Deck 19: Entropy and Free Energy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Entropy and Free Energy
1
As defined by Ludwig Boltzmann,the third law of thermodynamics states that
A) there is no disorder in a perfect crystal at 0 K.
B) in a spontaneous process,the entropy of the universe increases.
C) the total entropy of the universe is always increasing.
D) the total mass of the universe is constant.
E) mass and energy are conserved in all chemical reactions.
A) there is no disorder in a perfect crystal at 0 K.
B) in a spontaneous process,the entropy of the universe increases.
C) the total entropy of the universe is always increasing.
D) the total mass of the universe is constant.
E) mass and energy are conserved in all chemical reactions.
there is no disorder in a perfect crystal at 0 K.
2
A statement of the first law of thermodynamics is that
A) in a spontaneous process,the entropy of the universe increases.
B) there is no disorder in a perfect crystal at 0 K.
C) the total energy of the universe is always decreasing.
D) the total energy of the universe is constant.
E) mass and energy are conserved in all chemical reactions.
A) in a spontaneous process,the entropy of the universe increases.
B) there is no disorder in a perfect crystal at 0 K.
C) the total energy of the universe is always decreasing.
D) the total energy of the universe is constant.
E) mass and energy are conserved in all chemical reactions.
the total energy of the universe is constant.
3
Which of the following linear chain alcohols is likely to have the highest standard entropy in the liquid state?
A) CH3OH
B) CH3CH2OH
C) CH3CH2CH2OH
D) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
E) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
A) CH3OH
B) CH3CH2OH
C) CH3CH2CH2OH
D) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
E) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
4
In which reaction is rS° expected to be negative?
A) 2C2H6(g)+ 7O2(g) 4CO2(g)+ 6H2O(l)
B) Ga(l) Ga(s)
C) H2O(l)+ 2SO2(g) H2SO4(l)
D) CO2(g) CO2(s)
E) all of above
A) 2C2H6(g)+ 7O2(g) 4CO2(g)+ 6H2O(l)
B) Ga(l) Ga(s)
C) H2O(l)+ 2SO2(g) H2SO4(l)
D) CO2(g) CO2(s)
E) all of above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a chemical reaction occurs in a direction that has a positive change in entropy then
A) the change in enthalpy must be negative.
B) the reaction must be spontaneous.
C) heat goes from the system into the surroundings.
D) the reaction must be exothermic.
E) the disorder of the system increases.
A) the change in enthalpy must be negative.
B) the reaction must be spontaneous.
C) heat goes from the system into the surroundings.
D) the reaction must be exothermic.
E) the disorder of the system increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following changes lead to a in entropy?
A) the sublimation (vaporization)of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide)
B) sugar dissolving in coffee
C) evaporation of water from a lake
D) diffusion of perfume throughout a room
E) halving the volume of a gas
A) the sublimation (vaporization)of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide)
B) sugar dissolving in coffee
C) evaporation of water from a lake
D) diffusion of perfume throughout a room
E) halving the volume of a gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements concerning entropy change is/are true?
1)For a reversible process,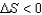 )
)
2)For a spontaneous process,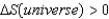 )
)
3)For a reversible process,such as a phase change, S = qrev/T .
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3
1)For a reversible process,
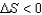 )
)2)For a spontaneous process,
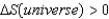 )
)3)For a reversible process,such as a phase change, S = qrev/T .
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following compounds has the highest standard entropy per mole at 298 K?
A) H2O(l)
B) CaCO3(s)
C) CO(g)
D) SiO2(s)
E) CH3OH(l)
A) H2O(l)
B) CaCO3(s)
C) CO(g)
D) SiO2(s)
E) CH3OH(l)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following processes occur spontaneously at 25 C.Which of these processes is/are endothermic?
1)NH4NO3 dissolving in water (which is accompanied by a cooling of the water).
2)the expansion of a real gas into a vacuum (which is accompanied by a cooling of the gas).
3)liquid water in an ice cube tray freezing into ice after being placed in a freezer.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1,2,and 3
1)NH4NO3 dissolving in water (which is accompanied by a cooling of the water).
2)the expansion of a real gas into a vacuum (which is accompanied by a cooling of the gas).
3)liquid water in an ice cube tray freezing into ice after being placed in a freezer.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When a chemical process occurs under standard conditions,which of the following conditions always apply?
1)Gaseous species are at a pressure of 1 bar.
2)Solution concentrations species are 1 molal.
3)The temperature is 298.15 K.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1,2,and 3
1)Gaseous species are at a pressure of 1 bar.
2)Solution concentrations species are 1 molal.
3)The temperature is 298.15 K.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is/are CORRECT?
1)Spontaneous changes only occur in the direction that leads to equilibrium.
2)Exothermic reactions are always spontaneous.
3)In any chemical reaction,energy must be conserved.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3
1)Spontaneous changes only occur in the direction that leads to equilibrium.
2)Exothermic reactions are always spontaneous.
3)In any chemical reaction,energy must be conserved.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements concerning entropy is correct?
A) The entropy of a system increases as the number of available microstates increases.
B) The entropy of a system is proportional to the natural log of the number of microstates.
C) In a spontaneous process, S(universe)indicates the extent to which energy is dispersed.
D) The dispersal of matter,such as the spontaneous expansion of a gas,cannot be explained by an increase in entropy.
E) Entropy is a measure of the extent of energy dispersal.
A) The entropy of a system increases as the number of available microstates increases.
B) The entropy of a system is proportional to the natural log of the number of microstates.
C) In a spontaneous process, S(universe)indicates the extent to which energy is dispersed.
D) The dispersal of matter,such as the spontaneous expansion of a gas,cannot be explained by an increase in entropy.
