Deck 17: Blood
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/126
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Blood
1
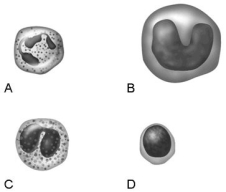
Figure 17.1
Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Neutrophil.
D
2

Figure 17.1
Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Lymphocyte.
B
3

Figure 17.1
Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Monocyte.
A
4
Match the following:
A) Basophil
B) Eosinophil
C) Neutrophil
D) Monocyte
E) Erythrocyte
Contains a U- or an S-shaped nucleus; granules stain very dark; releases histamine and heparin.
A) Basophil
B) Eosinophil
C) Neutrophil
D) Monocyte
E) Erythrocyte
Contains a U- or an S-shaped nucleus; granules stain very dark; releases histamine and heparin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5

Figure 17.1
Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Mounts a humoral immune response by producing antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

Figure 17.1
Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Releases granules that kill parasitic worms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Match the following:
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
Thrombin catalyzes the activation of these molecules present in plasma.
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
Thrombin catalyzes the activation of these molecules present in plasma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Match the following:
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
The major contributor to plasma osmotic pressure.
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
The major contributor to plasma osmotic pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Match the following:
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
Material absorbed from the digestive tract.Including simple sugars,amino acids and fatty acids.
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
Material absorbed from the digestive tract.Including simple sugars,amino acids and fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

Figure 17.1
Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
When activated becomes a macrophage that fights infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Match the following:
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
Ions in the plasma like sodium,potassium and chloride ions.
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
Ions in the plasma like sodium,potassium and chloride ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Match the following:
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
Makes up most of plasma protein.
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
Makes up most of plasma protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

Figure 17.1
Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Main bacteria killer during acute infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14

Figure 17.1
Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
A granulocyte,phagocyte and the most common white blood cell found in whole blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Match the following:
A) Basophil
B) Eosinophil
C) Neutrophil
D) Monocyte
E) Erythrocyte
Largest of the WBCs; crucial in defense against viruses; associated with chronic infections.
A) Basophil
B) Eosinophil
C) Neutrophil
D) Monocyte
E) Erythrocyte
Largest of the WBCs; crucial in defense against viruses; associated with chronic infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16

