Deck 18: Electric Current and Circuits
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Electric Current and Circuits
1
An ohm is equivalent to which of the following?
A) volt/meter
B) coulomb/volt
C) ampere/coulomb
D) volt/ampere
E) ampere·coulomb
A) volt/meter
B) coulomb/volt
C) ampere/coulomb
D) volt/ampere
E) ampere·coulomb
volt/ampere
2
One hundred meters of 2.00 mm diameter wire has a resistance of 0.532 Ω. What is the resistivity of the material from which the wire is made?
A) 1.59 × 10-8 Ω·m
B) 1.67 × 10-8 Ω·m
C) 2.35 × 10-8 Ω·m
D) 2.65 × 10-8 Ω·m
E) 5.40 × 10-8 Ω·m
A) 1.59 × 10-8 Ω·m
B) 1.67 × 10-8 Ω·m
C) 2.35 × 10-8 Ω·m
D) 2.65 × 10-8 Ω·m
E) 5.40 × 10-8 Ω·m
1.67 × 10-8 Ω·m
3
When current flows through a wire
A) electrons are moving in the direction of the current.
B) electrons are moving opposite the direction of the current.
C) protons are moving in the direction of the current.
D) protons are moving opposite the direction of the current.
E) both protons and electrons are moving in the direction of the current.
A) electrons are moving in the direction of the current.
B) electrons are moving opposite the direction of the current.
C) protons are moving in the direction of the current.
D) protons are moving opposite the direction of the current.
E) both protons and electrons are moving in the direction of the current.
electrons are moving opposite the direction of the current.
4
The resistance of a wire increases by 3.9% when the temperature of the wire is raised 100°C. What is the temperature coefficient of resistivity of the wire material?
A) 3.9°C−1
B) 0.39°C−1
C) 0.039°C−1
D) 0.0039°C−1
E) 0.00039°C−1
A) 3.9°C−1
B) 0.39°C−1
C) 0.039°C−1
D) 0.0039°C−1
E) 0.00039°C−1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A length L0 of wire has a resistance of 32.0 Ω. The wire is uniformly stretched (i.e., the total volume of the wire is unchanged during the stretching) to four times its original length, or 4 L0. If a length L0 is now cut from the stretched wire, what is its resistance?
A) 512 Ω
B) 128 Ω
C) 32.0 Ω
D) 8.00 Ω
E) 2.00 Ω
A) 512 Ω
B) 128 Ω
C) 32.0 Ω
D) 8.00 Ω
E) 2.00 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Aluminum has a resistivity of 2.65 × 10−8 Ω × m. What is the resistance of 15 m of aluminum wire with cross-sectional area 1.0 mm2?
A) 1.6 Ω
B) 0.40 Ω
C) 0.13 Ω
D) 1.3 × 102 Ω
E) 56 Ω
A) 1.6 Ω
B) 0.40 Ω
C) 0.13 Ω
D) 1.3 × 102 Ω
E) 56 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
One hundred meters of a certain type of wire has a resistance of 7.2 Ω. What is the resistance of 2.5 m of this wire?
A) 18 Ω
B) 1.8 Ω
C) 0.18 Ω
D) 3.0 Ω
E) 0.30 Ω
A) 18 Ω
B) 1.8 Ω
C) 0.18 Ω
D) 3.0 Ω
E) 0.30 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a liquid, a current is set up between points A and B. Positive ions flow from A to B and carry 6.0 coulombs of positive charge per second, while negative ions move from B to A with 2.0 coulombs of negative charge per second. What is the net current from A to B?
A) 8.0 A
B) −8.0 A
C) 4.0 A
D) −4.0 A
E) 12 A
A) 8.0 A
B) −8.0 A
C) 4.0 A
D) −4.0 A
E) 12 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A 1.56-V battery has an internal resistance of 0.120 Ω. What is the maximum current that can be drawn from this battery?
