Deck 26: Nuclear Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/79
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Nuclear Chemistry
1
Which of the following types of radiation will pass through a piece of paper,but will be stopped by 0.5 cm of lead?
A) ( )
B) ( )
C)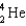
D) ( )
E) All of the above will pass through 0.5 cm of lead.
A) ( )
B) ( )
C)
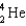
D) ( )
E) All of the above will pass through 0.5 cm of lead.
( )
2
What is the charge on a positron?
A) +2
B) +1
C) 0
D) -1
E) -2
A) +2
B) +1
C) 0
D) -1
E) -2
+1
3
Rank the following types of radiation from least penetrating to most penetrating: , or
A) ( < < )
B) ( < < )
C) ( < < )
D) ( < < < )
E) ( < < )
A) ( < < )
B) ( < < )
C) ( < < )
D) ( < < < )
E) ( < < )
( < < )
4
Which particle has the same mass as a beta particle?
A) a neutron
B) a proton
C) a gamma ray
D) an alpha particle
E) a positron
A) a neutron
B) a proton
C) a gamma ray
D) an alpha particle
E) a positron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What nucleus decays by successive , , emissions to produce uranium-236?
A)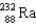
B)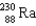
C)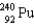
D)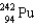
E)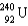
A)
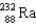
B)
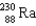
C)
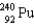
D)
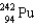
E)
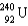

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In one type of decay process,a neutron in the nucleus is converted to a proton and another particle which is ejected (emitted)from the nucleus.What is the identity of the ejected particle?
A) positron
B) beta particle
C) alpha particle
D) deuteron
E) neutron
A) positron
B) beta particle
C) alpha particle
D) deuteron
E) neutron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When 61Cu undergoes electron capture,what is the product nuclide?
A) (60Ni)
B) (60Zn)
C) (60Cu)
D) (61Ni)
E) (61Zn)
A) (60Ni)
B) (60Zn)
C) (60Cu)
D) (61Ni)
E) (61Zn)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If a nucleus emits an alpha particle
A) its atomic number decreases by four and its mass number decreases by two.
B) its atomic number decreases by two and its mass number decreases by four.
C) its atomic number increases by two and its mass number decreases by two.
D) its atomic number is unchanged and its mass number is unchanged.
E) its atomic number is unchanged and its mass number decreases by four.
A) its atomic number decreases by four and its mass number decreases by two.
B) its atomic number decreases by two and its mass number decreases by four.
C) its atomic number increases by two and its mass number decreases by two.
D) its atomic number is unchanged and its mass number is unchanged.
E) its atomic number is unchanged and its mass number decreases by four.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If a nucleus gains a neutron and then undergoes beta emission,
A) its atomic number decreases by one and its mass number increases by one.
B) its atomic number is unchanged and its mass number increases by one.
C) both its atomic number and its mass number are unchanged.
D) its atomic number increases by one and its mass number is unchanged.
E) its atomic number increases by one and its mass number increases by one.
A) its atomic number decreases by one and its mass number increases by one.
B) its atomic number is unchanged and its mass number increases by one.
C) both its atomic number and its mass number are unchanged.
D) its atomic number increases by one and its mass number is unchanged.
E) its atomic number increases by one and its mass number increases by one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following reactions is an example of beta decay?
A)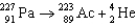
B)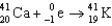
C)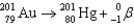
D)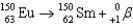
E)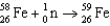
A)
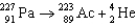
B)
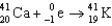
C)
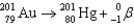
D)
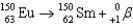
E)
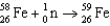

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following reactions is an example of beta emission?
A)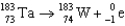
B)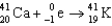
C)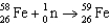
D)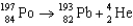
E)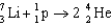
A)
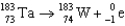
B)
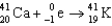
C)
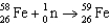
D)
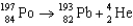
E)
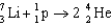