E) Entropy is a measure of the extent of energy dispersal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For a certain reversible process q = 57.40 kJ at 36.6 C.What is S for the process?
A) 0.185 J/K
B) 185 J/K
C) 1.57 J/K
D) (-0.185) J/K
E) 2130 J/K
A) 0.185 J/K
B) 185 J/K
C) 1.57 J/K
D) (-0.185) J/K
E) 2130 J/K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For which of the following reactions will the entropy of the system decrease?
A) 2 NH3(g) N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)
B) 2 C(s)+ O2(g) 2 CO(g)
C) CaCO3(s) CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
D) 2 NO2(g) N2O4(g)
E) NaOH(s) Na+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
A) 2 NH3(g) N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)
B) 2 C(s)+ O2(g) 2 CO(g)
C) CaCO3(s) CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
D) 2 NO2(g) N2O4(g)
E) NaOH(s) Na+(aq)+ OH-(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The second law of thermodynamics states that
A) in a spontaneous process,the entropy of the universe increases.
B) there is no disorder in a perfect crystal at 0 K.
C) the total energy of the universe is always increasing.
D) the total energy of the universe is constant.
E) mass and energy are conserved in all chemical reactions.
A) in a spontaneous process,the entropy of the universe increases.
B) there is no disorder in a perfect crystal at 0 K.
C) the total energy of the universe is always increasing.
D) the total energy of the universe is constant.
E) mass and energy are conserved in all chemical reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following reactions would be expected to have a positive entropy change, ∆rS° > 0?
1. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g)
2. Ba(OH)2(s) → BaO(s) + H2O(g)
3. CO(g)+ 2 H2(g) CH3OH(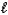 )
)
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1 and 3
1. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g)
2. Ba(OH)2(s) → BaO(s) + H2O(g)
3. CO(g)+ 2 H2(g) CH3OH(
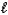 )
)A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Arrange the following reactions in order of increasing rS° value.
1.H2(g)+ F2(g) 2HF(g)
2)NH4NO3(s) N2O(g)+ 2H2O(l)
3)(NH4)2Cr2O7(s) Cr2O3(s)+ 4H2O(l)+ N2(g)
A) 1 < 2 < 3
B) 2 < 3 < 1
C) 3 < 1 < 2
D) 1 < 3 < 2
E) 2 < 1 < 3
1.H2(g)+ F2(g) 2HF(g)
2)NH4NO3(s) N2O(g)+ 2H2O(l)
3)(NH4)2Cr2O7(s) Cr2O3(s)+ 4H2O(l)+ N2(g)
A) 1 < 2 < 3
B) 2 < 3 < 1
C) 3 < 1 < 2
D) 1 < 3 < 2
E) 2 < 1 < 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the change in entropy for a system going from 189 possible microstates to 734 possible microstates? (k = 1.381 10-23 J/K)
A)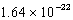 J/K
J/K
B)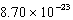 J/K
J/K
C) (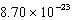 )J/K
)J/K
D)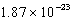 J/K
J/K
E) (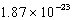 ) J/K
) J/K
A)
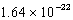 J/K
J/KB)
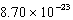 J/K
J/KC) (
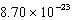 )J/K
)J/KD)
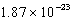 J/K
J/KE) (
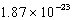 ) J/K
) J/K
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements concerning entropy is/are CORRECT?
1)The entropy of a substance increases when converted from a liquid to a solid.
2)The entropy of a substance decreases as its temperature increases.
3)All substances have positive entropy values at temperatures above 0 K.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1,2,and 3
1)The entropy of a substance increases when converted from a liquid to a solid.
2)The entropy of a substance decreases as its temperature increases.
3)All substances have positive entropy values at temperatures above 0 K.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements regarding the spontaneity of chemical and physical changes is correct?
A) A reaction may be spontaneous only in one direction.
B) A process can sometimes be spontaneous in the direction that moves it away from equilibrium.
C) Endothermic processes are never spontaneous.
D) A reactant favored process cannot be spontaneous.
E) Spontaneous changes occur only in the direction that leads to equilibrium.
A) A reaction may be spontaneous only in one direction.
B) A process can sometimes be spontaneous in the direction that moves it away from equilibrium.
C) Endothermic processes are never spontaneous.
D) A reactant favored process cannot be spontaneous.
E) Spontaneous changes occur only in the direction that leads to equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Diluting concentrated sulfuric acid with water can be dangerous.The temperature of the solution can increase rapidly.What are the signs of rH, rS,and rG for this process?
A) ( rH) < 0, rS > 0, rG < 0
B) ( rH) < 0, rS < 0, rG < 0
C) ( rH) < 0, rS > 0, rG > 0
D) ( rH) > 0, rS > 0, rG < 0
E) ( rH) > 0, rS < 0, rG > 0
A) ( rH) < 0, rS > 0, rG < 0
B) ( rH) < 0, rS < 0, rG < 0
C) ( rH) < 0, rS > 0, rG > 0
D) ( rH) > 0, rS > 0, rG < 0
E) ( rH) > 0, rS < 0, rG > 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Hydrogen gas is a non-polluting fuel.Hydrogen gas may be prepared by electrolysis of water.2 H2O(  ) 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)
) 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)
Predict the signs of rH and rS for the production of hydrogen gas by electrolysis of water.
A) ( rH) > 0 and rS > 0
B) ( rH) < 0 and rS > 0
C) ( rH) > 0 and rS < 0
D) ( rH) < 0 and rS < 0
E) ( rH) = 0 and rS < 0
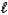 ) 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)
) 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)Predict the signs of rH and rS for the production of hydrogen gas by electrolysis of water.
