Deck 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/167
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory
1
Place the following in order of decreasing magnitude of lattice energy. NaF RbBr KCl
A) RbBr > NaF > KCl
B) NaF > KCl > RbBr
C) KCl > NaF > RbBr
D) NaF > RbBr > KCl
E) RbBr > KCl > NaF
A) RbBr > NaF > KCl
B) NaF > KCl > RbBr
C) KCl > NaF > RbBr
D) NaF > RbBr > KCl
E) RbBr > KCl > NaF
NaF > KCl > RbBr
2
Use the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the lattice energy of CaO. DH°(kJ)
Ca(s)→ Ca(g)193
Ca(g)→ Ca⁺(g)+ e⁻ 590
Ca⁺(g)→ Ca2⁺(g)+ e⁻ 1010
2 O(g)→ O2(g)-498
O(g)+ e⁻ → O⁻(g)-141
O⁻(g)+ e⁻ → O2⁻(g)878
Ca(s)+ O2(g)→ CaO(s)-635
O2(g)→ CaO(s)-635
A) -3414 kJ
B) +1397 kJ
C) -2667 kJ
D) +3028 kJ
E) -2144 kJ
Ca(s)→ Ca(g)193
Ca(g)→ Ca⁺(g)+ e⁻ 590
Ca⁺(g)→ Ca2⁺(g)+ e⁻ 1010
2 O(g)→ O2(g)-498
O(g)+ e⁻ → O⁻(g)-141
O⁻(g)+ e⁻ → O2⁻(g)878
Ca(s)+
 O2(g)→ CaO(s)-635
O2(g)→ CaO(s)-635A) -3414 kJ
B) +1397 kJ
C) -2667 kJ
D) +3028 kJ
E) -2144 kJ
-3414 kJ
3
Give the complete electronic configuration for Ca2+.
A) 1s22s22p63s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p5
D) 1s22s23p64s25p6
E) 1s22s2p63s2p6
A) 1s22s22p63s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p5
D) 1s22s23p64s25p6
E) 1s22s2p63s2p6
1s22s22p63s23p6
4
Give the complete electronic configuration for Br-.
A) 1s22s22p63s23p64s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p64s24d104p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p6
D) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p5
E) 1s22s2p63s2p64s23d104p6
A) 1s22s22p63s23p64s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p64s24d104p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p6
D) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p5
E) 1s22s2p63s2p64s23d104p6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Give the complete electronic configuration for S2-.
A) 1s22s22p63s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p5
D) 1s22s23p64s25p6
E) 1s22s2p63s2p6
A) 1s22s22p63s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p5
D) 1s22s23p64s25p6
E) 1s22s2p63s2p6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Use the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the second ionization energy of Ca. DH°(kJ)
Ca(s)→ Ca(g)193
Ca(g)→ Ca⁺(g)+ e⁻ 590.
2 O(g)→ O2(g)-498
O(g)+ e⁻ → O⁻(g)-141
O⁻(g)+ e⁻ → O2⁻(g)878
Ca(s)+ O2(g)→ CaO(s)-635
O2(g)→ CaO(s)-635
Ca2⁺(g)+ O2⁻(g)→ CaO(s)-3414
A) 1010 kJ
B) 1757 kJ
C) 1508 kJ
D) -3027 kJ
E) -1514 kJ
Ca(s)→ Ca(g)193
Ca(g)→ Ca⁺(g)+ e⁻ 590.
2 O(g)→ O2(g)-498
O(g)+ e⁻ → O⁻(g)-141
O⁻(g)+ e⁻ → O2⁻(g)878
Ca(s)+
 O2(g)→ CaO(s)-635
O2(g)→ CaO(s)-635Ca2⁺(g)+ O2⁻(g)→ CaO(s)-3414
A) 1010 kJ
B) 1757 kJ
C) 1508 kJ
D) -3027 kJ
E) -1514 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Place the following in order of increasing magnitude of lattice energy. CaO MgO SrS
A) MgO < CaO < SrS
B) SrS < MgO < CaO
C) SrS < CaO < MgO
D) CaO < MgO < SrS
E) CaO < SrS < MgO
A) MgO < CaO < SrS
B) SrS < MgO < CaO
C) SrS < CaO < MgO
D) CaO < MgO < SrS
E) CaO < SrS < MgO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following represents the Lewis structure for Ca2⁺?
A)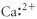
B)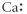
C)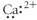
D)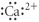
E)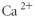
A)
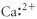
B)
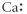
C)
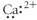
D)
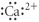
E)
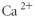