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How many alpha decays are required to convert 234U to 222Rn?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a nucleus undergoes positron particle emission
A) its atomic number decreases by four and its mass number decreases by two.
B) its atomic number decreases by two and its mass number decreases by four.
C) its atomic number increases by one and its mass number is unchanged.
D) its atomic number decreases by one and its mass number is unchanged.
E) its atomic number is unchanged and its mass number decreases by one.
A) its atomic number decreases by four and its mass number decreases by two.
B) its atomic number decreases by two and its mass number decreases by four.
C) its atomic number increases by one and its mass number is unchanged.
D) its atomic number decreases by one and its mass number is unchanged.
E) its atomic number is unchanged and its mass number decreases by one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following symbols represents a positron?
A)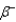
B)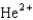
C)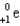
D)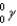
E)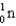
A)
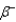
B)
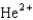
C)
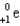
D)
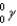
E)
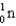

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the product nuclide if 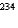 U undergoes five successive alpha decays?
U undergoes five successive alpha decays?
A)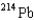
B)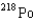
C)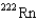
D)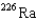
E)
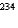 U undergoes five successive alpha decays?
U undergoes five successive alpha decays?A)
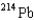
B)
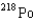
C)
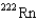
D)
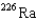
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When a nucleus undergoes radioactive decay,its new mass number is
A) always less than its original mass number.
B) never more than its original mass number.
C) never less than its original mass number.
D) always the same as its original mass number.
E) always more than its original mass number.
A) always less than its original mass number.
B) never more than its original mass number.
C) never less than its original mass number.
D) always the same as its original mass number.
E) always more than its original mass number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If astatine-207 decays by emission,followed by emission,followed by electron capture,what nucleus is produced?
A)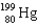
B)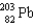
C)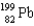
D)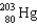
E)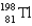
A)
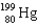
B)
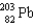
C)
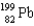
D)
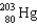
E)
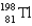

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which particle does the nuclide symbol  represent?
represent?
A) gamma ray
B) helium nucleus
C) electron
D) proton
E) positron
 represent?
represent?A) gamma ray
B) helium nucleus
C) electron
D) proton
E) positron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When the radioactive nuclide 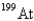
Undergoes alpha emission,what is the product nuclide?
A)
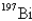
B)
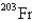
C)
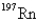
D)
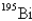
E)
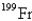
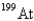
Undergoes alpha emission,what is the product nuclide?
A)
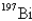
B)
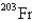
C)
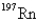
D)
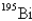
E)
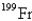

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a nucleus decays by successive , , particle emissions,its atomic number will
A) decrease by four.
B) decrease by two.
C) increase by four.
D) increase by two.
E) be unchanged.
A) decrease by four.
B) decrease by two.
C) increase by four.
D) increase by two.
E) be unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The half-life of 42K is 12.5 h.How much will remain after 83 h if the original sample contained 256 g of 42K?
A) 22 g
B) 2.6 g
C) 15 g
D) 20 g
E) 14 g
A) 22 g
B) 2.6 g
C) 15 g
D) 20 g
E) 14 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The molar nuclear mass of fluorine-19 is 18.99840 g/mol.The molar mass of a proton is 1.007825 g/mol.The molar mass of a neutron is 1.008665 g/mol.Calculate the binding energy (in J/mol)of F-19.(c = 2.998 108 m/s)
A) 6.753 1012 J/mol
B) 7.131 1012 J/mol
C) 1.426 1013 J/mol
D) 8.609 1014 J/mol
E) 8.538 1014 J/mol
A) 6.753 1012 J/mol
B) 7.131 1012 J/mol
C) 1.426 1013 J/mol
D) 8.609 1014 J/mol
E) 8.538 1014 J/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The point of maximum stability in the binding energy curve occurs in the vicinity of which one of the following isotopes?
A)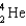
B)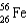
C)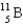
D)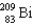
E)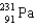
A)
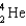
B)
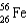
C)
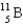
D)
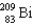
E)
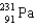

