Deck 21: Electrochemistry: Chemical Change and Electrical Work
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/102
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Electrochemistry: Chemical Change and Electrical Work
1
Which component of the following cell notation is the anode? P | Q || R | S
A) P
B) Q
C) R
D) S
E) One of the | symbols is the anode.
A) P
B) Q
C) R
D) S
E) One of the | symbols is the anode.
P
2
Which of the following statements about voltaic and electrolytic cells is correct?
A) The electrons in the external wire flow from cathode to anode in both types of cell.
B) Oxidation occurs at the cathode only in a voltaic cell.
C) The free energy change, G, is negative for an electrolytic cell.
D) The cathode is labeled as positive (+) in a voltaic cell but negative (-) in an electrolytic cell.
E) Reduction occurs at the anode in an electrolytic cell.
A) The electrons in the external wire flow from cathode to anode in both types of cell.
B) Oxidation occurs at the cathode only in a voltaic cell.
C) The free energy change, G, is negative for an electrolytic cell.
D) The cathode is labeled as positive (+) in a voltaic cell but negative (-) in an electrolytic cell.
E) Reduction occurs at the anode in an electrolytic cell.
The cathode is labeled as positive (+) in a voltaic cell but negative (-) in an electrolytic cell.
3
When the following redox equation is balanced with smallest whole number coefficients, the coefficient for the iodide ion will be _____. I-(aq) + NO3-(aq) NO(g) + I2(s) (acidic solution)
A) 2
B) 3
C) 6
D) 8
E) none of the above
A) 2
B) 3
C) 6
D) 8
E) none of the above
6
4
Consider the following balanced redox reaction
3CuO(s) + 2NH3(aq) N2(g) + 3H2O(l) + 3Cu(s)
Which of the following statements is true?
A) CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and copper is reduced.
B) CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and copper is oxidized.
C) CuO(s) is the reducing agent and copper is oxidized.
D) CuO(s) is the reducing agent and copper is reduced.
E) CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and N2(g) is the reducing agent.
3CuO(s) + 2NH3(aq) N2(g) + 3H2O(l) + 3Cu(s)
Which of the following statements is true?
A) CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and copper is reduced.
B) CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and copper is oxidized.
C) CuO(s) is the reducing agent and copper is oxidized.
D) CuO(s) is the reducing agent and copper is reduced.
E) CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and N2(g) is the reducing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the following balanced redox reaction
Mn2+(aq) + S2O82-(aq) + 2H2O(l) MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42-(aq)
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Mn2+(aq) is the oxidizing agent and is reduced.
B) Mn2+(aq) is the oxidizing agent and is oxidized.
C) Mn2+(aq) is the reducing agent and is oxidized.
D) Mn2+(aq) is the reducing agent and is reduced.
E) Manganese does not change its oxidation number in this reaction.
Mn2+(aq) + S2O82-(aq) + 2H2O(l) MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42-(aq)
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Mn2+(aq) is the oxidizing agent and is reduced.
B) Mn2+(aq) is the oxidizing agent and is oxidized.
C) Mn2+(aq) is the reducing agent and is oxidized.
D) Mn2+(aq) is the reducing agent and is reduced.
E) Manganese does not change its oxidation number in this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When the following redox equation is balanced with smallest whole number coefficients, the coefficient for zinc will be _____. Zn(s) + ReO4-(aq) Re(s) + Zn2+(aq) (acidic solution)
A) 2
B) 7
C) 8
D) 16
E) none of the above
A) 2
B) 7
C) 8
D) 16
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When the following redox equation is balanced with smallest whole number coefficients, the coefficient for the hydrogen sulfate ion will be ______.
Al(s) + HSO4-(aq) + OH-(aq) Al2O3(s) + S2-(aq) + H2O(l)
A) 1
B) 3
C) 4
D) 8
E) none of the above
Al(s) + HSO4-(aq) + OH-(aq) Al2O3(s) + S2-(aq) + H2O(l)
A) 1
B) 3
C) 4
D) 8
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When the following redox equation is balanced with smallest whole number coefficients, the coefficient for nitrogen dioxide will be _____.
I2(s) + HNO3(aq) HIO3(aq) + NO2(g) + H2O(l)
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 10
E) none of the above
I2(s) + HNO3(aq) HIO3(aq) + NO2(g) + H2O(l)
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 10
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the reaction CuO(s) + H2(g) Cu(s) + H2O(l)
In this reaction, which substances are the oxidant and reductant, respectively?
A) CuO and H2
B) H2 and CuO
C) CuO and Cu
D) H2O and H2
E) none of the above
In this reaction, which substances are the oxidant and reductant, respectively?
A) CuO and H2
B) H2 and CuO
C) CuO and Cu
D) H2O and H2
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Consider the following redox equation Mn(OH)2(s) + MnO4-(aq) MnO42-(aq) (basic solution)
When the equation is balanced with smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient for OH-(aq) and on which side of the equation is OH-(aq) present?
A) 4, reactant side
B) 4, product side
C) 6, reactant side
D) 6, product side
E) none of the above
When the equation is balanced with smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient for OH-(aq) and on which side of the equation is OH-(aq) present?
A) 4, reactant side
B) 4, product side
C) 6, reactant side
D) 6, product side
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A voltaic cell prepared using zinc and iodine has the following cell notation.
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || I-(aq) | I2(s) | C(graphite)
Which of the following equations correctly represents the balanced, spontaneous, cell reaction?
