Deck 4: Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity
1
Changing the orbit of a spacecraft by firing thrusters is an example of
A)Newton's first law of motion.
B)Newton's second law of motion.
C)Newton's third law of motion.
D)the universal law of gravitation.
E)none of the above.
A)Newton's first law of motion.
B)Newton's second law of motion.
C)Newton's third law of motion.
D)the universal law of gravitation.
E)none of the above.
C
2
The movement of a pool ball,after being struck by a cue,is an example of
A)Newton's first law of motion.
B)Newton's second law of motion.
C)Newton's third law of motion.
D)the universal law of gravitation.
E)conservation of momentum.
A)Newton's first law of motion.
B)Newton's second law of motion.
C)Newton's third law of motion.
D)the universal law of gravitation.
E)conservation of momentum.
B
3
If an object's velocity is doubled,its momentum is
A)halved.
B)unchanged.
C)doubled.
D)quadrupled.
E)dependent on its acceleration.
A)halved.
B)unchanged.
C)doubled.
D)quadrupled.
E)dependent on its acceleration.
C
4
Which of the following is an example in which you are traveling at constant speed but not at constant velocity?
A)rolling freely down a hill in a cart,traveling in a straight line
B)driving backward at exactly 50 km/hr
C)driving around in a circle at exactly 100 km/hr
D)jumping up and down,with a period of exactly 60 hops per minute
E)none of the above
A)rolling freely down a hill in a cart,traveling in a straight line
B)driving backward at exactly 50 km/hr
C)driving around in a circle at exactly 100 km/hr
D)jumping up and down,with a period of exactly 60 hops per minute
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose an object is moving in a straight line at 50 miles/hr.According to Newton's first law of motion,the object will
A)continue to move in the same way forever,no matter what happens.
B)continue to move in the same way until it is acted upon by a force.
C)eventually slow down and come to a stop.
D)continue to move in a straight line forever if it is in space,but slow and stop otherwise.
E)continually slow down but never quite come to a complete stop.
A)continue to move in the same way forever,no matter what happens.
B)continue to move in the same way until it is acted upon by a force.
C)eventually slow down and come to a stop.
D)continue to move in a straight line forever if it is in space,but slow and stop otherwise.
E)continually slow down but never quite come to a complete stop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What would happen if the Space Shuttle were launched with a speed greater than Earth's escape velocity?
A)It would travel away from Earth into the solar system.
B)It would travel in a higher orbit around Earth.
C)It would take less time to reach its bound orbit.
D)It would orbit Earth at a faster velocity.
E)It would be in an unstable orbit.
A)It would travel away from Earth into the solar system.
B)It would travel in a higher orbit around Earth.
C)It would take less time to reach its bound orbit.
D)It would orbit Earth at a faster velocity.
E)It would be in an unstable orbit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The fact that the Voyager spacecraft continues to travel out of the solar system,even though its rockets have no fuel,is an example of
A)Newton's first law of motion.
B)Newton's second law of motion.
C)Newton's third law of motion.
D)the universal law of gravitation.
E)none of the above.
A)Newton's first law of motion.
B)Newton's second law of motion.
C)Newton's third law of motion.
D)the universal law of gravitation.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
As long as an object is not gaining or losing mass,a net force on the object will cause a change in
A)acceleration.
B)direction.
C)weight.
D)speed.
E)velocity.
A)acceleration.
B)direction.
C)weight.
D)speed.
E)velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is not a conserved quantity?
A)energy
B)momentum
C)angular momentum
D)radiation
A)energy
B)momentum
C)angular momentum
D)radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If you drop a rock from a great height,about how fast will it be falling after 5 seconds,neglecting air resistance?
A)It depends on how heavy it is.
B)It depends on what shape it is.
C)10 m/s
D)15 m/s
E)50 m/s
A)It depends on how heavy it is.
B)It depends on what shape it is.
C)10 m/s
D)15 m/s
E)50 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
You are standing on a scale in an elevator.Suddenly you notice your weight decreases.What do you conclude?
A)The elevator is accelerating upwards.
B)The elevator is moving at a constant velocity upwards.