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When 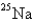
Undergoes beta emission,what is the product nuclide?
A)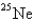
B)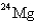
C)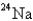
D)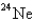
E)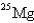
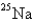
Undergoes beta emission,what is the product nuclide?
A)
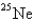
B)
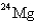
C)
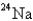
D)
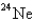
E)
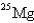

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When the radioactive nuclide 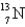
Undergoes positron emission,what is the product nuclide?
A)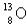
B)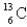
C)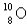
D)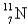
E)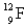
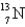
Undergoes positron emission,what is the product nuclide?
A)
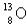
B)
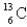
C)
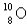
D)
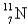
E)
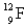

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
By what (single step)process does polonium-218 change to lead-214?
A) ( ) particle emission
B) ( ) particle emission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) neutron capture
A) ( ) particle emission
B) ( ) particle emission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) neutron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The bismuth-209 nucleus has a binding energy per nucleon of 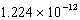 J.Determine the difference in mass between one mole of bismuth-209 nuclei and the component nucleons of which it is made.
J.Determine the difference in mass between one mole of bismuth-209 nuclei and the component nucleons of which it is made.
A) 1.71 10-3 kg
B) 3.92 10-8 kg
C) 8.20 10-6 kg
D) 2.56 10-10 kg
E) 6.81 10-4 kg
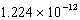 J.Determine the difference in mass between one mole of bismuth-209 nuclei and the component nucleons of which it is made.
J.Determine the difference in mass between one mole of bismuth-209 nuclei and the component nucleons of which it is made.A) 1.71 10-3 kg
B) 3.92 10-8 kg
C) 8.20 10-6 kg
D) 2.56 10-10 kg
E) 6.81 10-4 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Calculate the mass defect for an atom of 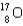 whose isotope mass is 16.9991 g/mol.mass of proton (
whose isotope mass is 16.9991 g/mol.mass of proton ( 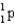 )
)
1)00783 g/mol.mass of neutron (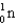 )
)
1)00867 g/mol.
A) 0.153 g/mol
B) 0.152 g/mol
C) 0.148 g/mol
D) 0.147 g/mol
E) 0.142 g/mol
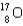 whose isotope mass is 16.9991 g/mol.mass of proton (
whose isotope mass is 16.9991 g/mol.mass of proton ( 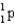 )
)1)00783 g/mol.mass of neutron (
 )
)1)00867 g/mol.
A) 0.153 g/mol
B) 0.152 g/mol
C) 0.148 g/mol
D) 0.147 g/mol
E) 0.142 g/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Calculate the energy released (per mole of deuterium consumed)for the following fusion reaction, 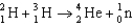 given the following molar masses of nucleons and nuclei.(c = 2.998 108 m/s)
given the following molar masses of nucleons and nuclei.(c = 2.998 108 m/s)
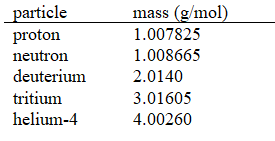
A) 5.63 106 J/mol
B) 1.69 1015 J/mol
C) 4.62 1013 J/mol
D) 8.44 1011 J/mol
E) 1.69 1012 J/mol
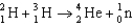 given the following molar masses of nucleons and nuclei.(c = 2.998 108 m/s)
given the following molar masses of nucleons and nuclei.(c = 2.998 108 m/s)
A) 5.63 106 J/mol
B) 1.69 1015 J/mol
C) 4.62 1013 J/mol
D) 8.44 1011 J/mol
E) 1.69 1012 J/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Radioactive isotopes with greater than 83 protons in the nucleus that sit below the band of stability are most likely to decay by what mode(s)?
A) alpha emission
B) beta emission
C) positron emission or alpha emission
D) electron capture or beta emission
E) electron capture or positron emission
A) alpha emission
B) beta emission
C) positron emission or alpha emission
D) electron capture or beta emission
E) electron capture or positron emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
By what (single step)process does americium-241 decay to neptunium-237?
A) ( ) particle emission
B) ( ) particle emission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) neutron capture
A) ( ) particle emission
B) ( ) particle emission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) neutron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the nuclear binding energy per nucleon of a 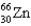 nucleus? (c = 3.00 108 m/s,1 amu = 1.66054 10-27 kg)
nucleus? (c = 3.00 108 m/s,1 amu = 1.66054 10-27 kg)

