Deck 6: Ecological Economics and Consumption- Wall to Wall, Cradle to Cradle: a Leading Carpet Company Takes a Chance on Going Green
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/58
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Ecological Economics and Consumption- Wall to Wall, Cradle to Cradle: a Leading Carpet Company Takes a Chance on Going Green
1
Why is the production of some ecosystem services considered priceless?
A) No one can afford to do it.
B) No one knows what it costs.
C) There currently are no substitutes for these services.
D) The technology to do these things is very expensive.
E) They require large amounts of fossil fuels.
A) No one can afford to do it.
B) No one knows what it costs.
C) There currently are no substitutes for these services.
D) The technology to do these things is very expensive.
E) They require large amounts of fossil fuels.
There currently are no substitutes for these services.
2
Which of the following is NOT an important reason to maintain an intact ecosystem?
A) An intact ecosystem provides numerous ecosystem services.
B) An intact ecosystem can renew and recycle resources.
C) If we use more resources and goods than the ecosystem can replenish, we will not be able to receive these goods and services.
D) Our future health and well-being will be threatened.
E) All of the above are important reasons to maintain intact ecosystems.
A) An intact ecosystem provides numerous ecosystem services.
B) An intact ecosystem can renew and recycle resources.
C) If we use more resources and goods than the ecosystem can replenish, we will not be able to receive these goods and services.
D) Our future health and well-being will be threatened.
E) All of the above are important reasons to maintain intact ecosystems.
All of the above are important reasons to maintain intact ecosystems.
3
Discuss how the ecosystem service of pollination benefits humans.
Many plants, such as fruit trees, berries, flowers, and some crops, need insects, bats, or other organisms to pollinate them. Without this service, the plants wouldn't bear fruit or seeds, and we wouldn't have them available to eat or enjoy.
4
A forest provides a(n) _________ in climate regulation and a(n) _______in plant-based pharmaceutical drugs.
A) ecological footprint; ecolabel
B) natural capital; natural interest
C) external cost; internal cost
D) triple-bottom line; economic system
E) ecosystem service; ecosystem good
A) ecological footprint; ecolabel
B) natural capital; natural interest
C) external cost; internal cost
D) triple-bottom line; economic system
E) ecosystem service; ecosystem good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A(n) ________ for a country is the amount of land needed to provide its resources and assimilate its waste.
A) closed-loop system
B) external cost
C) ecological footprint
D) ecolabel
E) ecosystem service
A) closed-loop system
B) external cost
C) ecological footprint
D) ecolabel
E) ecosystem service

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An example of natural capital is _________, and an example of a natural interest is ___________.
A) oxygen; new growth in a forest
B) trees; oceans
C) an increased fish population; new growth in a forest
D) wood; forests
E) forests; wetlands
A) oxygen; new growth in a forest
B) trees; oceans
C) an increased fish population; new growth in a forest
D) wood; forests
E) forests; wetlands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following would not be considered an ecosystem service?
A) oxygen provided by green plants
B) timber from trees
C) pollination of crops
D) nitrogen cycling in soil
E) water purification
A) oxygen provided by green plants
B) timber from trees
C) pollination of crops
D) nitrogen cycling in soil
E) water purification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
While placing a monetary value on ecosystem services can help us to understand that ecosystems provide us with valuable services, critics say that it is dangerous to put a price on ecosystem services. What are the limitations of such valuation of ecosystems?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Why would nutrient cycling be considered such a valuable ecosystem service to humans?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Infographic 6.1.
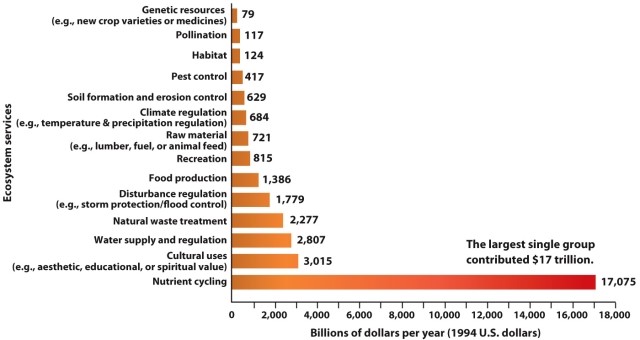
Refer to Infographic 6.1. Which ecosystem service is considered to be the most valuable to us?
A) water supply
B) cultural uses
C) nutrient cycling
D) food production
E) waste treatment

