Deck 18: Principles of Reactivity: Other Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/88
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Principles of Reactivity: Other Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria
1
What is the pH of the buffer that results when 32 g sodium acetate (NaCH3CO2)is mixed with 500.0 mL of 1.0 M acetic acid (CH3CO2H)and diluted with water to 1.0 L? (Ka of CH3CO2H = 1.8 10-5)
A) 2.52
B) 4.23
C) 4.44
D) 4.64
E) 4.74
A) 2.52
B) 4.23
C) 4.44
D) 4.64
E) 4.74
4.64
2
All of the following statements concerning acid-base buffers are true EXCEPT
A) buffers are resistant to pH changes upon addition of small quantities of strong acids or bases.
B) buffers are used as colored indicators in acid-base titrations.
C) the pH of a buffer is close to the pKa of the weak acid from which it is made.
D) buffers contain appreciable quantities of a weak acid and its conjugate base.
E) buffers are resistant to changes in pH when diluted with water.
A) buffers are resistant to pH changes upon addition of small quantities of strong acids or bases.
B) buffers are used as colored indicators in acid-base titrations.
C) the pH of a buffer is close to the pKa of the weak acid from which it is made.
D) buffers contain appreciable quantities of a weak acid and its conjugate base.
E) buffers are resistant to changes in pH when diluted with water.
buffers are used as colored indicators in acid-base titrations.
3
What is the pH of a solution made by combining 175 mL of 0.33 M NaC2H3O2 with 126 mL of 0.48 M HC2H3O2? The Ka of acetic acid is 1.75 10-5.
A) 4.74
B) 4.78
C) 5.79
D) 4.69
E) 5.24
A) 4.74
B) 4.78
C) 5.79
D) 4.69
E) 5.24
4.74
4
What is the pH of a buffer that results when 0.50 mole of H3PO4 is mixed with 0.25 mole of NaOH and diluted with water to 1.00 L? (The acid dissociation constants of phosphoric acid are Ka1 = 7.5 10-3,Ka2 = 6.2 10-8,and Ka3 = 3.6 10-13)
A) 1.82
B) 2.12
C) 6.91
D) 7.21
E) 12.44
A) 1.82
B) 2.12
C) 6.91
D) 7.21
E) 12.44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If 30 mL of 0.10 M NaOH is added to 40 mL of 0.20 M HC2H3O2,what is the pH of the resulting solution at 25°C? Ka for HC2H3O2 is 1.8 10-5 at 25°C.
A) 10.4
B) 4.3
C) 5.0
D) 2.7
E) 4.5
A) 10.4
B) 4.3
C) 5.0
D) 2.7
E) 4.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following combinations would be best to buffer an aqueous solution at a pH of 9.04?
A) H3PO4 and H2PO4-,Ka1 = 7.5 10-3
B) HNO2 and NO2-,Ka = 4.5 10-4
C) CH3CO2H and CH3COO-,Ka = 1.8 10-5
D) H2PO4- and HPO42-,Ka2 = 6.2 10-8
E) NH4+ and NH3,Ka = 5.7 10-10
A) H3PO4 and H2PO4-,Ka1 = 7.5 10-3
B) HNO2 and NO2-,Ka = 4.5 10-4
C) CH3CO2H and CH3COO-,Ka = 1.8 10-5
D) H2PO4- and HPO42-,Ka2 = 6.2 10-8
E) NH4+ and NH3,Ka = 5.7 10-10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Calculate the pH of a solution made by mixing 100.0 mL of 0.635 M NH3 with 100.0 mL of 0.100 M HCl.(Kb for NH3 = 1.8 10-5)
A) 9.98
B) 4.02
C) 8.53
D) 9.26
E) none of these
A) 9.98
B) 4.02
C) 8.53
D) 9.26
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the pH of a buffer composed of 0.35 M H2PO4-(aq)and 0.65 M HPO42-(aq)? (Ka of H2PO4- is 6.2 10-8)
A) 6.94
B) 7.21
C) 7.48
D) 7.73
E) 9.06
A) 6.94
B) 7.21
C) 7.48
D) 7.73
E) 9.06

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A 1.0-liter solution contains 0.25 M HF and 0.32 M NaF (Ka for HF is 7.2 10-4).If one adds 0.30 liters of 0.020 M KOH to the solution,what will be the in pH?
A) 0.02
B) 3.27
C) 0.13
D) -0.11
E) -0.28
A) 0.02
B) 3.27
C) 0.13
D) -0.11
E) -0.28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following mathematical expressions is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
A)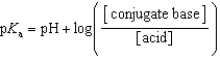
B)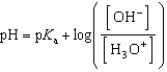
C)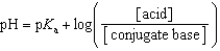
D)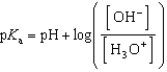
E)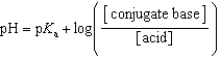
A)
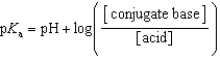
B)
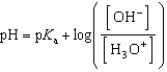
C)
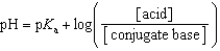
D)
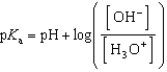
E)
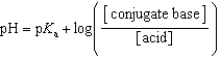

