maturation of the enamel matrix?
A)Turner tooth
B)Mulberry molar
C)Premature birth
D)Enamel hypocalcification
A)Turner tooth
B)Mulberry molar
C)Premature birth
D)Enamel hypocalcification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Enamel hypoplasia is the result of a disturbance of or damage to ameloblasts during enamel matrix formation. Which one of the following would not be a factor?
A)Genetics
B)Ingestion of high concentrations of fluoride during tooth development
C)Vitamin deficiency during tooth development
D)Shingles
A)Genetics
B)Ingestion of high concentrations of fluoride during tooth development
C)Vitamin deficiency during tooth development
D)Shingles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Pitting is the most common type of enamel hypoplasia seen in patients who have which condition during tooth development?
A)Febrile illness
B)Drinking water with 2.4 ppm of fluoride during tooth development
C)Congenital syphilis
D)Herpes simplex
A)Febrile illness
B)Drinking water with 2.4 ppm of fluoride during tooth development
C)Congenital syphilis
D)Herpes simplex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
For which condition would pulp vitality be nonvital?
A)Radicular cyst
B)Median mandibular cyst
C)Median palatal cyst
D)Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
A)Radicular cyst
B)Median mandibular cyst
C)Median palatal cyst
D)Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Another name for dens invaginatus is:
A)taurodontism.
B)dens in dente.
C)dens evaginatus.
D)enamel pearl.
A)taurodontism.
B)dens in dente.
C)dens evaginatus.
D)enamel pearl.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The developmental anomaly seen in this radiograph is: 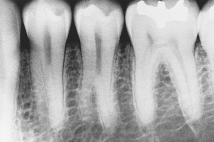
A)taurodontism.
B)mulberry molar.
C)supernumerary roots on the mandibular premolars.
D)dilaceration.

A)taurodontism.
B)mulberry molar.
C)supernumerary roots on the mandibular premolars.
D)dilaceration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which tooth is most commonly affected by dens in dente?
A)Maxillary central
B)Mandibular lateral
C)Maxillary lateral
D)A supernumerary tooth
A)Maxillary central
B)Mandibular lateral
C)Maxillary lateral
D)A supernumerary tooth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The projection of white material seen at the furcation area in this maxillary molar is a developmental anomaly. 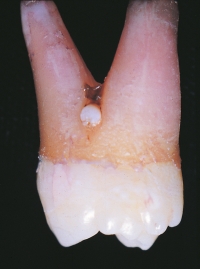 You suspect:
You suspect:
A)dens evaginatus.
B)enamel pearl.
C)supernumerary cusp.
D)calculus.
 You suspect:
You suspect:A)dens evaginatus.
B)enamel pearl.
C)supernumerary cusp.
D)calculus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Dens in dente is a developmental anomaly often seen with:
A)extra cusps.
B)a periapical lesion.
C)tuberculated premolars.
D)supernumerary roots.
A)extra cusps.
B)a periapical lesion.
C)tuberculated premolars.
D)supernumerary roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The pear-shaped radiolucency observed in this radiograph is most likely a _____ cyst. 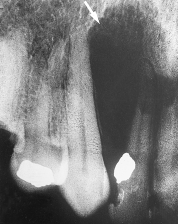
A)radicular
B)globulomaxillary
C)lateral periodontal
D)nasopalatine canal

A)radicular
B)globulomaxillary
C)lateral periodontal
D)nasopalatine canal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
This radiograph clearly shows which developmental anomaly? 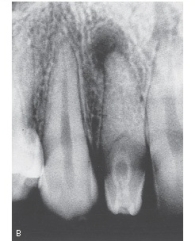
A)Dens in dente
B)Periapical pathology (PAP)
C)Caries
D)Open contacts