Refer to Infographic 6.1. Which ecosystem service is considered to be the most valuable to us?
A) water supply
B) cultural uses
C) nutrient cycling
D) food production
E) waste treatment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An essential ecological process that makes life on Earth possible is called ______.
A) sustainable development
B) an ecosystem service
C) the closed-loop system
D) an economic system
E) the triple-bottom line
A) sustainable development
B) an ecosystem service
C) the closed-loop system
D) an economic system
E) the triple-bottom line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is NOT an ecosystem service?
A) water purification
B) crop pollination
C) climate regulation
D) landfilling waste
E) pest control
A) water purification
B) crop pollination
C) climate regulation
D) landfilling waste
E) pest control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Infographic 6.5.
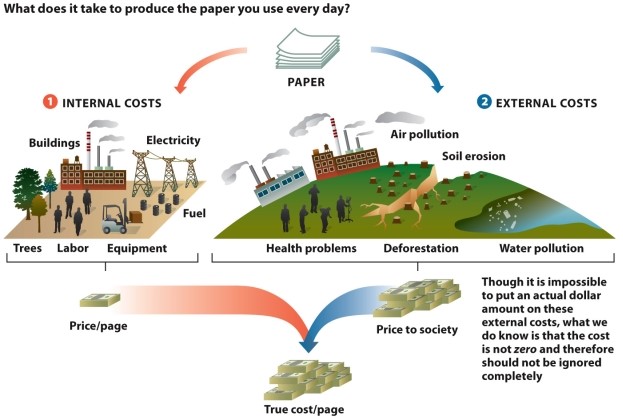
Refer to Infographic 6.5. Why is it important to consider the cost to an ecosystem when purchasing a product as well as considering the price of the object or service?

Refer to Infographic 6.5. Why is it important to consider the cost to an ecosystem when purchasing a product as well as considering the price of the object or service?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following choices is considered natural capital?
A) oxygen
B) water
C) trees
D) fish
E) All of the choices above are considered natural capital.
A) oxygen
B) water
C) trees
D) fish
E) All of the choices above are considered natural capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Infographic 6.1.
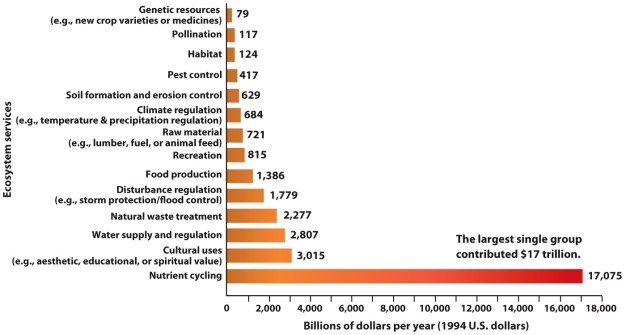
Refer to Infographic 6.1. What does the figure show?
A) the cost to restore a degraded ecosystem for particular ecosystem services
B) the price of maintaining ecosystems such that they can continue to provide specific ecosystem services without degrading the environment
C) the monetary value ascribed to particular ecosystem services
D) the ecological footprint value of specific ecosystem services
E) the cost differential between natural capital and natural interest

Refer to Infographic 6.1. What does the figure show?
A) the cost to restore a degraded ecosystem for particular ecosystem services
B) the price of maintaining ecosystems such that they can continue to provide specific ecosystem services without degrading the environment
C) the monetary value ascribed to particular ecosystem services
D) the ecological footprint value of specific ecosystem services
E) the cost differential between natural capital and natural interest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Infographic 6.1.
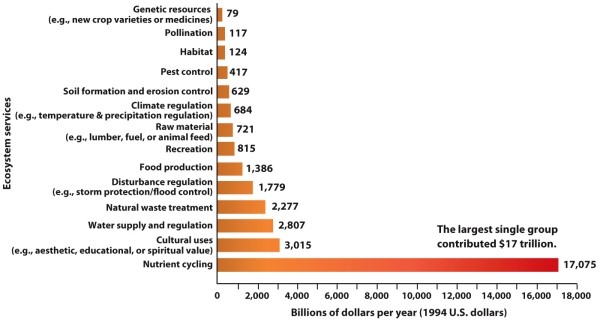
Refer to Infographic 6.1. Which of the following might be considered a "cultural use" of an ecosystem?
A) bees pollinating cherry trees
B) an open field and nearby forest used for a Civil War reenactment
C) carbon moving from a tree to a caterpillar to a bird to the soil
D) water percolating through soil in a wetland
E) rocks being weathered by the wind