Figure 17.1
Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Eosinophil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Match the following:
A) Basophil
B) Eosinophil
C) Neutrophil
D) Monocyte
E) Erythrocyte
Transports CO2 and oxygen.
A) Basophil
B) Eosinophil
C) Neutrophil
D) Monocyte
E) Erythrocyte
Transports CO2 and oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Match the following:
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
Forms the structural framework of a blood clot.
A) Albumin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Electrolytes
D) Organic nutrients
Forms the structural framework of a blood clot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Match the following:
A) Basophil
B) Eosinophil
C) Neutrophil
D) Monocyte
E) Erythrocyte
Nucleus has two lobes; contains granules of lysosomal enzymes; functions in attacking parasitic worms and plays complex roles in inflammatory diseases like allergies and asthma.
A) Basophil
B) Eosinophil
C) Neutrophil
D) Monocyte
E) Erythrocyte
Nucleus has two lobes; contains granules of lysosomal enzymes; functions in attacking parasitic worms and plays complex roles in inflammatory diseases like allergies and asthma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Match the following:
A) Basophil
B) Eosinophil
C) Neutrophil
D) Monocyte
E) Erythrocyte
Nucleus is multilobed; functions as a phagocyte; contains fine indistinct granules.
A) Basophil
B) Eosinophil
C) Neutrophil
D) Monocyte
E) Erythrocyte
Nucleus is multilobed; functions as a phagocyte; contains fine indistinct granules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
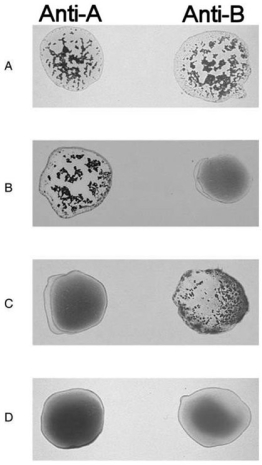 Figure 17.2
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Type O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
 Figure 17.2
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Type A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Match the following:
A) Hemoglobin
B) Factor VIII
C) Agglutination
D) Monocyte
E) Neutrophil
Adverse reaction of donor blood cells with recipient plasma.
A) Hemoglobin
B) Factor VIII
C) Agglutination
D) Monocyte
E) Neutrophil
Adverse reaction of donor blood cells with recipient plasma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
 Figure 17.2
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Universal donor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Match the following:
A) Alpha and beta globulins
B) Albumin
C) Gamma globulins
D) Fibrinogen
Main contributor to osmotic pressure.
A) Alpha and beta globulins
B) Albumin
C) Gamma globulins
D) Fibrinogen
Main contributor to osmotic pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Match the following:
A) Prostaglandin derivates such as Thromboxane A2
B) Erythropoietin
C) Spectrin
D) Heparin
E) Interleukins and CSFs
A fibrous protein that gives shape to an RBC plasma membrane.
A) Prostaglandin derivates such as Thromboxane A2
B) Erythropoietin
C) Spectrin
D) Heparin
E) Interleukins and CSFs
A fibrous protein that gives shape to an RBC plasma membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Match the following:
A) Hemoglobin
B) Factor VIII
C) Agglutination
D) Monocyte
E) Neutrophil
Polymorphonuclear leukocyte.
A) Hemoglobin
B) Factor VIII
C) Agglutination
D) Monocyte
E) Neutrophil
Polymorphonuclear leukocyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Match the following:
A) Prostaglandin derivates such as Thromboxane A2
B) Erythropoietin
C) Spectrin
D) Heparin
E) Interleukins and CSFs
Stimulates WBC production.
A) Prostaglandin derivates such as Thromboxane A2
B) Erythropoietin
C) Spectrin
D) Heparin
E) Interleukins and CSFs
Stimulates WBC production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Match the following:
A) Hemoglobin
B) Factor VIII
C) Agglutination
D) Monocyte
E) Neutrophil
Protein capable of changing shape and color in the presence of O2.
A) Hemoglobin
B) Factor VIII
C) Agglutination
D) Monocyte
E) Neutrophil
Protein capable of changing shape and color in the presence of O2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
 Figure 17.2
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Universal recipient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Match the following:
A) Hemoglobin
B) Factor VIII
C) Agglutination
D) Monocyte
E) Neutrophil
White blood cell without cytoplasmic granules.
A) Hemoglobin
B) Factor VIII
C) Agglutination
D) Monocyte
E) Neutrophil
White blood cell without cytoplasmic granules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Match the following:
A) Prostaglandin derivates such as Thromboxane A2
B) Erythropoietin
C) Spectrin
D) Heparin
E) Interleukins and CSFs
Produced by platelets.
A) Prostaglandin derivates such as Thromboxane A2
B) Erythropoietin
C) Spectrin
D) Heparin
E) Interleukins and CSFs
Produced by platelets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Match the following:
A) Prostaglandin derivates such as Thromboxane A2
B) Erythropoietin
C) Spectrin
D) Heparin
E) Interleukins and CSFs
Hormone that stimulates production of RBCs.
A) Prostaglandin derivates such as Thromboxane A2
B) Erythropoietin
C) Spectrin
D) Heparin
E) Interleukins and CSFs
Hormone that stimulates production of RBCs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Match the following:
A) Alpha and beta globulins
B) Albumin
C) Gamma globulins
D) Fibrinogen
Necessary for coagulation.
A) Alpha and beta globulins
B) Albumin
C) Gamma globulins
D) Fibrinogen
Necessary for coagulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Match the following:
A) Alpha and beta globulins
B) Albumin
C) Gamma globulins
D) Fibrinogen
Transport proteins like transferrin (that carries iron ions)or others that bind to lipids or fat-soluble vitamins.
A) Alpha and beta globulins
B) Albumin
C) Gamma globulins
D) Fibrinogen
Transport proteins like transferrin (that carries iron ions)or others that bind to lipids or fat-soluble vitamins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Match the following:
A) Prostaglandin derivates such as Thromboxane A2
B) Erythropoietin
C) Spectrin
