Deck 10: Standard Costing and Variance Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/216
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Standard Costing and Variance Analysis
1
The standard cost per unit of output for a particular input is calculated by multiplying the standard input price by the standard input allowed per unit of output produced.
True
2
The benefits of operational control under a standard cost system can extend to all manufacturing environments.
False
3
The unit standard quantity of inputs is vital to the computation of total amount of inputs allowed for the actual output and efficiency variances.
True
4
Currently attainable standards offer the most behavioral benefits because higher performance levels are attained through challenging, yet achievable, standards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Ideal standards can be achieved under efficient operating conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Currently attainable standards can be achieved under efficient operating conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Engineering studies are often too rigorous and may not be achievable by operating personnel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In setting standards, historical experience should be used with caution because it can perpetuate operating inefficiencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
One reason for adopting a standard cost system is to make product costing easier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Managers develop quantity standards when they decide what amount of input should be used per unit of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The standard cost sheet provides the input standards needed to compute the total amount of inputs allowed for the actual output, an essential component in computing efficiency variances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The quantity of each input that should be used to produce one unit of output is documented on the standard cost sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The standard quantity of materials allowed can be calculated by multiplying the unit labor standard by the actual output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The total budget variance is the difference between the actual cost of the input and its planned cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The actual quantity of input at the standard price less than the standard quantity of input at the standard price equals the usage variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Managers develop price standards when they determine what amount should be paid for the quantity of input to be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Ideal standards can be achieved only if everything operates perfectly, meaning that they do not allow for any machine breakdowns, slack, etc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Standard costs are developed for direct materials, direct labor, and variable overhead only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The standard unit cost is developed before the standard costs for direct materials, direct labor, and overhead can be set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
To compute the standard direct labor hours allowed, multiply the unit labor standard by the actual output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Although general responsibility for the volume variance is usually assigned to the purchasing department, responsibility on occasion may be assigned to the production department.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Responsibility for variable overhead spending and efficiency variances is generally assigned to production departments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The variable overhead variance is affected by input price changes only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A kaizen standard reflects the realized improvements for the past periods and a search for more improvements for the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The actual quantity of input at the actual price less the actual quantity of input at the standard price is the price variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The sum of the labor rate and labor efficiency variances will always add up to the total labor variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
For better control, the materials price variance is computed using actual quantity of materials purchased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Kaizen costing provides fixed standards which reflect continuous improvement efforts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Favorable variances are credits and unfavorable variances are debits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor hours, the variable overhead efficiency variance always has the same sign as the labor efficiency variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Fixed overhead costs are resources acquired as used and needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An acceptable range is established in order to determine if whether variances are significant.The acceptable range is the standard, plus or minus an allowable deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The volume variance is often interpreted as a measure of capacity utilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An unfavorable price variance occurs whenever the actual prices are greater than the standard prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The fixed overhead spending variance is affected primarily by changes in production levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Practical capacity is always used to calculate fixed overhead rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The materials price variance is computed using the actual quantity of materials used, and the materials usage variance is computed using the actual quantity of materials purchased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An unfavorable usage variance would occur when the actual usage of inputs is greater than the standard usage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The variable overhead spending variance is conceptually identical to the price variances of materials and labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The sum of the price and usage variances will add up to the total materials variance only if the materials purchased is equal to the materials used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not an advantage of standard costing over normal costing and actual costing?
A) A greater capacity for control.
B) Ability to easily distinguish the FIFO and weighted average methods of accounting for beginning inventory costs.
C) Computing a unit cost for each equivalent unit cost category is not necessary.
D) Providing for readily available unit cost information.
E) All of these are advantages of standard costing.
A) A greater capacity for control.
B) Ability to easily distinguish the FIFO and weighted average methods of accounting for beginning inventory costs.
C) Computing a unit cost for each equivalent unit cost category is not necessary.
D) Providing for readily available unit cost information.
E) All of these are advantages of standard costing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Price changes of variable overhead items are easily controlled by production supervisors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The _____ shows the quantity of each input that should be used to produce one unit of output.
A) standard cost sheet
B) production budget
C) time sheet
D) operator budget
E) None of these is correct.