Refer to Infographic 6.1. Which of the following might be considered a "cultural use" of an ecosystem?
A) bees pollinating cherry trees
B) an open field and nearby forest used for a Civil War reenactment
C) carbon moving from a tree to a caterpillar to a bird to the soil
D) water percolating through soil in a wetland
E) rocks being weathered by the wind

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Infographic 6.1.
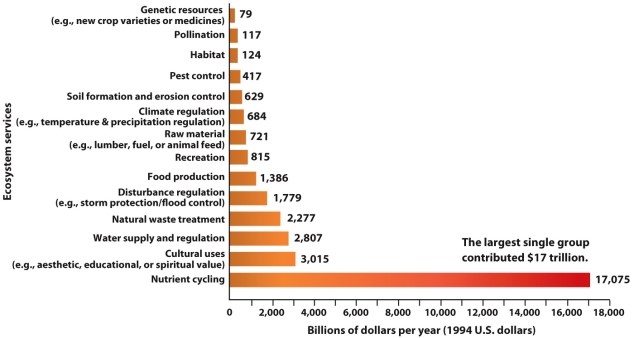
Refer to Infographic 6.1. Why is it useful to put a monetary value on ecosystem services?

Refer to Infographic 6.1. Why is it useful to put a monetary value on ecosystem services?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Infographic 6.1.
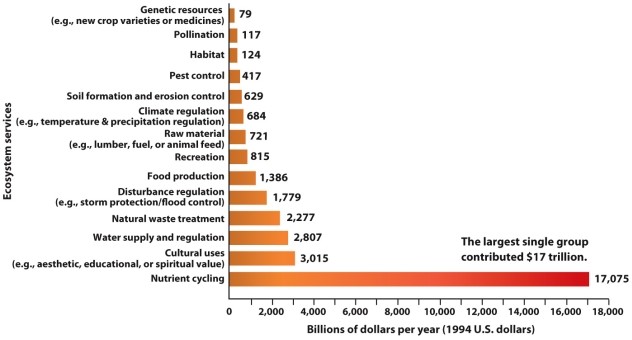
Refer to Infographic 6.1. Approximately, what is the value of services that affect our food supply?
A) $79 billion
B) $1386 billion
C) $417 billion
D) $2100 billion
E) $2807 billion