C)The elevator is accelerating downwards.
D)The elevator is moving at a constant velocity downwards.
E)Your diet is working.
A)The elevator is accelerating upwards.
B)The elevator is moving at a constant velocity upwards.
C)The elevator is accelerating downwards.
D)The elevator is moving at a constant velocity downwards.
E)Your diet is working.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How does the Space Shuttle take off?
A)Its rocket engines push against the launch pad propelling the shuttle upwards.
B)It converts mass-energy to kinetic energy.
C)It achieves lift from its wings in the same way that airplanes do.
D)Hot gas shoots out from the rocket and,by conservation of momentum,the shuttle moves in the opposite direction.
E)The hot rocket exhaust expands the air beneath the shuttle,propelling it forward.
A)Its rocket engines push against the launch pad propelling the shuttle upwards.
B)It converts mass-energy to kinetic energy.
C)It achieves lift from its wings in the same way that airplanes do.
D)Hot gas shoots out from the rocket and,by conservation of momentum,the shuttle moves in the opposite direction.
E)The hot rocket exhaust expands the air beneath the shuttle,propelling it forward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Momentum is defined as
A)mass times speed.
B)mass times velocity.
C)force times velocity.
D)mass times acceleration.
E)force times acceleration.
A)mass times speed.
B)mass times velocity.
C)force times velocity.
D)mass times acceleration.
E)force times acceleration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In which of the following cases would you feel weightless?
A)while walking on the Moon
B)while falling from an airplane with your parachute open
C)while traveling through space in an accelerating rocket
D)while falling from a roof
E)none of the above
A)while walking on the Moon
B)while falling from an airplane with your parachute open
C)while traveling through space in an accelerating rocket
D)while falling from a roof
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is not one of Newton's laws of motion?
A)What goes up must come down.
B)The rate of change of momentum of an object is equal to the net force applied to the object.
C)In the absence of a net force,an object moves with constant velocity.
D)For any force,there always is an equal and opposite reaction force.
E)All of the above are Newton's laws of motion.
A)What goes up must come down.
B)The rate of change of momentum of an object is equal to the net force applied to the object.
C)In the absence of a net force,an object moves with constant velocity.
D)For any force,there always is an equal and opposite reaction force.
E)All of the above are Newton's laws of motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Newton's second law of motion tells us that the net force applied to an object equals its
A)mass times energy.
B)momentum times velocity.
C)mass times velocity.
D)energy times acceleration.
E)mass times acceleration.
A)mass times energy.
B)momentum times velocity.
C)mass times velocity.
D)energy times acceleration.
E)mass times acceleration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If your mass is 60 kg on Earth,what would your mass be on the Moon?
A)10 lb
B)10 kg
C)50 kg
D)60 kg
E)60 lb
A)10 lb
B)10 kg
C)50 kg
D)60 kg
E)60 lb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A skater can spin faster by pulling her arms closer to her body or spin slower by spreading her arms out from her body.This is due to
A)the law of gravity.
B)Newton's third law.
C)conservation of momentum.
D)conservation of angular momentum.
E)conservation of energy.
A)the law of gravity.
B)Newton's third law.
C)conservation of momentum.
D)conservation of angular momentum.
E)conservation of energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What quantities does angular momentum depend upon?
A)mass and velocity
B)mass,velocity,and radius
C)force and radius
D)force,velocity,and radius
E)momentum and angular velocity
A)mass and velocity
B)mass,velocity,and radius
C)force and radius
D)force,velocity,and radius
E)momentum and angular velocity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the acceleration of gravity of Earth?
A)9.8 m/s² downward
B)9.8 m/s downward
C)9.8 km/s² downward
D)9.8 m²/s downward
E)9.8 km/s downward
A)9.8 m/s² downward
B)9.8 m/s downward
C)9.8 km/s² downward
D)9.8 m²/s downward
E)9.8 km/s downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following scenarios correctly demonstrates the transformation of mass into energy as given by Einstein's equation,E = mc²?
A)When hydrogen is fused into helium,whether in the Sun or in a nuclear bomb,the mass difference is turned into energy.
B)An object accelerated to a great speed has a lot of kinetic energy.