A) infinite (or at least 1000s of amps)
B) 1.56 A
C) 0.190 A
D) 13.0 A
E) 7.50 A
A) infinite (or at least 1000s of amps)
B) 1.56 A
C) 0.190 A
D) 13.0 A
E) 7.50 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A 2.50 A current is carried by a copper wire of radius 1.0 mm. If the density of conduction electrons is 8.0 × 1028 m−3, what is the drift velocity of the conduction electrons?
A) 3.0 × 108 m/s
B) 3.2 × 10−4 m/s
C) 1.6 × 10−5 m/s
D) 6.2 × 10−4 m/s
E) 6.2 × 10−5 m/s
A) 3.0 × 108 m/s
B) 3.2 × 10−4 m/s
C) 1.6 × 10−5 m/s
D) 6.2 × 10−4 m/s
E) 6.2 × 10−5 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A length of wire has a resistance of 18.0 Ω. When the wire is uniformly stretched (i.e., the total volume of the wire is unchanged during the stretching) to triple it original length, what resistance results?
A) 162 Ω
B) 54.0 Ω
C) 18.0 Ω
D) 6.00 Ω
E) 2.00 Ω
A) 162 Ω
B) 54.0 Ω
C) 18.0 Ω
D) 6.00 Ω
E) 2.00 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A variable resistor has a voltage of 12.0 V placed across it. If the resistance is increased 20%, what happens to the current flowing through it?
A) It increases 20%.
B) It increases 25%.
C) It decreases 20%.
D) It decreases 25%.
E) It decreases 17%.
A) It increases 20%.
B) It increases 25%.
C) It decreases 20%.
D) It decreases 25%.
E) It decreases 17%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Two copper wires, one with twice the diameter of the other, have the same current flowing through them. If the thinner wire has a drift velocity v1, and the thicker wire has a drift velocity v2, how do the drift velocities compare?
A) v1 = v2
B) v1 = 2 v2
C) 2 v1 = v2
D) v1 = 4 v2
E) 4 v1 = v2
A) v1 = v2
B) v1 = 2 v2
C) 2 v1 = v2
D) v1 = 4 v2
E) 4 v1 = v2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Silver contains 5.8 × 1028 conduction electrons per m3. How many conduction electrons are in a 1.0 m length of silver wire of diameter 2.6 mm?
A) 1.9 × 105
B) 4.7 × 104
C) 3.1 × 1023
D) 1.2 × 1024
E) 6.0 × 1023
A) 1.9 × 105
B) 4.7 × 104
C) 3.1 × 1023
D) 1.2 × 1024
E) 6.0 × 1023

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An ampere, A, is equivalent to a
A) V/m.
B) V·C.
C) C/s.
D) C·s.
E) N/V.
A) V/m.
B) V·C.
C) C/s.
D) C·s.
E) N/V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A potential difference of 12.4 V is placed across a 4.1 Ω resistor. What is the current in the resistor?
A) 51 A
B) 3.0 A
C) 0.33 A
D) 16 A
E) 8.3 A
A) 51 A
B) 3.0 A
C) 0.33 A
D) 16 A
E) 8.3 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If a 22 Ω resistor has a current of 2.0 A flowing through it, what is the potential difference across it?
A) 0.091 V
B) 44 V
C) 11 V
D) 24 V
E) 20 V
A) 0.091 V
B) 44 V
C) 11 V
D) 24 V
E) 20 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A resistor has a resistance of 30 Ω at 20°C. If the temperature coefficient of resistivity is 4.5 × 10−3 °C−1, what is its resistance at 200°C?
A) 24 Ω
B) 27 Ω
C) 48 Ω
D) 54 Ω
E) 57 Ω
A) 24 Ω
B) 27 Ω
C) 48 Ω
D) 54 Ω
E) 57 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If 64 coulombs flow along a wire in 4.0 seconds, what is the average current?