A) 2I-(aq) + Zn2+(aq) I2(s) + Zn(s)
B) I2(s) + Zn(s) 2I-(aq) + Zn2+(aq)
C) 2I-(aq) + Zn(s) I2(s) + Zn2+(aq)
D) I2(s) + Zn2+(aq) 2I-(aq) + Zn(s)
E) None of the above, since graphite must be in the equation.
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || I-(aq) | I2(s) | C(graphite)
Which of the following equations correctly represents the balanced, spontaneous, cell reaction?
A) 2I-(aq) + Zn2+(aq) I2(s) + Zn(s)
B) I2(s) + Zn(s) 2I-(aq) + Zn2+(aq)
C) 2I-(aq) + Zn(s) I2(s) + Zn2+(aq)
D) I2(s) + Zn2+(aq) 2I-(aq) + Zn(s)
E) None of the above, since graphite must be in the equation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which one of the following statements about electrochemical cells is correct?
A) In a salt bridge, current is carried by cations moving toward the anode, and anions toward the cathode.
B) In the external wire, electrons travel from cathode to anode.
C) The anode of a voltaic cell is labeled minus (-).
D) Oxidation occurs at the cathode, in an electrolytic cell.
E) None of the above statements is correct.
A) In a salt bridge, current is carried by cations moving toward the anode, and anions toward the cathode.
B) In the external wire, electrons travel from cathode to anode.
C) The anode of a voltaic cell is labeled minus (-).
D) Oxidation occurs at the cathode, in an electrolytic cell.
E) None of the above statements is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A voltaic cell prepared using aluminum and nickel has the following cell notation.
Al(s) | Al3+(aq) || Ni2+(aq) | Ni(s)
Which of the following represents the correctly balanced spontaneous reaction equation for the cell?
A) Ni2+(aq) + Al(s) Al3+(aq) + Ni(s)
B) 3Ni2+(aq) + 2Al(s) 2Al3+(aq) + 3Ni(s)
C) Ni(s) + Al3+(aq) Ni2+(aq) + Al(s)
D) 3Ni(s) + 2Al3+(aq) 3Ni2+(aq) + 2Al(s)
E) none of the above
Al(s) | Al3+(aq) || Ni2+(aq) | Ni(s)
Which of the following represents the correctly balanced spontaneous reaction equation for the cell?
A) Ni2+(aq) + Al(s) Al3+(aq) + Ni(s)
B) 3Ni2+(aq) + 2Al(s) 2Al3+(aq) + 3Ni(s)
C) Ni(s) + Al3+(aq) Ni2+(aq) + Al(s)
D) 3Ni(s) + 2Al3+(aq) 3Ni2+(aq) + 2Al(s)
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements about voltaic and electrolytic cells is correct?
A) The anode will definitely gain weight in a voltaic cell.
B) Oxidation occurs at the cathode of both cells.
C) The free energy change, G, is negative for the voltaic cell.
D) The electrons in the external wire flow from cathode to anode in an electrolytic cell.
E) None of the above statements is correct.
A) The anode will definitely gain weight in a voltaic cell.
B) Oxidation occurs at the cathode of both cells.
C) The free energy change, G, is negative for the voltaic cell.
D) The electrons in the external wire flow from cathode to anode in an electrolytic cell.
E) None of the above statements is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A voltaic cell is prepared using copper and silver. Its cell notation is shown below.
Cu(s) | Cu2+(aq) || Ag+(aq) | Ag(s)
Which of the following processes occurs at the cathode?
A) Cu(s) Cu2+(aq) + 2e-
B) Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Cu(s)
C) Ag(s) Ag+(aq) + e-
D) Ag+(aq) + e- Ag(s)
E) Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Cu(s) | Cu2+(aq) || Ag+(aq) | Ag(s)
Which of the following processes occurs at the cathode?
A) Cu(s) Cu2+(aq) + 2e-
B) Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Cu(s)
C) Ag(s) Ag+(aq) + e-
D) Ag+(aq) + e- Ag(s)
E) Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which one of the following is not a redox reaction?
A) Al(OH)4-(aq) + 4H+(aq) Al3+(aq) + 4H2O(l)
B) C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
C) Na6FeCl8(s) + 2Na(l) 8NaCl(s) + Fe(s)
D) 2H2O2(aq) 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
E) CO2(g) + H2(g) CO(g) + H2O(g)
A) Al(OH)4-(aq) + 4H+(aq) Al3+(aq) + 4H2O(l)
B) C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
C) Na6FeCl8(s) + 2Na(l) 8NaCl(s) + Fe(s)
D) 2H2O2(aq) 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
E) CO2(g) + H2(g) CO(g) + H2O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following solids is commonly used as an inactive electrode in electrochemical cells?
A) zinc
B) graphite
C) copper
D) iron
E) sodium
A) zinc
B) graphite
C) copper
D) iron
E) sodium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which one of the following pairs of substances could be used to construct a single redox electrode (i.e., they have an element in common, but in different oxidation states)?
A) HCl and Cl-
B) H+ and OH-
C) H2O and H+
D) Fe3+ and Fe2O3
E) MnO2 and Mn2+
A) HCl and Cl-
B) H+ and OH-
C) H2O and H+
D) Fe3+ and Fe2O3
E) MnO2 and Mn2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A voltaic cell prepared using aluminum and nickel has the following cell notation.
Al(s) | Al3+(aq) || Ni2+(aq) | Ni(s)
Which of the following reactions occurs at the anode?
A) Al(s) Al3+(aq) + 3e-
B) Al3+(aq) + 3e Al(s)
C) Ni(s) Ni2+(aq) + 2e-
D) Ni2+(aq) + 2e- Ni(s)
E) none of the above
Al(s) | Al3+(aq) || Ni2+(aq) | Ni(s)
Which of the following reactions occurs at the anode?
