Deck 25: Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/118
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation
1
Which of the following statements about sidereal and solar days is not true?
A)A solar day is 4 minutes longer than a sidereal day.
B)A solar day represents more than 360° of rotation for Earth.
C)The time it takes for a star to make one circuit of our sky is one sidereal day.
D)The time it takes for the Sun to make one circuit of our sky is one solar day.
E)The time it takes for the Moon to make one circuit of our sky is one solar day.
A)A solar day is 4 minutes longer than a sidereal day.
B)A solar day represents more than 360° of rotation for Earth.
C)The time it takes for a star to make one circuit of our sky is one sidereal day.
D)The time it takes for the Sun to make one circuit of our sky is one solar day.
E)The time it takes for the Moon to make one circuit of our sky is one solar day.
E
2
Suppose you live at latitude 40°N.Which of the following describes the conditions that make a star circumpolar?
A)Stars are circumpolar if they have declination > +50°.
B)Stars are circumpolar if they have declination > +40°.
C)Stars are circumpolar if they have right ascension > 6 hr.
D)Stars are circumpolar if they have right ascension < 6 hr.
E)No stars are circumpolar at this latitude.
A)Stars are circumpolar if they have declination > +50°.
B)Stars are circumpolar if they have declination > +40°.
C)Stars are circumpolar if they have right ascension > 6 hr.
D)Stars are circumpolar if they have right ascension < 6 hr.
E)No stars are circumpolar at this latitude.
A
3
What is the hour angle of a star crossing your meridian?
A)-6 hours
B)0 hours
C)6 hours
D)It depends on your latitude.
E)It depends on the right ascension of the star.
A)-6 hours
B)0 hours
C)6 hours
D)It depends on your latitude.
E)It depends on the right ascension of the star.
B
4
Which of the following best describes the Tropic of Cancer?
A)It is any place where it is always very warm.
B)It is another name for the equator.
C)It is a place where the Sun appears to remain stationary in the sky.
D)It is a place where the Sun is directly overhead at noon on the summer solstice.
E)It is a place where the Sun is directly overhead at noon on the spring equinox.
A)It is any place where it is always very warm.
B)It is another name for the equator.
C)It is a place where the Sun appears to remain stationary in the sky.
D)It is a place where the Sun is directly overhead at noon on the summer solstice.
E)It is a place where the Sun is directly overhead at noon on the spring equinox.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose the date is March 21 and the Sun passes through your zenith at noon.Where are you?
A)the equator
B)the Tropic of Cancer
C)the Tropic of Capricorn
D)the Arctic Circle
E)the Antarctic Circle
A)the equator
B)the Tropic of Cancer
C)the Tropic of Capricorn
D)the Arctic Circle
E)the Antarctic Circle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Our calendar has leap years because
A)there is one more sidereal day in a year than solar days.
B)a tropical year is slightly more than 365 days.
C)there is a difference between a sidereal year and a tropical year.
D)the perihelion of Earth's orbit is slowly advancing.
A)there is one more sidereal day in a year than solar days.
B)a tropical year is slightly more than 365 days.
C)there is a difference between a sidereal year and a tropical year.
D)the perihelion of Earth's orbit is slowly advancing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The lunar month is longer than the sidereal month because
A)the Moon completes the cycle of lunar phases before it completes a full orbit around Earth.
B)the Moon has to complete more than one full orbit around Earth to complete the cycle of lunar phases.
C)the Moon orbits Earth faster than Earth orbits the Sun.
D)the Moon orbits Earth faster than Earth rotates.
E)the lunar month is based on the Moon's orbit,while the sidereal month is based on Earth's orbit.
A)the Moon completes the cycle of lunar phases before it completes a full orbit around Earth.
B)the Moon has to complete more than one full orbit around Earth to complete the cycle of lunar phases.
C)the Moon orbits Earth faster than Earth orbits the Sun.
D)the Moon orbits Earth faster than Earth rotates.
E)the lunar month is based on the Moon's orbit,while the sidereal month is based on Earth's orbit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Based on our current Gregorian calendar,which of the following years is not a leap year?
A)2000
B)2004
C)2008
D)2012
E)All of the above are leap years.
A)2000
B)2004
C)2008
D)2012
E)All of the above are leap years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What kind of time can be read directly from a sundial?
A)apparent solar time
B)mean solar time
C)standard time
D)daylight saving time
E)sidereal time
A)apparent solar time
B)mean solar time
C)standard time
D)daylight saving time
E)sidereal time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose you live at latitude 40°N.Which of the following describes the path of the celestial equator through your sky?
A)It goes from due south on your horizon,to your zenith,to due north on your horizon.
B)It goes from due east on your horizon,to your zenith,to due west on your horizon.
C)It goes from due east on your horizon,to an altitude of 50° in the south,to due west on your horizon.
D)It goes from due east on your horizon,to an altitude of 40° in the south,to due west on your horizon.
E)It goes from due east on your horizon,to an altitude of 40° in the north,to due west on your horizon.
A)It goes from due south on your horizon,to your zenith,to due north on your horizon.
B)It goes from due east on your horizon,to your zenith,to due west on your horizon.
C)It goes from due east on your horizon,to an altitude of 50° in the south,to due west on your horizon.
D)It goes from due east on your horizon,to an altitude of 40° in the south,to due west on your horizon.
E)It goes from due east on your horizon,to an altitude of 40° in the north,to due west on your horizon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is the reason for the leap years?
A)precession of Earth's axis
B)the tilt of Earth's axis
C)the combined effect of the rotation of Earth and its orbit about the Sun
D)Earth year being a non-integer number of Earth days
E)the non-circular orbit of Earth around the Sun
A)precession of Earth's axis
B)the tilt of Earth's axis
C)the combined effect of the rotation of Earth and its orbit about the Sun
D)Earth year being a non-integer number of Earth days
E)the non-circular orbit of Earth around the Sun

