Deck 8: Elementary Quantitative Data Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Elementary Quantitative Data Analysis
1
Histograms are used to display the distribution of quantitative variables that vary along a continuum.
True
2
The process of checking data for errors after the data has been entered in a computer file is called error cleansing.
False
3
Measures of central tendency assess the extent to which cases are spread out through the distribution or clustered in just one location.
False
4
Use the following to answer questions 16-18:
In each set, match a concept from Group A to a definition or example from Group B.
Measures of central tendency and variation
Group A
1. Mean
2. Median
3. Mode
4. Range
5. Standard deviation
Group B
a. The point that divides the distribution in half
b. The average squared deviation of each case from the mean
c. The most frequent value in a distribution
d. The distance from the mean that covers about two-thirds of cases
e. The highest value in a distribution minus the lowest value plus one
f. The arithmetic average of the distribution
In each set, match a concept from Group A to a definition or example from Group B.
Measures of central tendency and variation
Group A
1. Mean
2. Median
3. Mode
4. Range
5. Standard deviation
Group B
a. The point that divides the distribution in half
b. The average squared deviation of each case from the mean
c. The most frequent value in a distribution
d. The distance from the mean that covers about two-thirds of cases
e. The highest value in a distribution minus the lowest value plus one
f. The arithmetic average of the distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Use the following to answer questions 16-18:
In each set, match a concept from Group A to a definition or example from Group B.
Data Displays
Group A
1. Bar chart
2. Histogram
3. Frequency polygon
4. Normal curve
Group B
a. A distribution containing solid bars separated by spaces
b. A continuous line connecting points that represent the number or percentage of cases at each value
c. A distribution presented as fractions of a whole
d. A bell-shaped distribution centered on the mean
e. A distribution of adjacent bars
In each set, match a concept from Group A to a definition or example from Group B.
Data Displays
Group A
1. Bar chart
2. Histogram
3. Frequency polygon
4. Normal curve
Group B
a. A distribution containing solid bars separated by spaces
b. A continuous line connecting points that represent the number or percentage of cases at each value
c. A distribution presented as fractions of a whole
d. A bell-shaped distribution centered on the mean
e. A distribution of adjacent bars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A frequency polygon is the most relevant graph for displaying discrete, nominal variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the following to answer questions 16-18:
In each set, match a concept from Group A to a definition or example from Group B.
Elements of a Crosstabulation
Group A
1. body of the table
2. cell
3. marginals
4. column
5. base number (N)
Group B
a. Typically divided into categories of the independent variable
b. Combinations of row and column values that represent unique combinations of values
c. The total number cases in the distribution
d. Typically divided into categories of the dependent variable
e. Part of table between row and column labels and row and column totals
f. Frequency distributions for independent and dependent variables
In each set, match a concept from Group A to a definition or example from Group B.
Elements of a Crosstabulation
Group A
1. body of the table
2. cell
3. marginals
4. column
5. base number (N)
Group B
a. Typically divided into categories of the independent variable
b. Combinations of row and column values that represent unique combinations of values
c. The total number cases in the distribution
d. Typically divided into categories of the dependent variable
e. Part of table between row and column labels and row and column totals
f. Frequency distributions for independent and dependent variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Outliers may render a range useless for determining the distribution of a variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Nominal variables should be displayed on:
A) Bar charts
B) Histograms
C) Frequency polygons
D) Both a and b
E) All of the above
A) Bar charts
B) Histograms
C) Frequency polygons
D) Both a and b
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Crosstabulations show relationships between ____________, while elaboration considers _____________.
A) one variable, two variables
B) two variables, three or more variables,
C) independent variables, independent and dependent variables
D) categoric variables, numeric variables
E) nominal variables, ratio variables
A) one variable, two variables
B) two variables, three or more variables,
C) independent variables, independent and dependent variables
D) categoric variables, numeric variables
E) nominal variables, ratio variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The measure of central tendency most appropriate for nominal variables is the mode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Standard deviation is defined as the square root of the variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Data cleaning occurs before data entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A normal distribution is generally bell-shaped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A frequency polygon contains solid bars separated by spaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In distributions with an even number of cases, the median is computed by taking the arithmetic average between the two middle cases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Means are affected by skewness, while medians are not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Descriptive statistics estimate the degree of confidence in generalizations made from a sample to a population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Chi square is an inferential statistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Elaboration analysis demonstrations the distribution of variables on x and y axes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the following distribution of the variable semesters completed, which is the range: 4, 3, 1, 0, 3, 3, 4, 0, 3, 2?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is not a guideline for constructing graphs?
