Deck 6: Elasticity of Demand and Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/118
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Elasticity of Demand and Supply
1
When a 2 per cent increase in price generates a greater than 2 per cent decrease in quantity demanded, then:
A) demand is price inelastic.
B) total revenue increases.
C) demand is positively sloped.
D) total revenue decreases.
A) demand is price inelastic.
B) total revenue increases.
C) demand is positively sloped.
D) total revenue decreases.
D
2
On a part of the demand curve where the price elasticity of demand is less than 1, a decrease in price:
A) is impossible.
B) will increase total revenue.
C) decreases quantity demanded.
D) will reduce total revenue.
A) is impossible.
B) will increase total revenue.
C) decreases quantity demanded.
D) will reduce total revenue.
D
3
Suppose the price of a bus ticket rises from $2.75 to $3 and the number of tickets sold falls from 10 000 to 8500, the price elasticity of demand is:
A) elastic.
B) unitary elastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) inelastic.
A) elastic.
B) unitary elastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) inelastic.
A
4
If demand price elasticity measures 2, this implies that consumers would:
A) buy twice as much of the product if the price drops 10 per cent.
B) require a 2 per cent drop in price to increase their purchases by 1 per cent.
C) buy 2 per cent more of the product in response to a 1 per cent drop in price.
D) require at least a $2 increase in price before showing any response to the price increase.
A) buy twice as much of the product if the price drops 10 per cent.
B) require a 2 per cent drop in price to increase their purchases by 1 per cent.
C) buy 2 per cent more of the product in response to a 1 per cent drop in price.
D) require at least a $2 increase in price before showing any response to the price increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The short-run price elasticity of demand for airline travel is 0.05, while the long-run elasticity is 2.36. This means that a significant increase in airline ticket prices will cause airline companies to:
A) collect less revenue from short-notice travellers.
B) collect more revenue from travellers who book well in advance.
C) lose money on short-notice travellers.
D) collect less revenue from travellers who book well in advance.
A) collect less revenue from short-notice travellers.
B) collect more revenue from travellers who book well in advance.
C) lose money on short-notice travellers.
D) collect less revenue from travellers who book well in advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the price elasticity of demand for football tickets is estimated to be 4.5, then a 10 per cent increase in football ticket prices would be expected to cause a:
A) 4.5 per cent decrease in quantity demanded.
B) 4.5 per cent increase in quantity demanded.
C) 45 per cent decrease in quantity demanded.
D) 45 per cent increase in quantity demanded.
A) 4.5 per cent decrease in quantity demanded.
B) 4.5 per cent increase in quantity demanded.
C) 45 per cent decrease in quantity demanded.
D) 45 per cent increase in quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Price elasticity of demand measures:
A) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in income.
B) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in consumers'
Preferences.
C) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a one percent change in price.
D) the reduction in the quantity demanded of a good when the price is reduced.
A) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in income.
B) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in consumers'
Preferences.
C) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a one percent change in price.
D) the reduction in the quantity demanded of a good when the price is reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If Sam, the Pizza Man, lowers the price of his pizzas from $6 to $5 and finds that sales increase from 400 to 600 pizzas per week, then the demand for Sam's pizzas in this range is:
A) 3.5.
B) 0.5.
C)1.
D) 2.2.
A) 3.5.
B) 0.5.
C)1.
D) 2.2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If Pete raises the price of his muffins from $2 to $3 and his sales revenue increases from $35 000 to $38 000, then:
A) the demand for Pete's muffins in this range is price elastic.
B) the demand for Pete's muffins in this range is price inelastic.
C) the demand for Pete's muffins in this range is unit elastic.
D) the percentage change in quantity demanded must exceed the percentage change in product price.
A) the demand for Pete's muffins in this range is price elastic.
B) the demand for Pete's muffins in this range is price inelastic.
C) the demand for Pete's muffins in this range is unit elastic.
D) the percentage change in quantity demanded must exceed the percentage change in product price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Karin is a popular hairdresser in a small town. She charges her clients $30 for a haircut and earned $60 000 last year only doing haircuts. This year, Karin decided to increase the price for the haircut by $5. What is the elasticity of demand for Karin's haircut, if the number of her clients has dropped to 1800 per year?
A) It is approximately equal to 2.3.
B) It is approximately equal to 1.68.