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When mixed in appropriate amounts,each of the following mixtures can produce an effective buffer solution EXCEPT
A) HCl and NaH2PO4
B) Na2HPO4 and Na3PO4.
C) NaHCO3 and Na2CO3.
D) NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4.
E) NaOH and NaF.
A) HCl and NaH2PO4
B) Na2HPO4 and Na3PO4.
C) NaHCO3 and Na2CO3.
D) NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4.
E) NaOH and NaF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the solution pH when 0.10 mol of H+ is added to a 2.0-liter buffered solution created from 0.45 M NH3 (Kb = 1.8 10-5)and 0.26 M NH4F.
A) 8.07
B) 4.63
C) 9.37
D) 10.34
E) 4.85
A) 8.07
B) 4.63
C) 9.37
D) 10.34
E) 4.85

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If 20 mL of 0.10 M NaOH is added to 35 mL of 0.20 M HC2H3O2,what is the pH of the resulting solution at 25°C? Ka for HC2H3O2 is 1.8 10-5 at 25°C.
A) 10.0
B) 4.2
C) 5.1
D) 2.7
E) 4.3
A) 10.0
B) 4.2
C) 5.1
D) 2.7
E) 4.3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A certain weak base B has a base-ionization constant Kb of 7.3 10-4 at 25°C.If strong acid is added to a solution of B,at what pH will [B] = [BH+]?
A) 8.5
B) 10.9
C) 7.0
D) 3.1
E) 5.5
A) 8.5
B) 10.9
C) 7.0
D) 3.1
E) 5.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the pH of the buffer that results when 12.0 g of NaH2PO4 and 8.00 g of Na2HPO4 are diluted with water to a volume of 0.50 L? (Ka of H2PO4- = 6.2 10-8,the molar masses of NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4 are 120.0 g/mol and 142.0 mol,respectively)
A) 4.10
B) 6.96
C) 7.21
D) 7.46
E) 9.90
A) 4.10
B) 6.96
C) 7.21
D) 7.46
E) 9.90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the pH of an aqueous solution composed of 0.64 M NH4+ and 0.20 M NH3? (Ka of NH4+ = 5.6 10-10)
A) 4.80
B) 8.75
C) 9.20
D) 9.25
E) 9.76
A) 4.80
B) 8.75
C) 9.20
D) 9.25
E) 9.76

