Deck 15: Lipid Structure and Function
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/98
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Lipid Structure and Function
1
Predict the structure of a fatty acid that is trans 16:1 ( 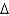 9).
9).
A)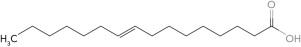
B)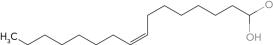
C)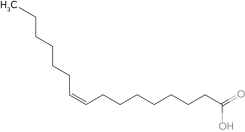
D)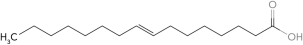
 9).
9).A)

B)

C)

D)

A
2
Compared with a fatty acid,a wax
A) contains a glycerol backbone.
B) has long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylate group.
C) has long hydrocarbon chains connected with an ester linkage.
D) contains a polar phosphate group.
A) contains a glycerol backbone.
B) has long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylate group.
C) has long hydrocarbon chains connected with an ester linkage.
D) contains a polar phosphate group.
C
3
Predict the structure of a fatty acid that is cis 16:1 (  9).
9).
A)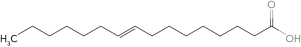
B)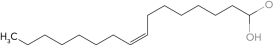
C)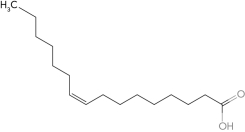
D)
 9).
9).A)

B)

C)

D)

C
4
Predict the essential  -6 fatty acid.
-6 fatty acid.
A) trans 18:2 (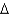
9,12)
B) cis 18:2 (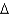
9,12)
C) trans 18:2 (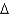
6,9)
D) cis 18:2 (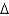
6,9)
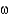 -6 fatty acid.
-6 fatty acid.A) trans 18:2 (
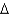
9,12)
B) cis 18:2 (
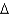
9,12)
C) trans 18:2 (
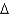
6,9)
D) cis 18:2 (
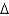
6,9)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
One advantage of using hydrogenation in the food industry is
A) decreased processing time.
B) reduction in heart disease.
C) increased shelf life.
D) decreased melting point.
A) decreased processing time.
B) reduction in heart disease.
C) increased shelf life.
D) decreased melting point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Predict the fatty acid with the highest melting point.
A) trans 14:1 (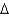
7)
B) cis 14:2 (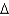
7,9)
C) trans 14:2 (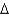
7,9)
D) cis 14:3 (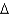
7,9,11)
A) trans 14:1 (
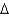
7)
B) cis 14:2 (
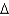
7,9)
C) trans 14:2 (
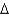
7,9)
D) cis 14:3 (
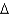
7,9,11)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Identify the  -6 fatty acid.
-6 fatty acid.
A)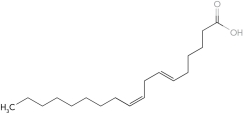
B)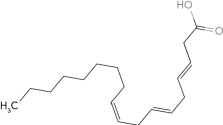
C)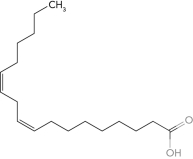
D)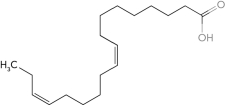
 -6 fatty acid.
-6 fatty acid.A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Predict the fatty acid with the lowest melting point.
A) trans 14:1 (
7)
B) cis 14:2 (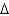
7,9)
C) trans 14:2 (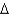
7,9)
D) cis 14:3 (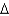
7,9,11)
A) trans 14:1 (
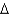
7)
B) cis 14:2 (
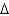
7,9)
C) trans 14:2 (
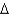
7,9)
D) cis 14:3 (
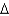
7,9,11)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Identify the 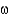 -3 fatty acid.
-3 fatty acid.
A)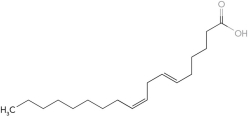
B)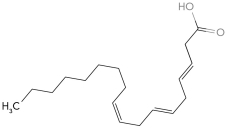
C)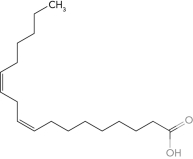
D)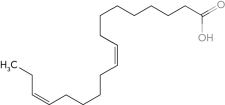
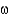 -3 fatty acid.
-3 fatty acid.A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify the wax.
A)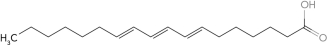
B)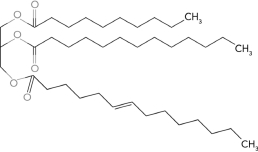
C)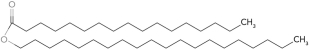
D)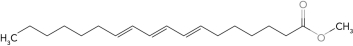
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Using common nomenclature,name the following fatty acid. 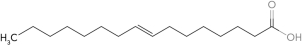
A) trans 18:1 (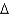
10)
B) cis 18:1 (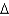
10)
C) trans 18:1 (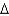
8)
D) cis 18:1 (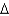
8)