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following represents the Lewis structure for Cl?
A)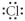
B)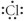
C)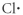
D)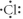
E)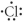
A)
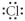
B)
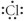
C)
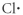
D)
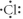
E)
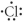

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following represents the Lewis structure for Br⁻?
A)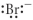
B)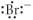
C)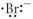
D)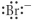
E)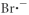
A)
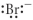
B)
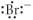
C)
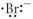
D)
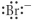
E)
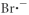

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Place the following in order of decreasing magnitude of lattice energy. K2O Rb2S Li2O
A) Li2O > K2O > Rb2S
B) Li2O > Rb2S > K2O
C) Rb2S > K2O > Li2O
D) Rb2S > Li2O > K2O
E) K2O > Li2O > Rb2S
A) Li2O > K2O > Rb2S
B) Li2O > Rb2S > K2O
C) Rb2S > K2O > Li2O
D) Rb2S > Li2O > K2O
E) K2O > Li2O > Rb2S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following represents the Lewis structure for S2⁻?
A)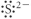
B)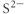
C)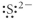
D)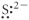
E)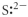
A)
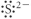
B)
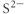
C)
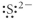
D)
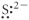
E)
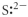

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the bond energy of O2. DH°(kJ)
Na(s)→ Na(g)107
Na(g)→ Na⁺(g)+ e⁻ 496
O(g)+ e⁻ → O⁻(g)-141
O⁻(g)+ e⁻ → O2⁻(g)878
2 Na(s)+ O2(g)→ Na2O(s)-416
O2(g)→ Na2O(s)-416
2 Na⁺(g)+ O2⁻(g)→ Na2O(s)-2608
A) 426 kJ
B) 249 kJ
C) 852 kJ
D) 498 kJ
E) 356 kJ
Na(s)→ Na(g)107
Na(g)→ Na⁺(g)+ e⁻ 496
O(g)+ e⁻ → O⁻(g)-141
O⁻(g)+ e⁻ → O2⁻(g)878
2 Na(s)+
 O2(g)→ Na2O(s)-416
O2(g)→ Na2O(s)-4162 Na⁺(g)+ O2⁻(g)→ Na2O(s)-2608
A) 426 kJ
B) 249 kJ
C) 852 kJ
D) 498 kJ
E) 356 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Use the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the electron affinity of Br. DH°(kJ)
K(s)→ K(g)89
K(g)→ K⁺(g)+ e⁻ 419
Br2(l)→ 2 Br(g)193
K(s)+ Br2(g)→ KBr(s)-394
Br2(g)→ KBr(s)-394
KBr(s)→ K⁺(g)+ Br⁻(g)674
A) -885 kJ
B) -325 kJ
C) +367 kJ
D) -464 kJ
E) +246 kJ
K(s)→ K(g)89
K(g)→ K⁺(g)+ e⁻ 419
Br2(l)→ 2 Br(g)193
K(s)+
 Br2(g)→ KBr(s)-394
Br2(g)→ KBr(s)-394KBr(s)→ K⁺(g)+ Br⁻(g)674
A) -885 kJ
B) -325 kJ
C) +367 kJ
D) -464 kJ
E) +246 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the heat of formation of KCl. DH°(kJ)
K(s)→ K(g)89
K(g)→ K⁺(g)+ e⁻ 418
Cl2(g)→ 2 Cl(g)244
Cl(g)+ e⁻ → Cl⁻(g)-349
KCl(s)→ K⁺(g)+ Cl⁻(g)717
A) -1119 kJ
B) -997 kJ
C) -437 kJ
D) +631 kJ
E) +158 kJ
K(s)→ K(g)89
K(g)→ K⁺(g)+ e⁻ 418
Cl2(g)→ 2 Cl(g)244
Cl(g)+ e⁻ → Cl⁻(g)-349
KCl(s)→ K⁺(g)+ Cl⁻(g)717
A) -1119 kJ
B) -997 kJ
C) -437 kJ
D) +631 kJ
E) +158 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following represents the Lewis structure for N?
A)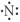
B)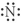
C)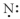
D)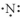
E)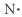
A)
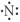
B)
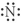
C)
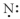
D)
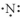
E)
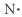