Refer to Infographic 6.1. Approximately, what is the value of services that affect our food supply?
A) $79 billion
B) $1386 billion
C) $417 billion
D) $2100 billion
E) $2807 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the monetary value attributed to essential ecosystem services? Who calculated this value, and how can it be useful to place a monetary value on ecosystem services?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The government must decide if a section of forest in north Wisconsin can be sold for lumber or if it should be added to the Nicolet National Forest. The social science that deals with how this resource should be allocated is called _______.
A) political science
B) economics
C) ecology
D) sociology
E) None of the choices above represent this concept.
A) political science
B) economics
C) ecology
D) sociology
E) None of the choices above represent this concept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a car company manufactures an electric car made of recycled and bio-based components and powers the car battery by leasing solar panels to its customers, then which of the following happens?
A) The car would not be considered a sustainable business.
B) The manufacturing system discounts the future value of the car.
C) I = (P x A)/T instead of I = P x A x T.
D) The process exclusively reflects a product-oriented economy.
E) The car cannot be given an ecolabel.
A) The car would not be considered a sustainable business.
B) The manufacturing system discounts the future value of the car.
C) I = (P x A)/T instead of I = P x A x T.
D) The process exclusively reflects a product-oriented economy.
E) The car cannot be given an ecolabel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is an example of an external cost?
A) a federal tax that is placed on a product sold by a business
B) a fee a company pays to have their product shipped internationally
C) health costs stemming from the hazardous wastes produced during the making of a product
D) the extra money a business pays to make their products or services sustainable
E) labor
A) a federal tax that is placed on a product sold by a business
B) a fee a company pays to have their product shipped internationally
C) health costs stemming from the hazardous wastes produced during the making of a product
D) the extra money a business pays to make their products or services sustainable
E) labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
_________ include manufacturing costs, labor, taxes, utilities, insurance, and rent.
A) Internal costs
B) External costs
C) Safety costs
D) Potential costs
E) True costs
A) Internal costs
B) External costs
C) Safety costs
D) Potential costs
E) True costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
All of the following actions would threaten the Earth's ability to provide ecosystem goods and services EXCEPT __________.
A) recycling
B) deforestation
C) overfishing
D) soil erosion
E) littering
A) recycling
B) deforestation
C) overfishing
D) soil erosion
E) littering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What three factors are multiplied in the IPAT model to gauge a population's ecological footprint?
A) predisposition, annual income, and taxation
B) population growth, agriculture, and textiles
C) perception, action, and time
D) population, affluence, and technology
E) people, animals, and technology
A) predisposition, annual income, and taxation
B) population growth, agriculture, and textiles
C) perception, action, and time
D) population, affluence, and technology
E) people, animals, and technology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The true cost of an item produced in a factory includes which of the following factors?
A) social costs
B) environmental costs
C) internal costs
D) external costs
E) It includes all of the factors listed above.
A) social costs
B) environmental costs
C) internal costs
D) external costs
E) It includes all of the factors listed above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The IPAT equation is used to estimate the size of a population's ecological footprint. Which of the following factors is NOT found in that equation?
A) productivity
B) affluence
C) technology
D) population
E) Choices C and D are not found in the IPAT equation.
A) productivity
B) affluence
C) technology
D) population
E) Choices C and D are not found in the IPAT equation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Of the next billion people added to Earth, over 99% will be born in less developed, poorer parts of the world. Is it fair to say that the overall impact of humans on the environment is mostly the fault of developing countries? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following would be part of an environmental economist's agenda?
A) to consider the long-term impact of our consumption choices on human society and the environment
B) to discount the future value of ecosystem goods and services
C) to price the product of a service such that costs associated with manufacturing, labor, and utilities are accounted for, but costs associated with pollution and resource depletion are not
D) to emphasize a linear, product-oriented economic system
E) to maximize the size of the ecological footprint associated with a product or service
A) to consider the long-term impact of our consumption choices on human society and the environment
B) to discount the future value of ecosystem goods and services
C) to price the product of a service such that costs associated with manufacturing, labor, and utilities are accounted for, but costs associated with pollution and resource depletion are not
D) to emphasize a linear, product-oriented economic system
E) to maximize the size of the ecological footprint associated with a product or service

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Today, if we were to purchase a good or service at its true cost, how would the price compare to what we are accustomed to paying for the good or service?
A) The price would be lower.
B) The price would be higher.
C) The price would stay the same.
D) The price would decrease exponentially.
E) We cannot predict how the price would change.
A) The price would be lower.
B) The price would be higher.
C) The price would stay the same.
D) The price would decrease exponentially.
E) We cannot predict how the price would change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Compare and contrast technology as a variable that increases and decreases a population's overall impact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Your company is in the process of developing an alternative to carpet tile. To make your product more desirable and profitable, what right costs of manufacturing carpet tiles should your designers focus on and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What are the internal and external costs associated with producing paper?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Ecosystem services would be discounted in the _________economic system.
A) environmental
B) ecological
C) triple-bottom line
D) mainstream
E) true cost accounting
A) environmental
B) ecological
C) triple-bottom line
D) mainstream
E) true cost accounting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
One of the limitations of mainstream economics is that it does not take into account ___________ costs when a price is assigned to a product or service.
A) safety
B) internal
C) external
D) marginal
E) fringe
A) safety
B) internal
C) external
D) marginal
E) fringe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An assessment of the cost of a good or service that includes the environmental, social, and economic costs is called the __________.
A) internal analysis
B) external analysis
C) complete valuation
D) triple-bottom line
E) validation cost
A) internal analysis
B) external analysis
C) complete valuation
D) triple-bottom line
E) validation cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Including both internal and external costs when setting a price for a good or service is an example of ______ cost.
A) overall
B) valuation
C) total
D) marginal
E) true
A) overall
B) valuation
C) total
D) marginal
E) true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Sustainable use of forests allows us to use the trees to produce goods without depleting them. The amount of net resources produced from the forest or any other form of natural capital is known as ____________.
A) an ecological footprint
B) internal cost
C) raw material
D) natural interest
E) true cost
A) an ecological footprint
B) internal cost
C) raw material
D) natural interest
E) true cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Infographic 6.5.
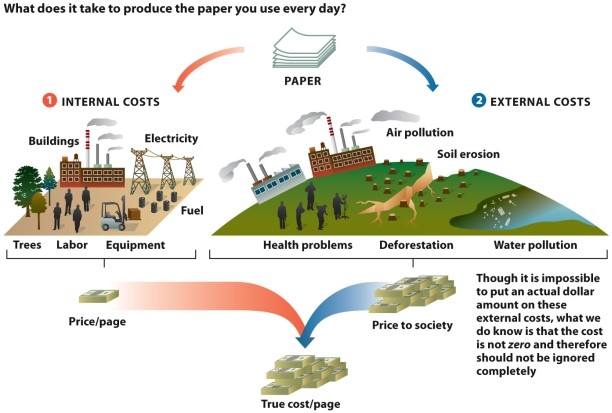
Refer to Infographic 6.5. You can find a double cheeseburger on the "dollar menu" at many fast-food chains. Use the infographic to describe how the true cost of that food product is not reflected by the sale price.