A) trans 18:1 (
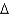
10)
B) cis 18:1 (
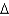
10)
C) trans 18:1 (
8)
D) cis 18:1 (
8)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Using common nomenclature,name the following fatty acid. 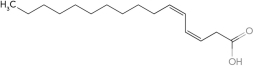
A) trans 16:2 (
11,13)
B) cis 16:2 (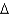
11,13)
C) trans 16:2 (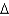
3,5)
D) cis 16:2 (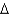
3,5)

A) trans 16:2 (
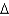
11,13)
B) cis 16:2 (
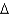
11,13)
C) trans 16:2 (
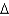
3,5)
D) cis 16:2 (
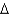
3,5)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Classify the following fatty acid. 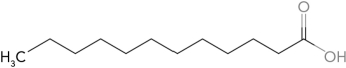
A) saturated
B) unsaturated
C) monounsaturated
D) polyunsaturated

A) saturated
B) unsaturated
C) monounsaturated
D) polyunsaturated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
One disadvantage of using partial hydrogenation in the food industry is that
A) the shelf life of the oils is not as long.
B) trans fats are formed during the process.
C) the oils tend to become rancid and have foul odors.
D) the oils cost more than animal fats.
A) the shelf life of the oils is not as long.
B) trans fats are formed during the process.
C) the oils tend to become rancid and have foul odors.
D) the oils cost more than animal fats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Identify the polyunsaturated fatty acid.
A)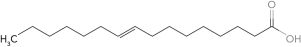
B)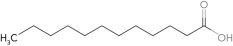
C)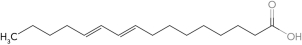
D)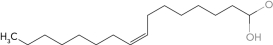
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Predict the fatty acid with the highest melting point.
A)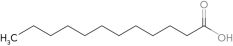
B)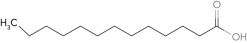
C)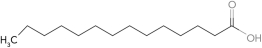
D)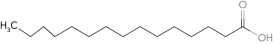
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Predict the structure of a fatty acid that is trans 18:2 (  9,11).
9,11).
A)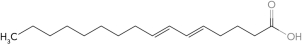
B)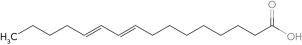
C)
D)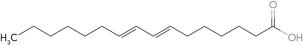
 9,11).
9,11).A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A fatty acid that has more than one double bond is referred to as
A) monosaturated.
B) monounsaturated.
C) polysaturated.
D) polyunsaturated.
A) monosaturated.
B) monounsaturated.
C) polysaturated.
D) polyunsaturated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Using common nomenclature,name the following fatty acid. 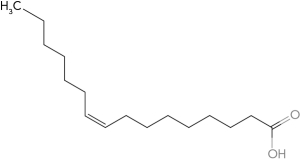
A) trans 14:1 (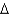
7)
B) cis 14:1 (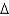
7)
C) trans 14:7 (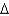
1)
D) cis 14:7 (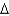
1)