A)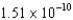 J/nucleon
J/nucleon
B)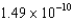 J/nucleon
J/nucleon
C)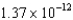 J/nucleon
J/nucleon
D)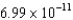 J/nucleon
J/nucleon
E)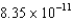 J/nucleon
J/nucleon
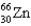 nucleus? (c = 3.00 108 m/s,1 amu = 1.66054 10-27 kg)
nucleus? (c = 3.00 108 m/s,1 amu = 1.66054 10-27 kg)
A)
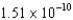 J/nucleon
J/nucleonB)
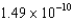 J/nucleon
J/nucleonC)
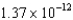 J/nucleon
J/nucleonD)
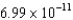 J/nucleon
J/nucleonE)
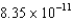 J/nucleon
J/nucleon
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A certain radioactive isotope has a rate constant of decay of 2.74 10-2 min-1.Calculate the time required for a sample of this isotope to decay to one-fourth of its initial value.
A) 25.3 min
B) 31.6 min
C) 0.0548 min
D) 50.6 min
E) 2.74 min
A) 25.3 min
B) 31.6 min
C) 0.0548 min
D) 50.6 min
E) 2.74 min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following nuclides has the highest nuclear binding energy per nucleon?
A)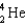
B)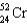
C)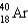
D)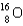
E)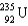
A)
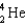
B)
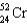
C)
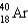
D)
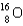
E)
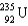

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Write a balanced reaction for the decay of barium-127 by positron emission.
A)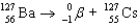
B)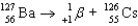
C)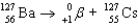
D)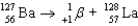
E)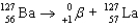
A)
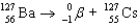
B)
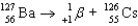
C)
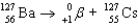
D)
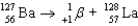
E)
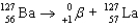

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
All of the following statements concerning nuclei are true EXCEPT
A) only hydrogen-1 and helium-3 have more protons than neutrons.
B) from He to Ca,stable nuclei have roughly equal numbers of protons and neutrons.
C) elements with odd atomic numbers have more stable isotopes than do those with even atomic numbers.
D) the neutron to proton ratio in stable nuclei increases as mass increases.
E) more stable isotopes have an even number of neutrons than an odd number.
A) only hydrogen-1 and helium-3 have more protons than neutrons.
B) from He to Ca,stable nuclei have roughly equal numbers of protons and neutrons.
C) elements with odd atomic numbers have more stable isotopes than do those with even atomic numbers.
D) the neutron to proton ratio in stable nuclei increases as mass increases.
E) more stable isotopes have an even number of neutrons than an odd number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is the most probable mode of radioactive decay for 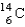 ?
?
A) beta emission
B) gamma emission
C) electron capture
D) alpha emission
E) positron emission
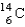 ?
?A) beta emission
B) gamma emission
C) electron capture
D) alpha emission
E) positron emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
All isotopes with atomic number greater than ____ are radioactive.
A) 43
B) 80
C) 86
D) 83
E) 90
A) 43
B) 80
C) 86
D) 83
E) 90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What nucleus decays by beta emission to produce chlorine-35?
A)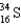
B)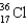
C)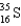
D)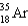
E)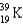
A)
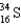
B)
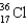
C)
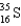
D)
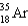
E)
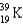