A) Al(s) Al3+(aq) + 3e-
B) Al3+(aq) + 3e Al(s)
C) Ni(s) Ni2+(aq) + 2e-
D) Ni2+(aq) + 2e- Ni(s)
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When the following redox equation is balanced with smallest whole number coefficients, the coefficient for Sn(OH)3- will be _____.
Bi(OH)3(s) + Sn(OH)3-(aq) Sn(OH)62-(aq) + Bi(s) (basic solution)
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
E) none of the above
Bi(OH)3(s) + Sn(OH)3-(aq) Sn(OH)62-(aq) + Bi(s) (basic solution)
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Examine the following half-reactions and select the strongest oxidizing agent among the species listed.
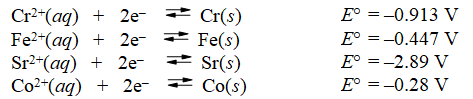
A) Cr2+(aq)
B) Fe(s)
C) Fe2+(aq)
D) Sr2+(aq)
E) Co2+(aq)
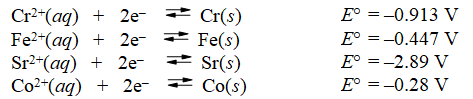
A) Cr2+(aq)
B) Fe(s)
C) Fe2+(aq)
D) Sr2+(aq)
E) Co2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The voltaic cell made up of cobalt, copper, and their M2+ ions, has E°cell = 0.62 V. If E° of the cathode half-cell is 0.34 V, what is E° of the anode half-cell?
Cu2+(aq) + Co(s) Cu(s) + Co2+(aq)
A) -0.28 V
B) -0.96 V
C) 0.28 V
D) 0.96 V
E) none of the above
Cu2+(aq) + Co(s) Cu(s) + Co2+(aq)
A) -0.28 V
B) -0.96 V
C) 0.28 V
D) 0.96 V
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the cell reaction below at 25°C? E°cell = 0.30 V Sn2+(aq) + Fe(s)  Sn(s) + Fe2+(aq)
Sn(s) + Fe2+(aq)
A) 1.2 × 105
B) 1.4 × 1010
C) 8.6 × 10-6
D) 7.1 × 10-11
E) 2.3 × 1023
 Sn(s) + Fe2+(aq)
Sn(s) + Fe2+(aq)A) 1.2 × 105
B) 1.4 × 1010
C) 8.6 × 10-6
D) 7.1 × 10-11
E) 2.3 × 1023

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Examine the following half-reactions and select the strongest oxidizing agent among the substances. ![<strong>Examine the following half-reactions and select the strongest oxidizing agent among the substances. </strong> A) [PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq) B) RuO<sub>4</sub>(s) C) HFeO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq) D) H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq) E) Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5833/11ec6d56_4024_79af_9cd1_139ef627c0ec_TB5833_11.jpg)
A) [PtCl4]2-(aq)
B) RuO4(s)
C) HFeO4- (aq)
D) H4XeO6(aq)
E) Cl-(aq)
![<strong>Examine the following half-reactions and select the strongest oxidizing agent among the substances. </strong> A) [PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq) B) RuO<sub>4</sub>(s) C) HFeO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq) D) H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq) E) Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5833/11ec6d56_4024_79af_9cd1_139ef627c0ec_TB5833_11.jpg)
A) [PtCl4]2-(aq)
B) RuO4(s)
C) HFeO4- (aq)
D) H4XeO6(aq)
E) Cl-(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The line notation, Pt | H2(g) | H+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s), indicates that
A) copper metal is a product of the cell reaction.
B) hydrogen gas (H2) is a product of the cell reaction.
C) Cu is the anode.
D) Pt is the cathode.
E) Cu2+ is the reducing agent.
A) copper metal is a product of the cell reaction.
B) hydrogen gas (H2) is a product of the cell reaction.
C) Cu is the anode.
D) Pt is the cathode.
E) Cu2+ is the reducing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following conditions is most likely to apply to a fully-charged secondary cell?
A) Ecell = E°cell
B) E°cell = 0
C) Q = 1
D) Q < K
E) Q = K
A) Ecell = E°cell
B) E°cell = 0
C) Q = 1
D) Q < K
E) Q = K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A voltaic cell has a standard cell potential equal to 0.74 V. If the standard electrode (reduction) potential for the anode is - 0.22 V, what is the standard electrode potential for the cathode?
A) 0.96 V
B) 0.52 V
C) -0.52 V
D) -0.96 V
E) Need to know the cell reaction in order to calculate the answer.
A) 0.96 V
B) 0.52 V
C) -0.52 V
D) -0.96 V
E) Need to know the cell reaction in order to calculate the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A battery is considered "dead" when
A) Q < 1.
B) Q = 1.
C) Q > 1.
D) Q = K.
E) Q/K = 0.
A) Q < 1.
B) Q = 1.
C) Q > 1.
D) Q = K.
E) Q/K = 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A cell can be prepared from copper and tin. What is the E°cell for the cell that forms from the following half-reactions?
Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Cu(s) E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s) E° = 0.34 V
Sn4+(aq) + 2e- Sn2+(aq) E° = 0.13 V
Sn2+(aq) E° = 0.13 V
A) 0.47 V
B) 0.21 V
C) -0.21 V
D) -0.47 V
E) 0.42 V
Cu2+(aq) + 2e-
 Cu(s) E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s) E° = 0.34 VSn4+(aq) + 2e-
 Sn2+(aq) E° = 0.13 V
Sn2+(aq) E° = 0.13 VA) 0.47 V
B) 0.21 V
C) -0.21 V
D) -0.47 V
E) 0.42 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the E°cell for the cell represented by the combination of the following half-reactions? 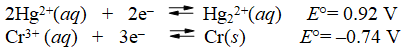
A) -0.18 V
B) 0.18 V
C) 1.28 V
D) 1.66 V
E) 2.12 V
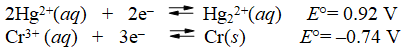
A) -0.18 V
B) 0.18 V
C) 1.28 V
D) 1.66 V
E) 2.12 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the E°cell for the cell represented by the combination of the following half-reactions? ClO4-(aq) + 8H+(aq) + 8e-  Cl-(aq) + 4H2O(l) E° = 1.389 V
Cl-(aq) + 4H2O(l) E° = 1.389 V
VO2+(aq) + 2H+(aq) + e- VO+(aq) + H2O(l) E° = 0.991 V
VO+(aq) + H2O(l) E° = 0.991 V
A) -0.398 V
B) -2.380 V
C) 0.398 V
D) 2.380 V
E) none of the above
 Cl-(aq) + 4H2O(l) E° = 1.389 V
Cl-(aq) + 4H2O(l) E° = 1.389 VVO2+(aq) + 2H+(aq) + e-
 VO+(aq) + H2O(l) E° = 0.991 V
VO+(aq) + H2O(l) E° = 0.991 VA) -0.398 V
B) -2.380 V
C) 0.398 V
D) 2.380 V
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Calculate E°cell and indicate whether the overall reaction shown is spontaneous or nonspontaneous.
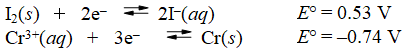
reaction: 2Cr(s) + 3I2(s) 2Cr3+(aq) + (aq) + 6I-(aq)
A) E°cell = -1.27 V, spontaneous
B) E°cell = -1.27 V, nonspontaneous
C) E°cell = 1.27 V, spontaneous
D) E°cell = 1.27 V, nonspontaneous
E) E°cell = 1.54 V, spontaneous
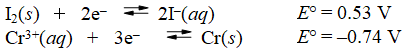
reaction: 2Cr(s) + 3I2(s) 2Cr3+(aq) + (aq) + 6I-(aq)
A) E°cell = -1.27 V, spontaneous
B) E°cell = -1.27 V, nonspontaneous
C) E°cell = 1.27 V, spontaneous
D) E°cell = 1.27 V, nonspontaneous
E) E°cell = 1.54 V, spontaneous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Examine the following half-reactions and select the weakest oxidizing agent among the species listed.
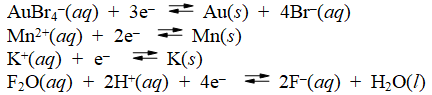
A) AuBr4-(aq)
B) Mn2+(aq)
C) K+(aq)
D) F2O(aq)
E) H+(aq)
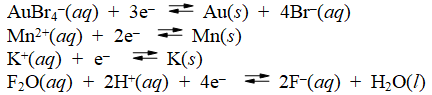
A) AuBr4-(aq)
B) Mn2+(aq)
C) K+(aq)
D) F2O(aq)
E) H+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Calculate E°cell and indicate whether the overall reaction shown is spontaneous or nonspontaneous.
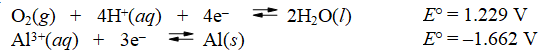
Overall reaction: 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) + 12H+(aq) 4Al3+(aq) + 6H2O(l)
A) E°cell = -2.891 V, nonspontaneous
B) E°cell = -2.891 V, spontaneous
C) E°cell = 2.891 V, nonspontaneous
D) E°cell = 2.891 V, spontaneous
E) Spontaneous, but none of the above values of E°cell is correct.
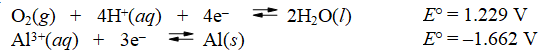
Overall reaction: 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) + 12H+(aq) 4Al3+(aq) + 6H2O(l)
A) E°cell = -2.891 V, nonspontaneous
B) E°cell = -2.891 V, spontaneous
C) E°cell = 2.891 V, nonspontaneous
D) E°cell = 2.891 V, spontaneous
E) Spontaneous, but none of the above values of E°cell is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When metal A is placed in a solution of metal ions B2+, a reaction occurs between A and B2+, and metal ions A2+ appear in the solution. When metal B is placed in acid solution, gas bubbles form on its surface. When metal A is placed in a solution of metal ions C2+, no reaction occurs. Which of the following reactions would not occur spontaneously?
A) C(s) + 2H+(aq) H2(g) + C2+(aq)
B) C(s) + A2+(aq) A(s) + C2+(aq)
C) B(s) + C2+(aq) C(s) + B2+(aq)
D) A(s) + 2H+(aq) H2(g) + A2+(aq)
E) B(s) + 2H+(aq) H2(g) + B2+(aq)
A) C(s) + 2H+(aq) H2(g) + C2+(aq)
B) C(s) + A2+(aq) A(s) + C2+(aq)
C) B(s) + C2+(aq) C(s) + B2+(aq)
D) A(s) + 2H+(aq) H2(g) + A2+(aq)
E) B(s) + 2H+(aq) H2(g) + B2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The redox reaction of peroxydisulfate with iodide has been used for many years as part of the iodine clock reaction which introduces students to kinetics. If E°cell = 1.587 V and E° of the cathode half-cell is 0.536 V, what is E° of the anode half-cell?