A) 64 A
B) 32 A
C) 16 A
D) 4.0 A
E) none of these choices are correct
A) 64 A
B) 32 A
C) 16 A
D) 4.0 A
E) none of these choices are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Of the common battery sizes AAA, AA, C, and D, which provides the highest emf?
A) AAA
B) AA
C) C
D) D
E) all have the same emf
A) AAA
B) AA
C) C
D) D
E) all have the same emf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Capacitors of values 1.0 F, 2.0 F, 3.0 F, and 6.0 F are connected in series across a 12 V power supply. Which capacitor has the greatest potential difference across it?
A) the 1.0 F capacitor
B) the 2.0 F capacitor
C) the 3.0 F capacitor
D) the 6.0 F capacitor
E) they all are equal
A) the 1.0 F capacitor
B) the 2.0 F capacitor
C) the 3.0 F capacitor
D) the 6.0 F capacitor
E) they all are equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the diagram, if the current through R1 is 5 A up, and the current through R3 is 3 A up, what is the current in R2? 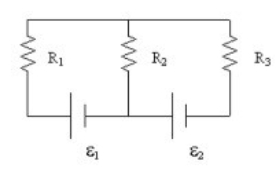
A) 8 A up
B) 8 A down
C) 2 A up
D) 2 A down
E) more information is needed

A) 8 A up
B) 8 A down
C) 2 A up
D) 2 A down
E) more information is needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If R1 = 6 Ω, R2 = 8 Ω, R3 = 2 Ω, ε1 = 4 V, and ε2 = 14 V, what is the current in R2? 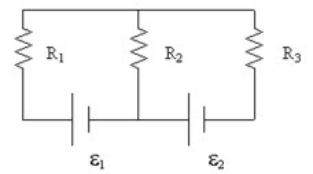
A) 1 A up
B) 1 A down
C) 2.5 A up
D) 2.5 A down
E) 5 A down

A) 1 A up
B) 1 A down
C) 2.5 A up
D) 2.5 A down
E) 5 A down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Four 12 Ω resistors are connected together. What is the least resistance that can be attained with these resistors by connecting them in various ways?
A) 12 Ω
B) 6.0 Ω
C) 3.0 Ω
D) 2.0 Ω
E) 1.0 Ω
A) 12 Ω
B) 6.0 Ω
C) 3.0 Ω
D) 2.0 Ω
E) 1.0 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A 6.0 Ω resistor and a 3.0 Ω resistor are connected in series to a 1.5 V battery of negligible internal resistance. What is the current in the 3.0 Ω resistor?
A) 2.0 A
B) 0.50 A
C) 0.25 A
D) 0.17 A
E) 0.75 A
A) 2.0 A
B) 0.50 A
C) 0.25 A
D) 0.17 A
E) 0.75 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Two capacitors of values 6.0 mF and 9.0 mF are connected in series to a 30.0 V power supply. What is the resulting potential difference across the 6.0 mF capacitor?
A) 30 V
B) 18 V
C) 12 V
D) 6.0 V
E) 3.0 V
A) 30 V
B) 18 V
C) 12 V
D) 6.0 V
E) 3.0 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Two capacitors of values 6.0 mF and 9.0 mF are connected in series. What is the capacitance of the combination?
A) 15 mF
B) 7.5 mF
C) 3.0 mF
D) 3.6 mF
E) 54 mF
A) 15 mF
B) 7.5 mF
C) 3.0 mF
D) 3.6 mF
E) 54 mF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A 12.0 V battery has an internal resistance of 0.080 Ω. If the battery supplies 100 A when connected to a starter motor, what is the resistance of the motor?
A) 0.080 Ω
B) 0.20 Ω
C) 0.0012 Ω
D) 0.040 Ω
E) 0.012 Ω
A) 0.080 Ω
B) 0.20 Ω
C) 0.0012 Ω
D) 0.040 Ω
E) 0.012 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Four 12 Ω resistors are connected together. Which of the following resistances cannot be formed using all 4 resistors?