A)Dens in dente
B)Periapical pathology (PAP)
C)Caries
D)Open contacts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The most common supernumerary tooth is called:
A)distomolar.
B)mesiodens.
C)mulberry molar.
D)Turner tooth.
A)distomolar.
B)mesiodens.
C)mulberry molar.
D)Turner tooth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A small elevated mass of thyroid tissue located near the foramen cecum or posterior lateral borders of the tongue, which forms as a result of failure of the embryonic thyroid tissue to migrate to its proper position, is called a(n):
A)ameloblastic fibroma.
B)hemangioma.
C)lingual thyroid nodule.
D)thyroglossal duct cyst.
A)ameloblastic fibroma.
B)hemangioma.
C)lingual thyroid nodule.
D)thyroglossal duct cyst.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When counting the maxillary anterior teeth of this adolescent patient, it appears that five are present, if the large tooth is counted as one. A radiograph reveals that this large central tooth has two roots. 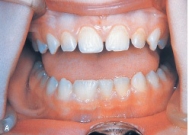 This tooth demonstrates:
This tooth demonstrates:
A)geminism.
B)concrescence.
C)dilaceration.
D)fusion.
 This tooth demonstrates:
This tooth demonstrates:A)geminism.
B)concrescence.
C)dilaceration.
D)fusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The deformity seen here with a bend in root apices is characteristic of: 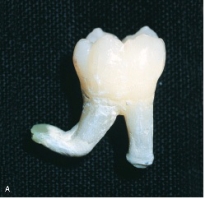
A)dilaceration.
B)gemination.
C)fusion.
D)concrescence.

A)dilaceration.
B)gemination.
C)fusion.
D)concrescence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When two or more teeth are joined by cementum, as shown in this picture, it is known as: 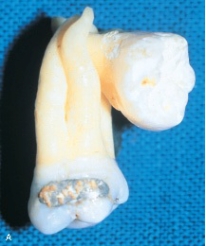
A)concrescence.
B)dilaceration.
C)enamel pearl.
D)gemination.

A)concrescence.
B)dilaceration.
C)enamel pearl.
D)gemination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The cyst that appears in the bone in this radiograph surrounds the fully formed crown of an unerupted premolar. 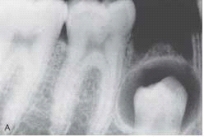 The dental hygienist should refer to this as a(n) _____ cyst.
The dental hygienist should refer to this as a(n) _____ cyst.
A)eruption
B)follicular
C)lateral periodontal
D)primordial
 The dental hygienist should refer to this as a(n) _____ cyst.
The dental hygienist should refer to this as a(n) _____ cyst.A)eruption
B)follicular
C)lateral periodontal
D)primordial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Proliferation is defined as:
A)congenital lack of teeth.
B)formation of dentin.
C)multiplication of cells.
D)disposition in favor of something.
A)congenital lack of teeth.
B)formation of dentin.
C)multiplication of cells.
D)disposition in favor of something.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
This patient exhibits an accessory cusp located in the cingulum of the maxillary right lateral permanent incisor. 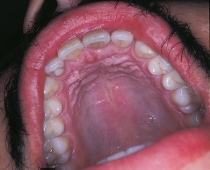 This can be diagnosed as a:
This can be diagnosed as a:
A)talon cusp.
B)dens in dente.
C)taurodontism.
D)dens evaginatus.
 This can be diagnosed as a:
This can be diagnosed as a:A)talon cusp.
B)dens in dente.
C)taurodontism.
D)dens evaginatus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
This enlargement on the lateral neck of this patient has been present for months and is slowly increasing in size. It is painless and feels soft. 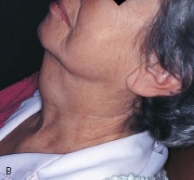 Histologic examination shows this to be an epithelium-lined sac filled with clear, yellow fluid. It is a _____ cyst.
Histologic examination shows this to be an epithelium-lined sac filled with clear, yellow fluid. It is a _____ cyst.
A)thyroglossal duct
B)branchial
C)median palatine
D)globulomaxillary
 Histologic examination shows this to be an epithelium-lined sac filled with clear, yellow fluid. It is a _____ cyst.
Histologic examination shows this to be an epithelium-lined sac filled with clear, yellow fluid. It is a _____ cyst.A)thyroglossal duct
B)branchial
C)median palatine
D)globulomaxillary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The only hypoplastic defect in a patient's dentition is located on the facial surface of a permanent maxillary central incisor. The most likely cause of this defect is:
A)a dietary deficiency during tooth formation.
B)absence of the primary mandibular central incisor.
C)physical injury of the primary maxillary central incisor.
D)neonatal hypoplasia of the primary anterior teeth.
A)a dietary deficiency during tooth formation.
B)absence of the primary mandibular central incisor.
C)physical injury of the primary maxillary central incisor.
D)neonatal hypoplasia of the primary anterior teeth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Deciduous teeth in which bone has fused to cementum and dentin, preventing exfoliation of the deciduous tooth and eruption of the underlying permanent tooth, are:
A)embedded.
B)ankylosed.
C)impacted.
D)erupted.
A)embedded.
B)ankylosed.
C)impacted.
D)erupted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Odontogenic keratocysts are a clinical component of:
A)nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome.
B)neurofibromatosis of von Recklinghausen.
C)cherubism.
D)Gardner syndrome.
A)nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome.
B)neurofibromatosis of von Recklinghausen.
C)cherubism.
D)Gardner syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
During tooth development, ectoderm and ectomesenchymal cells give rise to each of the following except one. Which one is the exception?
A)Periodontal ligament
B)Ameloblasts
C)Odontoblasts
D)Cementoblasts
A)Periodontal ligament
B)Ameloblasts
C)Odontoblasts
D)Cementoblasts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Periapical x-ray examination reveals a well-defined unilocular radiolucency located in the midline of the hard palate. 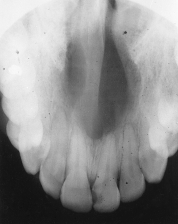 The diagnosis is _____ cyst.
The diagnosis is _____ cyst.
A)nasolabial
B)globulomaxillary
C)branchial cleft
D)median palatine
 The diagnosis is _____ cyst.
The diagnosis is _____ cyst.A)nasolabial
B)globulomaxillary
C)branchial cleft
D)median palatine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which one of the following tumors frequently arises from a dentigerous cyst?
A)Sarcoma
B)Ameloblastoma
C)Odontoma
D)Dens en dente
A)Sarcoma
B)Ameloblastoma
C)Odontoma
D)Dens en dente