A) trans 14:1 (
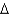
7)
B) cis 14:1 (
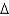
7)
C) trans 14:7 (
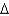
1)
D) cis 14:7 (
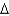
1)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Partial hydrogenation can result in the formation of
A)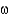 -3 fatty acids.
-3 fatty acids.
B)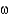 -6 fatty acids.
-6 fatty acids.
C) cis double bonds.
D) trans double bonds.
A)
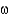 -3 fatty acids.
-3 fatty acids.B)
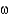 -6 fatty acids.
-6 fatty acids.C) cis double bonds.
D) trans double bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Spices such as eugenol are added to oils to enhance the flavor because of
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) dipole-dipole interactions.
C) hydrophilic interactions.
D) hydrophobic interactions.
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) dipole-dipole interactions.
C) hydrophilic interactions.
D) hydrophobic interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which is the step in glucagon signaling where adipose triglyceride lipase mediates a reaction?
1)A hydrolysis reaction cleaves a fatty acid from the stored triacylglycerols to generate diacylglycerol and a fatty acid.
2)Perilipin is phosphorylated on the surface of lipid droplets.
3)Albumin transports the free fatty acid.
4)A GDP-GTP exchange stimulates cyclic AMP production by the enzyme adenylate cyclase.
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
1)A hydrolysis reaction cleaves a fatty acid from the stored triacylglycerols to generate diacylglycerol and a fatty acid.
2)Perilipin is phosphorylated on the surface of lipid droplets.
3)Albumin transports the free fatty acid.
4)A GDP-GTP exchange stimulates cyclic AMP production by the enzyme adenylate cyclase.
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Chylomicrons contain a monolayer on the outside of the particle consisting of
A) cerebrosides and phospholipids.
B) cerebrosides and sphingolipids.
C) phospholipids and cholesterol.
D) cholesterol and sphingolipids.
A) cerebrosides and phospholipids.
B) cerebrosides and sphingolipids.
C) phospholipids and cholesterol.
D) cholesterol and sphingolipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The lipase-mediated release of fatty acids can always be expected to occur when a person is
A) hungry.
B) walking.
C) studying.
D) watching TV.
A) hungry.
B) walking.
C) studying.
D) watching TV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The water-soluble enzyme in the small intestine that hydrolyzes the acyl ester bonds in triacylglycerols is
A) adipocyte.
B) albumin.
C) lipase.
D) colipase.
A) adipocyte.
B) albumin.
C) lipase.
D) colipase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which step in glucagon signaling occurs in the Gs protein?
1)A hydrolysis reaction cleaves a fatty acid from the stored triacylglycerols to generate diacylglycerol and a fatty acid.
2)The regulatory protein G58 binds to adipose triglyceride lipase.
3)Perilipin is phosphorylated on the surface of lipid droplets.
4)Albumin transports the free fatty acid.
5)A GDP-GTP exchange stimulates cyclic AMP production by the enzyme adenylate cyclase.
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5
1)A hydrolysis reaction cleaves a fatty acid from the stored triacylglycerols to generate diacylglycerol and a fatty acid.
2)The regulatory protein G58 binds to adipose triglyceride lipase.
3)Perilipin is phosphorylated on the surface of lipid droplets.
4)Albumin transports the free fatty acid.
5)A GDP-GTP exchange stimulates cyclic AMP production by the enzyme adenylate cyclase.
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
During the process of saponification,fatty acid molecules are released from triacylglycerols by treatment(s)with a strong
A) base.
B) acid.
C) base and heat.
D) acid and heat.
A) base.
B) acid.
C) base and heat.
D) acid and heat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which particles transport triacylglycerols to adipose tissue for storage?
A) apolipoproteins
B) adipocytes
C) chylomicrons
D) perilipin
A) apolipoproteins
B) adipocytes
C) chylomicrons
D) perilipin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
VLDLs are produced in
A) liver cells.
B) intestinal epithelial cells.
C) stomach cells.
D) adipocytes.
A) liver cells.
B) intestinal epithelial cells.
C) stomach cells.
D) adipocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Arrange the following steps of glucagon signaling in the correct order.
1)A hydrolysis reaction cleaves a fatty acid from the stored triacylglycerols to generate diacylglycerol and a fatty acid.
2)The regulatory protein G58 binds to adipose triglyceride lipase.
3)Perilipin is phosphorylated on the surface of lipid droplets.
4)Albumin transports the free fatty acid.