C) It is approximately equal to 1.
D) It is approximately equal to 0.68.
A) It is approximately equal to 2.3.
B) It is approximately equal to 1.68.
C) It is approximately equal to 1.
D) It is approximately equal to 0.68.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Price elasticity of demand can be:
A) only greater than 1.
B) equal to 1, greater than 1, less than 1.
C) only less than 1.
D) only equal to 1.
A) only greater than 1.
B) equal to 1, greater than 1, less than 1.
C) only less than 1.
D) only equal to 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Using the midpoint formula, what would be the price elasticity of demand for a gallbladder operation if the number of operations fell from 7000 to 4000 per week after its price increased from $6000 to $15 000?
A) 0.254.
B) 0.636.
C) 0.801.
D) 1.25.
A) 0.254.
B) 0.636.
C) 0.801.
D) 1.25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An economist estimates that 0.67 is the price elasticity of demand for disposable diapers. This suggests that disposable diaper producers could:
A) advertise more to raise the price elasticity of demand.
B) encourage more parents to use cloth diapers.
C) lower the price of disposable diapers to raise more revenue.
D) raise the price of disposable diapers to raise more revenue.
A) advertise more to raise the price elasticity of demand.
B) encourage more parents to use cloth diapers.
C) lower the price of disposable diapers to raise more revenue.
D) raise the price of disposable diapers to raise more revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the statements below does not describe a demand curve that is unit elastic?
A) The percentage change in the quantity demanded equals the percentage change in product price.
B) An increase in product price will not change total revenue.
C) The price elasticity of demand equals one.
D) A change in price does not change quantity demanded.
A) The percentage change in the quantity demanded equals the percentage change in product price.
B) An increase in product price will not change total revenue.
C) The price elasticity of demand equals one.
D) A change in price does not change quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The president of Tucker Motors says, 'Lowering the price won't sell a single additional Tucker car'. The president believes that the price elasticity of demand is:
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) unitary elastic.
D) elastic.
Inelastic.
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) unitary elastic.
D) elastic.
Inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The price elasticity of demand for a vertical demand curve is:
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) unitary elastic.
D) elastic.
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) unitary elastic.
D) elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose the price of a bus ticket rises from $2.75 to $3.75 and the number of tickets sold falls from 10 000 to 8500, the price elasticity of demand, in absolute term, is:
A) 0.527.
B)1.
C) -0.527.
D) -1.
A) 0.527.
B)1.
C) -0.527.
D) -1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A health club sells 100 memberships when the monthly price is $70 and 120 memberships when the monthly price is $60. The price elasticity of demand for memberships at this health club is (using the midpoint formula):
A) 0.25.
B) 0.65.
C) 1.18.
D) 1.
A) 0.25.
B) 0.65.
C) 1.18.
D) 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the price elasticity of demand for a product measures 0.45, then:
A) this good has many available substitutes.
B) this good must be a non-essential good.
C) this good is a high-priced good.
D) this good is demand price inelastic.
A) this good has many available substitutes.
B) this good must be a non-essential good.
C) this good is a high-priced good.
D) this good is demand price inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose the price of a bus ticket rises from $2.75 to $3 and the number of tickets sold falls from 10 000 to 8500, the total revenue test:
A) shows a decrease in total revenue.
B) cannot be calculated.
C) shows no change in total revenue.
D) shows an increase in total revenue.
A) shows a decrease in total revenue.
B) cannot be calculated.
C) shows no change in total revenue.
D) shows an increase in total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Narrbegin Exhibit 5.1 Demand curves 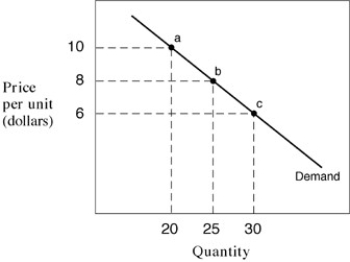
-In Exhibit 5.1, between points b and c, the price elasticity of demand measures
A) 4.27.
B) 1.5.
C) 1.56.
D) 0.636.

-In Exhibit 5.1, between points b and c, the price elasticity of demand measures
A) 4.27.
B) 1.5.
C) 1.56.
D) 0.636.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Cars have higher price elasticity of demand than tyres and tubes because:
A) tyres and tubes and cars are substitutes.