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the percent activity of a radioactive sample (relative to its original activity)that has undergone two half-lives of decay?
A) 25.0%
B) 12.5%
C) 6.25%
D) 3.13%
E) 75.0%
A) 25.0%
B) 12.5%
C) 6.25%
D) 3.13%
E) 75.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If a tree dies and the trunk remains undisturbed for 14874 years,what percentage of original 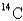 is still present? (half-life of
is still present? (half-life of 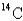
= 5730 years)
A) 33%
B) 25%
C) 83%
D) 17%
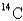 is still present? (half-life of
is still present? (half-life of 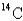
= 5730 years)
A) 33%
B) 25%
C) 83%
D) 17%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What role do the cadmium control rods play in a fission reactor?
A) The rods control the rate of fission by absorbing neutrons.
B) The cadmium combines with spent uranium fuel to produce a non-radioactive product.
C) The rods focus the neutrons toward the center of the reactor.
D) The cadmium acts as a catalyst,enabling fission to occur at lower temperatures.
E) The rods move forward and backward,driving the pistons that turn the turbines.
A) The rods control the rate of fission by absorbing neutrons.
B) The cadmium combines with spent uranium fuel to produce a non-radioactive product.
C) The rods focus the neutrons toward the center of the reactor.
D) The cadmium acts as a catalyst,enabling fission to occur at lower temperatures.
E) The rods move forward and backward,driving the pistons that turn the turbines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A sample of a radioactive isotope is found to have lost 14.0% of its original activity after 8.67 days.What is the rate constant for decay of this isotope?
A) 0.0174 d-1
B) 0.227 d-
C) 1.31 d-1
D) 0.0151 d-1
E) 0.514 d-1
A) 0.0174 d-1
B) 0.227 d-
C) 1.31 d-1
D) 0.0151 d-1
E) 0.514 d-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years.If a sample initially contains 2.67 mg carbon-14,what mass remains in the sample after 2.40 104 years?
A) 0.0 mg
B) 0.17 mg
C) 0.92 mg
D) 0.15 mg
E) 0.64 mg
A) 0.0 mg
B) 0.17 mg
C) 0.92 mg
D) 0.15 mg
E) 0.64 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
One means of enriching the percentage of uranium-235 for use as nuclear fuel is ____.
A) liquid distillation
B) gaseous centrifugation
C) mass spectroscopy
D) gamma ray bombardment
E) ion chromatography
A) liquid distillation
B) gaseous centrifugation
C) mass spectroscopy
D) gamma ray bombardment
E) ion chromatography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When 235U collides with one neutron,fission occurs.What is one possible set of products?
A) four neutrons,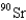
,and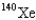
B) four neutrons,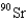
,and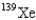
C) four neutrons,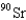
,and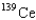
D) four neutrons,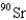
,and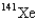
E) four neutrons,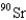
,and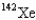
A) four neutrons,
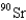
,and
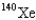
B) four neutrons,
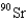
,and
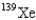
C) four neutrons,
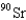
,and
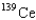
D) four neutrons,
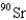
,and
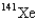
E) four neutrons,
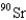
,and
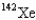

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The half-life for the spontaneous decay of technetium-99m is 6.0 hours.How much of a 0.20 g sample of this isotope remains after 4.5 hours?
A) 0.05 g
B) 0.08 g
C) 0.12 g
D) 0.15 g
E) 0.20 g
A) 0.05 g
B) 0.08 g
C) 0.12 g
D) 0.15 g
E) 0.20 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A sample of phosphorus-32 is found to have an activity of 885 disintegrations per hour (dph).After 25 hours the activity has decreased to 841 dph.What is the rate constant for the decay of phosphorus-32?
A) 0.0038 hr-1
B) 0.0020 hr-1
C) 0.15 hr-1
D) 490 hr-1
E) 0.12 hr-1
A) 0.0038 hr-1
B) 0.0020 hr-1
C) 0.15 hr-1
D) 490 hr-1
E) 0.12 hr-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A Geiger-M  ller counter measures radiation by detecting
ller counter measures radiation by detecting
A) cations produced from radiation colliding with phosphor gases.
B) alpha and beta particles as they strike a detector window.
C) the increase in temperature when a gas is struck by radiation.
D) flashes of light emitted from a phosphor affected by radiation.
E) electrons released when gas atoms are ionized by the radiation.
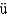 ller counter measures radiation by detecting
ller counter measures radiation by detectingA) cations produced from radiation colliding with phosphor gases.
B) alpha and beta particles as they strike a detector window.
C) the increase in temperature when a gas is struck by radiation.
D) flashes of light emitted from a phosphor affected by radiation.
E) electrons released when gas atoms are ionized by the radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Uranium-235 has a half-life of 7.04 108 years.How many years will it take for 99.9% of a U-235 sample to decay?
A) 7.0 105 yr
B) 1.0 106 yr
C) 4.7 109 yr
D) 4.9 109 yr
E) 7.0 109 yr
A) 7.0 105 yr
B) 1.0 106 yr
C) 4.7 109 yr
D) 4.9 109 yr
E) 7.0 109 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Complete the following fission reaction. 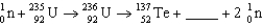
A)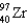
B)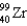
C)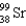
D)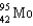
E)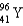
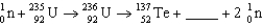
A)
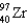
B)
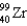
C)
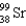
D)
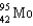
E)
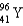