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the pH of a solution that is 0.028 M in HA and also 0.0054 M in NaA? (Ka = 3.2 10-6)
A) 8.21
B) 4.78
C) 6.21
D) 5.49
E) 7.22
A) 8.21
B) 4.78
C) 6.21
D) 5.49
E) 7.22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An acid-base equilibrium system is created by dissolving 0.50 mol CH3CO2H in water to a volume of 1.0 L.What is the effect of adding 0.50 mol CH3CO2-(aq)to this solution?
1)The pH of the solution will equal 7.00 because equal concentrations of a weak acid and its conjugate base are present.
2)Some CH3CO2H(aq)will ionize,increasing the concentration of CH3CO2-(aq)and increasing the pH.
3)Some CH3CO2-(aq)will react with H3O+,increasing the concentration of CH3CO2H(aq)and reestablishing the solution equilibrium.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3
1)The pH of the solution will equal 7.00 because equal concentrations of a weak acid and its conjugate base are present.
2)Some CH3CO2H(aq)will ionize,increasing the concentration of CH3CO2-(aq)and increasing the pH.
3)Some CH3CO2-(aq)will react with H3O+,increasing the concentration of CH3CO2H(aq)and reestablishing the solution equilibrium.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the effect of adding NaOH(aq)to an aqueous solution of ammonia?
1)The pH of the solution will increase.
2)The concentration of NH4+(aq)will decrease.
3)The concentration of NH3(aq)will increase.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3
1)The pH of the solution will increase.
2)The concentration of NH4+(aq)will decrease.
3)The concentration of NH3(aq)will increase.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A 1.0-liter solution contains 0.25 M HF and 0.41 M NaF (Ka for HF is 7.2 10-4).What is the pH of this solution?
A) 3.14
B) 3.36
C) 2.93
D) 0.21
E) 10.64
A) 3.14
B) 3.36
C) 2.93
D) 0.21
E) 10.64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If 25 mL of 0.750 M HCl are added to 100.mL of 0.392 M NaOH,what is the final pH?
A) 13.21
B) 0.79
C) 13.50
D) 0.50
E) 7.00
A) 13.21
B) 0.79
C) 13.50
D) 0.50
E) 7.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 50.00-mL solution of 0.0797 M ammonia (Kb = 1.8 10-5)is titrated with a 0.0315 M solution of hydrochloric acid as the titrant.What is the pH of the base solution after 23.88 mL of titrant have been added? (Kw = 1.00 10-14)
A) 11.08
B) 9.88
C) 4.12
D) 4.74
E) 12.90
A) 11.08
B) 9.88
C) 4.12
D) 4.74
E) 12.90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What mass of solid NaCH3CO2 (molar mass = 82.0 g/mol)should be added to 1.0 L of 0.50 M CH3CO2H to make a buffer with a pH of 7.21? (pKa of CH3CO2H = 7.21)
A) 0.0 g
B) 1.9 g
C) 41 g
D) 71 g
E) 1.6 102 g
A) 0.0 g
B) 1.9 g
C) 41 g
D) 71 g
E) 1.6 102 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A 50.0 mL sample of 0.155 M HNO2(aq)is titrated with 0.100 M NaOH(aq).What is the pH of a solution after the addition of 25.0 mL of NaOH? (Ka of HNO2 = 4.5 10-4)
A) 3.02
B) 3.22
C) 3.67
D) 3.86
E) 4.05
A) 3.02
B) 3.22
C) 3.67
D) 3.86
E) 4.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
You have 75.0 mL of 0.11 M HA.After adding 30.0 mL of 0.10 M NaOH,the pH is 5.50.What is the Ka value of HA?
A) 3.2 10-6
B) 1.8 10-6
C) 0.57
D) 1.1 10-6
E) none of these
A) 3.2 10-6
B) 1.8 10-6
C) 0.57
D) 1.1 10-6
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What molar ratio of acetic acid to sodium acetate is required to create a buffer solution having a pH of 4.89 at 25°C? Ka for HC2H3O2 is 1.8 10-5.
A) 0.72
B) 1.4
C) 0.56
D) 2.0
E) 2.9
A) 0.72
B) 1.4
C) 0.56
D) 2.0
E) 2.9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If 0.50 L of a buffer containing 1.0 mol H2PO4- and 1.0 mol HPO42- is diluted to a volume of 5.0 L,the pH
A) increases by 1.
B) decreases by 1.
C) increases by 10.
D) decreases by 10.
E) remains unchanged.
A) increases by 1.
B) decreases by 1.
C) increases by 10.
D) decreases by 10.
E) remains unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the ratio of acid to base in a buffer increases by a factor of 10,the pH of the buffer
A) increases by 1.
B) decreases by 1.
C) increases by 10.
D) decreases by 10.
E) remains unchanged.
A) increases by 1.
B) decreases by 1.
C) increases by 10.
D) decreases by 10.
E) remains unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the pH of a buffer that results when 0.40 mol NaHCO2 is mixed with 100.0 mL of 2.00 M HCl(aq)and diluted with water to 250 mL? (Ka of HCO2H = 1.8 10-4)
A) (-0.301)
B) 3.05
C) 3.44
D) 3.74
E) 4.05
A) (-0.301)
B) 3.05
C) 3.44
D) 3.74
E) 4.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which acid-base combination is depicted by this titration curve? The dot on the curve is located at the titrant volume where the titration solution pH equals 7. 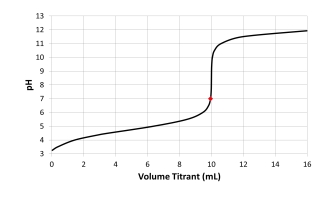
A) Titration of a weak acid with a strong base.
B) Titration of a strong acid with a strong base.
C) Titration of a weak base with a strong acid.
D) Titration of a strong base with a strong acid.
E) Not enough information provided.