B) tyres and tubes and cars are complements.
C) cars are a luxury and tyres and tubes are a necessity.
D) tyres and tubes are a luxury and cars are a necessity.
A) tyres and tubes and cars are substitutes.
B) tyres and tubes and cars are complements.
C) cars are a luxury and tyres and tubes are a necessity.
D) tyres and tubes are a luxury and cars are a necessity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The less important the good is in everyday consumption and the less the percentage of a budget that is spent on the good:
A) the greater will be the price elasticity of the good.
B) the greater will be the effect of the price increase on the decrease in the demand.
C) the smaller will be the price elasticity of the good.
D) the smaller will be the effect of the price increase on the increase in the demand.
A) the greater will be the price elasticity of the good.
B) the greater will be the effect of the price increase on the decrease in the demand.
C) the smaller will be the price elasticity of the good.
D) the smaller will be the effect of the price increase on the increase in the demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Narrbegin Exhibit 5.1 Demand curves 
-In Exhibit 5.1, the demand curve between points b and c is:
A) price elastic.
B) price inelastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) perfectly elastic.

-In Exhibit 5.1, the demand curve between points b and c is:
A) price elastic.
B) price inelastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a supplier faces a perfectly horizontal demand curve and sets his price slightly higher than the demand curve itself, he can expect:
A) no change in his total revenues.
B) everyone to begin buying his product.
C) a complete loss of revenues.
D) a new demand curve.
A) no change in his total revenues.
B) everyone to begin buying his product.
C) a complete loss of revenues.
D) a new demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Price elasticity of demand can be:
A) greater than 100 per cent.
B) equal to 100 per cent.
C) less than 1.
D) less than 100 per cent.
A) greater than 100 per cent.
B) equal to 100 per cent.
C) less than 1.
D) less than 100 per cent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consumers will reduce their demand if they believe that the price increase is:
A) negligible.
B) affordable.
C) avoidable.
D) temporary.
A) negligible.
B) affordable.
C) avoidable.
D) temporary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If a farmer lowers the price of his product from $15 to $5 and finds that sales increase from 500 to 1000 units per week, then the demand for the farmer's product in this range is (assuming midpoint formula for price elasticity of demand):
A) price inelastic.
B) price elastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) cross elastic.
A) price inelastic.
B) price elastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) cross elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Narrbegin Exhibit 5.1 Demand curves 
-In Exhibit 5.1, the demand curve between points a and b is:
A) price elastic.
B) price inelastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) perfectly elastic.

-In Exhibit 5.1, the demand curve between points a and b is:
A) price elastic.
B) price inelastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Any change in price along a perfectly inelastic demand curve produces:
A) greater change in the quantity demanded.
B) less change in the quantity demanded.
C) no change in the quantity demanded.
D) infinite change in the quantity demanded.
A) greater change in the quantity demanded.
B) less change in the quantity demanded.
C) no change in the quantity demanded.
D) infinite change in the quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the price of Pepsi-Cola increases from 40 cents to 50 cents per bottle and the quantity demanded decreases from 100 bottles to 50 bottles, then according to the averaging equation, the value of price elasticity of demand for Pepsi-Cola is:
A) 0.5.
B) 0.25.
C)1.
D) 3.
A) 0.5.
B) 0.25.
C)1.
D) 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If an increase in the price of a product from $1 to $2 per unit leads to a decrease in the quantity demanded from 100 to 80 units, then according to the averaging equation, the value of price elasticity of demand in absolute terms is:
A) 0.33.
B) 2.33.
C) 0.25.
D) 3.
A) 0.33.
B) 2.33.
C) 0.25.
D) 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The price elasticity of demand formula includes:
A) percentage change in quantity demanded.
B) percentage change in quantity supplied.
C) difference in quantity demanded.
D) difference in price.
A) percentage change in quantity demanded.
B) percentage change in quantity supplied.
C) difference in quantity demanded.
D) difference in price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Petrol has inelastic price elasticity of demand in both the short and long run but chinaware has elastic price elasticity of demand in the both short and long run because:
A) petrol is more important than chinaware.
B) petrol is a necessity and chinaware is a luxury.
C) petrol cannot be compared to chinaware.
D) petrol is a luxury and chinaware is a necessity.