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Strontium-90 is produced in nuclear fission reactors.If ingested it can replace calcium in the bones.The half-life of 90Sr is 27.7 years.If the activity of 90Sr in the bones of an exposed person were 90 disintegrations per second,how long would it take the activity of 90Sr to decrease to 7.8 disintegrations per second?
A) 98 years
B) 67 years
C) 46 years
D) 56 years
E) 77 years
A) 98 years
B) 67 years
C) 46 years
D) 56 years
E) 77 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which three steps,placed in the proper order,are required for a nuclear chain reaction?
A) propagation,equilibration,and termination
B) propagation,oxidation,equilibration
C) equilibration,propagation,termination
D) initiation,oxidation,propagation
E) initiation,propagation,and termination
A) propagation,equilibration,and termination
B) propagation,oxidation,equilibration
C) equilibration,propagation,termination
D) initiation,oxidation,propagation
E) initiation,propagation,and termination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following elements undergoes nuclear fusion to provide the primary source of energy from the sun?
A) helium
B) uranium
C) hydrogen
D) carbon
E) boron
A) helium
B) uranium
C) hydrogen
D) carbon
E) boron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements is/are CORRECT?
1)The transuranium elements are created in a nuclear reaction sequence that begins with bombardment of a lighter nucleus with low energy helium nuclei.
2)A low energy neutron may be captured by a nucleus,giving a product in which the mass number is increased by one unit.
3)Nuclear reactions involving neutron capture followed by gamma ray emission are referred to as (n, )reactions.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3
1)The transuranium elements are created in a nuclear reaction sequence that begins with bombardment of a lighter nucleus with low energy helium nuclei.
2)A low energy neutron may be captured by a nucleus,giving a product in which the mass number is increased by one unit.
3)Nuclear reactions involving neutron capture followed by gamma ray emission are referred to as (n, )reactions.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which two nuclei are the two fissionable isotopes most commonly used in nuclear reactors?
A)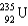 and
and 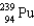
B)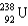 and
and 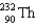
C)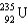 and
and 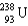
D)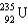 and
and 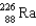
E)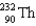 and
and 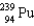
A)
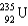 and
and 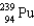
B)
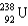 and
and 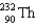
C)
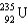 and
and 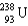
D)
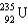 and
and 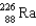
E)
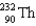 and
and 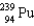