A) Begin the graph of a quantitative variable at zero on both axes.
B) Always use bars of equal width.
C) The two axes should be of approximately equal length.
D) Avoid "chart junk" that clutters the graph.
E) When possible, use graphics instead of bars.
A) Begin the graph of a quantitative variable at zero on both axes.
B) Always use bars of equal width.
C) The two axes should be of approximately equal length.
D) Avoid "chart junk" that clutters the graph.
E) When possible, use graphics instead of bars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The presence of outliers suggests what about the shape of a variable's distribution?
A) It is normal
B) It is skewed
C) It is unimodal
D) It is bimodal
E) It is multimodal
A) It is normal
B) It is skewed
C) It is unimodal
D) It is bimodal
E) It is multimodal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the following distribution of the variable semesters completed, which is closest to the mean: 4, 3, 1, 0, 3, 3, 4, 0, 3, 2?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What statistic is used to determine whether a significant relationship exists between two variables in a crosstab?
A) Alpha
B) Beta
C) Gamma
D) Delta
E) Epsilon
A) Alpha
B) Beta
C) Gamma
D) Delta
E) Epsilon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In which of the following can you control for an extraneous variable?
A) Bar chart
B) Frequency distribution
C) Frequency polygon
D) Elaboration analysis
E) Crosstabulation
A) Bar chart
B) Frequency distribution
C) Frequency polygon
D) Elaboration analysis
E) Crosstabulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a normal curve, about what percent of all cases falls within plus or minus two standard deviations?
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 68%
E) 95%
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 68%
E) 95%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the following distribution of the variable semesters completed, which is median: 4, 3, 1, 0, 3, 3, 4, 0, 3, 2, 4?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the following distribution of the variable semesters completed, which is the mode: 4, 3, 1, 0, 3, 3, 4, 0, 3, 2?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In a crosstabs, the cells display:
A) Counts
B) Percentages
C) Categories of the dependent variable
D) Both a and b
E) All of the above
A) Counts
B) Percentages
C) Categories of the dependent variable
D) Both a and b
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The process of checking data carefully for errors is known as:
A) Data reduction
B) Data cleaning
C) Data dredging
D) Data definition
E) Data analysis
A) Data reduction
B) Data cleaning
C) Data dredging
D) Data definition
E) Data analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which summary statistic should be used for nominal variables?
A) Range
B) Variance
C) Mean
D) Median
E) Mode
A) Range
B) Variance
C) Mean
D) Median
E) Mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When researchers analyze data that they did not collect, such as the General Social Survey, they are conducting what type of research?
A) Primary research
B) Data cleaning
C) Historical research
D) Secondary research
E) Repetition
A) Primary research
B) Data cleaning
C) Historical research
D) Secondary research
E) Repetition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The total number of cases in a distribution is called:
A) The base number N
B) The range
C) The row marginal
D) The mode
E) The frequency
A) The base number N
B) The range
C) The row marginal
D) The mode
E) The frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What measure of variability is most appropriate for a ratio variable with many outliers?