A) 48 Ω
B) 9.0 Ω
C) 12 Ω
D) 60 Ω
E) 20 Ω
A) 48 Ω
B) 9.0 Ω
C) 12 Ω
D) 60 Ω
E) 20 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A 6.0 Ω resistor and a 3.0 Ω resistor are connected in parallel to a 1.5 V battery of negligible internal resistance. What is the current in the 3.0 Ω resistor?
A) 2.0 A
B) 0.50 A
C) 0.25 A
D) 0.17 A
E) 0.75 A
A) 2.0 A
B) 0.50 A
C) 0.25 A
D) 0.17 A
E) 0.75 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Three wires are connected at a junction. One of the wires carries a current of 4 A into the junction, while another carries 5 A into the junction. What is the current in the third wire?
A) 4 A away from the junction
B) 9 A away from the junction
C) 4 A into the junction
D) 9 A into the junction
E) 1 A away from the junction
A) 4 A away from the junction
B) 9 A away from the junction
C) 4 A into the junction
D) 9 A into the junction
E) 1 A away from the junction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Two capacitors of values 6.00 mF and 9.00 mF are connected in series to a 30.0 V power supply. What is the resulting charge on the 6.00 mF capacitor?
A) 180 mC
B) 270 mC
C) 90.0 mC
D) 108 mC
E) 200 mC
A) 180 mC
B) 270 mC
C) 90.0 mC
D) 108 mC
E) 200 mC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A three-cell flashlight has 3 batteries in series, each with an emf of 1.5 V. If the bulb has a resistance of 50 Ω, what current flows when the flashlight is operating? (Assume the internal resistance of the batteries is negligible.)
A) 30 mA
B) 10 mA
C) 27 mA
D) 90 mA
E) 11 A
A) 30 mA
B) 10 mA
C) 27 mA
D) 90 mA
E) 11 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A 12.0 V battery is connected across a 4.00-Ω resistor. If the current through the resistor is 2.80 A, what is the internal resistance of the battery?
A) 0.200 Ω
B) 0.286 Ω
C) 4.29 Ω
D) 3.71 Ω
E) 0.800 Ω
A) 0.200 Ω
B) 0.286 Ω
C) 4.29 Ω
D) 3.71 Ω
E) 0.800 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The arrangement shown is composed of four 6.0 mF capacitors. What is the capacitance of the combination? 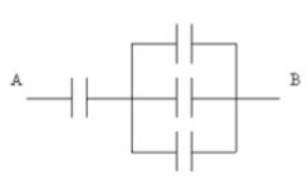
A) 24.0 mF
B) 4.5 mF
C) 8.0 mF
D) 9.0 mF
E) 12.5 mF

A) 24.0 mF
B) 4.5 mF
C) 8.0 mF
D) 9.0 mF
E) 12.5 mF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A 12.0 V battery is connected across a 4.00 Ω resistor. If the current through the resistor is 2.80 A, what is the terminal voltage of the battery?
A) 12.0 V
B) 12.8 V
C) 11.6 V
D) 11.2 V
E) 9.6 V
A) 12.0 V
B) 12.8 V
C) 11.6 V
D) 11.2 V
E) 9.6 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the diagram, each resistor is 3 ohms, and the battery is 9 volts. What is the current through the middle resistor? 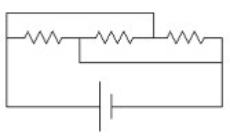
A) 3 A to the right
B) 3 A to the left
C) 9 A to the right
D) 9 A to the left
E) 1 A to the left

A) 3 A to the right
B) 3 A to the left
C) 9 A to the right
D) 9 A to the left
E) 1 A to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the resistance of this combination of resistors? 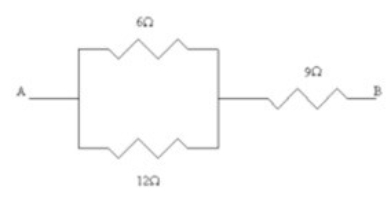
A) 4.0 Ω
B) 12 Ω
C) 13 Ω
D) 14 Ω
E) 15 Ω

A) 4.0 Ω
B) 12 Ω
C) 13 Ω
D) 14 Ω
E) 15 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Capacitors of values 1.0 F, 2.0 F, 3.0 F, and 6.0 F are connected in series across a 12 V power supply. Which capacitor has the greatest charge on it?
