Deck 2: Understanding Interests, interactions, and Institutions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Understanding Interests, interactions, and Institutions
1
Leaders within a country may want to enact democratic reform in order to increase voter participation.This is an example of what kind of state goal?
A)Security
B)Ideological
C)Economic gain
D)Material welfare
A)Security
B)Ideological
C)Economic gain
D)Material welfare
B
2
What is a strategic interaction?
A)A condition whereby different actors have different interests
B)A condition in which actors try to understand the other in order to cooperate
C)A condition in which both actors are uncertain of their future relationship
D)A condition in which each actor's plan is contingent upon its estimate of what the other actor is expected to do
A)A condition whereby different actors have different interests
B)A condition in which actors try to understand the other in order to cooperate
C)A condition in which both actors are uncertain of their future relationship
D)A condition in which each actor's plan is contingent upon its estimate of what the other actor is expected to do
D
3
You are competing against fellow students for the highest grade in the class.Given this competition,which of the following is the best example of a potential strategic interaction?
A)You study for the exam.
B)You calculate the scores and attendance of every student in the class.
C)Students in the class study for the exam individually.
D)Everyone collaborates to do better together.
A)You study for the exam.
B)You calculate the scores and attendance of every student in the class.
C)Students in the class study for the exam individually.
D)Everyone collaborates to do better together.
B
4
In international relations,actors can be any of the following EXCEPT:
A)international organizations.
B)groups.
C)ideologies.
D)states.
A)international organizations.
B)groups.
C)ideologies.
D)states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In contrast to the anticipated stockpiles of chemical and biological weapons,what was the condition of the Iraqi state during the 2003 Iraq War?
A)A largely unified and healthy population and infrastructure
B)A fully loyal and patriotic public willing to fight the United States
C)A society on the edge of collapse from economic sanctions
D)A population prepared to facilitate democratic transition
A)A largely unified and healthy population and infrastructure
B)A fully loyal and patriotic public willing to fight the United States
C)A society on the edge of collapse from economic sanctions
D)A population prepared to facilitate democratic transition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Cooperation is a type of:
A)institution that makes agreements easier for two actors.
B)institution that sets the rules for interactions between actors.
C)interaction in which one actor will receive more and the other actor less of the desired outcome.
D)interaction involving two or more actors working together to achieve some outcome that leaves at least one of them better off.
A)institution that makes agreements easier for two actors.
B)institution that sets the rules for interactions between actors.
C)interaction in which one actor will receive more and the other actor less of the desired outcome.
D)interaction involving two or more actors working together to achieve some outcome that leaves at least one of them better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The following are all examples of nongovernmental organizations EXCEPT:
A)Amnesty International.
B)the United Nations.
C)Greenpeace.
D)Doctors without Borders.
A)Amnesty International.
B)the United Nations.
C)Greenpeace.
D)Doctors without Borders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What role did crosscutting lines of authority play in the emergence of the Peace of Westphalia?
A)The overlapping allegiances created a source of constant conflict among cities,monarchies,and religious leaders.
B)The system was made doubly stable through all the linkages across the cities.
C)The lines of authority produced peaceful collaboration between the Holy Roman Empire and other countries.
D)Peace treaties often resulted from the crosscutting allegiances.
A)The overlapping allegiances created a source of constant conflict among cities,monarchies,and religious leaders.
B)The system was made doubly stable through all the linkages across the cities.
C)The lines of authority produced peaceful collaboration between the Holy Roman Empire and other countries.
D)Peace treaties often resulted from the crosscutting allegiances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following would be considered a threat to the nature of sovereignty?
A)A superior international government
B)Domestic markets
C)Urbanization
D)Journalism
A)A superior international government
B)Domestic markets
C)Urbanization
D)Journalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why did the United Nations Security Council not endorse the preventive war against Iraq in 2003?
A)The members of the Security Council believed that Iran was a bigger threat than Iraq,and that the council should direct its energy there instead.