A) standard cost sheet
B) production budget
C) time sheet
D) operator budget
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The sources of quantitative standards include
A) historical experience.
B) engineering studies.
C) input from operating personnel.
D) historical experience, engineering studies, and input from operating personnel.
E) None of these.
A) historical experience.
B) engineering studies.
C) input from operating personnel.
D) historical experience, engineering studies, and input from operating personnel.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is used to compute the standard quantity of material allowed for the actual output?
A) Fixed Quantity Standard × Standard Output
B) Fixed Quantity Standard × Actual Input
C) Unit Quantity Standard × Standard Input
D) Unit Quantity Standard × Actual Output
E) None of these
A) Fixed Quantity Standard × Standard Output
B) Fixed Quantity Standard × Actual Input
C) Unit Quantity Standard × Standard Input
D) Unit Quantity Standard × Actual Output
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Standard cost systems can enhance operational control through the use of
A) efficiency variances which indicate the need for corrective action.
B) price variances which indicate the need for better spending control.
C) standard costs which indicate the desired cost of a unit of input.
D) actual costs which indicate the price received for units sold.
E) All of these.
A) efficiency variances which indicate the need for corrective action.
B) price variances which indicate the need for better spending control.
C) standard costs which indicate the desired cost of a unit of input.
D) actual costs which indicate the price received for units sold.
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is not true regarding engineering studies?
A) They can determine the most efficient way to operate.
B) They are often achievable by operating personnel.
C) They provide very rigorous guidelines.
D) All of these statements are true.
E) More than two of these statements are true.
A) They can determine the most efficient way to operate.
B) They are often achievable by operating personnel.
C) They provide very rigorous guidelines.
D) All of these statements are true.
E) More than two of these statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements is true of a normal costing system?
A) It predetermines the overhead costs for product costing.
B) It assigns standard costs to direct materials and direct labor.
C) It assigns direct materials at a budgeted rate for product costing.
D) It assigns the actual costs of all three manufacturing inputs to products.
E) All of these are correct.
A) It predetermines the overhead costs for product costing.
B) It assigns standard costs to direct materials and direct labor.
C) It assigns direct materials at a budgeted rate for product costing.
D) It assigns the actual costs of all three manufacturing inputs to products.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Price standards are based on
A) the amount of input that should be used per unit of output.
B) the amount that should be paid for the total quantity of input to be used.
C) the amount that should be paid per unit of output.
D) the amount that should be paid per unit of input purchased.
E) None of these.
A) the amount of input that should be used per unit of output.
B) the amount that should be paid for the total quantity of input to be used.
C) the amount that should be paid per unit of output.
D) the amount that should be paid per unit of input purchased.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In setting price standards for materials and labor,
A) the purchasing department must consider discounts, freight, and quality.
B) personnel must consider payroll taxes, fringe benefits, and qualifications.
C) it is the joint responsibility of operations, purchasing, personnel, and accounting.
D) All of these.
E) None of these.
A) the purchasing department must consider discounts, freight, and quality.
B) personnel must consider payroll taxes, fringe benefits, and qualifications.
C) it is the joint responsibility of operations, purchasing, personnel, and accounting.
D) All of these.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Standard cost systems are adopted
A) to improve planning and control.
B) to facilitate product costing.
C) to improve planning and control, and to facilitate product costing.
D) to enhance the operational control of firms that emphasize continuous improvement.
E) for all of these reasons.
A) to improve planning and control.
B) to facilitate product costing.
C) to improve planning and control, and to facilitate product costing.
D) to enhance the operational control of firms that emphasize continuous improvement.
E) for all of these reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The standard cost system differs from the actual cost system in the assignment of
A) direct materials.
B) direct labor.
C) overhead.
D) all of the manufacturing inputs.
E) none of the manufacturing inputs.
A) direct materials.
B) direct labor.
C) overhead.
D) all of the manufacturing inputs.
E) none of the manufacturing inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is true regarding currently attainable standards?
A) They do not provide any allowance for any lack of skill.
B) They provide allowance for normal breakdowns, interruptions, etc.
C) They are can be achieved only if everything operates perfectly.
D) They demand the maximum efficiency of all the producing factors.
E) All of these.
A) They do not provide any allowance for any lack of skill.