Refer to Infographic 6.5. You can find a double cheeseburger on the "dollar menu" at many fast-food chains. Use the infographic to describe how the true cost of that food product is not reflected by the sale price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
By ignoring the ________, economies create a false idea of the _______ of particular choices.
A) internal costs; external cost
B) true costs; external cost
C) external costs; true cost
D) true costs; closed-loop system
E) internal costs; true cost
A) internal costs; external cost
B) true costs; external cost
C) external costs; true cost
D) true costs; closed-loop system
E) internal costs; true cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
It is predicted that there will soon be more cell phones in the world than people. Inside each phone is a metal called tantalum. This metal is mined from the Earth and is a nonrenewable resource. How could cell phone manufacturing become more cyclical in a closed-loop system? What can consumers do to help?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Infographic 6.6.
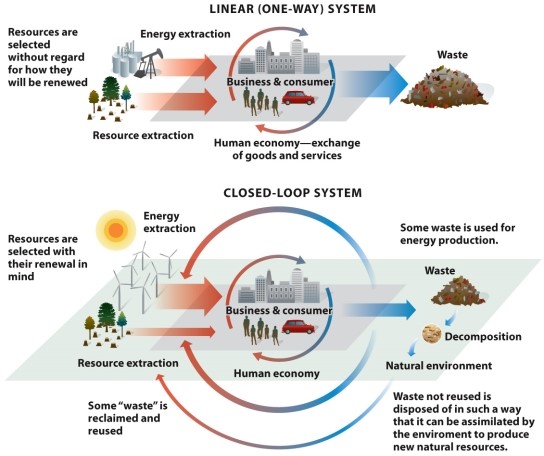
Refer to Infographic 6.6. What does each figure represent?
A) a = true cost accounting; b = green business
B) a = mainstream economics; b = environmental economics
C) a = ecological economics; b = discounting future value
D) a = service-oriented economics; b = product-oriented economics
E) a = external cost accounting; b = internal cost accounting

Refer to Infographic 6.6. What does each figure represent?
A) a = true cost accounting; b = green business
B) a = mainstream economics; b = environmental economics
C) a = ecological economics; b = discounting future value
D) a = service-oriented economics; b = product-oriented economics
E) a = external cost accounting; b = internal cost accounting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
One area where traditional economics differs from environmental economics is that traditional economics tends to give more weight to _________ benefits and costs than it does to ________ benefits and costs.
A) long-term; short-term
B) short-term; long-term
C) long-term; middle-term
D) short-term; middle-term
E) middle-term; long-term
A) long-term; short-term
B) short-term; long-term
C) long-term; middle-term
D) short-term; middle-term
E) middle-term; long-term