A) Titration of a weak acid with a strong base.
B) Titration of a strong acid with a strong base.
C) Titration of a weak base with a strong acid.
D) Titration of a strong base with a strong acid.
E) Not enough information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A volume of 25.0 mL of 0.100 M C6H5CO2H(aq)is titrated with 0.100 M NaOH(aq).What is the pH after the addition of 12.5 mL of NaOH? (Ka of benzoic acid = 6.3 10-5)
A) 2.60
B) 4.20
C) 5.40
D) 7.00
E) 8.60
A) 2.60
B) 4.20
C) 5.40
D) 7.00
E) 8.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A buffer is composed of 0.400 mol H2PO4- and 0.400 mol HPO42- diluted with water to a volume of 1.00 L.The pH of the buffer is 7.210.How many moles of HCl must be added to decrease the pH to 6.210?
A) 0.200 mol
B) 0.327 mol
C) 0.360 mol
D) 0.400 mol
E) 3.60 mol
A) 0.200 mol
B) 0.327 mol
C) 0.360 mol
D) 0.400 mol
E) 3.60 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A 50.00-mL solution of 0.0350 M quinoline (Kb = 8.0 10-10)is titrated with a 0.0137 M solution of hydrochloric acid as the titrant.What is the pH at the equivalence point? (Kw = 1.0 10-14)
A) 4.90
B) 3.45
C) 5.55
D) 9.10
E) 10.55
A) 4.90
B) 3.45
C) 5.55
D) 9.10
E) 10.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What mass of sodium hydroxide must be added to 40.0 mL of 0.607 M acetic acid in order to create a buffer with a pH of 4.66? Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 10-5.
A) 33 g
B) 0.44 g
C) 1.0 g
D) 0.000035 g
E) 0.97 g
A) 33 g
B) 0.44 g
C) 1.0 g
D) 0.000035 g
E) 0.97 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How many moles of solid NaF would have to be added to 1.0 L of 2.39 M HF solution to achieve a buffer of pH 3.35? Assume there is no volume change.(Ka for HF = 7.2 10-4)
A) 3.9
B) 0.50
C) 0.67
D) 1.0
E) 1.6
A) 3.9
B) 0.50
C) 0.67
D) 1.0
E) 1.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A buffer contains 0.50 mol NH4+ and 0.50 mol NH3 diluted with water to 1.0 L.How many moles of NaOH are required to increase the pH of the buffer to 10.00? (pKa of NH4+ = 9.25)
A) 0.035 mol
B) 0.15 mol
C) 0.35 mol
D) 0.41 mol
E) 2.8 mol
A) 0.035 mol
B) 0.15 mol
C) 0.35 mol
D) 0.41 mol
E) 2.8 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the pH of a buffer that results when 0.50 mole of H3PO4 is mixed with 0.75 mole of NaOH and diluted with water to 1.00 L? (The acid dissociation constants of phosphoric acid are Ka1 = 7.5 10-3,Ka2 = 6.2 10-8,and Ka3 = 3.6 10-13)
A) 1.82
B) 2.12
C) 6.91
D) 7.21
E) 12.44
A) 1.82
B) 2.12
C) 6.91
D) 7.21
E) 12.44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How many moles of HCl must be added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M NH3(aq)to make a buffer with a pH of 9.00? (pKa of NH4+ = 9.25)
A) 0.36 mol
B) 0.44 mol
C) 0.56 mol
D) 0.64 mol
E) 1.8 mol
A) 0.36 mol
B) 0.44 mol
C) 0.56 mol
D) 0.64 mol
E) 1.8 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When a weak base is titrated with a strong acid,the pH at the equivalence point is ___.
A) equal to 7
B) greater than 7.
C) less than 7.
D) equal to the acid pKa.
E) equal to the base pKb.
A) equal to 7
B) greater than 7.
C) less than 7.
D) equal to the acid pKa.
E) equal to the base pKb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following conditions is/are met at the equivalence point of the titration of a monoprotic weak base with a strong acid?
1)The moles of acid added from the buret equals the initial moles of weak base.
2)The volume of acid added from the buret must equal the volume of base titrated.
3)The pH of the solution is less than 7.00.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 3
1)The moles of acid added from the buret equals the initial moles of weak base.
2)The volume of acid added from the buret must equal the volume of base titrated.
3)The pH of the solution is less than 7.00.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The solubility of copper(II)oxalate is 3.2 10-3 g/L.What is the solubility product constant for copper(II)oxalate?
A) 4.4 10-10
B) 2.1 10-5
C) 1.0 10-5
D) 3.1 10-18
E) 3.7 10-14
A) 4.4 10-10
B) 2.1 10-5
C) 1.0 10-5
D) 3.1 10-18
E) 3.7 10-14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Titration of 0.5083 g of an unknown monoprotic acid dissolved in 25.00 mL of water requires 36.95 mL of 0.1067 M NaOH to reach the endpoint.What is the molar mass of the acid?
A) 128.9 g/mol
B) 0.007756 g/mol
C) 190.6 g/mol
D) 1.468 g/mol
E) 2.718 g/mol
A) 128.9 g/mol
B) 0.007756 g/mol
C) 190.6 g/mol
D) 1.468 g/mol
E) 2.718 g/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the pH of a saturated solution of Fe(OH)2? For Fe(OH)2,Ksp = 8.0 10-16 and Kw = 1.01 10-14.
A) 4.93
B) 8.77
C) 5.23
D) 9.07
E) 7.00
A) 4.93
B) 8.77
C) 5.23
D) 9.07
E) 7.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The Ksp of Ca(OH)2 is 5.5 10-5 at 25 C.What is the concentration of OH-(aq)in a saturated solution of Ca(OH)2(aq)?
A) 1.9 10-3 M
B) 7.4 10-3 M
C) 2.4 10-2 M
D) 4.0 10-2 M
E) 4.8 10-2 M
A) 1.9 10-3 M
B) 7.4 10-3 M
C) 2.4 10-2 M
D) 4.0 10-2 M
E) 4.8 10-2 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A 25.0 mL sample of 0.200 M HCO2H(aq)is titrated with 0.100 M KOH(aq).What is the pH at the equivalence point? (Ka of HCO2H = 1.8 10-4)
A) 5.71
B) 7.00
C) 8.28
D) 8.52
E) 10.26
A) 5.71
B) 7.00
C) 8.28
D) 8.52
E) 10.26

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The concentration of magnesium carbonate in a saturated aqueous solution at 25°C is 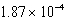 M.What is the Ksp of this sparingly soluble salt?
M.What is the Ksp of this sparingly soluble salt?
A)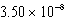
B)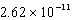
C)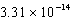
D)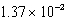
E)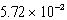
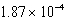 M.What is the Ksp of this sparingly soluble salt?
M.What is the Ksp of this sparingly soluble salt?A)
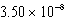
B)
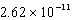
C)
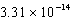
D)
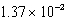
E)
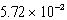