B) They provide allowance for normal breakdowns, interruptions, etc.
C) They are can be achieved only if everything operates perfectly.
D) They demand the maximum efficiency of all the producing factors.
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following formulas calculates the standard hours allowed for the actual output?
A) Unit Labor Standard × Actual Output
B) Total Labor Standard × Standard Output
C) Unit Labor Standard × Normal Input
D) Total Labor Standard × Real Input
E) None of these is correct.
A) Unit Labor Standard × Actual Output
B) Total Labor Standard × Standard Output
C) Unit Labor Standard × Normal Input
D) Total Labor Standard × Real Input
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is true about ideal standards?
A) Ideal standards demand maximum efficiency and no slack is allowed.
B) Ideal standards can be achieved under efficient operating conditions.
C) Ideal standards provide allowance for normal breakdowns and interruptions.
D) All of these.
E) None of these.
A) Ideal standards demand maximum efficiency and no slack is allowed.
B) Ideal standards can be achieved under efficient operating conditions.
C) Ideal standards provide allowance for normal breakdowns and interruptions.
D) All of these.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is true regarding standard cost systems in manufacturing environments that emphasize continuous improvement and just-in-time manufacturing and purchasing?
A) The standard cost system enhances the operational control.
B) The materials price variance may encourage the purchasing department to buy in smaller quantities to reduce inventories.
C) Variances can be computed and presented in reports to higher-level managers.
D) The operational level will benefit from the detailed computation of variances.
E) None of these.
A) The standard cost system enhances the operational control.
B) The materials price variance may encourage the purchasing department to buy in smaller quantities to reduce inventories.
C) Variances can be computed and presented in reports to higher-level managers.
D) The operational level will benefit from the detailed computation of variances.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following decisions is related to the amount of input that should be used per unit of output?
A)

B) The price decision
C)

D)

E)

A)

B) The price decision
C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following sources of quantitative standards should be used with caution because it can perpetuate inefficiencies?
A) Historical experience
B) Engineering studies
C) Input from operating personnel
D) Statistical methods
E) None of these
A) Historical experience
B) Engineering studies
C) Input from operating personnel
D) Statistical methods
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An accountant would refer to a cost sheet to perform which of the following actions?
A) Calculate standard cost per unit.
B) Calculate efficiency variances.
C) Calculate the total amount of inputs allowed for the actual output.
D) All of these.
A) Calculate standard cost per unit.
B) Calculate efficiency variances.
C) Calculate the total amount of inputs allowed for the actual output.
D) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a standard cost system, costs are assigned to all of the following, except for
A) direct materials.
B) direct labor.
C) variable overhead.
D) fixed overhead.
E) none of these.
A) direct materials.
B) direct labor.
C) variable overhead.
D) fixed overhead.
E) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
AquaMarine Company's standard cost is $750,000.The allowable deviation is ±5%.Its actual costs for three months are as follows:
 The upper and lower control limits are, respectively, _____.
The upper and lower control limits are, respectively, _____.
A) $712,500 and $643,500
B) $684,200 and $557,000
C) $787,500 and $712,500
D) $742,000 and $670,000
 The upper and lower control limits are, respectively, _____.
The upper and lower control limits are, respectively, _____.A) $712,500 and $643,500
B) $684,200 and $557,000
C) $787,500 and $712,500
D) $742,000 and $670,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is not true concerning control limits?
A) Control limits are the top and bottom measures of the allowable range.
B) The upper control limit is the standard plus the allowable deviation.
C) The lower control limit is the standard minus the allowable deviation.
D) In current practice, control limits are set objectively using standard formulas.
E) Variances that fall outside the control limits are investigated.
A) Control limits are the top and bottom measures of the allowable range.
B) The upper control limit is the standard plus the allowable deviation.
C) The lower control limit is the standard minus the allowable deviation.
D) In current practice, control limits are set objectively using standard formulas.
E) Variances that fall outside the control limits are investigated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is true concerning the materials price variance?
A) It is the difference between the actual and standard unit price of an input multiplied by the number of inputs used.
B) It is the difference between the actual and standard unit price of an output multiplied by the number of inputs used.
C) It is the difference between the actual and standard unit price of an input multiplied by the number of inputs purchased.