B)The Security Council is unable to endorse military action against sovereign countries.
C)The United Nations General Assembly would veto any action by the Security Council.
D)Several permanent members of the Security Council opposed going to war against Iraq and could veto any endorsement of the war.
A)The members of the Security Council believed that Iran was a bigger threat than Iraq,and that the council should direct its energy there instead.
B)The Security Council is unable to endorse military action against sovereign countries.
C)The United Nations General Assembly would veto any action by the Security Council.
D)Several permanent members of the Security Council opposed going to war against Iraq and could veto any endorsement of the war.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the figure,a point on the line segment ab represents what in relation to q?
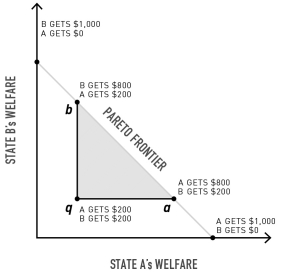
A)A gain only for actor A
B)A gain only for actor B
C)A loss for both actors
D)A gain for both actors

A)A gain only for actor A
B)A gain only for actor B
C)A loss for both actors
D)A gain for both actors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What does line segment qb represent?
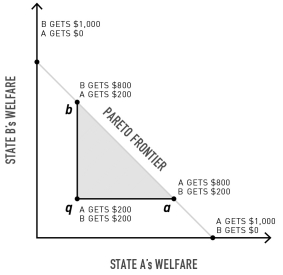
A)Possible improvements for actor A that do not affect the welfare of B
B)Possible improvements for actor B that do not affect the welfare of A
C)The set of all possible improvements for actors A and B
D)The zone of potential losses for both actors

A)Possible improvements for actor A that do not affect the welfare of B
B)Possible improvements for actor B that do not affect the welfare of A
C)The set of all possible improvements for actors A and B
D)The zone of potential losses for both actors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a potential example of state loss of sovereignty?
A)A state changes its currency from a cash system to an electronic system.
B)A state takes over all of its banks and declares itself the sole lender to its citizens.
C)A corporation successfully takes over the enactment and adjudication of a state's laws.
D)A state expands its control over ocean waterways.
A)A state changes its currency from a cash system to an electronic system.
B)A state takes over all of its banks and declares itself the sole lender to its citizens.
C)A corporation successfully takes over the enactment and adjudication of a state's laws.
D)A state expands its control over ocean waterways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is an example of a state?
A)The United Nations
B)Iraq
C)Saddam Hussein
D)The American Republican Party
A)The United Nations
B)Iraq
C)Saddam Hussein
D)The American Republican Party

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is an example of a failed state?
A)A state that suffers an industrial slump
B)A state that changes its flag to reflect a new leader
C)A state that experiences a major debt crisis
D)A state whose central government collapses
A)A state that suffers an industrial slump
B)A state that changes its flag to reflect a new leader
C)A state that experiences a major debt crisis
D)A state whose central government collapses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What does the triangle qba represent?
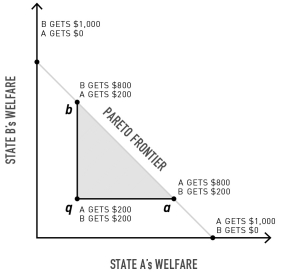
A)The set of all possible improvements for actor A
B)The set of all possible improvements for actors A and B
C)The zone in which neither actor would agree to a bargain
D)The zone of potential losses for both actors

A)The set of all possible improvements for actor A
B)The set of all possible improvements for actors A and B
C)The zone in which neither actor would agree to a bargain
D)The zone of potential losses for both actors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which entity is the most prominent actor in international relations?
A)States
B)People
C)Nongovernmental organizations
D)Terrorist groups
A)States
B)People
C)Nongovernmental organizations
D)Terrorist groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A person goes to college with the hope of improving his or her earning power and future income upon graduation.This is an example of which type of goal that an actor might have?