A) petrol is more important than chinaware.
B) petrol is a necessity and chinaware is a luxury.
C) petrol cannot be compared to chinaware.
D) petrol is a luxury and chinaware is a necessity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Narrbegin Exhibit 5.1 Demand curves 
-In Exhibit 5.1, between points a and c, the price elasticity of demand measures
A) 4.1.
B) 1.8.
C) 1.5.
D) 0.8.

-In Exhibit 5.1, between points a and c, the price elasticity of demand measures
A) 4.1.
B) 1.8.
C) 1.5.
D) 0.8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Price elasticity of demand measures:
A) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in income.
B) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in consumers'
Preferences.
C) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in the price of that good.
D) the reduction in the quantity demanded of a good when the price of that good is reduced.
A) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in income.
B) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in consumers'
Preferences.
C) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in the price of that good.
D) the reduction in the quantity demanded of a good when the price of that good is reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a 5 per cent decrease in the price of a good produces a 5 per cent increase in the quantity demanded, the price elasticity of demand is:
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) elastic.
D) unitary elastic.
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) elastic.
D) unitary elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Narrbegin Exhibit 5.1 Demand curves 
-In Exhibit 5.1, between points a and b, the price elasticity of demand measures:
A) 0.67.
B) 1.5.
C)2.
D) 1.

-In Exhibit 5.1, between points a and b, the price elasticity of demand measures:
A) 0.67.
B) 1.5.
C)2.
D) 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Avital and Joshua each have their own business selling lemonade in front of their houses. When they each charge 25 cents per glass, their total revenues are equal. However, when they each charge 40 cents per glass, Avital's revenues are bigger than Joshua's revenues. This is because:
A) Joshua faces a more inelastic demand curve.
B) Avital faces a more elastic demand curve.
C) Joshua faces a more elastic demand curve.
D) Avital faces a less inelastic demand curve.
A) Joshua faces a more inelastic demand curve.
B) Avital faces a more elastic demand curve.
C) Joshua faces a more elastic demand curve.
D) Avital faces a less inelastic demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
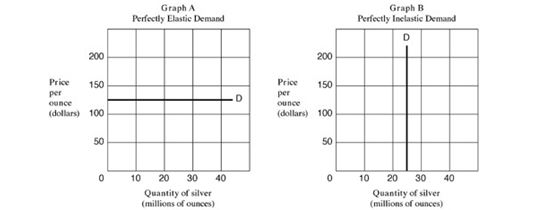
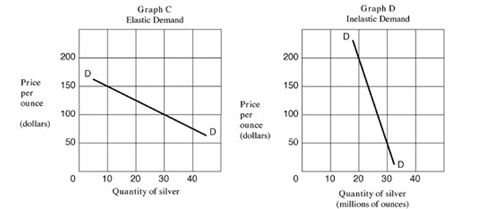
Refer to Exhibit 5.2. Assume that a wealthy buyer, Mr Hunt, declares that he will purchase any amount of silver at a price of $125 an ounce. In Exhibit 5.2, which graph illustrates the shape of the demand curve for silver?
A) Graph A.
B) Graph B.
C) Graph C.
D) Graph D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The price elasticity of demand for a particular good is influenced by which of the following factors?
A) The availability of inputs to produce the good.
B) The income of the sellers.
C) The availability of substitutes.
D) The level of competition among sellers.
A) The availability of inputs to produce the good.
B) The income of the sellers.
C) The availability of substitutes.
D) The level of competition among sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Demand sensitivity depends on all of the following except:
A) how low the price of the good is.
B) the sensitivity of a firm's output to changes in its price.
C) the consumer's income.
D) the availability and closeness of substitutes.
A) how low the price of the good is.
B) the sensitivity of a firm's output to changes in its price.
C) the consumer's income.
D) the availability and closeness of substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the short-run price elasticity of demand for hospital care is 0.27, then the long-run price elasticity is expected to be:
A) greater than 0.27.
B) greater than 1.
C) less than 0.27.
D) equal to 0.27.
A) greater than 0.27.
B) greater than 1.
C) less than 0.27.
D) equal to 0.27.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44


Refer to Exhibit 5.2, Graph C. Using midpoint formula calculate elasticity of demand if price was reduced from $150 to $100.
A) 0.1.