D) It is the difference between the actual and standard unit price of an output multiplied by the number of inputs purchased.
E) None of these.
A) It is the difference between the actual and standard unit price of an input multiplied by the number of inputs used.
B) It is the difference between the actual and standard unit price of an output multiplied by the number of inputs used.
C) It is the difference between the actual and standard unit price of an input multiplied by the number of inputs purchased.
D) It is the difference between the actual and standard unit price of an output multiplied by the number of inputs purchased.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following formulas is used to calculate the materials price variance?
A) (Actual Price × Actual Quantity) - (Standard Price × Standard Quantity)
B) (Variable Price × Actual Quantity) - (Total Price × Actual Quantity)
C) (Fixed Price × Average Quantity) - (Standard Price × Actual Quantity)
D) (Actual Price × Actual Quantity) - (Standard Price × Actual Quantity)
E) None of these.
A) (Actual Price × Actual Quantity) - (Standard Price × Standard Quantity)
B) (Variable Price × Actual Quantity) - (Total Price × Actual Quantity)
C) (Fixed Price × Average Quantity) - (Standard Price × Actual Quantity)
D) (Actual Price × Actual Quantity) - (Standard Price × Actual Quantity)
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Anemone Company manufactures model airplanes.During the month, it manufactured 20,000 airplanes.Each one used an average of 8 direct labor hours and an average of 2 sheets of aluminum.It normally manufactures 8,000 airplanes.Materials and labor standards for making the airplanes are as follows:
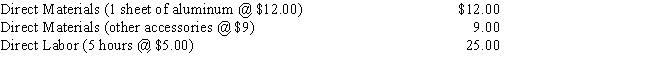 Compute the standard hours allowed for a volume of 20,000 airplanes.
Compute the standard hours allowed for a volume of 20,000 airplanes.
A) 100,000 hours
B) 420,000 hours
C) 70,000 hours
D) 65,000 hours
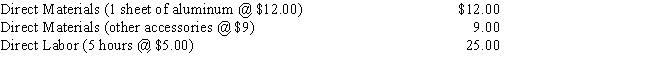 Compute the standard hours allowed for a volume of 20,000 airplanes.
Compute the standard hours allowed for a volume of 20,000 airplanes.A) 100,000 hours
B) 420,000 hours
C) 70,000 hours
D) 65,000 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
All of the following are true regarding variance investigation except
A) the investigation should be undertaken only if the anticipated benefits are greater than the expected costs.
B) managers must consider whether a variance will recur.
C) it is difficult to assess the costs and benefits of variance analysis on a case-by-case basis.
D) variances are not investigated unless they are large enough to be of a concern.
E) every variance is investigated.
A) the investigation should be undertaken only if the anticipated benefits are greater than the expected costs.
B) managers must consider whether a variance will recur.
C) it is difficult to assess the costs and benefits of variance analysis on a case-by-case basis.
D) variances are not investigated unless they are large enough to be of a concern.
E) every variance is investigated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is not true concerning direct materials variances?
A) The sum of the price and usage variances will add up to the total materials variance only if the materials purchased is equal to the materials used.
B) The materials price variance uses the actual quantity of materials purchased rather than the actual quantity of materials used.
C) The materials price variance always uses the actual quantity of materials used rather than the actual quantity of materials purchased.
D) The materials usage variance uses the actual quantity of materials used.
E) Separate materials variances can be computed for each type of material used.
A) The sum of the price and usage variances will add up to the total materials variance only if the materials purchased is equal to the materials used.
B) The materials price variance uses the actual quantity of materials purchased rather than the actual quantity of materials used.
C) The materials price variance always uses the actual quantity of materials used rather than the actual quantity of materials purchased.
D) The materials usage variance uses the actual quantity of materials used.
E) Separate materials variances can be computed for each type of material used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The difference between the actual cost of the input and its planned cost is
A) the total budget variance.
B) the usage variance.
C) the price variance.
D) the efficiency variance.
E) the budget variance.
A) the total budget variance.
B) the usage variance.
C) the price variance.
D) the efficiency variance.
E) the budget variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following formulas computes usage (efficiency) variance?