A) Median
B) Range
C) Interquartile range
D) Variance
E) Standard deviation
A) Median
B) Range
C) Interquartile range
D) Variance
E) Standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The diagram below is a: 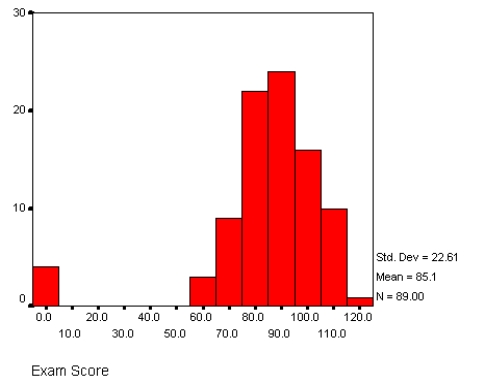
A) Mean
B) Mode
C) Bar chart
D) Frequency polygon
E) Histogram

A) Mean
B) Mode
C) Bar chart
D) Frequency polygon
E) Histogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The diagram below is a: 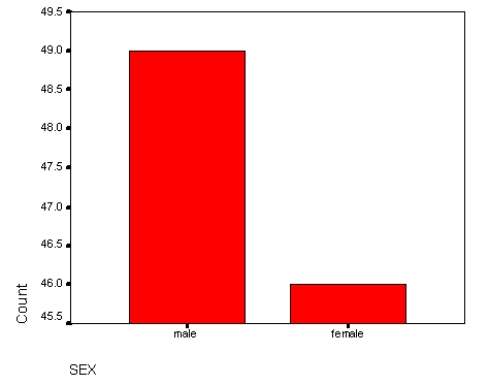
A) Mean
B) Mode
C) Bar chart
D) Frequency polygon
E) Histogram

A) Mean
B) Mode
C) Bar chart
D) Frequency polygon
E) Histogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The diagram below is a 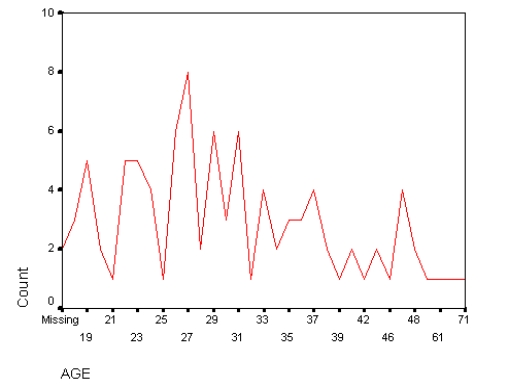
A) Mean
B) Mode
C) Bar chart
D) Frequency polygon
E) Histogram

A) Mean
B) Mode
C) Bar chart
D) Frequency polygon
E) Histogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following data displays would be most appropriate for displaying the distribution of gender (male, female, other)?
A) Mean
B) Median
C) Bar chart
D) Frequency polygon
E) Histogram
A) Mean
B) Median
C) Bar chart
D) Frequency polygon
E) Histogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following data displays represent data not as bars, but as connected points in a single line?
A) Mean
B) Mode
C) Bar chart
D) Frequency polygon
E) Histogram
A) Mean
B) Mode
C) Bar chart
D) Frequency polygon
E) Histogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A type of descriptive statistic that summarizes the strength of an association:
A) Measure of Significance
B) Measure of Central Tendency
C) Measure of Variation
D) Measure of Association
E) None of the above
A) Measure of Significance
B) Measure of Central Tendency
C) Measure of Variation
D) Measure of Association
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A student constructs the following frequency distribution based on this research hypothesis: A person's level of education predicts that person's level of prejudice. Find three things wrong with the table. Rewrite the table correctly, assuming that the sample had exactly 100 people in each category.
Table 1.1: Percent of respondents' level of prejudice by level of education.
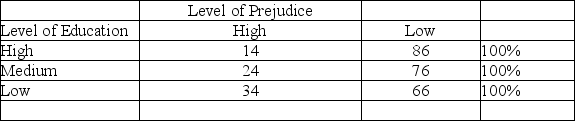
Table 1.1: Percent of respondents' level of prejudice by level of education.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Describe circumstances in which mean, median, and modes are best used as measures of central tendency, providing at least two concrete examples for each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Using the table below, explain the hypothesis presented and describe the association between the variables in the following table (data are hypothetical):
Level of Support for Eliminating Aid to Families with Dependent Children (AFDC) by Education
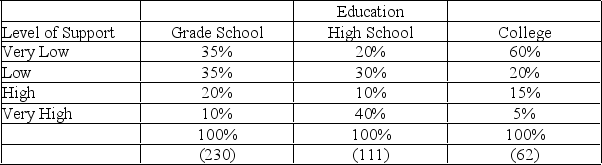
Level of Support for Eliminating Aid to Families with Dependent Children (AFDC) by Education


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Compute three measures of central tendency and two measures of variability for the following data set: When asked their age, ten college students responded: 21, 19, 20, 18, 18, 19, 33, 22, 19, 18. Given this distribution, which measures of central tendency and variability are most appropriate? Explain your decision, drawing a graph or creating a frequency distribution as necessary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consider the use of bar charts, histograms, and frequency polygons. When are each appropriate? Sketch each type of graph. What standards exist for presenting graphic data in social research?