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A 50.00-mL solution of 0.0729 M chloroacetic acid (Ka = 1.4 10-3)is titrated with a 0.0181 M solution of NaOH as the titrant.What is the pH of at the equivalence point? (Kw = 1.00 10-14)
A) 7.51
B) 11.65
C) 6.49
D) 11.15
E) 2.85
A) 7.51
B) 11.65
C) 6.49
D) 11.15
E) 2.85

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The hydroxide ion concentration of a saturated solution of Cu(OH)2 is 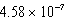 M.What is the solubility product constant for Cu(OH)2?
M.What is the solubility product constant for Cu(OH)2?
A)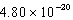
B)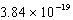
C)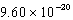
D)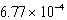
E)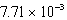
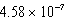 M.What is the solubility product constant for Cu(OH)2?
M.What is the solubility product constant for Cu(OH)2?A)
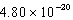
B)
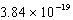
C)
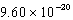
D)
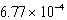
E)
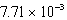

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following indicators is most suitable for the titration of a 25.00-mL sample of 0.140 M propionic acid,HC3H5O2,with strong base?
A) alizarin yellow (transition pH range: 10.0-12.0)
B) methyl red (transition pH range: 4.2-6.3)
C) methyl orange (transition pH range: 3.1-4.4)
D) thymol blue (transition pH range: 8.0-9.6)
E) bromothymol blue (transition pH range: 6.2-7.6)
A) alizarin yellow (transition pH range: 10.0-12.0)
B) methyl red (transition pH range: 4.2-6.3)
C) methyl orange (transition pH range: 3.1-4.4)
D) thymol blue (transition pH range: 8.0-9.6)
E) bromothymol blue (transition pH range: 6.2-7.6)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An impure sample of sodium carbonate,Na2CO3,is titrated with 0.113 M HCl according to the reaction below.
2 HCl(aq)+ Na2CO3(aq)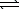 CO2(g)+ H2O(
CO2(g)+ H2O( 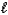 )+ 2 NaCl(aq)
)+ 2 NaCl(aq)
What is the percent of Na2CO3 in a 0.613 g sample if the titration requires 26.14 mL of HCl? The molar mass of Na2CO3 is 106.0 g/mol.
A) 0.295%
B) 15.7%
C) 25.5%
D) 51.1%
E) 67.9%
2 HCl(aq)+ Na2CO3(aq)
 CO2(g)+ H2O(
CO2(g)+ H2O( 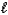 )+ 2 NaCl(aq)
)+ 2 NaCl(aq)What is the percent of Na2CO3 in a 0.613 g sample if the titration requires 26.14 mL of HCl? The molar mass of Na2CO3 is 106.0 g/mol.
A) 0.295%
B) 15.7%
C) 25.5%
D) 51.1%
E) 67.9%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A solution containing 10.mmol of CO32- and 5.0 mmol of HCO3-is titrated with 1.7 M HCl.What total volume of HCl must be added to reach the second equivalence point? (1 mmol = 0.001 mol)
A) 8.8 mL
B) 5.9 mL
C) 2.9 mL
D) 14.7 mL
E) 19.7 mL
A) 8.8 mL
B) 5.9 mL
C) 2.9 mL
D) 14.7 mL
E) 19.7 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which is the best colored indicator to use in the titration of 0.1 M CH3CO2H(aq)with NaOH(aq)? Why? (Ka of CH3CO2H = 1.8 10-5,Kb of CH3CO2- = 5.6 10-10)

A) Bromcresol Green.The equivalence point for a weak acid titration occurs at low pH.
B) Bromthymol Blue.The pH at the equivalence point is 7.0.
C) Bromcresol Green.The pKa of CH3CO2H and the pKa of the indicator are similar.
D) Phenolphthalein.The pKa of CH3CO2- and the pKb of the indicator are similar.
E) Phenolphthalein.The pH at the equivalence point is near the pKa of the indicator.

A) Bromcresol Green.The equivalence point for a weak acid titration occurs at low pH.
B) Bromthymol Blue.The pH at the equivalence point is 7.0.
C) Bromcresol Green.The pKa of CH3CO2H and the pKa of the indicator are similar.
D) Phenolphthalein.The pKa of CH3CO2- and the pKb of the indicator are similar.
E) Phenolphthalein.The pH at the equivalence point is near the pKa of the indicator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What color change is exhibited by phenolphthalein during a titration of aqueous acetic acid with aqueous sodium hydroxide?
A) colorless to pink
B) pink to colorless
C) green to yellow
D) yellow to blue
E) blue to yellow
A) colorless to pink
B) pink to colorless
C) green to yellow
D) yellow to blue
E) blue to yellow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the solubility product expression for Fe(OH)3?
A) Ksp =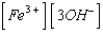
B) Ksp =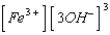
C) Ksp =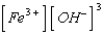
D) Ksp =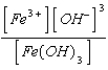
E) Ksp =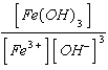
A) Ksp =
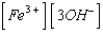
B) Ksp =
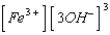
C) Ksp =
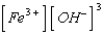
D) Ksp =
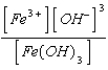
E) Ksp =
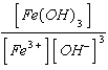