A) ( rH) > 0 and rS > 0
B) ( rH) < 0 and rS > 0
C) ( rH) > 0 and rS < 0
D) ( rH) < 0 and rS < 0
E) ( rH) = 0 and rS < 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Calculate S0 for O3(g)if the standard entropy change for the reaction below is 548 J/K.mol-rxn and S0[O2(g)] = 205 J/K.mol.
8O3(g) 12O2(g)
A) 364 J/K.mol-rxn
B) 478 J/K.mol-rxn
C) 239 J/K.mol-rxn
D) (-117) J/K.mol-rxn
E) (-59) J/K.mol-rxn
8O3(g) 12O2(g)
A) 364 J/K.mol-rxn
B) 478 J/K.mol-rxn
C) 239 J/K.mol-rxn
D) (-117) J/K.mol-rxn
E) (-59) J/K.mol-rxn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the sign of Hº(system)and Sº(system)if a chemical reaction is nonspontaneous at all temperatures under standard conditions?
A) ( Hº)(system)is negative,and Sº(system)is positive.
B) ( Hº)(system)is negative,and Sº(system)is negative.
C) ( Hº)(system)is positive,and Sº(system)is positive.
D) ( Hº)(system)is positive,and Sº(system)is negative.
E) none of these
A) ( Hº)(system)is negative,and Sº(system)is positive.
B) ( Hº)(system)is negative,and Sº(system)is negative.
C) ( Hº)(system)is positive,and Sº(system)is positive.
D) ( Hº)(system)is positive,and Sº(system)is negative.
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For the process Br2(l) 2Br(g),
A) ( H) is + and S is + for the reaction.
B) ( H) is + and S = 0 for the reaction.
C) ( H) is - and S is - for the reaction.
D) ( H) is - and S is + for the reaction.
E) ( H) is + and S is - for the reaction.
A) ( H) is + and S is + for the reaction.
B) ( H) is + and S = 0 for the reaction.
C) ( H) is - and S is - for the reaction.
D) ( H) is - and S is + for the reaction.
E) ( H) is + and S is - for the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If a chemical reaction is exothermic,but not spontaneous,which of the following must be true?
A) ( rG) > 0, rS > 0 and rH > 0
B) ( rG) < 0, rS > 0 and rH > 0
C) ( rG) > 0, rS < 0 and rH > 0
D) ( rG) < 0, rS < 0 and rH < 0
E) ( rG) > 0, rS < 0 and rH < 0
A) ( rG) > 0, rS > 0 and rH > 0
B) ( rG) < 0, rS > 0 and rH > 0
C) ( rG) > 0, rS < 0 and rH > 0
D) ( rG) < 0, rS < 0 and rH < 0
E) ( rG) > 0, rS < 0 and rH < 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Calculate the standard entropy change for the following reaction,
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g) 2 SO3(g)
Given S [SO2(g)] = 248.2 J/K.mol,S [O2(g)] = 205.1 J/K.mol,and S [SO3(g)] = 256.8 J/K.mol.
A) -196.5 J/K·mol-rxn
B) -94.0 J/K·mol-rxn
C) -187.9 J/K·mol-rxn
D) +187.9 J/K·mol-rxn
E) +196.5 J/K·mol-rxn
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g) 2 SO3(g)
Given S [SO2(g)] = 248.2 J/K.mol,S [O2(g)] = 205.1 J/K.mol,and S [SO3(g)] = 256.8 J/K.mol.
A) -196.5 J/K·mol-rxn
B) -94.0 J/K·mol-rxn
C) -187.9 J/K·mol-rxn
D) +187.9 J/K·mol-rxn
E) +196.5 J/K·mol-rxn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For the combustion of acetylene at 298.15 K,
2 C2H2(g)+ 5 O2(g) 4 CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
Calculate S (universe)given S (system)= -194.6 J/K and H (system)= -2511.2 kJ.
A) -2453.2 J/K
B) -186.2 J/K
C) +186.2 J/K
D) +1290.4 J/K
E) +8228.0 J/K
2 C2H2(g)+ 5 O2(g) 4 CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
Calculate S (universe)given S (system)= -194.6 J/K and H (system)= -2511.2 kJ.
A) -2453.2 J/K
B) -186.2 J/K
C) +186.2 J/K
D) +1290.4 J/K
E) +8228.0 J/K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When a real gas is compressed from low pressure to a higher pressure,its temperature increases.Predict the signs H and S.
A) ( H) < 0 and S < 0
B) ( H) < 0 and S > 0
C) ( H) > 0 and S < 0
D) ( H) > 0 and S > 0
E) ( H) < 0 and S = 0
A) ( H) < 0 and S < 0
B) ( H) < 0 and S > 0
C) ( H) > 0 and S < 0
D) ( H) > 0 and S > 0
E) ( H) < 0 and S = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If rG > 0 for a reaction at all temperatures,then rH is ____ and rS is ____.
A) negative,positive
B) positive,negative
C) negative,negative
D) positive,positive
E) positive,either positive or negative
A) negative,positive
B) positive,negative
C) negative,negative
D) positive,positive
E) positive,either positive or negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The dissolution of ammonium nitrate occurs spontaneously in water at 25 C.As NH4NO3 dissolves,the temperature of the water decreases.What are the signs of rH, rS,and rG for this process?