A)Security
B)Material welfare
C)Ideological
D)Power
A)Security
B)Material welfare
C)Ideological
D)Power

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which category of interest is usually considered the most basic and a prerequisite for other goals?
A)Security
B)Economic welfare
C)Ideological
D)Geographic land
A)Security
B)Economic welfare
C)Ideological
D)Geographic land

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is an example of cooperation?
A)A group of friends each contributing money to throw a party
B)A single corporation lobbying Congress for trade protection from foreign imports
C)A country unilaterally cutting back on its emission of greenhouse gases
D)Two water districts agreeing that each should get half of a local river's water
A)A group of friends each contributing money to throw a party
B)A single corporation lobbying Congress for trade protection from foreign imports
C)A country unilaterally cutting back on its emission of greenhouse gases
D)Two water districts agreeing that each should get half of a local river's water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Imposing some cost on others to reduce the value of the reversion outcome is known as:
A)coercion.
B)reversion.
C)linkage.
D)collaboration.
A)coercion.
B)reversion.
C)linkage.
D)collaboration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is an example of linkage?
A)You and your neighbor agree to take turns shoveling your driveways on snow days.
B)You agree to drive your little brother to school,and your older brother agrees to do the dishes when it is your turn.
C)Your friend doesn't share his lunch with you so you refuse to share yours the next day.
D)The president of the United States enacts tariffs on steel so the Chinese premier also enacts tariffs on steel.
A)You and your neighbor agree to take turns shoveling your driveways on snow days.
B)You agree to drive your little brother to school,and your older brother agrees to do the dishes when it is your turn.
C)Your friend doesn't share his lunch with you so you refuse to share yours the next day.
D)The president of the United States enacts tariffs on steel so the Chinese premier also enacts tariffs on steel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
________ interactions are the simplest kind of cooperation between actors.
A)Zero-sum
B)Coordination
C)Positive-sum
D)Collaborative
A)Zero-sum
B)Coordination
C)Positive-sum
D)Collaborative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is an example of iteration and reciprocity?
A)U.S.forces announce that they are leaving Afghanistan.
B)Entrenched forces enact a system of "live and let live" during a prolonged and uncertain war.
C)You leave a tip at a restaurant that you will never return to.
D)The Russians invade Crimea.
A)U.S.forces announce that they are leaving Afghanistan.
B)Entrenched forces enact a system of "live and let live" during a prolonged and uncertain war.
C)You leave a tip at a restaurant that you will never return to.
D)The Russians invade Crimea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the United Nations Security Council decides not to intervene to stop genocide,the reversion outcome would be that:
A)the Security Council members would return for more negotiations.
B)the genocide would be ended.
C)the genocide would continue.
D)economic sanctions would automatically be enacted.
A)the Security Council members would return for more negotiations.
B)the genocide would be ended.
C)the genocide would continue.
D)economic sanctions would automatically be enacted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A state wanting to free ride with regard to ozone depletion would:
A)sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases but continue to produce such ozone-depleting emissions,while other states decrease their own emissions.
B)sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases but reduce emissions only if all other signatories also reduce their emissions.
C)refuse to sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases because it would not trust other states to reduce their own emissions.
D)freely reduce emissions without signing any entangling agreements.
A)sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases but continue to produce such ozone-depleting emissions,while other states decrease their own emissions.
B)sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases but reduce emissions only if all other signatories also reduce their emissions.
C)refuse to sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases because it would not trust other states to reduce their own emissions.
D)freely reduce emissions without signing any entangling agreements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which is the best definition of a public good?
A)A benefit that is paid for by the government out of tax dollars collected from the general public
B)A product created by public agencies for the use of all citizens of a country
C)A product that cannot be withheld from anyone and whose use does not prohibit anyone else from enjoying it
D)The supplies that governments provide for infrastructure projects
A)A benefit that is paid for by the government out of tax dollars collected from the general public
B)A product created by public agencies for the use of all citizens of a country
C)A product that cannot be withheld from anyone and whose use does not prohibit anyone else from enjoying it
D)The supplies that governments provide for infrastructure projects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What kind of problem does the Prisoner's Dilemma story illustrate?