A) (Actual Quantity - Average Quantity) × Standard Price per Unit
B) (Actual Quantity - Standard Quantity) × Standard Price per Unit
C) (Actual Quantity - Fixed Quantity) × Standard Price per Unit
D) (Actual Quantity - Variable Quantity) × Standard Price per Unit
E) None of these.
A) (Actual Quantity - Average Quantity) × Standard Price per Unit
B) (Actual Quantity - Standard Quantity) × Standard Price per Unit
C) (Actual Quantity - Fixed Quantity) × Standard Price per Unit
D) (Actual Quantity - Variable Quantity) × Standard Price per Unit
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following is not true regarding the use of materials variance information?
A) The purchasing agent has the responsibility for controlling the materials price variance.
B) The production manager is generally responsible for materials usage.
C) The production manager is concerned with minimizing scrap, waste, and rework.
D) The purchasing department is responsible for acquiring quality materials.
E) All of these are true.
A) The purchasing agent has the responsibility for controlling the materials price variance.
B) The production manager is generally responsible for materials usage.
C) The production manager is concerned with minimizing scrap, waste, and rework.
D) The purchasing department is responsible for acquiring quality materials.
E) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is the difference between the actual cost of materials and the materials cost allowed for the actual level of activity?
A) Total materials variance
B) Total materials regression
C) Total materials cost
D) Total materials margin
E) None of these
A) Total materials variance
B) Total materials regression
C) Total materials cost
D) Total materials margin
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
During June, Zinc Company produced 10,000 chainsaw blades.The standard quantity of material allowed per unit was 2 pounds of steel per blade at a standard cost of $5 per pound.Zinc determined that it had a favorable materials usage variance of $1,500 for June.Calculate the actual quantity of materials used by Zinc Company in June.
A) 19,700 pounds
B) 13,305 pounds
C) 12,645 pounds
D) 17,425 pounds
A) 19,700 pounds
B) 13,305 pounds
C) 12,645 pounds
D) 17,425 pounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
During the month of March, Baker's Express purchased 10,000 pounds of flour at $1 per pound.At the end of March, Baker's Express found that it had a favorable materials price variance of $500.The standard cost per pound must be
A) $0.95
B) $1.00
C) $1.05
D) $1.95
A) $0.95
B) $1.00
C) $1.05
D) $1.95

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following mathematical expressions is used to compute the materials usage variance?
A) (Standard Price × Actual Quantity) - (Standard Price × Standard Quantity)
B) (Fixed Price × Standard Quantity) + (Variable Price × Actual Quantity)
C) (Average Price × Average Quantity) - (Standard Price × Standard Quantity)
D) (Actual Price × Standard Quantity) + (Actual Quantity × Standard Price)
E) None of these.
A) (Standard Price × Actual Quantity) - (Standard Price × Standard Quantity)
B) (Fixed Price × Standard Quantity) + (Variable Price × Actual Quantity)
C) (Average Price × Average Quantity) - (Standard Price × Standard Quantity)
D) (Actual Price × Standard Quantity) + (Actual Quantity × Standard Price)
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is true regarding variances?
A) Unfavorable variances occur whenever actual prices or actual usage of inputs are greater than standard prices or standard usage.
B) Favorable variances occur whenever actual prices or actual usage of inputs are greater than standard prices or standard usage.
C) Unfavorable variances are always credits.
D) Favorable variances are always debits.
E) None of these.
A) Unfavorable variances occur whenever actual prices or actual usage of inputs are greater than standard prices or standard usage.
B) Favorable variances occur whenever actual prices or actual usage of inputs are greater than standard prices or standard usage.
C) Unfavorable variances are always credits.
D) Favorable variances are always debits.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Flying High Company manufactures model airplanes.During the month, it manufactured 10,000 airplanes.Each one used an average of 6.5 direct labor hours and an average of 1.5 sheets of aluminum.It normally manufactures 7,500 airplanes.Materials and labor standards for making the airplanes are:
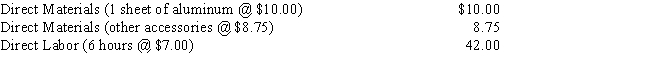 Compute the standard number of sheets of aluminum allowed for a volume of 10,000 airplanes.
Compute the standard number of sheets of aluminum allowed for a volume of 10,000 airplanes.