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Sun is rising in the east and will be on your meridian in 2 hours.What time is it?
A)2 A.M.
B)2 P.M.
C)10 A.M.
D)10 P.M.
E)noon
A)2 A.M.
B)2 P.M.
C)10 A.M.
D)10 P.M.
E)noon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The time between rising and setting of a star
A)is always 12 hours.
B)depends on the star's declination.
C)depends on the star's right ascension.
D)depends on the observer's latitude.
E)depends on the observer's longitude.
A)is always 12 hours.
B)depends on the star's declination.
C)depends on the star's right ascension.
D)depends on the observer's latitude.
E)depends on the observer's longitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The amount of time between successive passes of any given star across the meridian is
A)23 hours 56 minutes.
B)24 hours.
C)365.25 days.
D)12 years.
E)26,000 years.
A)23 hours 56 minutes.
B)24 hours.
C)365.25 days.
D)12 years.
E)26,000 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Suppose you lived at Earth's equator.Which of the following statements would not be true?
A)The north celestial pole is directly on your horizon,due north (with Polaris quite nearby).
B)The south celestial pole is directly on your horizon,due south.
C)Every day of the year,the Sun is above your horizon for 12 hours and below it for 12 hours.
D)The celestial equator goes through your sky from due east on your horizon,through 50° altitude in the south,to due west on the horizon.
E)No stars are circumpolar.
A)The north celestial pole is directly on your horizon,due north (with Polaris quite nearby).
B)The south celestial pole is directly on your horizon,due south.
C)Every day of the year,the Sun is above your horizon for 12 hours and below it for 12 hours.
D)The celestial equator goes through your sky from due east on your horizon,through 50° altitude in the south,to due west on the horizon.
E)No stars are circumpolar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The average length of a solar day is
A)23 hours 56 minutes.
B)24 hours.
C)365.25 days.
D)12 years.
E)26,000 years.
A)23 hours 56 minutes.
B)24 hours.
C)365.25 days.
D)12 years.
E)26,000 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is the reason for the solar day being longer than a sidereal day?
A)precession of Earth's axis
B)the tilt of Earth's axis
C)the combined effect of the rotation of Earth and its orbit about the Sun
D)Earth year being a non-integer number of Earth days
E)the non-circular orbit of Earth around the Sun
A)precession of Earth's axis
B)the tilt of Earth's axis
C)the combined effect of the rotation of Earth and its orbit about the Sun
D)Earth year being a non-integer number of Earth days
E)the non-circular orbit of Earth around the Sun