A)Coordination
B)Linkage
C)Coercion
D)Collaboration
A)Coordination
B)Linkage
C)Coercion
D)Collaboration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What was the key characteristic of the nuclear arms race between the United States and the Soviet Union that makes it applicable to the Prisoner's Dilemma?
A)Each side had real incentives to cheat in order to spend less money.
B)Each side wanted to collaborate in order to keep from blowing up the world in a nuclear war.
C)Each side had an incentive to cheat in order to maintain superiority over the other.
D)The United States provided evidence of nuclear weapons,while the Soviet Union remained quiet and thus defected instead of cooperating.
A)Each side had real incentives to cheat in order to spend less money.
B)Each side wanted to collaborate in order to keep from blowing up the world in a nuclear war.
C)Each side had an incentive to cheat in order to maintain superiority over the other.
D)The United States provided evidence of nuclear weapons,while the Soviet Union remained quiet and thus defected instead of cooperating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The most likely outcome for both participants in the Prisoner's Dilemma is that:
A)both keep quiet so that both go free.
B)both provide evidence against the other and go to jail.
C)one prisoner keeps quiet,while the other provides evidence and avoids jail.
D)both keep quiet and spend time in jail.
A)both keep quiet so that both go free.
B)both provide evidence against the other and go to jail.
C)one prisoner keeps quiet,while the other provides evidence and avoids jail.
D)both keep quiet and spend time in jail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
One means with which a country can coerce other countries is:
A)walking away from negotiations.
B)setting the agenda for negotiations.
C)threatening or using military force against the other countries.
D)having an international organization mediate the dispute.
A)walking away from negotiations.
B)setting the agenda for negotiations.
C)threatening or using military force against the other countries.
D)having an international organization mediate the dispute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why are countries more likely to cooperate when there is iteration?
A)Because countries are better able to threaten reciprocal punishment and cooperation in the future.
B)Because countries that are closer together are also more likely to cooperate.
C)Because countries are more likely to cooperate when no country is more powerful than the other.
D)Because multiple interactions make the threat of force less credible.
A)Because countries are better able to threaten reciprocal punishment and cooperation in the future.
B)Because countries that are closer together are also more likely to cooperate.
C)Because countries are more likely to cooperate when no country is more powerful than the other.
D)Because multiple interactions make the threat of force less credible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When bargaining with others,one actor will have an advantage if:
A)the actor is more satisfied with the reversion outcome than the others.
B)the actor cares more about the outcome of the bargain.
C)the actor needs to end the bargaining process quickly.
D)the actor has no other options but to come to an agreement.
A)the actor is more satisfied with the reversion outcome than the others.
B)the actor cares more about the outcome of the bargain.
C)the actor needs to end the bargaining process quickly.
D)the actor has no other options but to come to an agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two actors facing a coordination problem are:
A)unlikely to find a mutually acceptable solution to the problem.
B)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution only if one actor has more power than the other.
C)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution that is difficult to enforce.
D)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution that requires little enforcement.
A)unlikely to find a mutually acceptable solution to the problem.
B)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution only if one actor has more power than the other.
C)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution that is difficult to enforce.
D)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution that requires little enforcement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In which of the following situations would you expect defection?
A)Both actors have shared interests.
B)Individual interests of one are superseded by the collective interest.
C)Individual interests of one supersede the collective interest.
D)Both sets of individual interests are bolstered by the collective interest.
A)Both actors have shared interests.
B)Individual interests of one are superseded by the collective interest.
C)Individual interests of one supersede the collective interest.
D)Both sets of individual interests are bolstered by the collective interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If bargaining is a fixed-sum,what are the implications for the actors participating in it?
A)The pie can be expanded to make both better off.
B)The outcome can be fixed such that everyone wins.