5)A GDP-GTP exchange stimulates cyclic AMP production by the enzyme adenylate cyclase.
A)2,5,3,4,1
B)5,2,4,3,1
C)5,3,2,1,4
D)2,3,5,1,4
1)A hydrolysis reaction cleaves a fatty acid from the stored triacylglycerols to generate diacylglycerol and a fatty acid.
2)The regulatory protein G58 binds to adipose triglyceride lipase.
3)Perilipin is phosphorylated on the surface of lipid droplets.
4)Albumin transports the free fatty acid.
5)A GDP-GTP exchange stimulates cyclic AMP production by the enzyme adenylate cyclase.
A)2,5,3,4,1
B)5,2,4,3,1
C)5,3,2,1,4
D)2,3,5,1,4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In addition to triacylglycerols,which other lipid synthesized in the liver is transported by VLDLs?
A) sphingophospholipid
B) cerebroside
C) ganglioside
D) cholesterol
A) sphingophospholipid
B) cerebroside
C) ganglioside
D) cholesterol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Chylomicrons are produced in
A) liver cells.
B) intestinal epithelial cells.
C) stomach cells.
D) adipocytes.
A) liver cells.
B) intestinal epithelial cells.
C) stomach cells.
D) adipocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The biosynthesis of triacylglycerols in animals uses which citrate cycle intermediate in the liver?
A) malate
B) acetyl-CoA
C) isocitrate
D) succinate
A) malate
B) acetyl-CoA
C) isocitrate
D) succinate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Free fatty acids released from adipose tissue are transported throughout the body by a carrier protein called
A) adipocyte.
B) albumin.
C) lipase.
D) colipase.
A) adipocyte.
B) albumin.
C) lipase.
D) colipase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A wax is defined as
A) long chain fatty alcohols esterified to hydrocarbon chains.
B) three fatty acids linked to a glycerol backbone.
C) a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxylate group at the end.
D) two fatty acids and a phosphate group linked to a glycerol backbone.
A) long chain fatty alcohols esterified to hydrocarbon chains.
B) three fatty acids linked to a glycerol backbone.
C) a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxylate group at the end.
D) two fatty acids and a phosphate group linked to a glycerol backbone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identify the lipase whose activity is regulated by protein G58.
A) colipase
B) monoacylglycerol lipase
C) hormone-sensitive lipase
D) adipose triglyceride lipase
A) colipase
B) monoacylglycerol lipase
C) hormone-sensitive lipase
D) adipose triglyceride lipase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The lipase-mediated release of fatty acids can always be expected to occur when a person is
A) reading a book.
B) watching TV.
C) running from a bear.
D) eating.
A) reading a book.
B) watching TV.
C) running from a bear.
D) eating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Triacylglycerols are transported though the blood as
A) glycerophospholipids.
B) sphingolipids.
C) cerebrosides.
D) very low density lipoprotein particles.
A) glycerophospholipids.
B) sphingolipids.
C) cerebrosides.
D) very low density lipoprotein particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In comparison with glycerophospholipids,the structure of cerebrosides contains a
A) fatty acid.
B) sphingosine.
C) choline.
D) steroid ring.
A) fatty acid.
B) sphingosine.
C) choline.
D) steroid ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Soap traps dirt particles in
A) triacylglycerols.
B) micelles.
C) steroids.
D) glycerophospholipids.
A) triacylglycerols.
B) micelles.
C) steroids.
D) glycerophospholipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Tay-Sachs disease,Fabry disease,and Niemann-Pick disease are all symptomatic because of
A) defects in sphingolipid metabolism.
B) improper glycan storage.
C) cleavage of glycerophospholipids.
D) reduced cholesterol synthesis.
A) defects in sphingolipid metabolism.
B) improper glycan storage.
C) cleavage of glycerophospholipids.
D) reduced cholesterol synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The inner layer of the plasma membrane of human erythrocytes contains mostly __________ lipids.
A) phosphatidylserine
B) ganglioside
C) phosphatidylcholine
D) sphingomyelin
A) phosphatidylserine
B) ganglioside
C) phosphatidylcholine
D) sphingomyelin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which missing enzyme results in Fabry disease?
A) phospholipase A2
B) sphingomyelinase
C)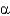 -galactosidase A
-galactosidase A
D) hexosaminidase A
A) phospholipase A2
B) sphingomyelinase
C)
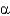 -galactosidase A
-galactosidase AD) hexosaminidase A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which missing enzyme results in Niemann-Pick disease?
A) phospholipase A2
B) sphingomyelinase
C)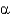 -galactosidase A
-galactosidase A
D) hexosaminidase A
A) phospholipase A2
B) sphingomyelinase
C)
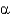 -galactosidase A