C)A mass raised to a great height has a lot of gravitational potential energy.
D)When you boil a pot of water,it has a high heat content,or thermal energy.
E)A burning piece of wood produces light and heat,therefore giving off radiative and thermal energy.
A)When hydrogen is fused into helium,whether in the Sun or in a nuclear bomb,the mass difference is turned into energy.
B)An object accelerated to a great speed has a lot of kinetic energy.
C)A mass raised to a great height has a lot of gravitational potential energy.
D)When you boil a pot of water,it has a high heat content,or thermal energy.
E)A burning piece of wood produces light and heat,therefore giving off radiative and thermal energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the formula E = mc²,what does E represent?
A)the kinetic energy of a moving object
B)the radiative energy carried by light
C)the gravitational potential energy of an object held above the ground
D)the mass-energy,or potential energy stored in an object's mass
E)the electric charge of the object
A)the kinetic energy of a moving object
B)the radiative energy carried by light
C)the gravitational potential energy of an object held above the ground
D)the mass-energy,or potential energy stored in an object's mass
E)the electric charge of the object

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is a form of electrical potential energy?
A)coal
B)energy coming to your house from power companies
C)energy from the Sun
D)light from a fluorescent bulb
E)moving blades on an electric mixer
A)coal
B)energy coming to your house from power companies
C)energy from the Sun
D)light from a fluorescent bulb
E)moving blades on an electric mixer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not a unit of energy?
A)Calorie
B)joule
C)calorie
D)kilowatt
E)British thermal unit
A)Calorie
B)joule
C)calorie
D)kilowatt
E)British thermal unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What does temperature measure?
A)the average mass of particles in a substance
B)the average size of particles in a substance
C)the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance
D)the total number of particles in a substance
E)the total potential energy of particles in a substance
A)the average mass of particles in a substance
B)the average size of particles in a substance
C)the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance
D)the total number of particles in a substance
E)the total potential energy of particles in a substance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The force of gravity is an inverse square law.This means that,if you double the distance between two large masses,the gravitational force between them
A)also doubles.
B)strengthens by a factor of 4.
C)weakens by a factor of 4.
D)weakens by a factor of 2.
E)is unaffected.
A)also doubles.
B)strengthens by a factor of 4.
C)weakens by a factor of 4.
D)weakens by a factor of 2.
E)is unaffected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Gasoline is useful in cars because it has
A)gravitational potential energy.
B)chemical potential energy.
C)electrical potential energy.
D)kinetic energy.
E)radiative energy.
A)gravitational potential energy.
B)chemical potential energy.
C)electrical potential energy.
D)kinetic energy.
E)radiative energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The amount of gravitational potential energy released as an object falls depends on
A)its mass and the distance it falls,as well as the rate of gravitational acceleration.
B)its mass and its speed at the time it begins falling.
C)only the distance it falls.
D)only its mass.
E)only its speed at the time it begins falling.
A)its mass and the distance it falls,as well as the rate of gravitational acceleration.
B)its mass and its speed at the time it begins falling.
C)only the distance it falls.
D)only its mass.
E)only its speed at the time it begins falling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to the universal law of gravitation,the force due to gravity is
A)directly proportional to the square of the distance between objects.
B)inversely proportional to the square of the distance between objects.
C)directly proportional to the distance between objects.
D)inversely proportional to the distance between objects.
E)not dependent on the distance between objects.
A)directly proportional to the square of the distance between objects.
B)inversely proportional to the square of the distance between objects.
C)directly proportional to the distance between objects.
D)inversely proportional to the distance between objects.
E)not dependent on the distance between objects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which object has the most kinetic energy?
A)a 4-ton truck moving 50 km/hr
B)a 3-ton truck moving 70 km/hr
C)a 2-ton truck moving 90 km/hr
D)a 1-ton truck moving 110 km/hr
E)A,B,C,and D all have the same kinetic energy.
A)a 4-ton truck moving 50 km/hr
B)a 3-ton truck moving 70 km/hr
C)a 2-ton truck moving 90 km/hr
D)a 1-ton truck moving 110 km/hr
E)A,B,C,and D all have the same kinetic energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
According to the universal law of gravitation,if you triple the distance between two objects,then the gravitational force between them will
A)increase by a factor of 3.