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 4.50-mg sample of a newly discovered radioactive nuclide was analyzed and found to contain only 3.25 mg after a period of 30.3 h.What is the half-life of the nuclide?
A) 76.3 h
B) 64.5 h
C) 73.8 h
D) 11.1 h
E) 17.6 h
A) 76.3 h
B) 64.5 h
C) 73.8 h
D) 11.1 h
E) 17.6 h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A radioactive isotope undergoes decay by emission of a positron.After 2.00 h,6.720% of the initial amount of the isotope remains undecayed.What is the half-life of this isotope?
A) 45.0 min
B) 30.8 min
C) 90.0 min
D) 15.0 min
E) 60.0 min
A) 45.0 min
B) 30.8 min
C) 90.0 min
D) 15.0 min
E) 60.0 min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following statements is/are CORRECT?
1)Naturally occurring isotopes account for only a small fraction of known radioactive isotopes.
2)A few radioactive isotopes with long half-lives,such as U-235 and U-238,are found in nature.
3)Trace quantities of some short-lived radioactive isotopes,such as C-14,are found in nature because they are formed continuously by nuclear reactions.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1,2,and 3
1)Naturally occurring isotopes account for only a small fraction of known radioactive isotopes.
2)A few radioactive isotopes with long half-lives,such as U-235 and U-238,are found in nature.
3)Trace quantities of some short-lived radioactive isotopes,such as C-14,are found in nature because they are formed continuously by nuclear reactions.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The rate constant for the decay of a radioactive isotope is 4.231 10-3 / day.What is the half-life of this isotope?
A) 327.6 days
B) 409.5 days
C) 81.90 days
D) 163.8 days
E) none of these
A) 327.6 days
B) 409.5 days
C) 81.90 days
D) 163.8 days
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Complete the following fusion reaction. 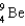 +
+ 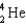
____ +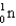
A)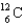
B)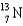
C)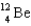
D)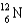
E)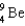
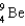 +
+ 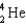
____ +
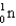
A)
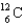
B)
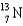
C)
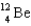
D)
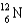
E)
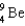

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What particle(s)are produced in the following reaction? 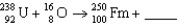
A)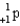
B)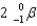
C)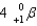
D)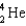
E)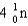
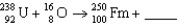
A)
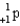
B)
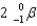
C)
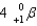
D)
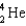
E)
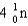

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain the treatment named boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Explain the difference between 1 rad and 1 rem of radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
At the high temperatures necessary for fusion,matter exists as a plasma,which is
A) a liquid form of a radioactive element.
B) a gaseous cloud of electrons and positrons.
C) a mixture of unbound nuclei and electrons.
D) an equal mixture of matter and anti-matter.
E) a dense solid composed of neutrons.
A) a liquid form of a radioactive element.
B) a gaseous cloud of electrons and positrons.
C) a mixture of unbound nuclei and electrons.
D) an equal mixture of matter and anti-matter.
E) a dense solid composed of neutrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT),boron-10 is injected into a tumor.When the tumor is irradiated with neutrons,boron nuclei capture the neutrons and disintegrate into two particles.These particles are lithium-7 and a(n)____.
A) alpha particle
B) beta particle
C) positron
D) deuterium nuclei
E) helium nuclei
A) alpha particle
B) beta particle
C) positron
D) deuterium nuclei
E) helium nuclei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In positron emission tomography (PET),a positron emitted from an unstable isotope travels a short distance before it is annihilated by
A) an electron,creating a proton that is detected by the instrument.
B) a neutron,creating two gamma rays that travel in opposite directions.
C) an electron,creating two gamma rays that travel in opposite directions.
D) an alpha particle,creating two protons that travel in opposite directions.
E) gamma ray,creating an electron that is detected by the instrument.
A) an electron,creating a proton that is detected by the instrument.
B) a neutron,creating two gamma rays that travel in opposite directions.
C) an electron,creating two gamma rays that travel in opposite directions.
D) an alpha particle,creating two protons that travel in opposite directions.
E) gamma ray,creating an electron that is detected by the instrument.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A 0.20-mL sample of a solution containing 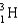 that produces 3.7 103 cps is injected into the bloodstream of an animal.After allowing circulatory equilibrium to be established,a 0.20-mL sample of blood is found to have an activity of 31 cps.Calculate the blood volume of the animal.
that produces 3.7 103 cps is injected into the bloodstream of an animal.After allowing circulatory equilibrium to be established,a 0.20-mL sample of blood is found to have an activity of 31 cps.Calculate the blood volume of the animal.
A) 24 mL
B) 0.60 L
C) 12 mL
D) 119 mL
E) none of these
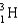 that produces 3.7 103 cps is injected into the bloodstream of an animal.After allowing circulatory equilibrium to be established,a 0.20-mL sample of blood is found to have an activity of 31 cps.Calculate the blood volume of the animal.
that produces 3.7 103 cps is injected into the bloodstream of an animal.After allowing circulatory equilibrium to be established,a 0.20-mL sample of blood is found to have an activity of 31 cps.Calculate the blood volume of the animal.A) 24 mL
B) 0.60 L
C) 12 mL
D) 119 mL
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following types of radiation has the greatest quality factor?
A) beta particles
B) alpha particles emitted within the body
C) gamma rays
D) low energy protons
E) low energy neutrons
A) beta particles
B) alpha particles emitted within the body
C) gamma rays
D) low energy protons
E) low energy neutrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements concerning neutron activation analysis is/are CORRECT?
1)In neutron activation analysis,a neutron is ejected from an atom creating a new isotope that is one mass unit lower.
2)Neutron activation analysis is destructive,but requires less than 1 g of sample.
3)Neutron activation analysis creates isotopes in the excited state that emit gamma rays to return to the ground state.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3
1)In neutron activation analysis,a neutron is ejected from an atom creating a new isotope that is one mass unit lower.
2)Neutron activation analysis is destructive,but requires less than 1 g of sample.
3)Neutron activation analysis creates isotopes in the excited state that emit gamma rays to return to the ground state.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following isotopes is used in the treatment of thyroid disorders?
A)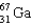
B)
C)
D)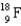
E)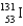
A)
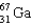
B)