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose the date is March 21 and the Sun crosses your meridian at an altitude of 23.5° in the north.Where are you?
A)the equator
B)the Tropic of Cancer
C)the Tropic of Capricorn
D)the Arctic Circle
E)the Antarctic Circle
A)the equator
B)the Tropic of Cancer
C)the Tropic of Capricorn
D)the Arctic Circle
E)the Antarctic Circle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The south celestial pole appears on your meridian at an altitude of 30° in the south.Where are you?
A)latitude = 30°S
B)latitude = 60°S
C)latitude = 30°N
D)latitude = 60°N
E)the South Pole
A)latitude = 30°S
B)latitude = 60°S
C)latitude = 30°N
D)latitude = 60°N
E)the South Pole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
All the following statements are true.Which one explains why mean solar time differs from apparent solar time?
A)The length of a solar day is not always exactly 24 hours.
B)Earth's rotation period is actually about 23 hours 56 minutes,not 24 hours.
C)Earth's axis precesses with a period of 26,000 years.
D)The Sun reaches the meridian at different times at different longitudes within the same time zone.
E)The path of the Sun through the sky depends on both latitude and date.
A)The length of a solar day is not always exactly 24 hours.
B)Earth's rotation period is actually about 23 hours 56 minutes,not 24 hours.
C)Earth's axis precesses with a period of 26,000 years.
D)The Sun reaches the meridian at different times at different longitudes within the same time zone.
E)The path of the Sun through the sky depends on both latitude and date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The constellation shaped like a W is
A)Cassiopeia.
B)Pegasus.
C)Canis Major.
D)Taurus.
E)Andromeda.
A)Cassiopeia.
B)Pegasus.
C)Canis Major.
D)Taurus.
E)Andromeda.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Our calendar is based on the length of the tropical year rather than the sidereal year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following explains why navigators a few hundred years ago found it much more difficult to determine their longitude than their latitude?
A)Determining longitude requires mathematical techniques that were not known at the time.
B)Determining longitude without modern instruments requires being able to see the Moon.
C)Determining longitude requires much more precise measurements of angles in the sky than does latitude.
D)Determining longitude requires having an accurate clock.
A)Determining longitude requires mathematical techniques that were not known at the time.
B)Determining longitude without modern instruments requires being able to see the Moon.
C)Determining longitude requires much more precise measurements of angles in the sky than does latitude.
D)Determining longitude requires having an accurate clock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The celestial coordinates of the Sun change from day to day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
No matter where you live on Earth,except the poles,your meridian extends from due south on your horizon,through your zenith,to due north on your horizon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose the date is June 21 and the Sun never sets,just touching your northern horizon at midnight.Where are you?
A)the equator
B)the Tropic of Cancer
C)the Tropic of Capricorn
D)the Arctic Circle
E)the Antarctic Circle
A)the equator
B)the Tropic of Cancer
C)the Tropic of Capricorn
D)the Arctic Circle
E)the Antarctic Circle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
No matter where you live on Earth,the Sun is always directly overhead at noon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The Sun is on your meridian,and you have a UT clock that tells you it is midnight in Greenwich.What is your longitude?
A)12° west of Greenwich
B)12° east of Greenwich
C)60° west of Greenwich
D)60° east of Greenwich
E)180° of longitude from Greenwich
A)12° west of Greenwich
B)12° east of Greenwich
C)60° west of Greenwich
D)60° east of Greenwich
E)180° of longitude from Greenwich

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The three bright stars that make up the Winter Triangle are
A)Polaris,Aldebaran,and Algol.
B)Polaris,Betelgeuse,and Sirius.
C)Betelgeuse,Procyon,and Sirius.
D)Betelgeuse,Rigel,and Aldebaran.
E)Capella,Procyon,and Sirius.
A)Polaris,Aldebaran,and Algol.
B)Polaris,Betelgeuse,and Sirius.
C)Betelgeuse,Procyon,and Sirius.
D)Betelgeuse,Rigel,and Aldebaran.
E)Capella,Procyon,and Sirius.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements about Betelgeuse is not true?
A)It is distinctly red in color.
B)We now know that it is a very massive star near the end of its life.
C)Its Arabic name means "the demon star."
D)It is one star of the three stars of the Winter Triangle,along with Procyon and Sirius.
E)It is the upper left shoulder star of the constellation Orion.
A)It is distinctly red in color.
B)We now know that it is a very massive star near the end of its life.
C)Its Arabic name means "the demon star."
D)It is one star of the three stars of the Winter Triangle,along with Procyon and Sirius.
E)It is the upper left shoulder star of the constellation Orion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The three stars of the Summer Triangle are
A)Antares,Arcturus,and Spica.
B)Arcturus,Vega,and Algol.
C)Deneb,Spica,and Vega.
D)Vega,Deneb,and Altair.
E)Altair,Antares,and Arcturus.
A)Antares,Arcturus,and Spica.
B)Arcturus,Vega,and Algol.
C)Deneb,Spica,and Vega.
D)Vega,Deneb,and Altair.
E)Altair,Antares,and Arcturus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
All directions are south from the North Pole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The coordinates used to locate a position on the celestial sphere are altitude and declination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The summer solstice is east of the vernal equinox by 6 hours of right ascension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Sun is on your meridian,and you have a UT clock that tells you it is 3 P.M.in Greenwich.What is your longitude?
A)3° west of Greenwich
B)3° east of Greenwich
C)45° west of Greenwich
D)45° east of Greenwich
E)30° west of Greenwich
A)3° west of Greenwich
B)3° east of Greenwich
C)45° west of Greenwich
D)45° east of Greenwich
E)30° west of Greenwich