-galactosidase AD) hexosaminidase A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Lipid rafts are thought to be discrete membrane regions that contain high concentrations of
A) phosphatidylinositol.
B) gangliosides.
C) phosphatidylcholine.
D) cholesterol.
A) phosphatidylinositol.
B) gangliosides.
C) phosphatidylcholine.
D) cholesterol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The outer layer of the plasma membrane of human erythrocytes contains mostly __________ lipids.
A) phosphatidylinositol
B) phosphatidylserine
C) phosphatidylcholine
D) phosphatidylethanolamine
A) phosphatidylinositol
B) phosphatidylserine
C) phosphatidylcholine
D) phosphatidylethanolamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
One of the functions of the lipid rafts is to
A) act as a storage mechanism for fatty acids.
B) control fluidity of the membrane.
C) coordinate cell signaling.
D) maintain sodium levels in the cell.
A) act as a storage mechanism for fatty acids.
B) control fluidity of the membrane.
C) coordinate cell signaling.
D) maintain sodium levels in the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Snake venom often secretes phospholipase A2 enzymes,which cleave
A) glycerophospholipids.
B) ceramides.
C) sphingosines.
D) gangliosides.
A) glycerophospholipids.
B) ceramides.
C) sphingosines.
D) gangliosides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following membranes would have the greatest fluidity based on the following percentage of cholesterol in the membrane?
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 30%
D) 40%
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 30%
D) 40%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following amino alcohols act as the functional group attached to a phosphate in a glycerophospholipid?
A) lysine
B) serine
C) glycine
D) alanine
A) lysine
B) serine
C) glycine
D) alanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which type of fatty acid plays important roles in cell recognition such as in ABO blood groups?
A) sphingomyelins
B) gangliosides
C) cerebrosides
D) glycerophospholipids
A) sphingomyelins
B) gangliosides
C) cerebrosides
D) glycerophospholipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The total content of __________ is approximately the same in both the inner and outer layer of the plasma membrane of human erythrocytes.
A) phosphatidylinositol
B) sphingomyelin
C) phosphatidylcholine
D) cholesterol
A) phosphatidylinositol
B) sphingomyelin
C) phosphatidylcholine
D) cholesterol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In comparison with gangliosides,the structure of phosphatidylcholine contains a
A) fatty acid.
B) sugar moiety.
C) glycerol moiety.
D) steroid ring.
A) fatty acid.
B) sugar moiety.
C) glycerol moiety.
D) steroid ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which missing enzyme results in Tay-Sachs disease?
A) phospholipase A2
B) sphingomyelinase
C)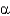 -galactosidase A
-galactosidase A
D) hexosaminidase A
A) phospholipase A2
B) sphingomyelinase
C)
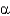 -galactosidase A
-galactosidase AD) hexosaminidase A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following amino alcohols act as the functional group attached to a phosphate in a glycerophospholipid?
A) methanolamine
B) ethanolamine
C) propanolamine
D) butanolamine
A) methanolamine
B) ethanolamine
C) propanolamine
D) butanolamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following membranes would have the least amount of fluidity based on the following percentage of cholesterol in the membrane?
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 30%
D) 40%
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 30%
D) 40%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The addition of phosphocholine to ceramides generates
A) glycerophospholipids.
B) gangliosides.
C) cerebrosides.
D) sphingomyelin.
A) glycerophospholipids.
B) gangliosides.
C) cerebrosides.
D) sphingomyelin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which membrane lipids are derivatives of long chain amino alcohols synthesized from palmitate and serine?
A) phosphatidylinositol
B) phosphatidylcholine
C) sphingosines
D) phosphatidylethanolamine
A) phosphatidylinositol
B) phosphatidylcholine
C) sphingosines
D) phosphatidylethanolamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Compared with other areas of the membrane,lipid rafts contain more
A) sphingolipids.
B) phosphatidylcholine.
C) phosphatidylinositol.
D) gangliosides.
A) sphingolipids.
B) phosphatidylcholine.
C) phosphatidylinositol.
D) gangliosides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In comparison with glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids,cholesterol contains a
A) fatty acid.
B) phosphate group.
C) glycerol moiety.
D) steroid ring.
A) fatty acid.
B) phosphate group.
C) glycerol moiety.