C)Both agents will lose something in the process.
D)One will be made worse off.
A)The pie can be expanded to make both better off.
B)The outcome can be fixed such that everyone wins.
C)Both agents will lose something in the process.
D)One will be made worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In 2003,why did Saddam Hussein keep it a secret that Iraq had destroyed its weapons of mass destruction?
A)Saddam Hussein thought Iran might attack if the Iranians knew he did not have any weapons of mass destruction.
B)Saddam Hussein thought that the United States would be deterred from invading if it thought Iraq still had weapons of mass destruction.
C)Saddam Hussein had been lied to by Iraqi scientists and thought that Iraq really did have weapons of mass destruction.
D)Saddam Hussein thought that inspectors from the United Nations would be able to find out for themselves that Iraq did not have weapons of mass destruction.
A)Saddam Hussein thought Iran might attack if the Iranians knew he did not have any weapons of mass destruction.
B)Saddam Hussein thought that the United States would be deterred from invading if it thought Iraq still had weapons of mass destruction.
C)Saddam Hussein had been lied to by Iraqi scientists and thought that Iraq really did have weapons of mass destruction.
D)Saddam Hussein thought that inspectors from the United Nations would be able to find out for themselves that Iraq did not have weapons of mass destruction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is an example of a public good?
A)A free lunch provided by a soup kitchen
B)The clean air resulting from laws reducing pollution
C)A tariff protecting an important national industry
D)Electric cars that reduce smog for everyone
A)A free lunch provided by a soup kitchen
B)The clean air resulting from laws reducing pollution
C)A tariff protecting an important national industry
D)Electric cars that reduce smog for everyone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is true if the status quo agreement is at point a?
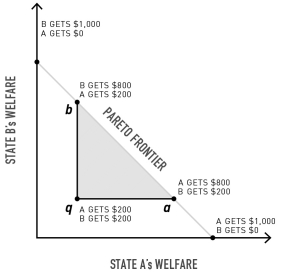
A)Any movement within the qba triangle is positive-sum.
B)Any movement along the line segment ab is zero-sum.
C)Agreement within triangle qba is likely.
D)Actor A will improve its share by making an agreement that is closer to point

A)Any movement within the qba triangle is positive-sum.
B)Any movement along the line segment ab is zero-sum.
C)Agreement within triangle qba is likely.
D)Actor A will improve its share by making an agreement that is closer to point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is an example of a solution to a coordination problem?
A)A driver sets flares on the road to mark an accident.
B)Airline pilots go on strike to raise wages.
C)Peacekeepers separate two armies in a civil war to stop the conflict.
D)Cybersecurity experts set a universal standard format for malware reporting so that all firms can share.
A)A driver sets flares on the road to mark an accident.
B)Airline pilots go on strike to raise wages.
C)Peacekeepers separate two armies in a civil war to stop the conflict.
D)Cybersecurity experts set a universal standard format for malware reporting so that all firms can share.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
For the game below,what is A2's payoff in cell CC?
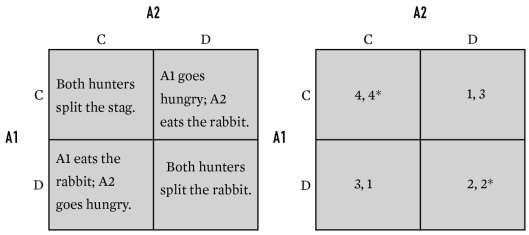
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Below is an example of which game?
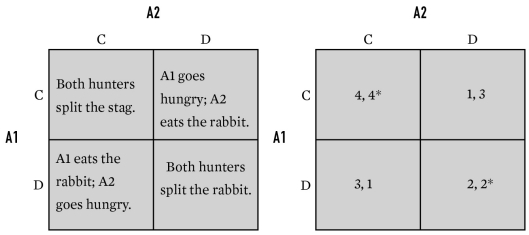
A)Chicken
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma
C)Stag Hunt
D)Coordination

A)Chicken
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma
C)Stag Hunt
D)Coordination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For the game below,what is A2's payoff in cell CD?