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Each of the following lists a constellation and a bright star.In all cases but one,the star is part of the constellation.Which one is the mismatch?
A)Scorpio,Vega
B)Cygnus,Deneb
C)Boötes,Arcturus
D)Virgo,Spica
E)Auriga,Capella
A)Scorpio,Vega
B)Cygnus,Deneb
C)Boötes,Arcturus
D)Virgo,Spica
E)Auriga,Capella

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
All of the following are true.Which of the following gives evidence that Earth's orbit is not perfectly circular?
A)The Sun's angular size changes throughout the year.
B)Earth's seasons are not of exactly equal length.
C)In North America,it is hotter in July than January.
D)Both A and C
E)Both A and B
A)The Sun's angular size changes throughout the year.
B)Earth's seasons are not of exactly equal length.
C)In North America,it is hotter in July than January.
D)Both A and C
E)Both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
On the equator,days and nights are always 12 hours long,no matter what time of year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The constellation shaped like a big square (the "great square of ...")is
A)Cassiopeia.
B)Pegasus.
C)Canis Major.
D)Taurus.
E)Andromeda.
A)Cassiopeia.
B)Pegasus.
C)Canis Major.
D)Taurus.
E)Andromeda.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
No matter where you live on Earth,the Sun always rises and sets each day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The Winter Triangle is formed by the stars Betelgeuse,Rigel,and Aldebaran.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Note to instructors: The following question assumes you gave a "lost at sea" question on your midterm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.1,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in the fall.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.
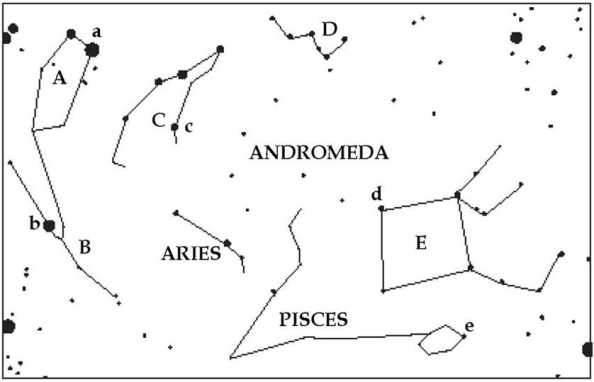
Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Aldebaran?

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Aldebaran?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For vacation,you decide to take a solo boat trip.While contemplating the universe,you lose track of your location.Fortunately,you have some astronomical tables and instruments,as well as a UT clock.You thereby put together the following description of your situation:
a.What is your latitude? How do you know?
b.What is your longitude? How do you know?
a.What is your latitude? How do you know?
b.What is your longitude? How do you know?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For vacation,you decide to take a solo boat trip.While contemplating the universe,you lose track of your location.Fortunately,you have some astronomical tables and instruments,as well as a UT clock.You thereby put together the following description of your situation:
∙ Your local time is midnight.
∙ Polaris appears at an altitude of 67° in the north.
∙ The UT clock reads 01:00.
a.What is your latitude? How do you know?
b.What is your longitude? How do you know?
∙ Your local time is midnight.
∙ Polaris appears at an altitude of 67° in the north.
∙ The UT clock reads 01:00.
a.What is your latitude? How do you know?
b.What is your longitude? How do you know?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
For vacation,you decide to take a solo boat trip.While contemplating the universe,you lose track of your location.Fortunately,you have some astronomical tables and instruments,as well as a UT clock.You thereby put together the following description of your situation:
∙ It is the day of the summer solstice.
∙ The Sun is on your meridian at an altitude of 67.5° in the north.
∙ The UT clock reads 06:00.
a.What is your latitude? How do you know?
b.What is your longitude? How do you know?
∙ It is the day of the summer solstice.
∙ The Sun is on your meridian at an altitude of 67.5° in the north.
∙ The UT clock reads 06:00.
a.What is your latitude? How do you know?
b.What is your longitude? How do you know?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.1,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in the fall.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which constellation (capital letters)is Pegasus?