B) 0.3.
C) 6.
D) 2.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Along a straight-line demand curve, the elasticity of demand:
A) is unitary elastic.
B) is more elastic as the price falls.
C) is different at every point along the curve.
D) is perfectly elastic.
A) is unitary elastic.
B) is more elastic as the price falls.
C) is different at every point along the curve.
D) is perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the demand is elastic, the total revenue test of price elasticity will show a/an:
A) decrease in revenue and a price decrease.
B) increase in revenue and a price decrease.
C) increase in revenue and a price increase.
D) decrease in revenue and a price increase.
A) decrease in revenue and a price decrease.
B) increase in revenue and a price decrease.
C) increase in revenue and a price increase.
D) decrease in revenue and a price increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47


Refer to Exhibit 5.2, Graph D. Using midpoint formula calculate elasticity of demand if price was reduced from $200 to $50.
A) 2.03.
B) 0.67.
C) 0.33.
D) 2.54.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Any downward-sloping straight line demand curve displays:
A) elastic and inelastic demand.
B) positive and strong demand.
C) elastic, inelastic and negligible demand.
D) elastic, inelastic and unitary elastic demand.
A) elastic and inelastic demand.
B) positive and strong demand.
C) elastic, inelastic and negligible demand.
D) elastic, inelastic and unitary elastic demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Within different price ranges along a linear demand curve, elasticities are:
A) constant.
B) different.
C) equal.
D) the same as slope.
A) constant.
B) different.
C) equal.
D) the same as slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
As price decreases and we move down further along a linear demand curve, the price elasticity of demand will:
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) stay the same.
D) approach infinity.
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) stay the same.
D) approach infinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The long-run price elasticity of demand is usually larger than the short-run price elasticity of demand because:
A) demand curves tend to become steeper over time.
B) economists take the absolute value of long-run price elasticities but not of short-run
Elasticities.
C) people have more time to find substitute goods.
D) incomes tend to rise over time.
A) demand curves tend to become steeper over time.
B) economists take the absolute value of long-run price elasticities but not of short-run
Elasticities.
C) people have more time to find substitute goods.
D) incomes tend to rise over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which statement about price elasticity of demand along a linear demand curve is true?
A) As the quantity demanded increases, so does the buyer's sensitivity to price.
B) When price elasticity of demand is equal to 1, consumers are indifferent to subtle price changes.
C) The ratio of current price to quantity demanded is a good estimate of the elasticity of demand.
D) The elasticity of demand is less elastic at a lower price.
A) As the quantity demanded increases, so does the buyer's sensitivity to price.
B) When price elasticity of demand is equal to 1, consumers are indifferent to subtle price changes.
C) The ratio of current price to quantity demanded is a good estimate of the elasticity of demand.
D) The elasticity of demand is less elastic at a lower price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Along a straight-line demand curve, the elasticity of demand:
A) is approximated by the slope of the curve.
B) is constant at every point on the curve.
C) is less elastic than along a non-linear demand curve.
D) becomes more inelastic as price falls.
A) is approximated by the slope of the curve.
B) is constant at every point on the curve.
C) is less elastic than along a non-linear demand curve.
D) becomes more inelastic as price falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
As one moves down a straight-line, down-sloping demand curve, price elasticity (measured by point elasticity method) will:
A) change from elastic to unit elastic, then to inelastic.
B) remain the same between any two points.
C) change from inelastic to elastic, then to unit elastic.
D) change from unit elastic to elastic, then to inelastic.
A) change from elastic to unit elastic, then to inelastic.
B) remain the same between any two points.
C) change from inelastic to elastic, then to unit elastic.
D) change from unit elastic to elastic, then to inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A lower price elasticity of demand coefficient occurs when:
A) the good has less substitutes.
B) the fall in price is fully compensated by an increase in quantity.
C) the fall in price causes the total revenue to increase.
D) there is a strong competition among producers.
A) the good has less substitutes.
B) the fall in price is fully compensated by an increase in quantity.
C) the fall in price causes the total revenue to increase.
D) there is a strong competition among producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The most important determinant of price elasticity of demand is:
A) the availability of substitutes.
B) the higher the price of the good.
C) the more of the budget that is spent on the good.
D) the longer the time the consumer has to adjust to price changes.