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) A covalent bond is formed through the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
B) A pair of electrons involved in a covalent bond is sometimes referred to as a "lone pair."
C) It is not possible for two atoms to share more than two electrons.
D) Single bonds are shorter than double bonds.
E) In a covalent bond, the shared electrons interact with the nuclei of both of the bonding atoms, thus lowering their potential energy.
A) A covalent bond is formed through the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
B) A pair of electrons involved in a covalent bond is sometimes referred to as a "lone pair."
C) It is not possible for two atoms to share more than two electrons.
D) Single bonds are shorter than double bonds.
E) In a covalent bond, the shared electrons interact with the nuclei of both of the bonding atoms, thus lowering their potential energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) An ionic bond is much stronger than most covalent bonds.
B) An ionic bond is formed through the sharing of electrons.
C) Ionic compounds at room temperature typically conduct electricity.
D) Once dissolved in water, ionic compounds rarely conduct electricity.
E) None of the above is true.
A) An ionic bond is much stronger than most covalent bonds.
B) An ionic bond is formed through the sharing of electrons.
C) Ionic compounds at room temperature typically conduct electricity.
D) Once dissolved in water, ionic compounds rarely conduct electricity.
E) None of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Use Lewis theory to determine the chemical formula for the compound formed between Al and O.
A) Al3O2
B) Al2O3
C) AlO2
D) Al2O
E) AlO
A) Al3O2
B) Al2O3
C) AlO2
D) Al2O
E) AlO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following represents the Lewis structure for Mg?
A)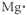
B)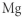
C)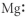
D)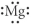
E)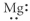
A)
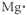
B)
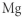
C)
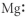
D)
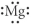
E)
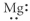

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Choose the best Lewis structure for SF4.
A)
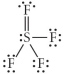
B)
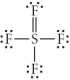
C)
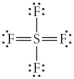
D)
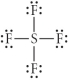
E)
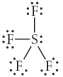
A)
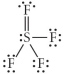
B)
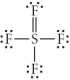
C)
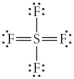
D)
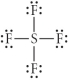
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Choose the best Lewis structure for SeO42⁻.
A)
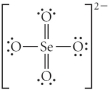
B)
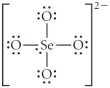
C)
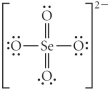
D)
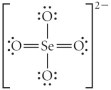
E)
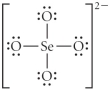
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Identify the shortest bond.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same length.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Choose the best Lewis structure for PO43⁻.
A)
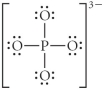
B)
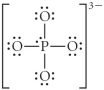
C)
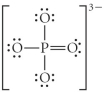
D)
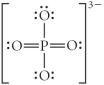
E)
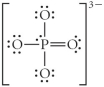
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)
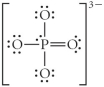

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Choose the best Lewis structure for OCl2.
A)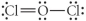
B)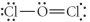
C)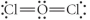
D)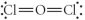
E)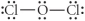
A)
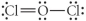
B)
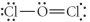
C)
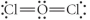
D)
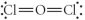
E)
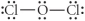