Which constellation (capital letters)is Pegasus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Suppose that you live in Sydney,Australia (latitude 34°S).Describe the path of the Sun through your sky for each of the following days:
a.the day of the spring equinox
b.the day of the summer solstice
c.the day of the winter solstice
a.the day of the spring equinox
b.the day of the summer solstice
c.the day of the winter solstice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.1,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in the fall.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which constellation (capital letters)is Cassiopeia?

Which constellation (capital letters)is Cassiopeia?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A year at the south pole consists of 6 months of darkness and 6 months of daylight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For vacation,you decide to take a solo boat trip.While contemplating the universe,you lose track of your location.Fortunately,you have some astronomical tables and instruments,as well as a UT clock.You thereby put together the following description of your situation:
∙ It is the day of the spring equinox.
∙ The Sun is on your meridian at an altitude of 75° in the south.
∙ The UT clock reads 22:00.
a.What is your latitude? How do you know?
b.What is your longitude? How do you know?
∙ It is the day of the spring equinox.
∙ The Sun is on your meridian at an altitude of 75° in the south.
∙ The UT clock reads 22:00.
a.What is your latitude? How do you know?
b.What is your longitude? How do you know?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.1,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in the fall.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which constellation (capital letters)is Taurus?

Which constellation (capital letters)is Taurus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Summer Triangle is formed by the stars Deneb,Vega,and Altair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose you live at the equator.Describe the path of the Sun through your sky for each of the following days:
a.the day of the spring equinox
b.the day of the summer solstice
c.the day of the winter solstice
a.the day of the spring equinox
b.the day of the summer solstice
c.the day of the winter solstice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose you live at the North Pole.Describe the path of the Sun through your sky for each of the following days:
a.the day of the spring equinox
b.the day of the summer solstice
c.the day of the winter solstice
a.the day of the spring equinox
b.the day of the summer solstice
c.the day of the winter solstice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Your Local Sky
a.Where is the north (or south)celestial pole in your sky?
b.Describe the meridian in your sky.
c.Describe the celestial equator in your sky.
d.What is the range of declinations that makes a star circumpolar in your sky? Explain.
e.Describe the path of the Sun through your sky on the fall equinox.
f.Describe the path of the Sun through your sky on the winter solstice.
a.Where is the north (or south)celestial pole in your sky?
b.Describe the meridian in your sky.
c.Describe the celestial equator in your sky.
d.What is the range of declinations that makes a star circumpolar in your sky? Explain.
e.Describe the path of the Sun through your sky on the fall equinox.
f.Describe the path of the Sun through your sky on the winter solstice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.1,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in the fall.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which constellation (capital letters)is Auriga?

Which constellation (capital letters)is Auriga?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.1,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in the fall.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which constellation (capital letters)is Perseus?

Which constellation (capital letters)is Perseus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.1,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in the fall.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Capella?

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Capella?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.1,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in the fall.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Algol,the "demon star"?

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Algol,the "demon star"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Choose the appropriate star from Table S1.1 for the following questions:
Table S1.1
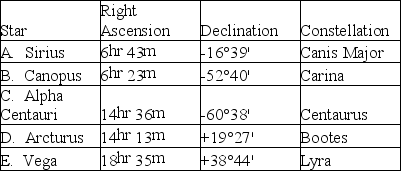
Suppose you live at latitude 20°N.Which star passes closest to your zenith on its daily path through your sky?
Table S1.1

Suppose you live at latitude 20°N.Which star passes closest to your zenith on its daily path through your sky?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.2,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in winter.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.
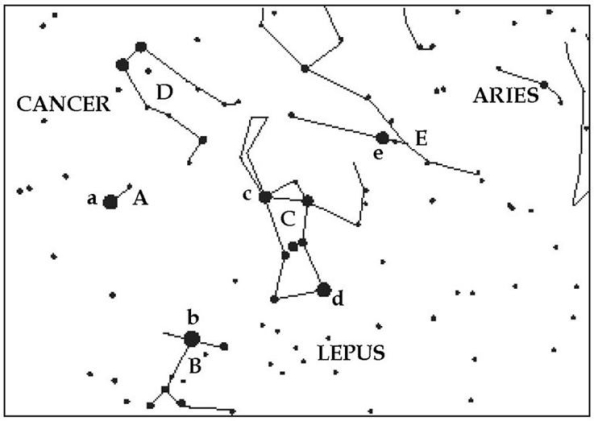
Which constellation (capital letters)is Orion?