A) the 1.0 F capacitor
B) the 2.0 F capacitor
C) the 3.0 F capacitor
D) the 6.0 F capacitor
E) they are all equal
A) the 1.0 F capacitor
B) the 2.0 F capacitor
C) the 3.0 F capacitor
D) the 6.0 F capacitor
E) they are all equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Four 12 Ω resistors are connected together. What is the maximum resistance that can be attained with these resistors by connecting them in various ways?
A) 12 Ω
B) 24 Ω
C) 36 Ω
D) 48 Ω
E) 44 Ω
A) 12 Ω
B) 24 Ω
C) 36 Ω
D) 48 Ω
E) 44 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A capacitor is connected in series with a resistor and a switch. With the switch open, the capacitor is charged to 9.0 V. When the switch is closed, how long will it take for the voltage across the capacitor to drop to 6.0 V if the time constant of the circuit is 4.0 s?
A) 0.3 s
B) 1.2 s
C) 1.6 s
D) 2.7 s
E) 12 s
A) 0.3 s
B) 1.2 s
C) 1.6 s
D) 2.7 s
E) 12 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Three resistors, R1 = 9.0 Ω, R2 = 3.0 Ω, and R3 = 1.0 Ω, are connected in parallel to a 9.0 V battery. What is the power dissipated by R2?
A) 2.0 W
B) 3.0 W
C) 9.0 W
D) 27 W
E) 81 W
A) 2.0 W
B) 3.0 W
C) 9.0 W
D) 27 W
E) 81 W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A 2.0 Ω resistor is connected across a 6.0 V power supply. An ammeter with internal resistance of 1.0 Ω is used to measure the current in this circuit. What is the ammeter reading?
A) 4.0 A
B) 3.0 A
C) 2.0 A
D) 1.0 A
E) an ammeter with less resistance than the rest of the circuit will not produce a reading
A) 4.0 A
B) 3.0 A
C) 2.0 A
D) 1.0 A
E) an ammeter with less resistance than the rest of the circuit will not produce a reading

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A flashlight, which uses two 1.5 V batteries in series, is turned on for 2.0 minutes. If the current in the flashlight is 100 mA, what is the energy dissipated?
A) 12 J
B) 9.0 J
C) 72 J
D) 36 J
E) 18 J
A) 12 J
B) 9.0 J
C) 72 J
D) 36 J
E) 18 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a series circuit consisting of a 12.0 V source of emf, a 2.00 mF capacitor, a 1.00 kΩ resistor and a switch, what is the voltage across the capacitor at a time of one time constant t after the switch is closed?
A) 0.632 V
B) 6.32 V
C) 7.59 V
D) 8.65 V
A) 0.632 V
B) 6.32 V
C) 7.59 V
D) 8.65 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Three resistors, R1 = 4.0 Ω, R2 = 3.0 Ω, and R3 = 2.0 Ω, are connected in series to a 9.0 V battery. What is the total power dissipated by the circuit?
A) 2.0 W
B) 4.0 W
C) 5.1 W
D) 9.0 W
E) 20 W
A) 2.0 W
B) 4.0 W
C) 5.1 W
D) 9.0 W
E) 20 W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A good ammeter has ________ resistance and a good voltmeter has ________ resistance. "Good" means that it affects the system being measured by very little.