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP)is used to standardize sodium hydroxide.If 35.39 mL of NaOH(aq)is required to titrate 0.8246 g KHP to the equivalence point,what is the concentration of the NaOH(aq)? (The molar mass of KHP = 204.2 g/mol)
HC8H4O4-(aq)+ OH-(aq)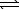 C8H4O42-(aq)+ H2O(
C8H4O42-(aq)+ H2O(  )
)
A) 0.02318 M
B) 0.05705 M
C) 0.0859 M
D) 0.1141 M
E) 0.1429 M
HC8H4O4-(aq)+ OH-(aq)
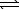 C8H4O42-(aq)+ H2O(
C8H4O42-(aq)+ H2O(  )
)A) 0.02318 M
B) 0.05705 M
C) 0.0859 M
D) 0.1141 M
E) 0.1429 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The solubility of barium carbonate (BaCO3)in water at 25°C is 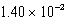 g/L.What is the Ksp of this sparingly soluble salt?
g/L.What is the Ksp of this sparingly soluble salt?
A)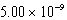
B)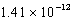
C)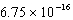
D)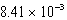
E)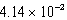
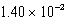 g/L.What is the Ksp of this sparingly soluble salt?
g/L.What is the Ksp of this sparingly soluble salt?A)
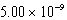
B)
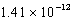
C)
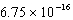
D)
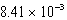
E)
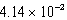

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 25.00-mL sample of propionic acid,HC3H5O2,of unknown concentration was titrated with 0.143 M KOH.The equivalence point was reached when 43.76 mL of base had been added.What was the original concentration of the propionic acid?
A) 0.295 M
B) 0.125 M
C) 0.082 M
D) 0.143 M
E) 0.250 M
A) 0.295 M
B) 0.125 M
C) 0.082 M
D) 0.143 M
E) 0.250 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A solution containing 10.mmol of CO32-and 5.0 mmol of HCO3-is titrated with 1.2 M HCl.What volume of HCl must be added to reach the first equivalence point? (1 mmol = 0.001 mol)
A) 23.3 mL
B) 4.2 mL
C) 8.3 mL
D) 18.3 mL
E) 13.3 mL
A) 23.3 mL
B) 4.2 mL
C) 8.3 mL
D) 18.3 mL
E) 13.3 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A 25.0 mL sample of 0.10 M sodium benzoate is titrated with 0.10 M HCl(aq).What is the pH after the addition of 32.0 mL of HCl(aq)? (Kb of C6H5CO2- = 1.6 10-10)
A) 1.00
B) 1.25
C) 1.91
D) 4.20
E) 9.79
A) 1.00
B) 1.25
C) 1.91
D) 4.20
E) 9.79