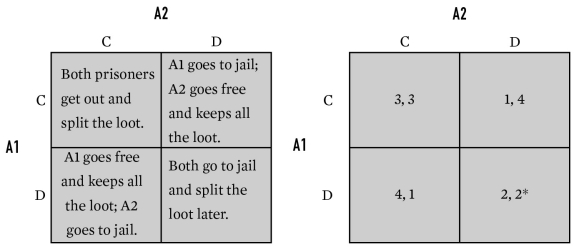
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The best example of institutional bias (reflecting the history of its creation)is the:
A)one country-one vote procedure in the United Nations General Assembly.
B)unanimous consent of the Council of Ministers of the European Economic Community before 1986.
C)veto power of the five permanent members on the United Nations Security Council.
D)consensus procedure in the World Trade Organization (WTO).
A)one country-one vote procedure in the United Nations General Assembly.
B)unanimous consent of the Council of Ministers of the European Economic Community before 1986.
C)veto power of the five permanent members on the United Nations Security Council.
D)consensus procedure in the World Trade Organization (WTO).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An actor using agenda-setting power during bargaining:
A)makes the last (and decisive)move.
B)uses knowledge of the agenda to create coalitions with other actors.
C)links items on the agenda to other issues,in order to coerce other actors.
D)acts first and therefore changes what choices are available to the other actors.
E)keeps the official record of the proceedings and uses this to promote its own description of the agreement or treaty.
A)makes the last (and decisive)move.
B)uses knowledge of the agenda to create coalitions with other actors.
C)links items on the agenda to other issues,in order to coerce other actors.
D)acts first and therefore changes what choices are available to the other actors.
E)keeps the official record of the proceedings and uses this to promote its own description of the agreement or treaty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the purpose of setting clear standards of behavior?
A)It allows others to determine if an agent is defecting.
B)It carries automatic moral authority.
C)So that states can punish their own politicians.
D)It increases the costs of joint decision making.
A)It allows others to determine if an agent is defecting.
B)It carries automatic moral authority.
C)So that states can punish their own politicians.
D)It increases the costs of joint decision making.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For the game below,what is the equilibrium (or equilibria)for A1 and A2?
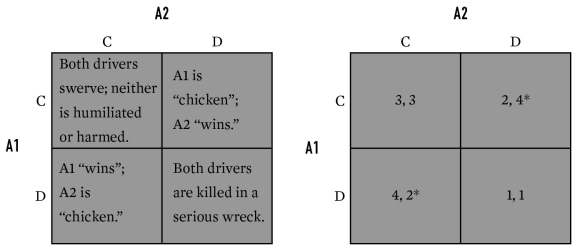
A)C,C
B)D,D
C)C,D and D,C
D)C,C; D,D; and C,D

A)C,C
B)D,D
C)C,D and D,C
D)C,C; D,D; and C,D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is an example of a game of Chicken?
A)A trade agreement in which each side wants more concessions from the other country.
B)A nuclear crisis in which each side wants to take a tough stance.
C)A peacekeeping mission for which countries are reluctant to send their troops.
D)An invasion of a small country by a large coalition of countries that did not want to attack alone.
A)A trade agreement in which each side wants more concessions from the other country.
B)A nuclear crisis in which each side wants to take a tough stance.
C)A peacekeeping mission for which countries are reluctant to send their troops.
D)An invasion of a small country by a large coalition of countries that did not want to attack alone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is an example of an institution helping to verify compliance?
A)The United Nations banning the use of satellites and planes to spy on other countries.
B)The North American Free Trade Agreement having 22 chapters of detailed rules on trade and investment between the member countries.
C)International Atomic Energy Agency inspectors searching for nuclear weapons that would violate the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons.
D)The United Nations Security Council approving the use of military force to remove Iraqi troops from Kuwait in 1990.