B)decrease by a factor of 3.
C)decrease by a factor of 6.
D)increase by a factor of 9.
E)decrease by a factor of 9.
A)increase by a factor of 3.
B)decrease by a factor of 3.
C)decrease by a factor of 6.
D)increase by a factor of 9.
E)decrease by a factor of 9.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Radiative energy is
A)heat energy.
B)energy from nuclear power plants.
C)energy carried by light.
D)energy used to power home radiators.
E)energy of motion.
A)heat energy.
B)energy from nuclear power plants.
C)energy carried by light.
D)energy used to power home radiators.
E)energy of motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Where does the energy come from that your body uses to keep you alive?
A)It is produced from the radiative energy of the Sun on your skin.
B)It comes from the foods you eat.
C)It comes from the water you drink.
D)It is in the air that you breathe.
E)It is created during the time that you rest or sleep.
A)It is produced from the radiative energy of the Sun on your skin.
B)It comes from the foods you eat.
C)It comes from the water you drink.
D)It is in the air that you breathe.
E)It is created during the time that you rest or sleep.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose you heat up an oven and boil a pot of water.Which of the following explains why you would be burned by sticking your hand briefly in the pot but not by sticking your hand briefly in the oven?
A)The oven has a higher temperature than the water.
B)The water has a higher temperature than the oven.
C)The oven has a higher heat content than the water.
D)The molecules in the water are moving faster than the molecules in the oven.
E)The water has a higher heat content than the oven because of density.
A)The oven has a higher temperature than the water.
B)The water has a higher temperature than the oven.
C)The oven has a higher heat content than the water.
D)The molecules in the water are moving faster than the molecules in the oven.
E)The water has a higher heat content than the oven because of density.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Absolute zero is
A)0° Kelvin.
B)0° Celsius.
C)0° Fahrenheit.
D)32° Fahrenheit.
E)273° Celsius.
A)0° Kelvin.
B)0° Celsius.
C)0° Fahrenheit.
D)32° Fahrenheit.
E)273° Celsius.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Of the temperature ranges below,which range represents the smallest range of actual temperature?
A)50-100° Kelvin
B)50-100° Celsius
C)50-100° Fahrenheit
D)They all represent the same change in temperature.
A)50-100° Kelvin
B)50-100° Celsius
C)50-100° Fahrenheit
D)They all represent the same change in temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Considering Einstein's famous equation,E = mc²,which of the following statements is true?
A)Mass can be turned into energy,but energy cannot be turned back into mass.
B)It takes a large amount of mass to produce a small amount of energy.
C)A small amount of mass can be turned into a large amount of energy.
D)You can make mass into energy if you can accelerate the mass to the speed of light.
E)One kilogram of mass represents 1 joule of energy.
A)Mass can be turned into energy,but energy cannot be turned back into mass.
B)It takes a large amount of mass to produce a small amount of energy.
C)A small amount of mass can be turned into a large amount of energy.
D)You can make mass into energy if you can accelerate the mass to the speed of light.
E)One kilogram of mass represents 1 joule of energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When a rock is held above the ground,we say it has some potential energy.When we let it go,it falls and we say the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy.Finally,the rock hits the ground.What has happened to the energy?
A)The energy goes into the ground and,as a result,the orbit of the earth about the Sun is slightly changed.
B)The energy goes to producing sound and to heating the ground,rock,and surrounding air.
C)The rock keeps the energy inside it (saving it for later use).
D)It is lost forever.Energy does not have to be conserved.
E)It is transformed back into gravitational potential energy.
A)The energy goes into the ground and,as a result,the orbit of the earth about the Sun is slightly changed.
B)The energy goes to producing sound and to heating the ground,rock,and surrounding air.
C)The rock keeps the energy inside it (saving it for later use).
D)It is lost forever.Energy does not have to be conserved.
E)It is transformed back into gravitational potential energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements correctly describes the law of conservation of energy?