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The radiograph of this patient exhibits a biloculated, well-defined radiolucency lateral to the tooth root. It is asymptomatic. 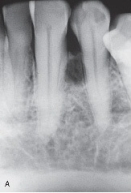 This is a _____ cyst.
This is a _____ cyst.
A)residual
B)follicular
C)lateral periodontal
D)primordial
 This is a _____ cyst.
This is a _____ cyst.A)residual
B)follicular
C)lateral periodontal
D)primordial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
This patient is perfectly healthy, with no history of local or systemic infection or disease. All of the patient's teeth are caries free, as are all of the teeth of all of the patients who exhibit this defect. 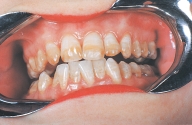 This is characteristic of:
This is characteristic of:
A)fluorosis.
B)Hutchinson incisors.
C)a Turner tooth.
D)attrition.
 This is characteristic of:
This is characteristic of:A)fluorosis.
B)Hutchinson incisors.
C)a Turner tooth.
D)attrition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Microdontia most commonly occurs in:
A)maxillary laterals and third molars.
B)maxillary canine.
C)mandibular molars.
D)mandibular incisors and molars.
A)maxillary laterals and third molars.
B)maxillary canine.
C)mandibular molars.
D)mandibular incisors and molars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
During embryonic development of the face, the frontal process divides into three parts. These three parts include the median nasal process, the right lateral nasal process, and the left lateral nasal process.
A)Both statements are true.
B)Both statements are false.
C)The first statement is true; the second is false.
D)The first statement is false; the second is true.
A)Both statements are true.
B)Both statements are false.
C)The first statement is true; the second is false.
D)The first statement is false; the second is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which term best describes a disorder caused by abnormalities in the genetic makeup transmitted from parent to offspring?
A)Anomaly
B)Inherited
C)Congenital
D)Developmental
A)Anomaly
B)Inherited
C)Congenital
D)Developmental

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Odontogenesis in the human embryo takes place at approximately:
A)five weeks.
B)two months.
C)three months.
D)at birth.
A)five weeks.
B)two months.
C)three months.
D)at birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