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Identify the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons in water.
A) 1 bonding pair and 1 lone pair
B) 1 bonding pair and 2 lone pairs
C) 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
D) 2 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair
E) 3 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
A) 1 bonding pair and 1 lone pair
B) 1 bonding pair and 2 lone pairs
C) 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
D) 2 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair
E) 3 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Define electronegativity.
A) the ability of an atom to repel neutrons in a chemical bond
B) the ability of an atom to repel electrons in a chemical bond
C) the ability of an atom to attract protons to itself in a chemical bond
D) the ability of an atom to attract neutrons to itself in a chemical bond
E) the ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a chemical bond
A) the ability of an atom to repel neutrons in a chemical bond
B) the ability of an atom to repel electrons in a chemical bond
C) the ability of an atom to attract protons to itself in a chemical bond
D) the ability of an atom to attract neutrons to itself in a chemical bond
E) the ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a chemical bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Choose the best Lewis structure for BeF2.
A)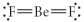
B)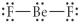
C)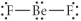
D)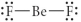
E)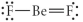
A)
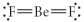
B)
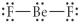
C)
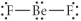
D)
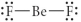
E)
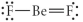

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Give the number of valence electrons for SO42-.
A) 32
B) 30
C) 34
D) 28
E) 36
A) 32
B) 30
C) 34
D) 28
E) 36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Give the number of valence electrons for ICl5.
A) 36
B) 40
C) 42
D) 44
E) 46
A) 36
B) 40
C) 42
D) 44
E) 46

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Choose the best Lewis structure for XeI2.
A)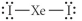
B)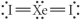
C)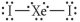
D)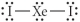
E)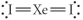
A)
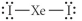
B)
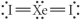
C)
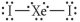
D)
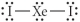
E)
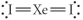

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Choose the best Lewis structure for ICl5.
A)
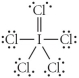
B)
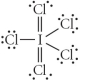
C)
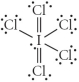
D)
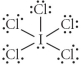
E)
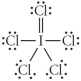
A)
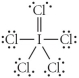
B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Give the number of valence electrons for XeI2.
A) 22
B) 20
C) 18
D) 24
E) 16
A) 22
B) 20
C) 18
D) 24
E) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Choose the best Lewis structure for SO42⁻.
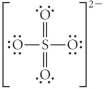
A)
B)
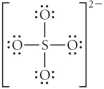
C)
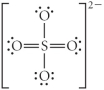
D)
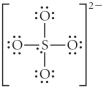
E)
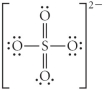
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Identify the strongest bond.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same strength.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same strength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Choose the best Lewis structure for NO3⁻.
A)
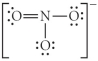
B)
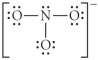
C)
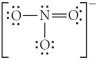
D)
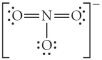
E)
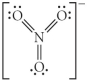
A)
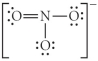
B)
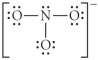
C)
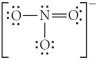
D)
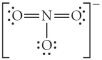
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Identify the weakest bond.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same strength.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same strength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Choose the best Lewis structure for CH2Cl2.
A)
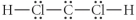
B)
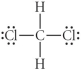
C)
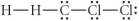
D)
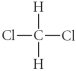
E)
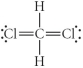
A)
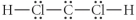
B)

C)
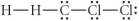
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Using periodic trends,place the following bonds in order of increasing ionic character. Si-P Si-Cl Si-S
A) Si-P < Si-Cl < Si-S
B) Si-P < Si-S < Si-Cl
C) Si-S < Si-Cl < Si-P
D) Si-Cl < Si-P < Si-S
E) Si-Cl < Si-S < Si-P
A) Si-P < Si-Cl < Si-S
B) Si-P < Si-S < Si-Cl
C) Si-S < Si-Cl < Si-P
D) Si-Cl < Si-P < Si-S
E) Si-Cl < Si-S < Si-P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Choose the best Lewis structure for BF3.
A)
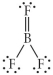
B)
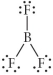
C)
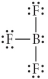
D)
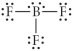
E)
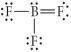
A)
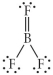
B)