A)An object always has the same amount of energy.
B)Energy can change between many different forms,such as potential,kinetic,and thermal,but it is ultimately destroyed.
C)The total quantity of energy in the universe never changes.
D)The fact that you can fuse hydrogen into helium to produce energy means that helium can be turned into hydrogen to produce energy.
E)It is not really possible for an object to gain or lose potential energy,because energy cannot be destroyed.
A)An object always has the same amount of energy.
B)Energy can change between many different forms,such as potential,kinetic,and thermal,but it is ultimately destroyed.
C)The total quantity of energy in the universe never changes.
D)The fact that you can fuse hydrogen into helium to produce energy means that helium can be turned into hydrogen to produce energy.
E)It is not really possible for an object to gain or lose potential energy,because energy cannot be destroyed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The ultimate source of energy that powers the Sun is
A)chemical potential energy of hydrogen burning into helium.
B)mass energy of hydrogen fusing into helium.
C)gravitational potential energy of the contraction of the gas cloud that formed the Sun.
D)kinetic energy of the orbital motion of the Sun.
E)thermal energy of the hydrogen atoms in the Sun.
A)chemical potential energy of hydrogen burning into helium.
B)mass energy of hydrogen fusing into helium.
C)gravitational potential energy of the contraction of the gas cloud that formed the Sun.
D)kinetic energy of the orbital motion of the Sun.
E)thermal energy of the hydrogen atoms in the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If you double the mass of fusion material in a hydrogen bomb,you quadruple the amount of energy generated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The mass of Jupiter can be calculated by
A)measuring the orbital period and distance of Jupiter's orbit around the Sun.
B)measuring the orbital period and distance of one of Jupiter's moons.
C)measuring the orbital speed of one of Jupiter's moons.
D)knowing the Sun's mass and measuring how Jupiter's speed changes during its elliptical orbit around the Sun.
E)knowing the Sun's mass and measuring the average distance of Jupiter from the Sun.
A)measuring the orbital period and distance of Jupiter's orbit around the Sun.
B)measuring the orbital period and distance of one of Jupiter's moons.
C)measuring the orbital speed of one of Jupiter's moons.
D)knowing the Sun's mass and measuring how Jupiter's speed changes during its elliptical orbit around the Sun.
E)knowing the Sun's mass and measuring the average distance of Jupiter from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
At which lunar phase(s)are tides least pronounced (e.g. ,the lowest high tides)?
A)first quarter
B)new Moon
C)full Moon
D)both new and full Moons
E)both first and third quarters
A)first quarter
B)new Moon
C)full Moon
D)both new and full Moons
E)both first and third quarters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Suppose a lone asteroid happens to be passing relatively near Jupiter (but not near any of its moons),following a hyperbolic orbit as it approaches Jupiter.Which of the following statements would be true?
A)Jupiter's gravity would capture the asteroid,making it a new moon of Jupiter.
B)The asteroid's orbit around Jupiter would not change,and it would go out on the same hyperbolic orbit that it came in on.
C)Jupiter would probably expel the asteroid far out into the solar system.
D)The asteroid would slowly spiral into Jupiter until it crashed into the atmosphere.
E)Any of these scenarios is possible.
A)Jupiter's gravity would capture the asteroid,making it a new moon of Jupiter.
B)The asteroid's orbit around Jupiter would not change,and it would go out on the same hyperbolic orbit that it came in on.
C)Jupiter would probably expel the asteroid far out into the solar system.
D)The asteroid would slowly spiral into Jupiter until it crashed into the atmosphere.
E)Any of these scenarios is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Imagine we've discovered a planet orbiting another star at 1 AU every 6 months.The planet has a moon that orbits the planet at the same distance as our Moon,but it takes 2 months.What can we infer about this planet?
A)It is more massive than Earth.
B)It is less massive than Earth.
C)It has the same mass as Earth.
D)We cannot answer the question without knowing the mass of the star.
E)We cannot answer the question without knowing the mass of the moon.
A)It is more massive than Earth.
B)It is less massive than Earth.
C)It has the same mass as Earth.
D)We cannot answer the question without knowing the mass of the star.