A)( rH) > 0, rS < 0, rG > 0
B) ( rH) > 0, rS > 0, rG > 0
C) ( rH) > 0, rS > 0, rG < 0
D)( rH) < 0, rS < 0, rG < 0
E) ( rH) < 0, rS > 0, rG > 0
A)( rH) > 0, rS < 0, rG > 0
B) ( rH) > 0, rS > 0, rG > 0
C) ( rH) > 0, rS > 0, rG < 0
D)( rH) < 0, rS < 0, rG < 0
E) ( rH) < 0, rS > 0, rG > 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The standard entropy for the formation of SF6(g)from the elements,
S(s)+ 3 F2(g) SF6(g)
Is -348.7 J/K.mol-rxn at 298.15 K.Calculate the standard molar entropy of SF6(g)given S [S(s)] = 32.1 J/K.mol and S [F2(g)] = 202.8 J/K.mol.
A) -988.6 J/K.mol
B) +291.8 J/K.mol
C) -291.8 J/K.mol
D) -113.2 J/K.mol
E) +113.8 J/K.mol
S(s)+ 3 F2(g) SF6(g)
Is -348.7 J/K.mol-rxn at 298.15 K.Calculate the standard molar entropy of SF6(g)given S [S(s)] = 32.1 J/K.mol and S [F2(g)] = 202.8 J/K.mol.
A) -988.6 J/K.mol
B) +291.8 J/K.mol
C) -291.8 J/K.mol
D) -113.2 J/K.mol
E) +113.8 J/K.mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a cube of ice at 0 C is placed outside on a warm summer day,the ice will melt spontaneously.What are the signs of rH, rS,and rG for this process?
A) ( rH) < 0, rS > 0, rG < 0
B) ( rH) < 0, rS < 0, rG < 0
C) ( rH) < 0, rS > 0, rG > 0
D) ( rH) > 0, rS > 0, rG < 0
E) ( rH) > 0, rS < 0, rG > 0
A) ( rH) < 0, rS > 0, rG < 0
B) ( rH) < 0, rS < 0, rG < 0
C) ( rH) < 0, rS > 0, rG > 0
D) ( rH) > 0, rS > 0, rG < 0
E) ( rH) > 0, rS < 0, rG > 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A change of state that occurs in a system is accompanied by 58.8 kJ of heat,which is transferred to the surroundings at a constant pressure and a constant temperature of 300.K.For this process S(surroundings)is:
A) -196 J/K
B) -58.8 kJ/K
C) 196 J/K
D) 58.8 kJ/K
E) 241 kJ/K
A) -196 J/K
B) -58.8 kJ/K
C) 196 J/K
D) 58.8 kJ/K
E) 241 kJ/K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Calculate the standard entropy change for the following reaction.
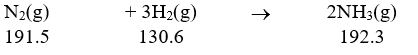
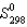 (J/mol.K)
(J/mol.K)
A) -198.7 J/K.mol-rxn
B) 198.7 J/K.mol-rxn
C) 184.3 J/K.mol-rxn
D) -184.3 J/K.mol-rxn
E) -129.8 J/K.mol-rxn
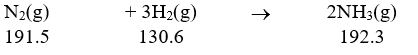
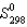 (J/mol.K)
(J/mol.K)A) -198.7 J/K.mol-rxn
B) 198.7 J/K.mol-rxn
C) 184.3 J/K.mol-rxn
D) -184.3 J/K.mol-rxn
E) -129.8 J/K.mol-rxn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is true for the vaporization of a liquid substance?
A) ( S) = 0 and H = 0.
B) ( S) < 0 and H < 0.
C) ( S) < 0 and H > 0.
D) ( S) > 0 and H > 0.
E) ( S) > 0 and H < 0.
A) ( S) = 0 and H = 0.
B) ( S) < 0 and H < 0.
C) ( S) < 0 and H > 0.
D) ( S) > 0 and H > 0.
E) ( S) > 0 and H < 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use the following thermodynamic data
Species
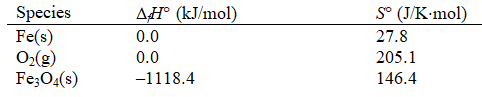
To calculate S (universe)for the formation of Fe2O3(s)at 298.15 K.
3 Fe(s)+ 2 O2(g) Fe3O4(s)
A) -3404 J/K
B) -1162 J/K
C) +561.2 J/K
D) +3404 J/K
E) +7639 J/K
Species
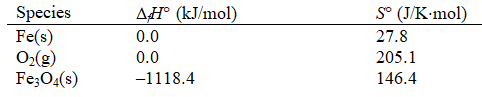
To calculate S (universe)for the formation of Fe2O3(s)at 298.15 K.
3 Fe(s)+ 2 O2(g) Fe3O4(s)
A) -3404 J/K
B) -1162 J/K
C) +561.2 J/K
D) +3404 J/K
E) +7639 J/K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A flask containing helium gas is released into a closed room.Which of the following ideas regarding entropy is
A) ( S)(system)> 0
B) Matter is dispersed.
C) ( S)(universe)> 0
D) This process is spontaneous.
E) All of these statements are true.
A) ( S)(system)> 0
B) Matter is dispersed.
C) ( S)(universe)> 0
D) This process is spontaneous.
E) All of these statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A 100-mL sample of water is placed in a coffee cup calorimeter.When 1.0 g of an ionic solid is added,the temperature decreases from 21.5°C to 20.8°C as the solid dissolves.For the dissolving of the solid
A) ( H) < 0
B) ( S)(universe)> 0
C) ( S)(system)< 0
D) ( S)(surroundings)> 0
E) none of these
A) ( H) < 0
B) ( S)(universe)> 0
C) ( S)(system)< 0
D) ( S)(surroundings)> 0
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
For the reaction given below, H0 = -1516 kJ at 25 C and S0 = -432.8 J/K at 25 C.This reaction is spontaneous ____.