D) Heparin
E) Interleukins and CSFs
Natural anticoagulant found in basophils.
A) Prostaglandin derivates such as Thromboxane A2
B) Erythropoietin
C) Spectrin
D) Heparin
E) Interleukins and CSFs
Natural anticoagulant found in basophils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
 Figure 17.2
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Type AB.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Match the following:
A) Hemoglobin
B) Factor VIII
C) Agglutination
D) Monocyte
E) Neutrophil
Lacking in hemophilia type A.
A) Hemoglobin
B) Factor VIII
C) Agglutination
D) Monocyte
E) Neutrophil
Lacking in hemophilia type A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Match the following:
A) Alpha and beta globulins
B) Albumin
C) Gamma globulins
D) Fibrinogen
Antibodies released by plasma cells during immune response.
A) Alpha and beta globulins
B) Albumin
C) Gamma globulins
D) Fibrinogen
Antibodies released by plasma cells during immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
 Figure 17.2
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
A) B
B) D
C) C
D) A
Type B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Match the following:
A) Embolism
B) Polycythemia
C) Anemia
D) Thrombocytopenia
E) Leukemia
Condition in which blood has abnormally low oxygen-carrying capacity.
A) Embolism
B) Polycythemia
C) Anemia
D) Thrombocytopenia
E) Leukemia
Condition in which blood has abnormally low oxygen-carrying capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Leukopenia is an abnormally low number of leukocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Diapedesis is the process by which red blood cells move into tissue spaces from the interior of blood capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Myeloid stem cells give rise to all leukocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Leukemia refers to cancerous conditions involving white blood cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Each hemoglobin molecule can transport two molecules of oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Basophils increase in number when parasitic invasion occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The primary source of RBCs in the adult human being is the bone marrow in the shafts of the long bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Positive chemotaxis is a feedback system that signals leukocyte migration into damaged areas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Hemorrhagic anemias result from blood loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The immediate response to blood vessel injury is clotting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Hemoglobin is made up of the protein heme and the red pigment globin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
White blood cells are produced through the action of colony-stimulating factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Clotting factor activation turns clotting factors into enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Match the following:
A) Embolism
B) Polycythemia
C) Anemia
D) Thrombocytopenia
E) Leukemia
Cancerous condition involving white blood cells.
A) Embolism
B) Polycythemia
C) Anemia
D) Thrombocytopenia
E) Leukemia
Cancerous condition involving white blood cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The normal RBC "graveyard" is the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Match the following:
A) Embolism
B) Polycythemia
C) Anemia
D) Thrombocytopenia
E) Leukemia
Platelet deficiency resulting in spontaneous bleeding from small blood vessels.
A) Embolism
B) Polycythemia
C) Anemia
D) Thrombocytopenia
E) Leukemia
Platelet deficiency resulting in spontaneous bleeding from small blood vessels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Match the following:
A) Embolism
B) Polycythemia
C) Anemia
D) Thrombocytopenia
E) Leukemia
Abnormal excess of erythrocytes resulting in an increase in blood viscosity.
A) Embolism
B) Polycythemia
C) Anemia
D) Thrombocytopenia
E) Leukemia
Abnormal excess of erythrocytes resulting in an increase in blood viscosity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Match the following:
A) Embolism
B) Polycythemia
C) Anemia
D) Thrombocytopenia
E) Leukemia
Free-floating thrombus in the bloodstream.
A) Embolism
B) Polycythemia
C) Anemia
D) Thrombocytopenia
E) Leukemia
Free-floating thrombus in the bloodstream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The process of fibrinolysis disposes of bacteria when healing has occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Lipids (either nutrients or hormones)are insoluble in water but are found traveling in the plasma of the blood.Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this?
A) Lipids are carried in plasma bound to soluble plasma transport proteins
B) Lipids are carried only in the lymph which is primarily composed of unsaturated fats
C) Lipids are carried inside blood cells
D) Enzymes in the plasma convert lipids to soluble forms.
A) Lipids are carried in plasma bound to soluble plasma transport proteins
B) Lipids are carried only in the lymph which is primarily composed of unsaturated fats
C) Lipids are carried inside blood cells
D) Enzymes in the plasma convert lipids to soluble forms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen than does adult hemoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Loss of fibrinogen within the plasma would most likely cause which of the following?
A) fever with pain
B) loss of blood clotting
C) edema (swelling)
D) pallor (pale skin)
A) fever with pain
B) loss of blood clotting
C) edema (swelling)
D) pallor (pale skin)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
With a patient that is administered an injection of erythropoietin (EPO)you would expect to see ________.
A) increased white blood cell count
B) decreased hematocrit
C) increased hematocrit
D) decreased white blood cell count
A) increased white blood cell count
B) decreased hematocrit
C) increased hematocrit
D) decreased white blood cell count