A) the availability of substitutes.
B) the higher the price of the good.
C) the more of the budget that is spent on the good.
D) the longer the time the consumer has to adjust to price changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The longer the time period under study:
A) the more elastic is the price elasticity of demand.
B) the less sensitive consumers will be to price changes.
C) the less adjustment consumers will make to price changes.
D) the more inelastic is the price elasticity of demand.
A) the more elastic is the price elasticity of demand.
B) the less sensitive consumers will be to price changes.
C) the less adjustment consumers will make to price changes.
D) the more inelastic is the price elasticity of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If a straight-line demand curve slopes down, price elasticity (measured by point elasticity method) will not:
A) remain the same at all points on the demand curve.
B) change between any two points along the demand curve.
C) always be greater than one.
D) always equal one.
A) remain the same at all points on the demand curve.
B) change between any two points along the demand curve.
C) always be greater than one.
D) always equal one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The straight line demand curve represents the price elasticity of demand that:
A) increases as the price decreases.
B) decreases as the price decreases.
C) increases as the price increases.
D) decreases as the price increases.
A) increases as the price decreases.
B) decreases as the price decreases.
C) increases as the price increases.
D) decreases as the price increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The price-elastic portion of the linear demand curve lies:
A) in the high price range.
B) anywhere to the left of current market prices.
C) below the point where total revenue is maximised.
D) at the intersection with the supply curve.
A) in the high price range.
B) anywhere to the left of current market prices.
C) below the point where total revenue is maximised.
D) at the intersection with the supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A study of consumers in an area found that as family income increased from $25 000 per year to $35 000 per year and other factors held constant, the number of houses purchased increased from 7000 per year to 11 000 per year. This finding indicates an income elasticity of demand coefficient for housing over this family income range of:
A) 0.22.
B) 0.75.
C) 1.33.
D) 4.50.
A) 0.22.
B) 0.75.
C) 1.33.
D) 4.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The income elasticity coefficient is:
A) important because we need to know the impact of recession on sales.
B) irrelevant because we cannot compute it.
C) too complicated and therefore is not widely used in economics.
D) never used to estimate the impact on inferior goods.
A) important because we need to know the impact of recession on sales.
B) irrelevant because we cannot compute it.
C) too complicated and therefore is not widely used in economics.
D) never used to estimate the impact on inferior goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The major determinants of price elasticity of demand are:
A) availability of complements.
B) availability of substitutes.
C) availability of normal goods.
D) availability of supply.
A) availability of complements.
B) availability of substitutes.
C) availability of normal goods.
D) availability of supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The elasticity of demand for food would most likely be:
A) perfectly elastic.
B) unit elastic.
C) relatively more elastic than the elasticity of demand for bread.
D) perfectly inelastic.
A) perfectly elastic.
B) unit elastic.
C) relatively more elastic than the elasticity of demand for bread.
D) perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the long run, price elasticities of demand are usually:
A) less than they are in the short run because people can adjust.
B) the same as they are in the short run because tastes don't change.
C) greater than they are in the short run because prices rise over time.
D) greater than they are in the short run because consumers have time to adjust.
A) less than they are in the short run because people can adjust.
B) the same as they are in the short run because tastes don't change.
C) greater than they are in the short run because prices rise over time.
D) greater than they are in the short run because consumers have time to adjust.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The income elasticity of demand for shoes is estimated to be 1.5. We can conclude that shoes:
A) have a relatively steep demand curve.
B) have a relatively flat demand curve.
C) are a normal good.
D) are an inferior good.
A) have a relatively steep demand curve.
B) have a relatively flat demand curve.
C) are a normal good.
D) are an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The income elasticity of demand is the ratio of the percentage change in:
A) the quality demanded of a good to the percentage change in income.
B) the quantity demanded of a good to the percentage change in income.
C) income to the percentage change in quantity demanded of a good.
D) the quantity demanded of a good to the percentage change in price.
A) the quality demanded of a good to the percentage change in income.
B) the quantity demanded of a good to the percentage change in income.
C) income to the percentage change in quantity demanded of a good.
D) the quantity demanded of a good to the percentage change in price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following goods is likely to have the most elastic demand curve?
A) Tobacco products.
B) Petrol.
C) Medical care.
D) Honda automobiles.
A) Tobacco products.