S2O82-(aq) + 2H+ + 2I-(aq) 2HSO4-(aq) + I2(aq)
A) -1.051 V
B) -2.123 V
C) 1.051 V
D) 2.123 V
E) none of the above
S2O82-(aq) + 2H+ + 2I-(aq) 2HSO4-(aq) + I2(aq)
A) -1.051 V
B) -2.123 V
C) 1.051 V
D) 2.123 V
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Examine the following half-reactions and select the strongest reducing agent among the species listed.
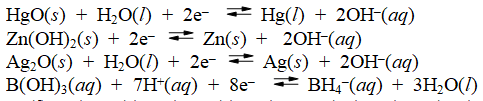
A) Hg(l)
B) Zn(s)
C) Ag(s)
D) BH4-(aq)
E) Zn(OH)2(s)
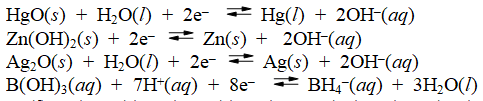
A) Hg(l)
B) Zn(s)
C) Ag(s)
D) BH4-(aq)
E) Zn(OH)2(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The line notation, Al(s) | Al3+(aq) || Co2+(aq) | Co(s), indicates that
A) Co is the reducing agent.
B) Co2+ ions are oxidized.
C) Al is the reducing agent.
D) Al3+ is the reducing agent.
E) aluminum metal is the cathode.
A) Co is the reducing agent.
B) Co2+ ions are oxidized.
C) Al is the reducing agent.
D) Al3+ is the reducing agent.
E) aluminum metal is the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Calculate the potential of a voltaic cell (E°cell) if it is required to do 5.43 × 10-3 kJ of work when a charge of 2.50 C is transferred.
A) 2.17 × 103 V
B) 2.17 × 10-3 V
C) 2.17 V
D) 13.6 V
E) 1.36 × 10-2 V
A) 2.17 × 103 V
B) 2.17 × 10-3 V
C) 2.17 V
D) 13.6 V
E) 1.36 × 10-2 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Given that E° for X + e- F Y is greater than E° for A + 2e- B, it is correct to say that, under standard conditions
A) X will oxidize A.
B) Y will oxidize A.
C) Y will reduce A.
D) B will oxidize X.
E) B will reduce X.
A) X will oxidize A.
B) Y will oxidize A.
C) Y will reduce A.
D) B will oxidize X.
E) B will reduce X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider the reaction of iodine with manganese dioxide
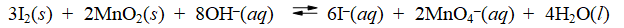
The equilibrium constant for the overall reaction is 8.30 × 10-7. Calculate G° for the reaction at 25°C.
A) -15.1 kJ
B) -34.7 kJ
C) 15.1 kJ
D) 34.7 kJ
E) none of the above
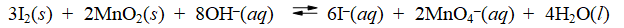
The equilibrium constant for the overall reaction is 8.30 × 10-7. Calculate G° for the reaction at 25°C.
A) -15.1 kJ
B) -34.7 kJ
C) 15.1 kJ
D) 34.7 kJ
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction of nickel(II) ions with cadmium metal is 1.17 × 105. Calculate G° for the reaction at 25°C.
A) -12.6 kJ
B) -28.9 kJ
C) 12.6 kJ
D) 28.9 kJ
E) none of the above
A) -12.6 kJ
B) -28.9 kJ
C) 12.6 kJ
D) 28.9 kJ
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A voltaic cell consists of an Au/Au3+ electrode (E° = 1.50 V) and a Cu/Cu2+ electrode (E° = 0.34 V). Calculate [Au3+] if [Cu2+] = 1.20 M and Ecell = 1.13 V at 25°C.
A) 0.001 M
B) 0.002 M
C) 0.01 M
D) 0.02 M
E) 0.04 M
A) 0.001 M
B) 0.002 M
C) 0.01 M
D) 0.02 M
E) 0.04 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Calculate E°cell for the reaction of nickel(II) ions with cadmium metal at 25°C. K = 1.17 × 105
Ni2+(aq) + Cd(s) Cd2+(aq) + Ni(s)
A) 0.075 V
B) 0.10 V
C) 0.12 V
D) 0.15 V
E) 0.30 V
Ni2+(aq) + Cd(s) Cd2+(aq) + Ni(s)
A) 0.075 V
B) 0.10 V
C) 0.12 V
D) 0.15 V
E) 0.30 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which, if any, of the following metals would be capable of acting as a sacrificial anode when used with iron pipe? E°Fe = -0.44 V; all E° values refer to the M2+/M half-cell reactions.
A) copper, Cu, E° = 0.15 V
B) cobalt, Co, E° = -0.28 V
C) chromium, Cr, E° = -0.74 V
D) tin, Sn, E° = -0.14 V
E) None of these metals would be capable of acting as a sacrificial anode with iron.
A) copper, Cu, E° = 0.15 V
B) cobalt, Co, E° = -0.28 V
C) chromium, Cr, E° = -0.74 V
D) tin, Sn, E° = -0.14 V
E) None of these metals would be capable of acting as a sacrificial anode with iron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which, if any, of the following metals would not be capable of acting as a sacrificial anode when used with iron E°Fe = -0.44 V; all E° values refer to the M2+/M half-cell reactions.
A) manganese, Mn, E° = -1.18 V
B) cadmium, Cd, E° = -0.40 V
C) magnesium, Mg, E° = -2.37 V
D) zinc, Zn, E° = -0.76 V
E) All of these metals are capable of acting as sacrificial anodes with iron.