SiH4(g)+ 2O2(g) SiO2(s)+ 2H2O
A) only below a certain temperature
B) only above a certain temperature
C) at all temperatures
D) at no temperatures
E) cannot tell from the information available
SiH4(g)+ 2O2(g) SiO2(s)+ 2H2O
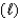
A) only below a certain temperature
B) only above a certain temperature
C) at all temperatures
D) at no temperatures
E) cannot tell from the information available

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
At what temperatures will a reaction be spontaneous if rH = +117 kJ and rS = -35 J/K?
A) All temperatures below 94.1 K
B) Temperatures between 12.7 K and 135 K
C) All temperatures above 94.1 K
D) The reaction will be spontaneous at any temperature.
E) The reaction will never be spontaneous.
A) All temperatures below 94.1 K
B) Temperatures between 12.7 K and 135 K
C) All temperatures above 94.1 K
D) The reaction will be spontaneous at any temperature.
E) The reaction will never be spontaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
All of the following relationships are true EXCEPT
A)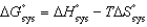 .
.
B)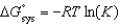 .
.
C)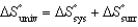 .
.
D)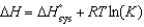 .
.
E)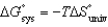 .
.
A)
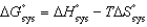 .
.B)
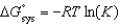 .
.C)
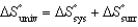 .
.D)
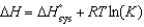 .
.E)
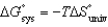 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Estimate the boiling point of ethanol given the following thermodynamic parameters.
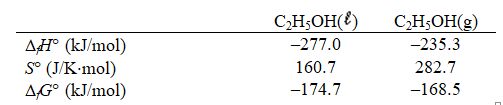
A) 22 C
B) 44 C
C) 61 C
D) 69 C
E) 91 C
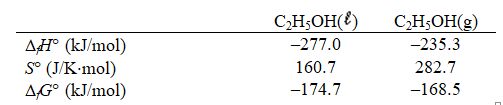
A) 22 C
B) 44 C
C) 61 C
D) 69 C
E) 91 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
At what temperatures will a reaction be spontaneous if rH = +62.4 kJ and rS = +301 J/K?
A) All temperatures below 207 K.
B) All temperatures above 207 K.
C) Temperatures between 179 K and 235 K.
D) The reaction will be spontaneous at any temperature.
E) The reaction will never be spontaneous.
A) All temperatures below 207 K.
B) All temperatures above 207 K.
C) Temperatures between 179 K and 235 K.
D) The reaction will be spontaneous at any temperature.
E) The reaction will never be spontaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Calculate rG for the reaction below at 25.0 C
2 Na(s)+ 2 H2O( ) 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)
) 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)
Given rH = -366.6 kJ/mol-rxn and rS = -154.2 J/K.mol-rxn.
A) -371.2 kJ/mol-rxn
B) -320.6 kJ/mol-rxn
C) -215.4 kJ/mol-rxn
D) +371.2 kJ/mol-rxn
E) +4634.9 kJ/mol-rxn
2 Na(s)+ 2 H2O(
 ) 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)
) 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)Given rH = -366.6 kJ/mol-rxn and rS = -154.2 J/K.mol-rxn.
A) -371.2 kJ/mol-rxn
B) -320.6 kJ/mol-rxn
C) -215.4 kJ/mol-rxn
D) +371.2 kJ/mol-rxn
E) +4634.9 kJ/mol-rxn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is rG° at 500.0 K for the following reaction?
Zn(s)+ H2O(g) ZnO(s)+ H2(g)

A) 80.7 kJ/mol-rxn
B) -80.7 kJ/mol-rxn
C) 92.0 kJ/mol-rxn
D) -92.0 kJ/mol-rxn
E) -136.7 kJ/mol-rxn
Zn(s)+ H2O(g) ZnO(s)+ H2(g)

A) 80.7 kJ/mol-rxn
B) -80.7 kJ/mol-rxn
C) 92.0 kJ/mol-rxn
D) -92.0 kJ/mol-rxn
E) -136.7 kJ/mol-rxn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Given the following,determine rG° at 298 K for the precipitation reaction,
Ag+(aq)+I-(aq) AgI(s)
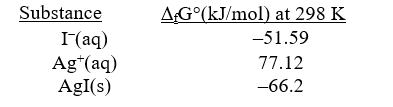
A) -91.7 kJ/mol-rxn
B) -40.7 kJ/mol-rxn
C) 91.7 kJ/mol-rxn
D) 40.7 kJ/mol-rxn
E) 62.5 kJ/mol-rxn
Ag+(aq)+I-(aq) AgI(s)
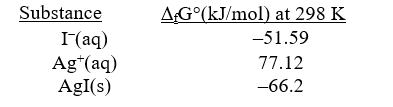
A) -91.7 kJ/mol-rxn
B) -40.7 kJ/mol-rxn
C) 91.7 kJ/mol-rxn
D) 40.7 kJ/mol-rxn
E) 62.5 kJ/mol-rxn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is G° at 298 K for the following reaction?
H2(g)+ Br2(g) 2HBr(g); rH = -103.8 kJ/mol-rxn; rS = 21.3 J/K.mol-rxn at 298 K
A) -97.45 kJ/mol-rxn
B) 110.1 kJ/mol-rxn
C) -110.1 kJ/mol-rxn
D) 6.451 103 kJ/mol-rxn
E) -6.451 103 kJ/mol-rxn
H2(g)+ Br2(g) 2HBr(g); rH = -103.8 kJ/mol-rxn; rS = 21.3 J/K.mol-rxn at 298 K
A) -97.45 kJ/mol-rxn
B) 110.1 kJ/mol-rxn
C) -110.1 kJ/mol-rxn
D) 6.451 103 kJ/mol-rxn
E) -6.451 103 kJ/mol-rxn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For which of the following substances is the standard free energy of formation not equal to zero at 298 K?