B) Petrol.
C) Medical care.
D) Honda automobiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The price elasticity of demand coefficient for a good will be lower if which of the following occurs?
A) There are many substitutes for the good.
B) A price change persists for longer.
C) The less of the budget is spent on the good.
D) The higher the price of complements.
A) There are many substitutes for the good.
B) A price change persists for longer.
C) The less of the budget is spent on the good.
D) The higher the price of complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The number of music CDs purchased increased by 50 per cent when consumer income increased by 10 per cent. Assuming other factors are held constant, music CDs would be classified as:
A) inferior goods.
B) normal goods.
C) Giffen goods.
D) social goods.
A) inferior goods.
B) normal goods.
C) Giffen goods.
D) social goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If bus travel is an inferior good, then its income elasticity of demand will be:
A) strictly greater than one.
B) positive.
C) equal to zero.
D) negative.
A) strictly greater than one.
B) positive.
C) equal to zero.
D) negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The price elasticity of demand coefficient for a good will be greater:
A) if close substitutes exist.
B) if minor complements exist.
C) in the short run.
D) if a small portion of the budget will be spent on it.
A) if close substitutes exist.
B) if minor complements exist.
C) in the short run.
D) if a small portion of the budget will be spent on it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) Price elasticity of demand for basic foods is low.
B) When price elasticity of demand is very high, we say there is brand loyalty.
C) The availability and price of substitutes affect the elasticity of demand for a good
Or service.
D) When goods have very low prices, the elasticity of demand is usually quite low.
A) Price elasticity of demand for basic foods is low.
B) When price elasticity of demand is very high, we say there is brand loyalty.
C) The availability and price of substitutes affect the elasticity of demand for a good
Or service.
D) When goods have very low prices, the elasticity of demand is usually quite low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
For many people with diabetes, insulin would have an elasticity of demand of:
A) infinity.
B) one.
C) zero.
D) greater than one.
E) indeterminate.
A) infinity.
B) one.
C) zero.
D) greater than one.
E) indeterminate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The smaller the proportion of your income is spent on a good, the more likely it is to be:
A) relatively inelastic.
B) highly elastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) unit elastic.
A) relatively inelastic.
B) highly elastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If the income elasticity for a particular good is 1.8, we would expect to see more of that good:
A) consumed in low-income communities.
B) consumed by people on higher incomes.
C) on supermarket shelves.
D) consumed equally by all citizens.
A) consumed in low-income communities.
B) consumed by people on higher incomes.
C) on supermarket shelves.
D) consumed equally by all citizens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the income elasticity of demand for a good is 1.75, then it is what type of good?
A) Price elastic.
B) Price inelastic.
C) Income inelastic.
D) Income elastic.
A) Price elastic.
B) Price inelastic.
C) Income inelastic.
D) Income elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If a good only takes up a small proportion of your income, the elasticity of demand is likely to be:
A) relatively elastic.
B) relatively inelastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) unit elastic.
A) relatively elastic.
B) relatively inelastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The price elasticity coefficient of demand is:
A) negatively related to the percentage of one's budget spent on a good or service.
B) not related to the availability of good substitutes for a good or service.
C) related to the availability of good complements for a good or service.
D) higher the longer a price change persists.
A) negatively related to the percentage of one's budget spent on a good or service.
B) not related to the availability of good substitutes for a good or service.
C) related to the availability of good complements for a good or service.
D) higher the longer a price change persists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following statements is most likely to be true?
A) The elasticity of demand for a night at a caravan park is likely to be more elastic than a night at a five-star resort.
B) The elasticity of demand for the latest model Porsche is likely to be less elastic than that for a toy model of a Porsche.
C) The elasticity of demand for a meal at an exclusive restaurant is likely to be less elastic than that for a packet of two-minute noodles.
D) The elasticity of demand for salt is likely to be less elastic than that for chinaware.
A) The elasticity of demand for a night at a caravan park is likely to be more elastic than a night at a five-star resort.
B) The elasticity of demand for the latest model Porsche is likely to be less elastic than that for a toy model of a Porsche.
C) The elasticity of demand for a meal at an exclusive restaurant is likely to be less elastic than that for a packet of two-minute noodles.
D) The elasticity of demand for salt is likely to be less elastic than that for chinaware.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