Answer Key
Answer Key

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When a researcher has a distribution in which two nonadjacent categories have about the same number of cases, this is referred to as a:
A) Mean
B) Bimodal
C) Binomial
D) Unimodal
E) Frequency
A) Mean
B) Bimodal
C) Binomial
D) Unimodal
E) Frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is false about standard deviations?
A) It tells how wide the variation of any set of cases is.
B) It is the square root of the variance.
C) It is the square root of the average squared deviation of each case from the mean.
D) It is the preferred measure of variability when a variable in normally distributed.
E) It is a measure of central tendency.
A) It tells how wide the variation of any set of cases is.
B) It is the square root of the variance.
C) It is the square root of the average squared deviation of each case from the mean.
D) It is the preferred measure of variability when a variable in normally distributed.
E) It is a measure of central tendency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider the relationship between gender, wages, and years of experience on the job. Draw a table in which you propose a hypothesis that involves a bivariate relationship between two of these variables, but considers the third as an extraneous variable (obviously, the cells will remain empty in this table). Explain your rationale for choosing the extraneous variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What does statistical significance mean with regard to the association between two variables?
A) Association is likely to be due to chance.
B) Association is not likely to be due to chance.
C) Association is likely to be due to a third variable.
D) Association is not likely to be due to a third variable.
E) Association exists and is deemed to be strong.
A) Association is likely to be due to chance.
B) Association is not likely to be due to chance.
C) Association is likely to be due to a third variable.
D) Association is not likely to be due to a third variable.
E) Association exists and is deemed to be strong.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What three features are important for describing the shape of a variable's distribution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
John is using GSS data in order to conduct his study so that he doesn't have to collect his own data. He will most likely be conducting:
A) Secondary data analysis
B) Data cleaning
C) Qualitative data analysis
D) Primary data analysis
E) None of the above
A) Secondary data analysis
B) Data cleaning
C) Qualitative data analysis
D) Primary data analysis
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A graph with a normal distribution looks like which of the following?
A) A balance beam with two equal size bags on either side of the median
B) A box with a wide base and short sides
C) A bell with a hump in the middle and sloping sides
D) A pyramid with broad based extension across the range of cases
E) A barbell with equal weight on either side
A) A balance beam with two equal size bags on either side of the median
B) A box with a wide base and short sides
C) A bell with a hump in the middle and sloping sides
D) A pyramid with broad based extension across the range of cases
E) A barbell with equal weight on either side

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Describe situations in which a variable's variability is best measured by the range, interquartile range, and standard deviation, providing at least two concrete examples of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the purpose of using statistics in social science? What are the advantages and disadvantages of relying on statistics?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following would best illustrate marital status in a diagram as explained in the text?
A) Histogram
B) Frequency polygon
C) Box plot
D) Bar chart
E) Pie chart
A) Histogram
B) Frequency polygon
C) Box plot
D) Bar chart
E) Pie chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How can statistics be unethically manipulated? Outline the specific ethical considerations associated with using statistics for social data analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is not a measure of variation?
A) Range
B) Mean
C) Standard deviation
D) Variance
E) Normal distribution
A) Range
B) Mean
C) Standard deviation
D) Variance
E) Normal distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Answer the following from the data presented below: What is the range for GPA in the sample? What is the mean age of the sample? What is the modal age of the sample? What is the median age of the sample? What is the mean age of the male sub-sample? What is the median GPA of juniors? What is the modal major of the sample? Based on means, how much higher is the male GPA than the female GPA? What is the modal class of the sample? What is the median class of the sample?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