A) low, low
B) low, high
C) high, high
D) high, low
E) medium, no
A) low, low
B) low, high
C) high, high
D) high, low
E) medium, no

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A series circuit consists of a 12.0 V source of emf, a 2.00 mF capacitor, a 1000 Ω resistor, and a switch. What is the time constant for this circuit?
A) 10.0 s
B) 2.00 s
C) 0.693 s
D) 0.0825 s
E) 1.00 ms
A) 10.0 s
B) 2.00 s
C) 0.693 s
D) 0.0825 s
E) 1.00 ms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
By how much does the current fall after the switch is closed in a series RC circuit when three time constants have elapsed?
A) 5.0%
B) 38%
C) 62%
D) 95%
E) 100% since after 2 time constants the current is 0
A) 5.0%
B) 38%
C) 62%
D) 95%
E) 100% since after 2 time constants the current is 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Raising the current through a resistor from 8.50 A to 11.3 A increases the power by
A) 33%.
B) 77%.
C) 113%.
D) 157%.
E) 0% (no change).
A) 33%.
B) 77%.
C) 113%.
D) 157%.
E) 0% (no change).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A series circuit consists of a 12.0 V source of emf, a 2.00 mF capacitor, a 1000 Ω resistor, and a switch. When the switch is closed, how long does it take for the current to reach one-tenth its maximum value?
A) 0.693 s
B) 2.30 s
C) 4.61 s
D) 9.00 s
E) 18.0 s
A) 0.693 s
B) 2.30 s
C) 4.61 s
D) 9.00 s
E) 18.0 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Three resistors, R1 = 9.00 Ω, R2 = 3.00 Ω, and R3 = 1.00 Ω, are connected in parallel to a 9.00 V battery. What is the total power dissipated in the circuit?
A) 180 W
B) 117 W
C) 99.0 W
D) 80.1 W
E) 18.0 W
A) 180 W
B) 117 W
C) 99.0 W
D) 80.1 W
E) 18.0 W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A variable resistor is connected to a constant voltage source. When the resistance is increased from 5.5 Ω to 9.3 Ω, what happens to the power dissipated?
A) no change
B) a 35% decrease
C) a 41% decrease
D) a 59% decrease
E) a 69% decrease
A) no change
B) a 35% decrease
C) a 41% decrease
D) a 59% decrease
E) a 69% decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A series circuit consists of a 12.0 V source of emf, a 2.00 mF capacitor, a 1000 Ω resistor, and a switch. When the switch is closed, how long does it take for the current to reach one-half its maximum value?
A) 0.693 s
B) 1.39 s
C) 2.00 s
D) 1.69 s
E) 0.0250 s
A) 0.693 s
B) 1.39 s
C) 2.00 s
D) 1.69 s
E) 0.0250 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Three resistors, R1 = 4 Ω, R2 = 3.0 Ω, and R3 = 2.0 Ω, are connected in series to a 9.0 V battery. What is the power dissipated by R1?
A) 2.0 W
B) 4.0 W
C) 5.1 W
D) 9.0 W
E) 2.3 W
A) 2.0 W
B) 4.0 W
C) 5.1 W
D) 9.0 W
E) 2.3 W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When the voltage across a resistor is decreased by 50%, what happens to the power dissipated?
A) It increases by 50%.
B) It decreases by 50%.
C) It decreases by 25%.
D) It decreases by 71%.
E) It decreases by 75%.
A) It increases by 50%.
B) It decreases by 50%.
C) It decreases by 25%.
D) It decreases by 71%.
E) It decreases by 75%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 1000 Ω resistor is in a circuit with 30.0 mA flowing through it. A voltmeter with internal resistance 1000 Ω is used to measure the voltage across the resistor. What is the reading on the voltmeter if a total current of 30.0 mA still flows in the circuit?