A) manganese, Mn, E° = -1.18 V
B) cadmium, Cd, E° = -0.40 V
C) magnesium, Mg, E° = -2.37 V
D) zinc, Zn, E° = -0.76 V
E) All of these metals are capable of acting as sacrificial anodes with iron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which one of the following statements relating to the glass electrode is correct?
A) The glass electrode detects hydrogen gas.
B) The glass of a glass electrode serves to conduct electrons.
C) When pH is measured, only a single electrode, the glass electrode, need be used.
D) The potential of the glass electrode varies linearly with the pH of the solution.
E) None of the above statements is correct.
A) The glass electrode detects hydrogen gas.
B) The glass of a glass electrode serves to conduct electrons.
C) When pH is measured, only a single electrode, the glass electrode, need be used.
D) The potential of the glass electrode varies linearly with the pH of the solution.
E) None of the above statements is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A concentration cell consists of two Al/Al3+electrodes. The electrolyte in compartment A is 0.050 M Al(NO3)3 and in compartment B is 1.25 M Al(NO3)3. What is the voltage of the cell at 25°C?
A) 0.083 V
B) 0.062 V
C) 0.041V
D) 0.028 V
E) none of the above
A) 0.083 V
B) 0.062 V
C) 0.041V
D) 0.028 V
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A voltaic cell consists of a Hg/Hg22+ electrode (E° = 0.85 V) and a Sn/Sn2+ electrode (E° = -0.14 V). Calculate [Sn2+] if [Hg22+] = 0.24 M and Ecell = 1.04 V at 25°C.
A) 0.0001 M
B) 0.0007 M
C) 0.005 M
D) 0.03 M
E) 0.05 M
A) 0.0001 M
B) 0.0007 M
C) 0.005 M
D) 0.03 M
E) 0.05 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A voltaic cell consists of a Ag/Ag+ electrode (E° = 0.80 V) and a Fe2+/Fe3+ electrode (E° = 0.77 V) with the following initial molar concentrations: [Fe2+] = 0.30 M;
[Fe3+] = 0.10 M; [Ag+] = 0.30 M. What is the equilibrium concentration of Fe3+? (Assume the anode and cathode solutions are of equal volume, and a temperature of 25°C.)
A) 0.030 M
B) 0.043 M
C) 0.085 M
D) 0.11 M
E) 0.17 M
[Fe3+] = 0.10 M; [Ag+] = 0.30 M. What is the equilibrium concentration of Fe3+? (Assume the anode and cathode solutions are of equal volume, and a temperature of 25°C.)
A) 0.030 M
B) 0.043 M
C) 0.085 M
D) 0.11 M
E) 0.17 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The following half-reactions occur in the mercury battery used in calculators. If E°cell = 1.357 V, calculate the equilibrium constant for the cell reaction at 25°C. (Assume the stoichiometric coefficients in the cell reaction are all equal to 1.) HgO(s) + H2O(l) + 2e-  Hg(l) + 2OH-(aq)
Hg(l) + 2OH-(aq)
ZnO(s) + H2O(l) + 2e- Zn(s) + 2OH-(aq)
Zn(s) + 2OH-(aq)
A) 9.4 × 1022
B) 7.5 × 1045
C) 6.4 × 1063
D) 7.8 × 1091
E) > 9.9 × 1099
 Hg(l) + 2OH-(aq)
Hg(l) + 2OH-(aq)ZnO(s) + H2O(l) + 2e-
 Zn(s) + 2OH-(aq)
Zn(s) + 2OH-(aq)A) 9.4 × 1022
B) 7.5 × 1045
C) 6.4 × 1063
D) 7.8 × 1091
E) > 9.9 × 1099

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A voltaic cell consists of a Mn/Mn2+ electrode (E° = -1.18 V) and a Fe/Fe2+ electrode (E° = -0.44 V). Calculate [Fe2+] if [Mn2+] = 0.050 M and Ecell = 0.78 V at 25°C.
A) 0.040 M
B) 0.24 M
C) 1.1 M
D) 1.8 M
E) none of the above
A) 0.040 M
B) 0.24 M
C) 1.1 M
D) 1.8 M
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A voltaic cell consists of a Cd/Cd2+ electrode (E° = -0.40 V) and a Fe/Fe2+ electrode (E° = -0.44 V). If Ecell = 0 and the temperature is 25°C, what is the ratio [Fe2+]/[Cd2+]?
A) 2 × 101
B) 1 × 101
C) 1
D) 1 × 10-1
E) 5 × 10-2
A) 2 × 101
B) 1 × 101
C) 1
D) 1 × 10-1
E) 5 × 10-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A battery that cannot be recharged is a
A) fuel cell.
B) primary battery.
C) secondary battery.
D) simple battery.
E) flow battery.
A) fuel cell.
B) primary battery.
C) secondary battery.
D) simple battery.
E) flow battery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the cell reaction below at 25°C? E°cell = 0.61 V 2Cr(s) + 3Pb2+(aq)  3Pb(s) + 2Cr3+(aq)
3Pb(s) + 2Cr3+(aq)
A) 4.1 × 1020
B) 8.2 × 1030
C) 3.3 × 1051
D) 7.4 × 1061
E) > 9.9 × 1099
 3Pb(s) + 2Cr3+(aq)
3Pb(s) + 2Cr3+(aq)A) 4.1 × 1020
B) 8.2 × 1030
C) 3.3 × 1051
D) 7.4 × 1061
E) > 9.9 × 1099

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Consider the non-aqueous cell reaction 2Na(l) + FeCl2(s)  2NaCl(s) + Fe(s)
2NaCl(s) + Fe(s)
For which E°cell = 2.35 V at 200°C. G° at this temperature is
A) 453 kJ.