C)
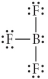
D)
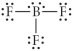
E)
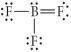

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Draw the Lewis structure for CO32- including any valid resonance structures.Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) The CO32- ion contains one C-O single bond and two C O double bonds.
O double bonds.
B) The CO32- ion contains two C-O single bonds and one C O double bond.
O double bond.
C) The CO32- ion contains three C-O double bonds.
D) The CO32- ion contains two C-O single bonds and one C O triple bond.
O triple bond.
E) None of the above is true.
A) The CO32- ion contains one C-O single bond and two C
 O double bonds.
O double bonds.B) The CO32- ion contains two C-O single bonds and one C
 O double bond.
O double bond.C) The CO32- ion contains three C-O double bonds.
D) The CO32- ion contains two C-O single bonds and one C
 O triple bond.
O triple bond.E) None of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Place the following in order of decreasing bond length. H-F H-I H-Br
A) H-F > H-Br > H-I
B) H-I > H-F > H-Br
C) H-I > H-Br > H-F
D) H-Br > H-F > H-I
E) H-F > H-I > H-Br
A) H-F > H-Br > H-I
B) H-I > H-F > H-Br
C) H-I > H-Br > H-F
D) H-Br > H-F > H-I
E) H-F > H-I > H-Br

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Rank the following molecules in decreasing bond energy. Cl2 Br2 F2 I2
A) I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
B) Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2
C) I2 > Cl2 > Br2 > F2
D) Cl2 > I2 > F2 > Br2
A) I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
B) Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2
C) I2 > Cl2 > Br2 > F2
D) Cl2 > I2 > F2 > Br2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Draw the best Lewis structure for Cl3⁻.What is the formal charge on the central Cl atom?
A) -1
B) 0
C) +1
D) +2
E) -2
A) -1
B) 0
C) +1
D) +2
E) -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Place the following in order of increasing bond length. C-O C-C C-N
A) C-C < C-N < C-O
B) C-N < C-O < C-C
C) C-O < C-C < C-N
D) C-O < C-N < C-C
E) C-C < C-O < C-N
A) C-C < C-N < C-O
B) C-N < C-O < C-C
C) C-O < C-C < C-N
D) C-O < C-N < C-C
E) C-C < C-O < C-N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which compound has the shortest carbon-carbon bond length?
A) CH3CH3
B) CH2CH2
C) HCCH
D) All bond lengths are the same.
A) CH3CH3
B) CH2CH2
C) HCCH
D) All bond lengths are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Using Lewis structures and formal charge,which of the following ions is most stable,? OCN⁻ ONC⁻ NOC⁻
A) OCN⁻
B) ONC⁻
C) NOC⁻
D) None of these ions are stable according to Lewis theory.
E) All of these compounds are equally stable according to Lewis theory.
A) OCN⁻
B) ONC⁻
C) NOC⁻
D) None of these ions are stable according to Lewis theory.
E) All of these compounds are equally stable according to Lewis theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following resonance structures for OCN⁻ will contribute most to the correct structure of OCN⁻?
A) O C
C
 N, with two lone pairs on O and two lone pairs on N
N, with two lone pairs on O and two lone pairs on N
B) O C-N, with one lone pair on O and three lone pairs on N
C-N, with one lone pair on O and three lone pairs on N
C) O C
C
 N, with one lone pair on O, two lone pairs on C, and one lone pair on N
N, with one lone pair on O, two lone pairs on C, and one lone pair on N
D) O-C N, with three lone pairs on O and one lone pair on N
N, with three lone pairs on O and one lone pair on N
E) They all contribute equally to the correct structure of OCN⁻.
A) O
 C