C)

D)
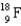
E)
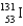

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
All isotopes of atomic number greater than ________ are unstable and radioactive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following statements concerning radiation absorption by living tissue is/are CORRECT?
1)The "quality factor" takes into account the differences in damaging power of the various forms of radiation.
2)One gray denotes the absorption of 1 joule per kilogram of tissue.
3)The SI unit for biological damage is a sievert (Sv),which is determined by multiplying grays by the quality factor.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3
1)The "quality factor" takes into account the differences in damaging power of the various forms of radiation.
2)One gray denotes the absorption of 1 joule per kilogram of tissue.
3)The SI unit for biological damage is a sievert (Sv),which is determined by multiplying grays by the quality factor.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A unit used to quantify biological damage is called the ________ or rem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Neutron ________ analysis is a non-destructive process in which a sample is irradiated with neutrons.The neutrons react with nuclei to form isotopes with masses one unit higher than the original nuclei.The nuclei are formed in excited states and they emit gamma radiation that can be used to both identify the presence of an element and quantify how much is present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The becquerel is an SI unit for the measurement of radiation.One Bq represents
A) 1 J energy absorbed per kg of tissue.
B) 3.7 1010 disintegrations per second.
C) 1 disintegration per second.
D) 0.01 J energy absorbed per kg of tissue.
E) 1 calorie energy absorbed per kg of tissue.
A) 1 J energy absorbed per kg of tissue.
B) 3.7 1010 disintegrations per second.
C) 1 disintegration per second.
D) 0.01 J energy absorbed per kg of tissue.
E) 1 calorie energy absorbed per kg of tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Technetium-99m is routinely used in medical imaging.The italics m means the nucleus is ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Complete the following fusion reaction. 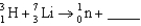
A)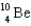
B)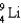
C)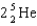
D)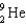
E)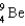
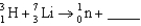
A)
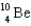
B)
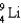
C)
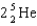
D)
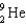
E)
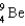

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What percentage of the world's electricity is supplied by nuclear fusion reactors?
A) 0%
B) 3%
C) 8%
D) 17%
E) 39%
A) 0%
B) 3%
C) 8%
D) 17%
E) 39%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