B) -453 kJ.
C) 907 kJ.
D) -907 kJ.
E) none of the above.
 2NaCl(s) + Fe(s)
2NaCl(s) + Fe(s)For which E°cell = 2.35 V at 200°C. G° at this temperature is
A) 453 kJ.
B) -453 kJ.
C) 907 kJ.
D) -907 kJ.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The value of E°cell for the reaction 2Cr3+(aq) + 6Hg(l) 2Cr(s) + 3Hg22+(aq)
Is 1.59 V. Calculate G° for the reaction.
A) -921 kJ
B) -767 kJ
C) -460 kJ
D) -307 kJ
E) none of the above
Is 1.59 V. Calculate G° for the reaction.
A) -921 kJ
B) -767 kJ
C) -460 kJ
D) -307 kJ
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider the reaction in the lead-acid cell
Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) 2PbSO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
For which E°cell = 2.04 V at 298 K. G° for this reaction is
A) -3.94 × 105 kJ.
B) -3.94 × 102 kJ.
C) -1.97 × 105 kJ.
D) -7.87 × 102 kJ.
E) none of the above.
Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) 2PbSO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
For which E°cell = 2.04 V at 298 K. G° for this reaction is
A) -3.94 × 105 kJ.
B) -3.94 × 102 kJ.
C) -1.97 × 105 kJ.
D) -7.87 × 102 kJ.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A concentration cell consists of two Zn/Zn2+ electrodes. The electrolyte in compartment A is 0.10 M Zn(NO3)2 and in compartment B is 0.60 M Zn(NO3)2. What is the voltage of the cell at 25°C?
A) 0.010 V
B) 0.020 V
C) 0.023 V
D) 0.046 V
E) none of the above
A) 0.010 V
B) 0.020 V
C) 0.023 V
D) 0.046 V
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider the reaction of iodine with manganese dioxide 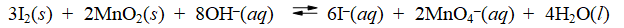
The equilibrium constant for the overall reaction is 8.30 × 10-7. Calculate E°cell for the reaction at 25°C.
A) -0.36 V
B) -0.18 V
C) -0.12 V
D) -0.060 V
E) none of the above
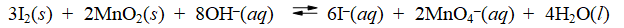
The equilibrium constant for the overall reaction is 8.30 × 10-7. Calculate E°cell for the reaction at 25°C.
A) -0.36 V
B) -0.18 V
C) -0.12 V
D) -0.060 V
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the electrolysis of aqueous sodium sulfate at electrodes of platinum, predict the products of the cell reaction.
A) sodium and sulfur
B) hydrogen and sulfur
C) oxygen and sulfur
D) oxygen and sulfuric acid
E) hydrogen and oxygen
A) sodium and sulfur
B) hydrogen and sulfur
C) oxygen and sulfur
D) oxygen and sulfuric acid
E) hydrogen and oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following elements can be isolated by electrolysis of the aqueous salt shown?
A) phosphorus from K3PO4(aq)
B) sodium from NaBr(aq)
C) aluminum from AlCl3(aq)
D) fluorine from KF(aq)
E) iodine from NaI(aq)
A) phosphorus from K3PO4(aq)
B) sodium from NaBr(aq)
C) aluminum from AlCl3(aq)
D) fluorine from KF(aq)
E) iodine from NaI(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A solution is prepared by dissolving 32.0 g of NiSO4 in water. What current would be needed to deposit all of the nickel in 5.0 hours?
A) 1.1 A
B) 2.2 A
C) 3.3 A
D) 4.4 A
E) 5.5 A
A) 1.1 A
B) 2.2 A
C) 3.3 A
D) 4.4 A
E) 5.5 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following elements could be prepared by electrolysis of the aqueous solution shown?
A) sodium from Na3PO4(aq)
B) sulfur from K2SO4(aq)
C) oxygen from H2SO4(aq)
D) potassium from KCl(aq)
E) nitrogen from AgNO3(aq)
A) sodium from Na3PO4(aq)
B) sulfur from K2SO4(aq)
C) oxygen from H2SO4(aq)
D) potassium from KCl(aq)
E) nitrogen from AgNO3(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What product forms at the cathode during the electrolysis of molten lithium iodide?
A) Li+(l)
B) Li(l)
C) I-(l)
D) I2(g)
E) I3-(l)
A) Li+(l)
B) Li(l)
C) I-(l)
D) I2(g)
E) I3-(l)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Predict the products of the cell reaction when a molten salt mixture of sodium bromide and calcium fluoride is electrolyzed (spectator ions are not considered to be products).
A) calcium and bromine
B) sodium and fluorine
C) calcium bromide
D) calcium and fluorine
E) sodium and bromine
A) calcium and bromine
B) sodium and fluorine
C) calcium bromide
D) calcium and fluorine
E) sodium and bromine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A galvanic cell is constructed using the two hypothetical half-reactions 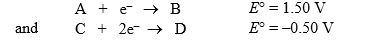 a. Write down the balanced equation representing the cell reaction.
a. Write down the balanced equation representing the cell reaction.
b. Calculate the standard potential of this cell, E°cell.
c. Calculate G° for the cell reaction.
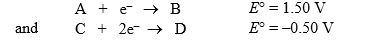 a. Write down the balanced equation representing the cell reaction.
a. Write down the balanced equation representing the cell reaction.b. Calculate the standard potential of this cell, E°cell.
c. Calculate G° for the cell reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What mass of silver will be formed when 15.0 A are passed through molten AgCl for 25.0 minutes?