E)We cannot answer the question without knowing the mass of the moon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A basketball player jumps to make a basket,and remains in the air for a moment.A sportscaster,talking about the game,then remarks that she has "defied gravity." Which of the following accurately describes the situation?
A)The player did stay in the air in spite of the Law of Gravitation,but a single counter-observation is not enough to warrant revisiting a theory that usually works.
B)The player produced enough force with her legs to accelerate up into the air,and gravity brought her back down with an acceleration of 9.8 m/s².
C)The player only seemed to defy gravity,but part of the Universal Law of Gravitation makes an exception for basketball players.
D)The player has defied gravity,so scientists must go back into the lab to refine their theory.
A)The player did stay in the air in spite of the Law of Gravitation,but a single counter-observation is not enough to warrant revisiting a theory that usually works.
B)The player produced enough force with her legs to accelerate up into the air,and gravity brought her back down with an acceleration of 9.8 m/s².
C)The player only seemed to defy gravity,but part of the Universal Law of Gravitation makes an exception for basketball players.
D)The player has defied gravity,so scientists must go back into the lab to refine their theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The allowed shapes for orbits under the force of gravity are
A)ellipses only.
B)ellipses and spirals.
C)ellipses,parabolas,and hyperbolas.
D)ellipses,spirals,and parabolas.
E)spirals,circles,and squares.
A)ellipses only.
B)ellipses and spirals.
C)ellipses,parabolas,and hyperbolas.
D)ellipses,spirals,and parabolas.
E)spirals,circles,and squares.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
At which lunar phase(s)are tides most pronounced (e.g. ,the highest high tides)?
A)first quarter
B)new Moon
C)full Moon
D)both new and full Moons
E)both first and third quarters
A)first quarter
B)new Moon
C)full Moon
D)both new and full Moons
E)both first and third quarters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When energy is converted from one form to another,a tiny amount is inevitably lost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The orbital period of a geosynchronous satellite is
A)23 hours 56 minutes.
B)24 hours.
C)365.25 days.
D)12 years.
E)26,000 years.
A)23 hours 56 minutes.
B)24 hours.
C)365.25 days.
D)12 years.
E)26,000 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following best describes the origin of ocean tides on Earth?
A)Tides are caused by the difference in the force of gravity exerted by the Moon across the sphere of the earth.
B)The Moon's gravity pulls harder on water than on land,because water is less dense than rock.
C)Tides are caused by the 23 1/2° tilt of the earth's rotational axis to the ecliptic plane.
D)Tides are caused primarily by the gravitational force of the Sun.
E)Tides are caused on the side of Earth nearest the Moon because the Moon's gravity attracts the water.
A)Tides are caused by the difference in the force of gravity exerted by the Moon across the sphere of the earth.
B)The Moon's gravity pulls harder on water than on land,because water is less dense than rock.
C)Tides are caused by the 23 1/2° tilt of the earth's rotational axis to the ecliptic plane.
D)Tides are caused primarily by the gravitational force of the Sun.
E)Tides are caused on the side of Earth nearest the Moon because the Moon's gravity attracts the water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
According to what we now know from Newton's laws,which of the following best explains why Kepler's second law is true?
A)A planet's angular momentum must be conserved as it moves around its orbit.
B)Orbits must be elliptical in shape.
C)Gravity is an inverse cube law.
D)This effect happens because of the influence of other planets on a particular planet's orbit.
A)A planet's angular momentum must be conserved as it moves around its orbit.
B)Orbits must be elliptical in shape.
C)Gravity is an inverse cube law.
D)This effect happens because of the influence of other planets on a particular planet's orbit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Speed and velocity are the same thing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The Moon is constantly falling toward Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If you are driving at 30 miles per hour and increase your speed to 60 miles per hour,you quadruple your kinetic energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
According to the universal law of gravitation,if you double the masses of both attracting objects,then the gravitational force between them will
A)not change at all.
B)increase by a factor of 2.
C)decrease by a factor of 2.
D)increase by a factor of 4.
E)decrease by a factor of 4.
A)not change at all.
B)increase by a factor of 2.
C)decrease by a factor of 2.