C N, with two lone pairs on O and two lone pairs on N
N, with two lone pairs on O and two lone pairs on NB) O
 C-N, with one lone pair on O and three lone pairs on N
C-N, with one lone pair on O and three lone pairs on NC) O
 C
C N, with one lone pair on O, two lone pairs on C, and one lone pair on N
N, with one lone pair on O, two lone pairs on C, and one lone pair on ND) O-C
 N, with three lone pairs on O and one lone pair on N
N, with three lone pairs on O and one lone pair on NE) They all contribute equally to the correct structure of OCN⁻.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Choose the best Lewis structure for NH4⁺.
A)
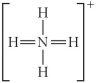
B)
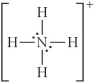
C)
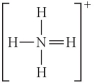
D)
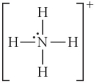
E)
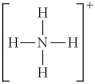
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Identify the bond with the highest bond energy.
A) Si=O
B) N=N
C) C=C
D) C=N
E) O=O
A) Si=O
B) N=N
C) C=C
D) C=N
E) O=O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Define bond energy.
A) energy required to form 1 mole of the bond in the solid phase
B) energy required to form 1 mole of the bond in the gas phase
C) energy required to break 1 mole of the bond in the liquid phase
D) energy required to break 1 mole of the bond in the gas phase
E) energy required to break 1 mole of the bond in the solid phase
A) energy required to form 1 mole of the bond in the solid phase
B) energy required to form 1 mole of the bond in the gas phase
C) energy required to break 1 mole of the bond in the liquid phase
D) energy required to break 1 mole of the bond in the gas phase
E) energy required to break 1 mole of the bond in the solid phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Place the following in order of decreasing XO bond length,where "X" represents the central atom in each of the following compounds or ions. SiO32⁻ CO2 CO32⁻
A) CO2 > SiO32⁻ > CO32⁻
B) CO2 > CO32⁻ > SiO32⁻
C) CO32⁻ > CO2 > SiO32⁻
D) CO32⁻ > SiO32⁻ > CO2
E) SiO32⁻ > CO32⁻ > CO2
A) CO2 > SiO32⁻ > CO32⁻
B) CO2 > CO32⁻ > SiO32⁻
C) CO32⁻ > CO2 > SiO32⁻
D) CO32⁻ > SiO32⁻ > CO2
E) SiO32⁻ > CO32⁻ > CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Lewis structure of sulfuric acid contains
A) 2 double bonds, 4 single bonds, and 8 lone pairs.
B) 4 double bonds, and two single bonds.
C) 2 double bonds and 4 single bonds.
D) 6 single bonds and 4 lone pairs.
E) 2 double bonds, 4 single bonds, and 4 lone pairs.
A) 2 double bonds, 4 single bonds, and 8 lone pairs.
B) 4 double bonds, and two single bonds.
C) 2 double bonds and 4 single bonds.
D) 6 single bonds and 4 lone pairs.
E) 2 double bonds, 4 single bonds, and 4 lone pairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which compound has the highest carbon-carbon bond strength?
A) CH3CH3
B) CH2CH2
C) HCCH
D) All bond strengths are the same.
A) CH3CH3
B) CH2CH2
C) HCCH
D) All bond strengths are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How many electrons does an hydroxyl radical contain?
A) 7 electrons
B) 6 electrons
C) 8 electrons
D) 9 electrons
E) 5 electrons
A) 7 electrons
B) 6 electrons
C) 8 electrons
D) 9 electrons
E) 5 electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Place the following in order of increasing bond length. NO2⁻ NO3⁻ NO
A) NO < NO2⁻ < NO3⁻
B) NO2⁻ < NO3⁻ < NO
C) NO3⁻ < NO < NO2⁻
D) NO < NO3⁻ < NO2⁻
E) NO3⁻ < NO2⁻ < NO
A) NO < NO2⁻ < NO3⁻
B) NO2⁻ < NO3⁻ < NO
C) NO3⁻ < NO < NO2⁻
D) NO < NO3⁻ < NO2⁻
E) NO3⁻ < NO2⁻ < NO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Draw the Lewis structure for NO2⁻ including any valid resonance structures.Describe the resonance hybrid of the nitrite ion.