A) 15,000 sheets
B) 10,000 sheets
C) 7,500 sheets
D) 11,250 sheets
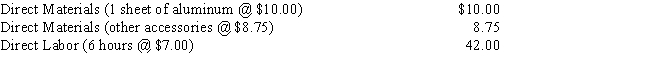 Compute the standard number of sheets of aluminum allowed for a volume of 10,000 airplanes.
Compute the standard number of sheets of aluminum allowed for a volume of 10,000 airplanes.A) 15,000 sheets
B) 10,000 sheets
C) 7,500 sheets
D) 11,250 sheets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Highland Company's standard cost is $250,000.The allowable deviation is ±10%.Its actual costs for six months are
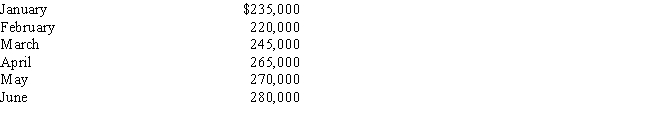 The actual cost which is lower than the lower control limit is
The actual cost which is lower than the lower control limit is
A) $220,000
B) $280,000
C) $265,000
D) $235,000
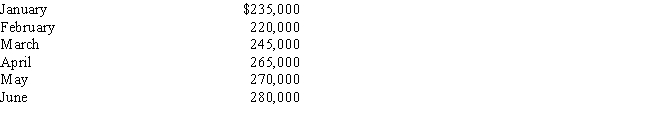 The actual cost which is lower than the lower control limit is
The actual cost which is lower than the lower control limit isA) $220,000
B) $280,000
C) $265,000
D) $235,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Highland Company's standard cost is $250,000.The allowable deviation is ±10%.Its actual costs for six months are
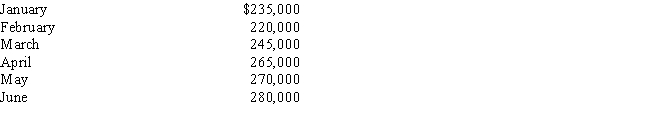 The upper and lower control limits are, respectively,
The upper and lower control limits are, respectively,
A) $250,000 and $225,000
B) $305,000 and $195,000
C) $275,000 and $250,000
D) $275,000 and $225,000
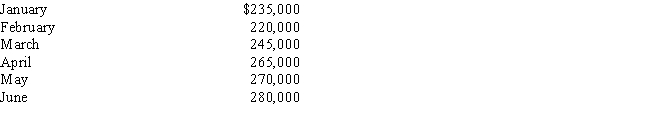 The upper and lower control limits are, respectively,
The upper and lower control limits are, respectively,A) $250,000 and $225,000
B) $305,000 and $195,000
C) $275,000 and $250,000
D) $275,000 and $225,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
During the month of March, Rexelegg purchased 25,000 pounds of flour at $2 per pound.At the end of March, Rexelegg found that it had an unfavorable materials price variance of $750.The standard cost per pound must be:
A) $0.71.
B) $0.60.
C) $0.80.
D) $1.97.
A) $0.71.
B) $0.60.
C) $0.80.
D) $1.97.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Glascro Company's standard cost is $500,000.The allowable deviation is ±15%.Its actual costs for six months are as follows:
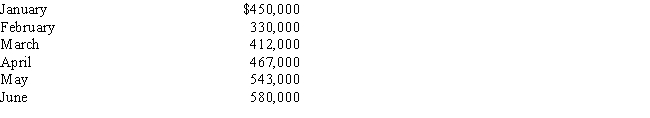 The actual cost which is higher than the upper control limit is _____.
The actual cost which is higher than the upper control limit is _____.
A) $450,000
B) $575,000
C) $330,000
D) $467,000
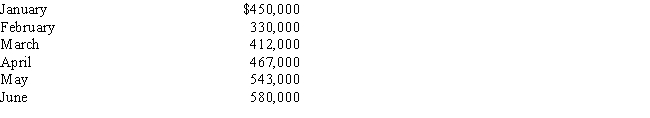 The actual cost which is higher than the upper control limit is _____.
The actual cost which is higher than the upper control limit is _____.A) $450,000
B) $575,000
C) $330,000
D) $467,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