A) He(g)
B) Er(s)
C) Cl2(g)
D) Ba(g)
E) Fe(s)
A) He(g)
B) Er(s)
C) Cl2(g)
D) Ba(g)
E) Fe(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
For a reaction, rH = -208.8 kJ and rS = -308.2 J/K.At what temperature will rG = 0.00 kJ?
A) 0.68 K
B) 677.5 K
C) 1476 K
D) 6435 K
E) ( G) is less than 0.00 kJ at any temperature.
A) 0.68 K
B) 677.5 K
C) 1476 K
D) 6435 K
E) ( G) is less than 0.00 kJ at any temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Thermodynamics can be used to determine all of the following EXCEPT
A) the temperature at which a reaction is spontaneous.
B) the extent to which a reaction occurs.
C) the direction in which a reaction is spontaneous.
D) the rate of reaction.
E) the entropy change of a reaction.
A) the temperature at which a reaction is spontaneous.
B) the extent to which a reaction occurs.
C) the direction in which a reaction is spontaneous.
D) the rate of reaction.
E) the entropy change of a reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Given that
S(g)+ O2(g) SO2(g) rG = -300.1 kJ/mol-rxn
2 S(g)+ 3 O2(g) 2 SO3(g) rG = -742.1 kJ/mol-rxn
Calculate fG of the following reaction:
SO2(g)+ 1/2 O2(g) SO3(g)
A) -1042.2 kJ/mol-rxn
B) -71.0 kJ/mol-rxn
C) +2.47 kJ/mol-rxn
D) +71.0 kJ/mol-rxn
E) +1042.2 kJ/mol-rxn
S(g)+ O2(g) SO2(g) rG = -300.1 kJ/mol-rxn
2 S(g)+ 3 O2(g) 2 SO3(g) rG = -742.1 kJ/mol-rxn
Calculate fG of the following reaction:
SO2(g)+ 1/2 O2(g) SO3(g)
A) -1042.2 kJ/mol-rxn
B) -71.0 kJ/mol-rxn
C) +2.47 kJ/mol-rxn
D) +71.0 kJ/mol-rxn
E) +1042.2 kJ/mol-rxn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Given the following and that R = 8.314 J/K.mol,determine K at 298K for the reaction,
AgCl(s) Ag+(aq)+ Cl-(aq)
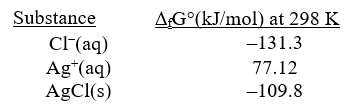
A)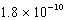
B)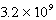
C)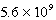
D)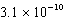
E)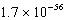
AgCl(s) Ag+(aq)+ Cl-(aq)
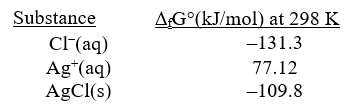
A)
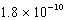
B)
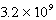
C)
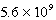
D)
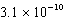
E)
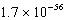

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A reaction is product-favored when
A) Q < K and rG < 0.
rG < 0.
B) Q < K and rG > 0.
rG > 0.
C) Q = K and rG = 0.
rG = 0.
D) Q > K and rG < 0.
rG < 0.
E) Q > K and rG > 0.
rG > 0.
A) Q < K and
 rG < 0.
rG < 0.B) Q < K and
 rG > 0.
rG > 0.C) Q = K and
 rG = 0.
rG = 0.D) Q > K and
 rG < 0.
rG < 0.E) Q > K and
 rG > 0.
rG > 0.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Calculate rG for the reaction below at 25.0 C
CH4(g)+ H2O(g) 3 H2(g)+ CO(g)
Given fG [CH4(g)] = -50.8 kJ/mol, fG 10 [H2O(g)] = -228.6 kJ/mol, fG 10 [H2(g)] = 0.0 kJ/mol,and fG [CO(g)] = -137.2 kJ/mol.
A) -416.3 kJ/mol-rxn
B) -142.2 kJ/mol-rxn
C) +142.2 kJ/mol-rxn
D) +315.0 kJ/mol-rxn
E) +416.3 kJ/mol-rxn
CH4(g)+ H2O(g) 3 H2(g)+ CO(g)
Given fG [CH4(g)] = -50.8 kJ/mol, fG 10 [H2O(g)] = -228.6 kJ/mol, fG 10 [H2(g)] = 0.0 kJ/mol,and fG [CO(g)] = -137.2 kJ/mol.
A) -416.3 kJ/mol-rxn
B) -142.2 kJ/mol-rxn
C) +142.2 kJ/mol-rxn
D) +315.0 kJ/mol-rxn
E) +416.3 kJ/mol-rxn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Given the following,determine fG° at 298 K for PbO.
Pb(s)+ PbO2(s) 2PbO(s); rG° = -158.5 kJ/mol-rxn at 298K
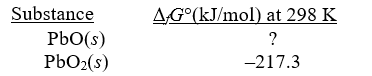
A) -187.9 kJ/mol
B) -375.8 kJ/mol
C) 58.8 kJ/mol
D) 29.4 kJ/mol
E) 117.6 kJ/mol
Pb(s)+ PbO2(s) 2PbO(s); rG° = -158.5 kJ/mol-rxn at 298K
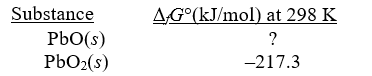
A) -187.9 kJ/mol
B) -375.8 kJ/mol
C) 58.8 kJ/mol
D) 29.4 kJ/mol
E) 117.6 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
For a chemical system, rG and rG are equal when
A) the system is in equilibrium.
B) the reactants and products are in standard state conditions.
C) the equilibrium constant,K,equals 0.
D) the reaction quotient,Q,is less than 1.