A) 30.0 V
B) 29.9 V
C) 27.0 V
D) 15.0 V
E) 3.00 V
A) 30.0 V
B) 29.9 V
C) 27.0 V
D) 15.0 V
E) 3.00 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Copper has 8.5 × 1028 current-carrying electrons per m3. A copper wire of radius 0.15 mm carries a current of 17 mA. What is the average drift velocity for the electrons?
A) 2.7 × 10−9 m/s
B) 56 × 10−6 m/s
C) 18 × 10−6 m/s
D) more information is needed for this calculation
A) 2.7 × 10−9 m/s
B) 56 × 10−6 m/s
C) 18 × 10−6 m/s
D) more information is needed for this calculation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The watt, W, is equivalent to which of the following?
A) A·V
B) C·J
C) C/J
D) A/V
E) V2/A
A) A·V
B) C·J
C) C/J
D) A/V
E) V2/A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If R1 = 6.0 Ω, R2 = 8.0 Ω, R3 = 2.0 Ω, ε1 = 4.0 V, and ε2 = 14 V, what is the power supplied to the circuit by ε1? 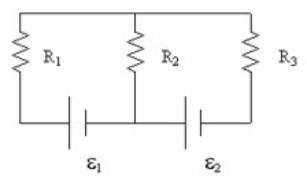
A) 4.0 W
B) 8.0 W
C) 12 W
D) 16 W
E) 20 W

A) 4.0 W
B) 8.0 W
C) 12 W
D) 16 W
E) 20 W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Two carbon cylinders have radii r and 2r, and they both have length L. What is the resistance of the first if the resistance of the second is 12Ω?
A) 48 Ω
B) 12 Ω
C) 24 Ω
D) 3 Ω
E) 6 Ω
A) 48 Ω
B) 12 Ω
C) 24 Ω
D) 3 Ω
E) 6 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In an RC circuit with an initially uncharged capacitor, the time constant is the time that is required for the current through the resistor to reach what percentage of its initial value?
A) 63%
B) 90%
C) 37%
D) 100%
E) 50%
A) 63%
B) 90%
C) 37%
D) 100%
E) 50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A capacitor in an RC circuit is charged, storing 1.25 mJ of energy. What is the time required to discharge this capacitor (say, to 1% of its initial charge), as compared to the time required to discharge (to 1%) an identical capacitor in an identical RC circuit which has stored 2.5 mJ of energy instead?
A) twice the time
B) half the time
C) the same time
D) the answer depends on the values of R and C.
A) twice the time
B) half the time
C) the same time
D) the answer depends on the values of R and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A wire of radius 0.15 mm is made of an unknown metal and carries a current of 8.4 mA. The drift velocity for electrons in the wire is measured to be 36 × 10−6 m/s. What is the charge carrier density of the metal from which the wire is made?
A) 1.3 × 1029 m−3
B) 2.1 × 1028 m−3
C) need more information to do this calculation.
D) 4.2 × 1030 m−3
A) 1.3 × 1029 m−3
B) 2.1 × 1028 m−3
C) need more information to do this calculation.
D) 4.2 × 1030 m−3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In order to protect a delicate electronic component in a circuit from large currents, a fuse should be placed
A) internally inside the component.
B) in contact with the ground and the component.
C) in series with the component.
D) in parallel with the component.
A) internally inside the component.
B) in contact with the ground and the component.
C) in series with the component.
D) in parallel with the component.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Two identical circuits have a capacitor in series with a resistor and a switch. In circuit A, the resistor has resistance R, while in circuit B, its resistance is 4R. The capacitors are identical. Each capacitor begins fully charged, and each circuit is open. When each circuit is completed (i.e., the switch in them is closed), the capacitor will begin to discharge. If a time t is required for circuit A's capacitor to fully discharge (say, by 99%), what time will be required for circuit B's capacitor to do the same?