A) The nitrite ion contains one N-O single bond and one N O double bond.
O double bond.
B) The nitrite ion contains two N-O bonds that are equivalent to 1 bonds.
bonds.
C) The nitrite ion contains two N O double bonds.
O double bonds.
D) The nitrite ion contains two N-O single bonds.
E) None of the above is true.
A) The nitrite ion contains one N-O single bond and one N
 O double bond.
O double bond.B) The nitrite ion contains two N-O bonds that are equivalent to 1
 bonds.
bonds.C) The nitrite ion contains two N
 O double bonds.
O double bonds.D) The nitrite ion contains two N-O single bonds.
E) None of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A reaction is exothermic when
A) weak bonds break and strong bonds form.
B) strong bonds break and weak bonds form.
C) weak bonds break and weak bonds form.
D) strong bonds break and strong bonds form.
A) weak bonds break and strong bonds form.
B) strong bonds break and weak bonds form.
C) weak bonds break and weak bonds form.
D) strong bonds break and strong bonds form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Draw the Lewis structure for SO42⁻.How many equivalent resonance structures can be drawn?
A) 6
B) 2
C) 4
D) 3
E) 8
A) 6
B) 2
C) 4
D) 3
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which compound has the longest carbon-carbon bond length?
A) CH3CH3
B) CH2CH2
C) HCCH
D) All bond lengths are the same.
A) CH3CH3
B) CH2CH2
C) HCCH
D) All bond lengths are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Identify the compound with ionic bonding.
A) LiBr
B) Na
C) H2O
D) Ne
E) O
A) LiBr
B) Na
C) H2O
D) Ne
E) O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Identify the compound with covalent bonding.
A) KBr
B) K
C) H2Se
D) Ne
E) O
A) KBr
B) K
C) H2Se
D) Ne
E) O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Identify the property of metals that is NOT explained by the electron sea model.
A) metals conduct heat
B) metals conduct electricity
C) malleability of metals
D) most metals are liquids
E) ductility of metals
A) metals conduct heat
B) metals conduct electricity
C) malleability of metals
D) most metals are liquids
E) ductility of metals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the bond energies provided to estimate ΔH°rxn for the reaction below. CH3OH(l)+ 2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)ΔH°rxn = ?
Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
C-H 414
C-O 360
C=O 799
O=O 498
O-H 464
A) +473 kJ
B) -91 kJ
C) -486 kJ
D) -392 kJ
E) +206 kJ
Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
C-H 414
C-O 360
C=O 799
O=O 498
O-H 464
A) +473 kJ
B) -91 kJ
C) -486 kJ
D) -392 kJ
E) +206 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use Lewis theory to determine the chemical formula for the compound formed between Li and S.
A) LiS
B) LiS2
C) Li2S
D) Li2S3
E) Li3S2
A) LiS
B) LiS2
C) Li2S
D) Li2S3
E) Li3S2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the bond energies provided to estimate ΔH°rxn for the reaction below. XeF2 + 2 F2 → XeF6 ΔH°rxn = ?
Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
Xe-F 147
F-F 159
A) -429 kJ
B) +159 kJ
C) -660 kJ
D) +176 kJ
E) -270 kJ
Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
Xe-F 147
F-F 159
A) -429 kJ
B) +159 kJ
C) -660 kJ
D) +176 kJ
E) -270 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Identify the bond with the lowest bond energy.
A) Si=O
B) N=N
C) C=C
D) C=N
E) O=O
A) Si=O
B) N=N
C) C=C
D) C=N
E) O=O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use Lewis theory to determine the chemical formula for the compound formed between Al and F.
A) Al3F2
B) Al2F3
C) AlF2
D) AlF
E) AlF3
A) Al3F2
B) Al2F3
C) AlF2
D) AlF