E) the reactants and products are in the gas phase.
A) the system is in equilibrium.
B) the reactants and products are in standard state conditions.
C) the equilibrium constant,K,equals 0.
D) the reaction quotient,Q,is less than 1.
E) the reactants and products are in the gas phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
G < 0 for a reaction indicates that
A) the reaction favors formation of reactants.
B) the reaction is spontaneous.
C) the reaction is nonspontaneous.
D) the reaction is at equilibrium.
E) the reaction cannot reach equilibrium.
A) the reaction favors formation of reactants.
B) the reaction is spontaneous.
C) the reaction is nonspontaneous.
D) the reaction is at equilibrium.
E) the reaction cannot reach equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is correct for the condensation of gaseous ammonia at -38°C? The normal boiling point of ammonia is -33°C.
A) ( H) < 0, S > 0,and G > 0.
B) ( H) < 0, S < 0,and G < 0.
C) ( H) > 0, S < 0,and G < 0.
D) ( H) = 0, S = 0,and G < 0.
E) ( H) > 0, S > 0,and G > 0.
A) ( H) < 0, S > 0,and G > 0.
B) ( H) < 0, S < 0,and G < 0.
C) ( H) > 0, S < 0,and G < 0.
D) ( H) = 0, S = 0,and G < 0.
E) ( H) > 0, S > 0,and G > 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
For a chemical reaction,if rG = 0,then ____.
A) K > 1
B) K = 0
C) K < 0
D) K < 1
E) K = 1
A) K > 1
B) K = 0
C) K < 0
D) K < 1
E) K = 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the equilibrium constant for reaction below at 25 C? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
2 NO(g)+ O2(g)![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant for reaction below at 25 <sup> \circ </sup>C? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol) 2 NO(g)+ O<sub>2</sub>(g) 2 NO<sub>2</sub>(g) Given \Delta <sub>f</sub>G<sup> \circ </sup>[NO(g)] = +86.6 kJ/mol and \Delta <sub>f</sub>G<sup> \circ </sup> [NO<sub>2</sub>(g)] = +51.2 kJ/mol.</strong> A) 3.9 \times 10<sup>-13</sup> B) 1.0 C) 2.6 \times 10<sup>12</sup> D) 1.6 \times 10<sup>6</sup> E) 3.8 \times 10<sup>28</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab99_797e_a16d_5fbb5905faab_TB4499_11.jpg) 2 NO2(g)
2 NO2(g)
Given fG [NO(g)] = +86.6 kJ/mol and fG [NO2(g)] = +51.2 kJ/mol.
A) 3.9 10-13
B) 1.0
C) 2.6 1012
D) 1.6 106
E) 3.8 1028
2 NO(g)+ O2(g)
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant for reaction below at 25 <sup> \circ </sup>C? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol) 2 NO(g)+ O<sub>2</sub>(g) 2 NO<sub>2</sub>(g) Given \Delta <sub>f</sub>G<sup> \circ </sup>[NO(g)] = +86.6 kJ/mol and \Delta <sub>f</sub>G<sup> \circ </sup> [NO<sub>2</sub>(g)] = +51.2 kJ/mol.</strong> A) 3.9 \times 10<sup>-13</sup> B) 1.0 C) 2.6 \times 10<sup>12</sup> D) 1.6 \times 10<sup>6</sup> E) 3.8 \times 10<sup>28</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab99_797e_a16d_5fbb5905faab_TB4499_11.jpg) 2 NO2(g)
2 NO2(g)Given fG [NO(g)] = +86.6 kJ/mol and fG [NO2(g)] = +51.2 kJ/mol.
A) 3.9 10-13
B) 1.0
C) 2.6 1012
D) 1.6 106
E) 3.8 1028

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The total entropy of the universe is always increasing.This is a statement of the ________ law of thermodynamics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the standard entropies for liquid water and steam to estimate the enthalpy of vaporization of water at its normal boiling point. S [H2O( ![Use the standard entropies for liquid water and steam to estimate the enthalpy of vaporization of water at its normal boiling point. \Delta S<sup> \circ </sup> [H<sub>2</sub>O( )] = 69.9 J/K.mol and \Delta S<sup> \circ </sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O(g)] = 188.8 J/K.mol.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab99_eeb1_a16d_fdc061ac3323_TB4499_11.jpg) )] = 69.9 J/K.mol and S [H2O(g)] = 188.8 J/K.mol.
)] = 69.9 J/K.mol and S [H2O(g)] = 188.8 J/K.mol.
![Use the standard entropies for liquid water and steam to estimate the enthalpy of vaporization of water at its normal boiling point. \Delta S<sup> \circ </sup> [H<sub>2</sub>O( )] = 69.9 J/K.mol and \Delta S<sup> \circ </sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O(g)] = 188.8 J/K.mol.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab99_eeb1_a16d_fdc061ac3323_TB4499_11.jpg) )] = 69.9 J/K.mol and S [H2O(g)] = 188.8 J/K.mol.
)] = 69.9 J/K.mol and S [H2O(g)] = 188.8 J/K.mol. 
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
________ changes only occur in the direction that leads toward chemical equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
For any process,the change in entropy of the universe equals the sum of the entropy changes for the system and for the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
At what temperature (in kelvin units)is the entropy of a pure crystal 0.0 J/K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The standard free energy change associated with the dissolution of ammonium nitrate in water is -6.73 kJ/mol at 298.15 K.