D) steroid ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Vitamin D3 is converted to 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in the __________ cells.
A) skin
B) kidney
C) muscle
D) liver
A) skin
B) kidney
C) muscle
D) liver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which eicosanoid regulates blood vessel constriction?
A) prostaglandin
B) prostacyclin
C) thromboxane
D) leukotriene
A) prostaglandin
B) prostacyclin
C) thromboxane
D) leukotriene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which eicosanoid controls platelet formation?
A) prostaglandin
B) prostacyclin
C) thromboxane
D) leukotriene
A) prostaglandin
B) prostacyclin
C) thromboxane
D) leukotriene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Inhibition of the COX-1 enzyme results in
A) reduced pain and fever.
B) reduced mucin secretion.
C) increased risk of heart disease.
D) increased platelet aggregation.
A) reduced pain and fever.
B) reduced mucin secretion.
C) increased risk of heart disease.
D) increased platelet aggregation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Propose a reason that a diet rich in 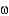
-3 fatty acids would result in a decrease in cardiovascular disease.
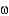
-3 fatty acids would result in a decrease in cardiovascular disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Compare and contrast the structure of a wax to that of a fatty acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Predict the following fatty acid structures.
a. cis 18:2 (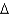
9,12)
b. trans 18:1 (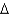
9)
c. trans 20:2 (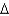
11,13)
a. cis 18:2 (
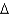
9,12)
b. trans 18:1 (
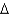
9)
c. trans 20:2 (
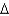
11,13)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following molecules aid in the absorption of dietary lipids?
A) prostaglandin
B) cortisol
C) glycocholate
D) aldosterone
A) prostaglandin
B) cortisol
C) glycocholate
D) aldosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is partial hydrogenation? Outline the pros and cons of using partial hydrogenation in the food industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Why do long chain,saturated fatty acids have a higher melting point than unsaturated fatty acids?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Compared with the COX-2 enzyme,COX-1 has
A) a larger active site.
B) a smaller active site.
C) a more elongated three-dimensional structure.
D) more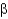
-barrels.
A) a larger active site.
B) a smaller active site.
C) a more elongated three-dimensional structure.
D) more
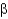
-barrels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Compare and contrast saturated,monounsaturated,and polyunsaturated fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A patient is having problems regulating blood pressure and has poor kidney function.Which steroid could be responsible for this?
A) progesterone
B) cortisol
C) aldosterone
D) estradiol
A) progesterone
B) cortisol
C) aldosterone
D) estradiol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Cortisol is a glucocorticoid that regulates
A) blood pressure.
B) ion transport in the kidneys.
C) testosterone.
D) liver metabolism.
A) blood pressure.
B) ion transport in the kidneys.
C) testosterone.
D) liver metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Using common nomenclature,name the following fatty acid structures.
a.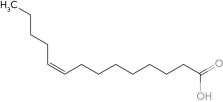
b.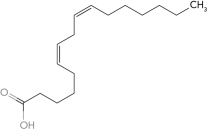
c.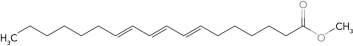
a.

b.

c.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids are synthesized in the
A) kidneys.
B) adrenal glands.
C) liver.
D) corpus luteum.
A) kidneys.
B) adrenal glands.
C) liver.
D) corpus luteum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which eicosanoid acts as an inflammatory mediator that also regulates smooth muscle contraction?
A) prostaglandin
B) prostacyclin
C) thromboxane
D) leukotriene
A) prostaglandin
B) prostacyclin
C) thromboxane
D) leukotriene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which steroid hormone is synthesized in the corpus luteum?
A) cortisol
B) progesterone
C) testosterone
D) estradiol
A) cortisol
B) progesterone
C) testosterone
D) estradiol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which steroid hormone is synthesized in the ovaries?
A) cortisol
B) progesterone
C) testosterone
D) estradiol
A) cortisol
B) progesterone
C) testosterone
D) estradiol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which eicosanoid modulates the secretion of proteoglycans that protects the stomach lining from the effects of low pH?
A) prostaglandin
B) prostacyclin
C) thromboxane
D) leukotriene
A) prostaglandin
B) prostacyclin
C) thromboxane
D) leukotriene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