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A mismatch of blood types during a transfusion is dangerous because ________.
A) white blood cells from the donor's blood cause inflammation
B) antibodies in the donor's plasma will attack and kill the recipient's healthy blood cells
C) clotting factors in the donor's blood will cause unwanted clots known as thrombus
D) preformed antibodies in the recipient's blood will bind and clump (agglutinate) the donated cells
A) white blood cells from the donor's blood cause inflammation
B) antibodies in the donor's plasma will attack and kill the recipient's healthy blood cells
C) clotting factors in the donor's blood will cause unwanted clots known as thrombus
D) preformed antibodies in the recipient's blood will bind and clump (agglutinate) the donated cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Diabetes can cause a condition called nephrotic syndrome in which a person will suffer a loss of osmotic pressure with fluid from the plasma leaving blood vessels causing Edema (swelling).Which of the following is likely the cause of this condition?
A) a loss of intrinsic factor from the plasma via the urine
B) a loss of hypoxia-inducible factor via the urine
C) release of albumin protein into the urine
D) an increase in EPO production by the kidneys
A) a loss of intrinsic factor from the plasma via the urine
B) a loss of hypoxia-inducible factor via the urine
C) release of albumin protein into the urine
D) an increase in EPO production by the kidneys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Higher viscosity of blood will increase the amount of stress placed on the heart while it is pumping.Viscosity of blood is highest when ________.
A) hemoglobin levels are lowest
B) plasma levels are highest
C) hematocrit is highest
D) HbA1C levels are lowest
A) hemoglobin levels are lowest
B) plasma levels are highest
C) hematocrit is highest
D) HbA1C levels are lowest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following would provide no benefit to a person suffering any one of the various types of anemia?
A) treatment with synthetic erythropoietin
B) supplemental bilirubin injection
C) supplemental oxygen delivered by mask
D) blood transfusion
A) treatment with synthetic erythropoietin
B) supplemental bilirubin injection
C) supplemental oxygen delivered by mask
D) blood transfusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
People that have a single allele (gene copy)for sickle cell anemia are typically not sick from the disease and are said to be carriers of sickle cell trait.These people will more often live in the malaria belt of sub-Saharan Africa.The most likely explanation for this is ________.
A) sickle cell trait is passed on to the biting mosquitoes as malaria
B) the tropical climate attracts people with sickle cell trait
C) malaria is a cause of sickle cell trait
D) people with sickle cell trait have a better chance of surviving malaria
A) sickle cell trait is passed on to the biting mosquitoes as malaria
B) the tropical climate attracts people with sickle cell trait
C) malaria is a cause of sickle cell trait
D) people with sickle cell trait have a better chance of surviving malaria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
All lymphocytes are leukocytes,but not all leukocytes are lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following would you expect to have the least effect on hematocrit percentage?
A) prolonged or excessive fever
B) living at higher altitude
C) dehydration
D) injection with erythropoietin (EPO)
A) prolonged or excessive fever
B) living at higher altitude
C) dehydration
D) injection with erythropoietin (EPO)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If you centrifuge (spin)whole blood,you will find the red blood cells (erythrocytes)at the bottom of the tube and white blood cells atop them.This implies that ________.
A) red blood cells are larger than white blood cells
B) white blood cells are fewer in number than red blood cells
C) white blood cells are smaller than red blood cells
D) red blood cells have a greater density than white blood cells
A) red blood cells are larger than white blood cells
B) white blood cells are fewer in number than red blood cells
C) white blood cells are smaller than red blood cells
D) red blood cells have a greater density than white blood cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
With a patient administered an injection of colony stimulating factor (CSF)you would expect to see ________.
A) decreased Red blood cell count
B) decreased white blood cell count
C) increased Red blood cell count
D) increased white blood cell count
A) decreased Red blood cell count
B) decreased white blood cell count
C) increased Red blood cell count
D) increased white blood cell count

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A person with an extremely high count of neutrophils is likely suffering ________.
A) a bacterial infection
B) a viral infection
C) anemia
D) polycythemia
A) a bacterial infection
B) a viral infection
C) anemia
D) polycythemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following plasma components is most likely to rise in concentration during an acute infection?
A) fibrinogen
B) gamma globulins
C) platelets
D) albumin
A) fibrinogen
B) gamma globulins
C) platelets
D) albumin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Granulocytes called neutrophils are phagocytic and are the most numerous of all white blood cell types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A person with type B blood could receive blood from a person with either type B or type O blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Myelocytic leukemia involves a cancerous condition of lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Leukocytes move through the circulatory system by amoeboid motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A person exhibiting suppression of immunity,clotting disorder as well as low oxygen carrying capacity is likely suffering which of the following?
A) pernicious anemia
B) hemorrhagic anemia
C) aplastic anemia
D) iron deficiency anemia
A) pernicious anemia
B) hemorrhagic anemia
C) aplastic anemia
D) iron deficiency anemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