A) 4t
B) 2t
C) t
D) 0.5t
E) 0.25t
A) 4t
B) 2t
C) t
D) 0.5t
E) 0.25t

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In a circuit, three pieces of wire labeled A, B and C are joined at a common point D. If wire B carries 1.5 mA in a direction away from D, and wire C carries current 1.3 mA toward D, what does wire A carry?
A) 0.2 mA toward D
B) 0.2 mA away from D
C) 2.8 mA toward D
D) unable to determine
E) 2.8 mA away from D
A) 0.2 mA toward D
B) 0.2 mA away from D
C) 2.8 mA toward D
D) unable to determine
E) 2.8 mA away from D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An electron beam contains 1.5 × 1017 electrons per m3 and is confined to circular cross-sectional region of diameter 0.025 mm. The electrons in the beam are extremely energetic and travel at nearly the speed of light. What is the current in the beam?
A) 1.4 A
B) 3.5 mA
C) 350 mA
D) 14 mA
A) 1.4 A
B) 3.5 mA
C) 350 mA
D) 14 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A bird can safely land on a bare, high-voltage power line because
A) if both feet are touching the bare wire, they are at approximately the same potential, and therefore little or no current flows through the bird's body.
B) its internal resistance is very high, so very little current will flow.
C) the line cannot deliver enough current to harm it.
D) its feet are good insulators, and therefore it is protected.
A) if both feet are touching the bare wire, they are at approximately the same potential, and therefore little or no current flows through the bird's body.
B) its internal resistance is very high, so very little current will flow.
C) the line cannot deliver enough current to harm it.
D) its feet are good insulators, and therefore it is protected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A carbon resistor is made of a cylinder of carbon, of diameter 7.4 mm. If the resistivity of carbon is 3.5 × 10−5 W·m, and a potential difference of 0.15 V causes a current of 12 A to flow through the resistor, what is the length of the cylinder?
A) 6.1 cm
B) 1.5 cm
C) 0.15 cm
D) 0.5 cm
A) 6.1 cm
B) 1.5 cm
C) 0.15 cm
D) 0.5 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A carbon resistor is made of a cylinder of carbon, of length 1.5 cm. If the resistivity of carbon is 3.5 × 10−5 Ω·m, and a potential difference of 0.15 V causes a current of 12 A to flow through the resistor, what is the radius of the cylinder?
A) 6.5 mm
B) 12 mm
C) 3.7 mm
D) 1.2 mm
A) 6.5 mm
B) 12 mm
C) 3.7 mm
D) 1.2 mm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In a three-pronged plug, the purpose of the third prong is to
A) provide a short circuit to ground.
B) prevent excessive power use by inefficient appliances.
C) create a stronger connection to the outlet when plugged in.
D) provide a path to ground in the event of a short circuit to the case of an appliance.
A) provide a short circuit to ground.
B) prevent excessive power use by inefficient appliances.
C) create a stronger connection to the outlet when plugged in.
D) provide a path to ground in the event of a short circuit to the case of an appliance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Copper has 8.5 × 1028 current carrying electrons per m3. A copper wire carries a current of 17 mA, and the drift velocity of the electrons is measured to be 18 × 10−6 m/s. What is the wire's radius?
A) 0.15 mm
B) 0.27 mm
C) 2.7 mm
D) 1.5 mm
A) 0.15 mm
B) 0.27 mm
C) 2.7 mm
D) 1.5 mm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Two carbon cylinders have radii 2r and r, and the first has length 2L, while the second has length L. What is the resistance of the first if the resistance of the second is 12 Ω?
A) 48 Ω
B) 6 Ω
C) 12 Ω
D) 24 Ω
A) 48 Ω
B) 6 Ω
C) 12 Ω
D) 24 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In an RC circuit with an initially uncharged capacitor, the time constant is the time that is required for the charge on the capacitor to reach what percentage of its final value?
A) 50%
B) 37%
C) 100%
D) 63%
E) 90%
A) 50%
B) 37%
C) 100%
D) 63%
E) 90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