D)increase by a factor of 4.
E)decrease by a factor of 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The center of mass of a binary star system is
A)the center of the most massive of the two stars.
B)the center of the least massive of the two stars.
C)the point halfway in between them.
D)the point at which the two objects would balance if they were somehow connected.
E)the average mass of the two stars.
A)the center of the most massive of the two stars.
B)the center of the least massive of the two stars.
C)the point halfway in between them.
D)the point at which the two objects would balance if they were somehow connected.
E)the average mass of the two stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Each of the following lists two facts.Which pair can be used with Newton's version of Kepler's third law to determine the mass of the Sun?
A)Mercury is 0.387 AU from the Sun,and Earth is 1 AU from the Sun.
B)The mass of Earth is 6 × 10²⁴ kg,and Earth orbits the Sun in 1 year.
C)Earth rotates in 1 day and orbits the Sun in 1 year.
D)Earth is 150 million km from the Sun and orbits the Sun in 1 year.
E)Jupiter is the most massive planet and has a mass of 1.9 × 10²⁷ kg.
A)Mercury is 0.387 AU from the Sun,and Earth is 1 AU from the Sun.
B)The mass of Earth is 6 × 10²⁴ kg,and Earth orbits the Sun in 1 year.
C)Earth rotates in 1 day and orbits the Sun in 1 year.
D)Earth is 150 million km from the Sun and orbits the Sun in 1 year.
E)Jupiter is the most massive planet and has a mass of 1.9 × 10²⁷ kg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The tides on Earth are an example of
A)Newton's first law of motion.
B)Newton's second law of motion.
C)Newton's third law of motion.
D)the universal law of gravitation.
E)none of the above
A)Newton's first law of motion.
B)Newton's second law of motion.
C)Newton's third law of motion.
D)the universal law of gravitation.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Kepler deduced his laws of planetary motion once Newton had published his universal law of gravitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
State Newton's three laws of motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Tidal friction caused by Earth's stretching from the Moon's gravity is gradually slowing down the rotation of Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Give an example in which kinetic energy can be converted to thermal energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Imagine another solar system,with a star of the same mass as the Sun.Suppose there is a planet in that solar system with a mass of 2MEₐᵣth orbiting at a distance of 1 AU from the star.What (approximately)is the orbital period of this planet? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Briefly explain why Earth feels a greater tidal force from the Moon than from the Sun,even though it feels a greater gravitational force from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Process of Science: Gravity only affects very massive objects and we can therefore only test theories about it when looking at the orbits of planets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The Moon orbits Earth in an average of 27.3 days at an average distance of 384,000 kilometers.Using Newton's version of Kepler's third law
p² =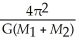 a³ determine the mass of Earth.You may neglect the mass of the Moon in comparison to the mass of Earth.
a³ determine the mass of Earth.You may neglect the mass of the Moon in comparison to the mass of Earth.
p² =
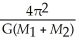 a³ determine the mass of Earth.You may neglect the mass of the Moon in comparison to the mass of Earth.
a³ determine the mass of Earth.You may neglect the mass of the Moon in comparison to the mass of Earth.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Explain what synchronous rotation is.What is it caused by? Give an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Give an example in which thermal energy might be converted to gravitational energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose a solar system has a star that is four times more massive than our Sun.If that solar system has a planet the same size as Earth,orbiting at a distance of 1 AU,what is the orbital period of the planet? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The escape velocity from Earth is greater for larger rockets than for small ones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose it takes 6 seconds for a watermelon to fall to the ground after being dropped from a tall building.If there were no air resistance,so that the watermelon would fall with the acceleration of gravity,about how fast would it be going when it hit the ground?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The Moon is slowly moving away from Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Explain how we can use Newton's version of Kepler's third law to measure the total mass of two stars in a binary system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Doubling the distance between two objects halves the gravitational force between them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Under what conditions is an object weightless?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
There is no gravity in space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Suppose a satellite is in a low-Earth orbit.Is it possible that the satellite will eventually fall to the ground? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Unbound orbits have more orbital energy than bound orbits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The center of mass for Earth orbiting the Sun lies inside the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