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider the titration of 300.0 mL of 0.569 M NH3 (Kb = 1.8 10-5)with 0.500 M HNO3.After 150.0 mL HNO3 has been added,what is the pH of the solution?
A) 4.64
B) 9.36
C) 6.36
D) 11.36
E) 7.00
A) 4.64
B) 9.36
C) 6.36
D) 11.36
E) 7.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Calculate the molar concentration of uncomplexed Zn2+(aq)in a solution that contains 0.24 M Zn(NH3)42+ and 0.3671 M NH3 at equilibrium.Kf for Zn(NH3)42+ is 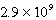 .
.
A)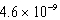 M
M
B)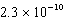 M
M
C)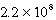 M
M
D)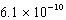 M
M
E)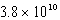 M
M
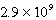 .
.A)
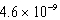 M
MB)
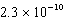 M
MC)
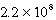 M
MD)
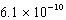 M
ME)
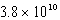 M
M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the concentration of silver(I)ion in a saturated solution of silver(I)carbonate containing 0.0024 M Na2CO3? For Ag2CO3,Ksp = 8.6 10-12.
A) 6.0 10-4 M
B) 2.0 10-9 M
C) 8.0 10-9 M
D) 6.0 10-5 M
E) 8.0 10-4 M
A) 6.0 10-4 M
B) 2.0 10-9 M
C) 8.0 10-9 M
D) 6.0 10-5 M
E) 8.0 10-4 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An aqueous solution contains 0.010 M Br- and 0.010 M I-.If Ag+ is added until AgBr(s)just begins to precipitate,what are the concentrations of Ag+ and I-? (Ksp of AgBr = 5.4 10-13,Ksp of AgI = 8.5 10-17)
A) [Ag+] = 5.4 10-11 M,[I-] = 1.0 10-2 M
B) [Ag+] = 8.5 10-15 M,[I-] = 1.0 10-2 M
C) [Ag+] = 5.4 10-11 M,[I-] = 1.6 10-6 M
D) [Ag+] = 8.5 10-15 M,[I-] = 6.4 101 M
E) [Ag+] = 8.5 10-15 M,[I-] = 1.6 10-6 M
A) [Ag+] = 5.4 10-11 M,[I-] = 1.0 10-2 M
B) [Ag+] = 8.5 10-15 M,[I-] = 1.0 10-2 M
C) [Ag+] = 5.4 10-11 M,[I-] = 1.6 10-6 M
D) [Ag+] = 8.5 10-15 M,[I-] = 6.4 101 M
E) [Ag+] = 8.5 10-15 M,[I-] = 1.6 10-6 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the value of the dissociation constant,Kd,for the complex ion Cd(NH3)42+? For Cd(NH3)42+,Kf = 1.0 107.
A) 1.0 10-7
B) 2.5 106
C) 1.0 107
D) 5.6 101
E) 1.0 10 -7
A) 1.0 10-7
B) 2.5 106
C) 1.0 107
D) 5.6 101
E) 1.0 10 -7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In which of the following solutions would silver(I)phosphate,Ag3PO4,be least soluble?
A) 0.10 M Na3PO4
B) 0.10 M AgNO3
C) 0.10 M Na2HPO4
D) 0.10 M HNO3
E) 0.10 M NaH2PO4
A) 0.10 M Na3PO4
B) 0.10 M AgNO3
C) 0.10 M Na2HPO4
D) 0.10 M HNO3
E) 0.10 M NaH2PO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The Ksp of BaSO4 is 1.1 10-10 at 25 C.What mass of BaSO4 (molar mass = 233.4 g/mol)will dissolve in 1.0 L of water at 25 C?
A) 2.6 10-8 g
B) 4.5 10-8 g
C) 1.0 10-5 g
D) 1.6 10-4 g
E) 2.4 10-3 g
A) 2.6 10-8 g
B) 4.5 10-8 g
C) 1.0 10-5 g
D) 1.6 10-4 g
E) 2.4 10-3 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the molar solubility of silver(I)bromide at 25°C? The solubility product constant for silver(I)bromide is 5.0 10-13 at 25°C.
A) 7.1 10-7 M
B) 2.5 10-13 M
C) 4.2 10-4 M
D) 5.0 10-5 M
E) 5.0 10-13 M
A) 7.1 10-7 M
B) 2.5 10-13 M
C) 4.2 10-4 M
D) 5.0 10-5 M
E) 5.0 10-13 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the molar solubility of Mn(OH)2(s)in a solution that is buffered at pH 8.00 at 25 C? The Ksp of Mn(OH)2 is 1.9 10-13 at 25 C.
A) 3.6 10-8 mol/L
B) 1.9 10-7 mol/L
C) 3.6 10-5 mol/L
D) 1.9 10-1 mol/L
E) 1.9 103 mol/L
A) 3.6 10-8 mol/L
B) 1.9 10-7 mol/L
C) 3.6 10-5 mol/L
D) 1.9 10-1 mol/L
E) 1.9 103 mol/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the minimum concentration of Cu2+ required to begin precipitating Cu(OH)2(s)in a solution buffered at pH 10.63? The Ksp of Cu(OH)2 is 2.6 10-19 and Kw = 1.01 10-14.
A) 2.1 10-4 M
B) 1.1 10-8 M
C) 6.1 10-16 M
D) 1.4 10-12 M
E) 2.3 10-21 M
A) 2.1 10-4 M
B) 1.1 10-8 M
C) 6.1 10-16 M
D) 1.4 10-12 M
E) 2.3 10-21 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The concentration of Pb2+ in an aqueous solution is 5.5 10-3 M.What concentration of SO42- is required to begin precipitating PbSO4? The Ksp of PbSO4 is 2.5 10-8.
A) 1.4 10-10 M
B) 4.5 10-6 M
C) 1.6 10-4 M
D) 8.3 10-4 M
E) 2.9 10-2 M
A) 1.4 10-10 M
B) 4.5 10-6 M
C) 1.6 10-4 M
D) 8.3 10-4 M
E) 2.9 10-2 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If 500 mL of 1.2 10-6 M AgNO3 is mixed with 500 mL of 1.2 10-6 M NaBr,what will occur? For AgBr,Ksp = 5 10-13.
A) Silver(I)bromide will precipitate.
B) The concentration of Ag+ will be 1.2 10-6 M.
C) 6.0 10-7 mol of AgBr will form.
D) No precipitation will occur.
E) Sodium bromide will precipitate.
A) Silver(I)bromide will precipitate.
B) The concentration of Ag+ will be 1.2 10-6 M.
C) 6.0 10-7 mol of AgBr will form.
D) No precipitation will occur.
E) Sodium bromide will precipitate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the molar solubility of Fe(OH)3(s)in a solution that is buffered at pH 2.50 at 25 C? The Ksp of Fe(OH)3 is 6.3 10-38 at 25 C.
A) 6.9 10-28 mol/L
B) 2.0 10-26 mol/L
C) 1.3 10-13 mol/L
D) 2.0 10-3 mol/L
E) 5.0 102 mol/L
A) 6.9 10-28 mol/L
B) 2.0 10-26 mol/L
C) 1.3 10-13 mol/L
D) 2.0 10-3 mol/L
E) 5.0 102 mol/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Consider the reaction
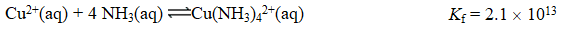
If the Ksp for Cu(OH)2 is 2.2 10-20,what is the value of the equilibrium constant,K,for the reaction below?
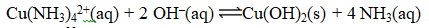
A) 1.0 10-33
B) 4.6 10-7
C) 2.1 1013
D) 2.2 106
E) 9.5 1032
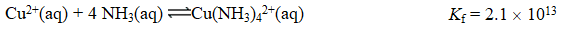
If the Ksp for Cu(OH)2 is 2.2 10-20,what is the value of the equilibrium constant,K,for the reaction below?
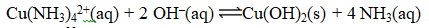
A) 1.0 10-33
B) 4.6 10-7
C) 2.1 1013
D) 2.2 106
E) 9.5 1032