A)The United Nations banning the use of satellites and planes to spy on other countries.
B)The North American Free Trade Agreement having 22 chapters of detailed rules on trade and investment between the member countries.
C)International Atomic Energy Agency inspectors searching for nuclear weapons that would violate the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons.
D)The United Nations Security Council approving the use of military force to remove Iraqi troops from Kuwait in 1990.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
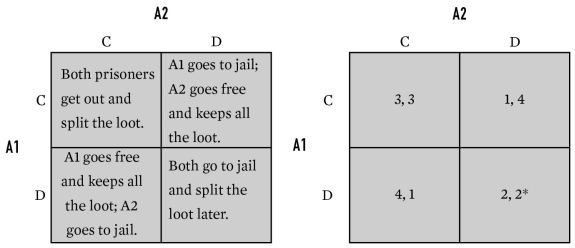
50
Below is an example of which game?
A)Chicken
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma
C)Stag Hunt
D)Cooperation.

A)Chicken
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma
C)Stag Hunt
D)Cooperation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
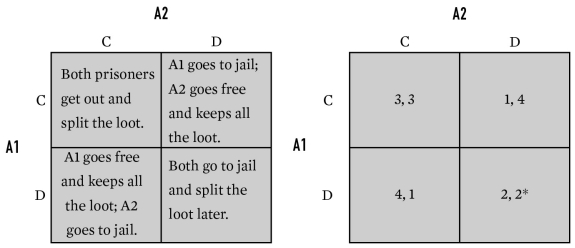
For the game below,what is A2's payoff in cell DD?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is an example of an informal institution?
A)The United Nations
B)International Monetary Fund
C)norms against slavery
D)World Trade Organization
A)The United Nations
B)International Monetary Fund
C)norms against slavery
D)World Trade Organization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When an actor can get a better deal through alternatives to reaching a bargain,this is sometimes referred to as:
A)the reversion outcome.
B)an outside option.
C)negotiation.
D)iterative retaliation.
A)the reversion outcome.
B)an outside option.
C)negotiation.
D)iterative retaliation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
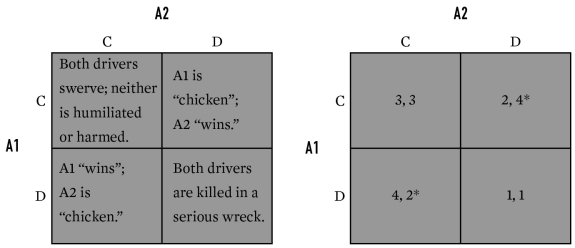
54
Below is an example of which game?
A)Chicken
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma
C)Stag Hunt
D)Coordination

A)Chicken
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma
C)Stag Hunt
D)Coordination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is one effect of creating clear rules within institutions like the United Nations?
A)It makes it possible for the United Nations to force states to comply.
B)It reduces the cost and energy associated with making collective decisions.
C)It undermines sovereignty.
D)It creates a natural harmony of interests that inspires peace among warring actors.
A)It makes it possible for the United Nations to force states to comply.
B)It reduces the cost and energy associated with making collective decisions.
C)It undermines sovereignty.
D)It creates a natural harmony of interests that inspires peace among warring actors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Why do powerful countries bother to follow the rules of the WTO?
A)Powerful countries receive greater benefits by maintaining a system where everyone plays by the rules.
B)The WTO locks in the powerful participants and binds them permanently to the institution.
C)Powerful countries see moral value in helping poorer countries.
D)Powerful countries are fooled into thinking they obtain benefits.
A)Powerful countries receive greater benefits by maintaining a system where everyone plays by the rules.
B)The WTO locks in the powerful participants and binds them permanently to the institution.
C)Powerful countries see moral value in helping poorer countries.
D)Powerful countries are fooled into thinking they obtain benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How did the norm of election monitoring spread even to less democratic elections?