NH4NO3(s)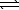 NH4NO3(aq)
NH4NO3(aq)
What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) 1.9 10-3
B) 6.6 10-2
C) 1.0
D) 15
E) 5.2 102
NH4NO3(s)
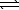 NH4NO3(aq)
NH4NO3(aq)What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) 1.9 10-3
B) 6.6 10-2
C) 1.0
D) 15
E) 5.2 102

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The standard free energy change for a chemical reaction is +13.3 kJ/mol.What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 125 C? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) 2.8 10-6
B) 2.0 10-5
C) 4.7 10-3
D) 1.8 10-2
E) 2.1 102
A) 2.8 10-6
B) 2.0 10-5
C) 4.7 10-3
D) 1.8 10-2
E) 2.1 102

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The solubility product equilibrium constant,Ksp,of silver bromide is
5.4 10-13 at 298 K.AgBr(s)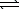 Ag+(aq)+ Br-(aq)
Ag+(aq)+ Br-(aq)
What is rG ? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) (-3.0 101) kJ/mol
B) (-5.87 )kJ/mol
C) 5.87 kJ/mol
D) 3.0 101 kJ/mol
E) 7.0 101 kJ/mol
5.4 10-13 at 298 K.AgBr(s)
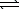 Ag+(aq)+ Br-(aq)
Ag+(aq)+ Br-(aq)What is rG ? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) (-3.0 101) kJ/mol
B) (-5.87 )kJ/mol
C) 5.87 kJ/mol
D) 3.0 101 kJ/mol
E) 7.0 101 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Does the formation of complex molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids from more simple molecules contradict the second law of thermodynamics?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In any chemical process,energy must be conserved.This is a statement of the ________ law of thermodynamics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction below at 25 C? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
MgCO3(s)![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction below at 25 <sup> \circ </sup>C? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol) MgCO<sub>3</sub>(s) MgO(s)+ CO<sub>2</sub>(g) Given \Delta <sub>f</sub>G<sup> \circ </sup>[MgCO<sub>3</sub>(s)] = -1028.2 kJ/mol, \Delta <sub>f</sub>G [MgO(s)] = -568.8 kJ/mol,and \Delta <sub>f</sub>G<sup> \circ </sup> [CO<sub>2</sub>(g)] = -394.4 kJ/mol.</strong> A) 4.0 \times 10<sup>-12</sup> B) 0.97 C) 1.0 D) 1.0 \times 10<sup>4</sup> E) 2.5 \times 10<sup>11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab99_797d_a16d_89fd859b0f8a_TB4499_11.jpg) MgO(s)+ CO2(g)
MgO(s)+ CO2(g)
Given fG [MgCO3(s)] = -1028.2 kJ/mol, fG [MgO(s)] = -568.8 kJ/mol,and fG [CO2(g)] = -394.4 kJ/mol.
A) 4.0 10-12
B) 0.97
C) 1.0
D) 1.0 104
E) 2.5 1011
MgCO3(s)
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction below at 25 <sup> \circ </sup>C? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol) MgCO<sub>3</sub>(s) MgO(s)+ CO<sub>2</sub>(g) Given \Delta <sub>f</sub>G<sup> \circ </sup>[MgCO<sub>3</sub>(s)] = -1028.2 kJ/mol, \Delta <sub>f</sub>G [MgO(s)] = -568.8 kJ/mol,and \Delta <sub>f</sub>G<sup> \circ </sup> [CO<sub>2</sub>(g)] = -394.4 kJ/mol.</strong> A) 4.0 \times 10<sup>-12</sup> B) 0.97 C) 1.0 D) 1.0 \times 10<sup>4</sup> E) 2.5 \times 10<sup>11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab99_797d_a16d_89fd859b0f8a_TB4499_11.jpg) MgO(s)+ CO2(g)
MgO(s)+ CO2(g)Given fG [MgCO3(s)] = -1028.2 kJ/mol, fG [MgO(s)] = -568.8 kJ/mol,and fG [CO2(g)] = -394.4 kJ/mol.
A) 4.0 10-12
B) 0.97
C) 1.0
D) 1.0 104
E) 2.5 1011

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The change in entropy for any process is not dependent upon the pathway by which the process occurs.In other words,the change in entropy for any process is a(n)________ function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Calculate rG for the following reaction at 425 C,
2 HI(g)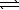 H2(g)+ I2(g)
H2(g)+ I2(g)
Given K = 0.018.(R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) 6.12 103 J
B) 1.05 104 J
C) 1.42 104 J
D) 2.33 104 J
E) 3.34 105 J
2 HI(g)
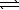 H2(g)+ I2(g)
H2(g)+ I2(g)Given K = 0.018.(R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) 6.12 103 J
B) 1.05 104 J
C) 1.42 104 J
D) 2.33 104 J
E) 3.34 105 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The standard free energy of formation of KBr(s)is -380.4 kJ/mol. rG° for the reaction 2KBr(s) 2K(s)+ Br2(l)is:
A) 760.8 kJ
B) 380.4 kJ
C) -760.8 kJ
D) -380.4 kJ
E) none of these
A) 760.8 kJ
B) 380.4 kJ
C) -760.8 kJ
D) -380.4 kJ
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Consider the following reaction:
2C(s)+ 2H2(g) C2H4(g); rH° = 52.47 kJ; rS° = -53.5 J/K at 298 K
What is the equilibrium constant at 298 K for this reaction? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) 1.0 10-12
B) 1.0
C) 1.6 10-3
D) 9.8 1011
E) 6.4 10-10
2C(s)+ 2H2(g) C2H4(g); rH° = 52.47 kJ; rS° = -53.5 J/K at 298 K
What is the equilibrium constant at 298 K for this reaction? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) 1.0 10-12
B) 1.0
C) 1.6 10-3
D) 9.8 1011
E) 6.4 10-10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