Which constellation (capital letters)is Orion?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Choose the appropriate star from Table S1.1 for the following questions:
Table S1.1

Suppose you live at latitude 30°N.Which star is never visible in your sky?
Table S1.1

Suppose you live at latitude 30°N.Which star is never visible in your sky?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.2 which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in winter.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.
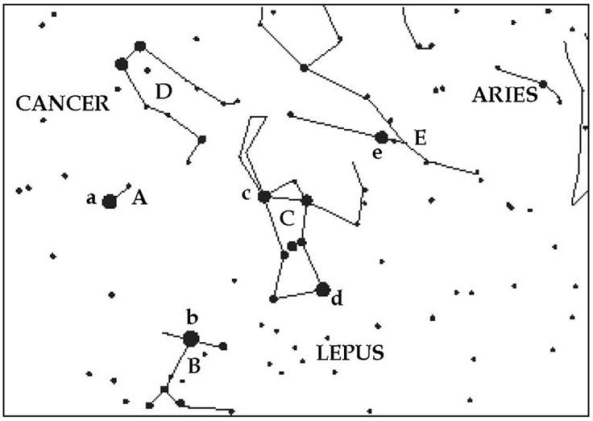
Which constellation (capital letters)is Canis Minor?

Which constellation (capital letters)is Canis Minor?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.2 which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in winter.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Aldebaran?

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Aldebaran?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.2 which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in winter.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Sirius?

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Sirius?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.2 which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in winter.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Rigel?

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Rigel?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Choose the appropriate star from Table S1.1 for the following questions:
Table S1.1

Suppose it is late June.Which star crosses your meridian around midnight? Assume you live at a latitude where all the stars on this list rise above your horizon each day.
Table S1.1

Suppose it is late June.Which star crosses your meridian around midnight? Assume you live at a latitude where all the stars on this list rise above your horizon each day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Choose the appropriate star from Table S1.1 for the following questions:
Table S1.1

Suppose you live at latitude 20°S.Which star passes closest to your zenith on its daily path through your sky?
Table S1.1

Suppose you live at latitude 20°S.Which star passes closest to your zenith on its daily path through your sky?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Choose the appropriate star from Table S1.2 for the following questions:
Table S1.2
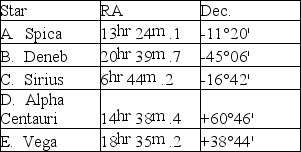
Which star remains above the horizon for the longest time each day at latitude 40°N?
Table S1.2

Which star remains above the horizon for the longest time each day at latitude 40°N?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.2 which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in winter.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Betelgeuse?

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Betelgeuse?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Choose the appropriate star from Table S1.1 for the following questions:
Table S1.1

Which star lies closest to the south celestial pole on the celestial sphere?
Table S1.1

Which star lies closest to the south celestial pole on the celestial sphere?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Choose the appropriate star from Table S1.1 for the following questions:
Table S1.1

Which star lies closest to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere?
Table S1.1

Which star lies closest to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Choose the appropriate star from Table S1.2 for the following questions:
Table S1.2

Which star can never be seen at latitude 40°N?
Table S1.2

Which star can never be seen at latitude 40°N?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.2,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in winter.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which constellation (capital letters)is Canis Major?

Which constellation (capital letters)is Canis Major?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.2,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in winter.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which constellation (capital letters)is Taurus?

Which constellation (capital letters)is Taurus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Choose the appropriate star from Table S1.2 for the following questions:
Table S1.2

Which star appears nearest to the south celestial pole?
Table S1.2

Which star appears nearest to the south celestial pole?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Choose the appropriate star from Table S1.1 for the following questions:
Table S1.1

Which star lies closest to the north celestial pole on the celestial sphere?
Table S1.1

Which star lies closest to the north celestial pole on the celestial sphere?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.2 which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in winter.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Procyon?

Which bright star (lowercase letters)is Procyon?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
For the following questions,refer to Figure S1.2,which shows a portion of the sky visible in the early evenings in winter.Note that five bright stars are labeled with lowercase letters and five constellations are labeled with capitals.A few hints are also given.

Which constellation (capital letters)is Gemini?

Which constellation (capital letters)is Gemini?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