E) AlF3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Identify an ionic bond.
A) Electrons are pooled.
B) Electrons are shared.
C) Electrons are transferred.
D) Neutrons are gained.
E) Electrons are lost.
A) Electrons are pooled.
B) Electrons are shared.
C) Electrons are transferred.
D) Neutrons are gained.
E) Electrons are lost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Identify the compound with metallic bonding.
A) LiI
B) Na
C) H2O
D) He
E) S
A) LiI
B) Na
C) H2O
D) He
E) S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Ozone absorbs
A) infrared light entering Earth's atmosphere.
B) ultraviolet light exiting Earth's atmosphere.
C) ultraviolet light entering Earth's atmosphere.
D) visible light entering Earth's atmosphere.
E) infrared light exiting Earth's atmosphere.
A) infrared light entering Earth's atmosphere.
B) ultraviolet light exiting Earth's atmosphere.
C) ultraviolet light entering Earth's atmosphere.
D) visible light entering Earth's atmosphere.
E) infrared light exiting Earth's atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use Lewis theory to determine the chemical formula for the compound formed between Ba and F.
A) BaF
B) Ba2F3
C) Ba3F2
D) BaF2
E) Ba2F
A) BaF
B) Ba2F3
C) Ba3F2
D) BaF2
E) Ba2F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the bond energies provided to estimate ΔH°rxn for the reaction below. C2H4(g)+ H2(g)→ C2H6(g)ΔH°rxn = ?
Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
C-C 347
C-H 414
C=C 611
C≡C 837
H-H 436
A) -128 kJ
B) +98 kJ
C) +700 kJ
D) -102 kJ
E) -166 kJ
Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
C-C 347
C-H 414
C=C 611
C≡C 837
H-H 436
A) -128 kJ
B) +98 kJ
C) +700 kJ
D) -102 kJ
E) -166 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Identify the bond with the highest bond energy.
A) C≡O
B) C≡C
C) C≡N
D) N≡N
A) C≡O
B) C≡C
C) C≡N
D) N≡N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use Lewis theory to determine the chemical formula for the compound formed between Sr and N.
A) SrN
B) Sr3N2
C) SrN2
D) Sr2N
E) Sr2N3
A) SrN
B) Sr3N2
C) SrN2
D) Sr2N
E) Sr2N3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the bond energies provided to estimate ΔH°rxn for the reaction below. PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)→ PCl5(l)ΔH°rxn = ?
Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
Cl-Cl 243
P-Cl 331
A) -243 kJ
B) -419 kJ
C) -662 kJ
D) -67 kJ
E) -905 kJ
Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
Cl-Cl 243
P-Cl 331
A) -243 kJ
B) -419 kJ
C) -662 kJ
D) -67 kJ
E) -905 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the bond energies provided to estimate ΔH°rxn for the reaction below. 2 Br2(l)+ C2H2(g)→ C2H2Br4(l)ΔH°rxn = ?
Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
Br-Br 193
C≡C 837
C-C 347
C-Br 276
C-H 414
A) +407 kJ
B) -324 kJ
C) -228 kJ
D) +573 kJ
E) -648 kJ
Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
Br-Br 193
C≡C 837
C-C 347
C-Br 276
C-H 414
A) +407 kJ
B) -324 kJ
C) -228 kJ
D) +573 kJ
E) -648 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Identify the bond with the highest bond energy.
A) C≡O
B) C≡C
C) C≡N
D) N≡N
A) C≡O
B) C≡C
C) C≡N
D) N≡N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Identify the substance that conducts electricity.
A) KBr dissolved in water
B) solid KBr
C) rubbing alcohol
D) solid baking soda
E) sugar dissolved in water.
A) KBr dissolved in water
B) solid KBr
C) rubbing alcohol
D) solid baking soda
E) sugar dissolved in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Identify the chemical formula for ozone.
A) O3
B) O2
C) O
D) O2-
E) O-
A) O3
B) O2
C) O
D) O2-
E) O-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