A)Pseudo-democrats began copying true democrats in order to access foreign aid.
B)Election monitoring made countries more honest about their elections.
C)The United Nations began to name and shame nonparticipating countries.
D)Widespread election fraud was eliminated.
A)Pseudo-democrats began copying true democrats in order to access foreign aid.
B)Election monitoring made countries more honest about their elections.
C)The United Nations began to name and shame nonparticipating countries.
D)Widespread election fraud was eliminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Even though currently powerful countries like Germany,Brazil,and Japan would like a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council,they have not started their own competing international organization and have kept their protests within the United Nations' system.This is an example of what?
A)It is often cheaper and easier to use existing institutions even if they do not exactly match an actor's preferences.
B)Institutions with self-enforcement are more likely to last.
C)Institutions are created to reflect the biases of those who have the most power at that time.
D)Institutions are most effective when they serve multiple roles,such as assisting in verifying compliance and reducing costs of joint decision making.
A)It is often cheaper and easier to use existing institutions even if they do not exactly match an actor's preferences.
B)Institutions with self-enforcement are more likely to last.
C)Institutions are created to reflect the biases of those who have the most power at that time.
D)Institutions are most effective when they serve multiple roles,such as assisting in verifying compliance and reducing costs of joint decision making.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
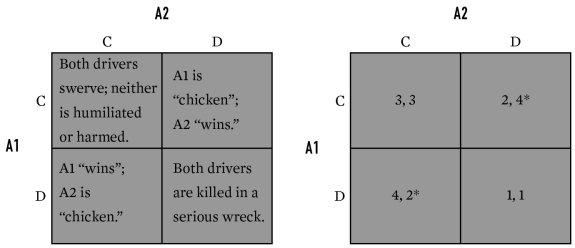
59
For the game below,what is the equilibrium (or equilibria)for A1 and A2?
A)C,C
B)C,D
C)D,C
D)D,D

A)C,C
B)C,D
C)D,C
D)D,D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Why is enforcement by institutions actually "self-enforcement"?
A)Institutions can force their own members to comply with their agreements without outside help.
B)There is no central international authority capable of forcing actors to cooperate.
C)To force members to cooperate,actors pay dues to their institutions to create their own enforcement agency.
D)Each institution is defined as a sovereign entity or "self."
A)Institutions can force their own members to comply with their agreements without outside help.
B)There is no central international authority capable of forcing actors to cooperate.
C)To force members to cooperate,actors pay dues to their institutions to create their own enforcement agency.
D)Each institution is defined as a sovereign entity or "self."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Discuss the ways in which informal international institutions might be more effective than formal ones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the Prisoner's Dilemma game,and why is mutual defection the expected outcome of the game?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What are the lessons of the Peace of Westphalia and how do they help us understand the way in which the contemporary state-based system works?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Does the United Nations have an institutional bias against the United States? In the General Assembly? In the Security Council?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How does bargaining differ from cooperation? Provide examples in international relations that demonstrate the difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Despite the fact that states are usually given priority over individuals and institutions,under which kinds of conditions are individuals and institutions potentially more important?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the difference between a national interest and the interest of a politician acting as a head of state? Give an example of each to illustrate your point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When states comply with international institutions,such as complying with the United Nations under conditions of peacekeeping,does this constitute a dilution of sovereignty?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Explain how access to information affects the probability of successful cooperation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What are public goods,and does the Internet count as a public good? Should it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Under what conditions are both hunters likely to cooperate in the Stag Hunt game?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Of the different mechanisms in bargaining (coercion,outside options,agenda setting)how often are each of these available to small states? Which of these is likely to benefit small states versus large states?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Explain how the number of actors,iteration,the importance of the future,and information contribute to successful cooperation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the role of international inspectors and treaties in helping to overcome Prisoner's Dilemmas? How does it affect the payoffs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Does the spread of election monitoring mean that eventually most election systems will be fair and free? What other methods might be helpful beyond this informal institution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