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose 50.00 mL of 2.0 10-6 M Fe(NO3)3 is added to 50.00 mL of 2.0 10-4 M KIO3.Which of the following statements is true? For Fe(IO3)3,Ksp = 1.0 10-14.
A) A precipitate forms because Qc > Ksp.
B) A precipitate forms because Qc < Ksp.
C) No precipitate forms because Qc < Ksp.
D) No precipitate forms because Qc = Ksp.
E) No precipitate forms because Qc > Ksp.
A) A precipitate forms because Qc > Ksp.
B) A precipitate forms because Qc < Ksp.
C) No precipitate forms because Qc < Ksp.
D) No precipitate forms because Qc = Ksp.
E) No precipitate forms because Qc > Ksp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is the maximum hydroxide-ion concentration that a 0.027 M MgCl2 solution could have without causing the precipitation of Mg(OH)2? For Mg(OH)2,Ksp = 1.8 10-11.
A) 4.2 10-6
B) 1.7 10-4
C) 1.2 10-8
D) 6.7 10-9
E) 2.6 10-5
A) 4.2 10-6
B) 1.7 10-4
C) 1.2 10-8
D) 6.7 10-9
E) 2.6 10-5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Given the following reactions,
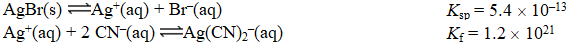
Determine the equilibrium constant for the reaction below.
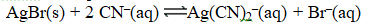
A) 4.5 10-34
B) 1.5 10-9
C) 6.5 108
D) 1.2 1021
E) 2.2 1033
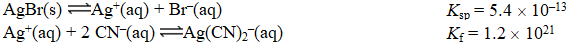
Determine the equilibrium constant for the reaction below.
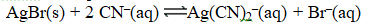
A) 4.5 10-34
B) 1.5 10-9
C) 6.5 108
D) 1.2 1021
E) 2.2 1033

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The following anions can be separated by precipitation as silver salts: Cl-,Br-,I-,CrO42-.If Ag+ is added to a solution containing the four anions,each at a concentration of 0.10 M,in what order will they precipitate?

A) AgCl Ag2CrO4 AgBr AgI
B) AgI AgBr Ag2CrO4 AgCl
C) Ag2CrO4 AgCl AgBr AgI
D) Ag2CrO4 AgI AgBr AgCl
E) AgI AgBr AgCl Ag2CrO4

A) AgCl Ag2CrO4 AgBr AgI
B) AgI AgBr Ag2CrO4 AgCl
C) Ag2CrO4 AgCl AgBr AgI
D) Ag2CrO4 AgI AgBr AgCl
E) AgI AgBr AgCl Ag2CrO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the concentration of Cd2+(aq)in a mixture of 0.010 mol Cd(NO3)2 and 1.0 mol NH3 diluted to 1.00 L? For Cd(NH3)42+, Kf = 1.0 107.
A) 3.2 10-5 M
B) 1.0 10-9 M
C) 1.2 10-9 M
D) 3.2 10-4 M
E) 1.0 10-2 M
A) 3.2 10-5 M
B) 1.0 10-9 M
C) 1.2 10-9 M
D) 3.2 10-4 M
E) 1.0 10-2 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the minimum mass of Cs2CO3 (molar mass = 325.821 g/mol)that must be added to 54.8 mL of a 5.0 10-4 M AgNO3 solution in order for precipitation to occur? The Ksp of Ag2CO3 is 8.6 10-12.Assume no volume change occurs upon addition of Cs2CO3.
A) 8.9 10-3 g
B) 9.6 10-4 g
C) 4.5 10-3 g
D) 3.1 10-7 g
E) 6.1 10-4 g
A) 8.9 10-3 g
B) 9.6 10-4 g
C) 4.5 10-3 g
D) 3.1 10-7 g
E) 6.1 10-4 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A 4.0 10-4 M solution of MnSO4 is gradually made more basic by adding NaOH.At what pH will manganese(II)hydroxide begin to precipitate? The Ksp of Mn(OH)2 is 2.0 10-13 and Kw = 1.01 10-14.
A) 4.70
B) 9.57
C) 4.65
D) 9.35
E) 9.30
A) 4.70
B) 9.57
C) 4.65
D) 9.35
E) 9.30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