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A computer company leases rather than sells its computers to consumers for a monthly fee. The company maintains the computers and replaces them as needed. The old computers are either refurbished or recycled. What does this business model represent?
A) cradle-to-cradle management
B) a closed-loop system
C) green business
D) a service-oriented economy
E) all of the above
A) cradle-to-cradle management
B) a closed-loop system
C) green business
D) a service-oriented economy
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An item most likely to be a part of a closed-loop system would be _________.
A) a computer
B) coal
C) natural gas
D) an aluminum can
E) None of the choices listed above fit the description.
A) a computer
B) coal
C) natural gas
D) an aluminum can
E) None of the choices listed above fit the description.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A linear economic model would include which of the following items?
A) recyclable products
B) crude oil as an energy source
C) cow manure
D) reclaimable waste
E) All of the items listed above would fit that description.
A) recyclable products
B) crude oil as an energy source
C) cow manure
D) reclaimable waste
E) All of the items listed above would fit that description.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following animals does NOT live sustainably with the environment?
A) sharks
B) ants
C) humans
D) birds
E) rabbits
A) sharks
B) ants
C) humans
D) birds
E) rabbits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What are assumptions of mainstream economics that fall short?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
One major difference between mainstream and environmental economics is that mainstream economics assumes that waste can be disposed of in a(n) _______ system.
A) closed-loop
B) open-loop
C) two-way
D) linear
E) bilinear
A) closed-loop
B) open-loop
C) two-way
D) linear
E) bilinear

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What are the differences and similarities between environmental and ecological economics?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The company you are currently working for follows a linear (one-way) system. Explain why this system will eventually fail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A product system in which the product is folded back into the resource stream when the consumer is finished with it is a(n) _________.
A) open-loop system
B) closed-loop system
C) linear system
D) one-way system
E) cradle-to-grave system
A) open-loop system
B) closed-loop system
C) linear system
D) one-way system
E) cradle-to-grave system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The two schools of economic thought that consider the environment when making economic decisions are __________ and _____________.
A) deep ecology; Western
B) environmental; ecological
C) Western; environmental
D) deep ecology; environmental
E) Western; ecological
A) deep ecology; Western
B) environmental; ecological
C) Western; environmental
D) deep ecology; environmental
E) Western; ecological

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is a closed-loop system? How could an automatic car wash become more cyclical in a closed-loop system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In what way does environmental economics differ from ecological economics?
A) Unlike environmental economics, ecological economics focuses on improving technology to increase production efficiency and reduce waste.
B) In contrast to ecological economics, environmental economics promotes a shift away from a dependence on nonrenewable resources.
C) Environmental economics applies the tools of modern economics to solve environmental problems with current economic systems that emphasize unlimited economic growth, while ecological economics operates under the assumption that economic growth does have limits.
D) While ecological economics operates within a closed-loop, service-oriented economic system, environmental economics is a linear, product-oriented economic system.
E) Though environmental economics works on internalizing external costs through true cost accounting, ecological economics discounts future value.
A) Unlike environmental economics, ecological economics focuses on improving technology to increase production efficiency and reduce waste.
B) In contrast to ecological economics, environmental economics promotes a shift away from a dependence on nonrenewable resources.
C) Environmental economics applies the tools of modern economics to solve environmental problems with current economic systems that emphasize unlimited economic growth, while ecological economics operates under the assumption that economic growth does have limits.
D) While ecological economics operates within a closed-loop, service-oriented economic system, environmental economics is a linear, product-oriented economic system.
E) Though environmental economics works on internalizing external costs through true cost accounting, ecological economics discounts future value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which statement is correct?
A) Traditional economics discounts short-term benefits and costs more than it does long-term ones.
B) Natural and human resources are infinite.
C) In a closed-loop system, models of production follow a linear sequence.
D) Linear systems are sustainable in business and economic models.
E) Mainstream economics assumes that economic growth will increase forever.
A) Traditional economics discounts short-term benefits and costs more than it does long-term ones.
B) Natural and human resources are infinite.
C) In a closed-loop system, models of production follow a linear sequence.
D) Linear systems are sustainable in business and economic models.
E) Mainstream economics assumes that economic growth will increase forever.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Mainstream economics makes the inaccurate assumption that natural resources are _______ and that substitutes can be found if needed.
A) finite
B) unimportant
C) limited
D) infinite
E) fixed
A) finite
B) unimportant
C) limited
D) infinite
E) fixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