A) 0.419 g
B) 6.29 g
C) 12.6 g
D) 25.2 g
E) 33.4 g
A) 0.419 g
B) 6.29 g
C) 12.6 g
D) 25.2 g
E) 33.4 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A concentration cell is based on the aqueous reaction
Cu2+(1.00 M) Cu2+(0.0100 M)
The cell consists of copper electrodes dipping into solutions of Cu2+ ions. The anions present are sulfate ions. Write the shorthand cell notation for this cell.
Cu2+(1.00 M) Cu2+(0.0100 M)
The cell consists of copper electrodes dipping into solutions of Cu2+ ions. The anions present are sulfate ions. Write the shorthand cell notation for this cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How many grams of oxygen gas will be produced in the electrolysis of water, for every gram of hydrogen gas formed? Reaction: 2H2O(l) 2H2(g) + O2(g)
A) 31.7 g
B) 15.9 g
C) 7.94 g
D) 3.97 g
E) 1.98 g
A) 31.7 g
B) 15.9 g
C) 7.94 g
D) 3.97 g
E) 1.98 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What mass of copper will be deposited when 18.2 A are passed through a CuSO4 solution for 45.0 minutes?
A) 16.2 g
B) 33.4 g
C) 40.6 g
D) 81.3 g
E) 163 g
A) 16.2 g
B) 33.4 g
C) 40.6 g
D) 81.3 g
E) 163 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Chromium metal is electroplated from acidic aqueous solutions containing the dichromate ion, Cr2O72-. What is the minimum time needed to plate out 10.0 g of chromium metal from such a solution, if the current is 50.0 A?
A) 6.2 minutes
B) 12.4 minutes
C) 18.6 minutes
D) 24.7 minute
E) 37.1 minutes
A) 6.2 minutes
B) 12.4 minutes
C) 18.6 minutes
D) 24.7 minute
E) 37.1 minutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In one or two short sentences each, explain what is meant by the following terms.
a. galvanic or voltaic cell
b. electrolytic cell
c. salt bridge
d. secondary battery or cell
e. primary battery or cell
f. glass electrode
a. galvanic or voltaic cell
b. electrolytic cell
c. salt bridge
d. secondary battery or cell
e. primary battery or cell
f. glass electrode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A concentration cell is based on the aqueous reaction
Cu2+(1.00 M) Cu2+(0.0100 M)
Calculate the potential of this cell if it operates at 25.0°C.
Cu2+(1.00 M) Cu2+(0.0100 M)
Calculate the potential of this cell if it operates at 25.0°C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Two cells are connected in series, so that the same current flows through two electrodes where the following half-reactions occur Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Cu(s) and Ag+(aq) + e- Ag(s)
For every 1.00 g of copper produced in the first process, how many grams of silver will be produced in the second one?
A) 0.294 g
B) 0.588 g
C) 0.850 g
D) 1.70 g
E) 3.40 g
For every 1.00 g of copper produced in the first process, how many grams of silver will be produced in the second one?
A) 0.294 g
B) 0.588 g
C) 0.850 g
D) 1.70 g
E) 3.40 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A concentration cell is based on the aqueous reaction
Cu2+(1.00 M) Cu2+(0.0100 M)
The cell consists of copper electrodes dipping into solutions of Cu2+ ions. The anions present are sulfate ions. Draw a neat diagram to represent this cell, showing and labeling all necessary components including: anode, cathode, electron flow, cation flow, and anion flow.
Cu2+(1.00 M) Cu2+(0.0100 M)
The cell consists of copper electrodes dipping into solutions of Cu2+ ions. The anions present are sulfate ions. Draw a neat diagram to represent this cell, showing and labeling all necessary components including: anode, cathode, electron flow, cation flow, and anion flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A much-studied cell in electrochemistry has the following cell notation:
Ag(s) | AgCl(s) | HCl(aq) | H2(g) | Pt(s)
Bearing in mind that HCl(aq) consists of H+(aq) and Cl-(aq), and that this solution is in contact with both electrodes (there is no salt bridge), write down balanced equations for
a. the anode half-reaction.
b. the cathode half-reaction.
c. the cell reaction.
Ag(s) | AgCl(s) | HCl(aq) | H2(g) | Pt(s)
Bearing in mind that HCl(aq) consists of H+(aq) and Cl-(aq), and that this solution is in contact with both electrodes (there is no salt bridge), write down balanced equations for
a. the anode half-reaction.
b. the cathode half-reaction.
c. the cell reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the electrolysis of aqueous potassium nitrate using inert electrodes, which one of the following species is oxidized?
A) potassium ion
B) nitrate ion
C) water
D) oxygen
E) hydronium ion
A) potassium ion
B) nitrate ion
C) water
D) oxygen
E) hydronium ion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What product forms at the anode during the electrolysis of molten NaBr?
A) Na+(l)
B) Na(l)
C) Br-(l)
D) Br3-(l)
E) Br2(g)
A) Na+(l)
B) Na(l)
C) Br-(l)
D) Br3-(l)
E) Br2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A current of 250. A flows for 24.0 hours at an anode where the reaction occurring is
Mn2+(aq) + 2H2O(l) MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e-
What mass of MnO2 is deposited at this anode?
A) 19.5 kg
B) 12.9 kg
C) 4.87 kg
D) 2.43 kg
E) none of the above
Mn2+(aq) + 2H2O(l) MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e-
What mass of MnO2 is deposited at this anode?
A) 19.5 kg
B) 12.9 kg
C) 4.87 kg
D) 2.43 kg
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



