Deck 24: Savings, Investment Spending
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/398
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Savings, Investment Spending
1
Which of the following is considered investment spending in macroeconomics?
A) GM builds a new plant.
B) Ryan Jones buys GM stock.
C) Ryan Jones buys GM bonds.
D) Ryan Jones buys GM stock and bonds.
A) GM builds a new plant.
B) Ryan Jones buys GM stock.
C) Ryan Jones buys GM bonds.
D) Ryan Jones buys GM stock and bonds.
GM builds a new plant.
2
Which of the following is an advantage to the recipient of foreign investment?
A) Foreigners are content to receive lower profits and interest rates than are domestic investors.
B) Foreigners don't expect to receive profits and interest as often as do domestic investors.
C) Domestic firms with foreign investors are exempt from domestic income taxes on a portion of their net income.
D) Foreign companies often bring new technology to the recipient country, and this increases productivity.
A) Foreigners are content to receive lower profits and interest rates than are domestic investors.
B) Foreigners don't expect to receive profits and interest as often as do domestic investors.
C) Domestic firms with foreign investors are exempt from domestic income taxes on a portion of their net income.
D) Foreign companies often bring new technology to the recipient country, and this increases productivity.
Foreign companies often bring new technology to the recipient country, and this increases productivity.
3
A budget surplus exists when:
A) taxes are greater than government spending.
B) taxes are less than government spending.
C) taxes are less than government spending plus investment.
D) investment is less than government spending less taxes.
A) taxes are greater than government spending.
B) taxes are less than government spending.
C) taxes are less than government spending plus investment.
D) investment is less than government spending less taxes.
taxes are greater than government spending.
4
In a simple closed economy, all investment spending must come from:
A) savings.
B) money creation.
C) debt issuance.
D) foreign borrowing.
A) savings.
B) money creation.
C) debt issuance.
D) foreign borrowing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is (are) a source (sources) of funding for private investment spending? I. savings of the owners of a family business
II) profits of a large corporation
III) borrowing
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I, II, and III
II) profits of a large corporation
III) borrowing
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: Closed Economy S = I
GDP is $12 trillion this year in a closed economy. Consumption is $8 trillion and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion.
(Scenario: Closed Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Closed Economy S = I. How much is national saving?
A) $3.5 trillion
B) $3 trillion
C) $2.5 trillion
D) $2 trillion
Scenario: Closed Economy S = I
GDP is $12 trillion this year in a closed economy. Consumption is $8 trillion and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion.
(Scenario: Closed Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Closed Economy S = I. How much is national saving?
A) $3.5 trillion
B) $3 trillion
C) $2.5 trillion
D) $2 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: Closed Economy S = I
GDP is $12 trillion this year in a closed economy. Consumption is $8 trillion and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion.
(Scenario: Closed Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Closed Economy S = I. What is the government budget balance?
A) a surplus of $1.5 trillion
B) a deficit of $1.5 trillion
C) a surplus of $0.5 trillion
D) a deficit of $0.5 trillion
Scenario: Closed Economy S = I
GDP is $12 trillion this year in a closed economy. Consumption is $8 trillion and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion.
(Scenario: Closed Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Closed Economy S = I. What is the government budget balance?
A) a surplus of $1.5 trillion
B) a deficit of $1.5 trillion
C) a surplus of $0.5 trillion
D) a deficit of $0.5 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: Closed Economy S = I
GDP is $12 trillion this year in a closed economy. Consumption is $8 trillion and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion.
(Scenario: Closed Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Closed Economy S = I. How much is private saving?
A) $4 trillion
B) $2.5 trillion
C) $3.5 trillion
D) -$0.5 trillion
Scenario: Closed Economy S = I
GDP is $12 trillion this year in a closed economy. Consumption is $8 trillion and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion.
(Scenario: Closed Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Closed Economy S = I. How much is private saving?
A) $4 trillion
B) $2.5 trillion
C) $3.5 trillion
D) -$0.5 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following do economists view as investment spending?
A) stocks
B) bonds
C) spending on physical capital
D) mutual fund investing
A) stocks
B) bonds
C) spending on physical capital
D) mutual fund investing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Private savings equals:
A) income after taxes minus consumption.
B) taxes minus government spending on goods and services.
C) the total amount of savings accounts plus stocks plus bonds owned by households.
D) income plus investment.
A) income after taxes minus consumption.
B) taxes minus government spending on goods and services.
C) the total amount of savings accounts plus stocks plus bonds owned by households.
D) income plus investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is an example of investment spending in macroeconomics?
A) The owner of a Domino's Pizza store has employed two students to deliver pizzas.
B) The manager of a Domino's Pizza store has deposited cash in the bank.
C) A Domino's Pizza store has purchased a new pizza oven.
D) The owner of the Domino's Pizza store has bought stock in Domino's.
A) The owner of a Domino's Pizza store has employed two students to deliver pizzas.
B) The manager of a Domino's Pizza store has deposited cash in the bank.
C) A Domino's Pizza store has purchased a new pizza oven.
D) The owner of the Domino's Pizza store has bought stock in Domino's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Physical capital is purchased through investment spending, which in turn is mostly financed out of:
A) taxes.
B) savings.
C) import tariffs.
D) consumption expenditure.
A) taxes.
B) savings.
C) import tariffs.
D) consumption expenditure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is (are) source(s) of funds for Facebook's investment spending? I. investors who purchase shares of stock in the company
II) borrowing from savers
A) I only
B) II only
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II
II) borrowing from savers
A) I only
B) II only
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Most physical capital, except for infrastructure, is provided by: I. governments through public education
II) investment spending by private sector firms
A) I only
B) II only
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II
II) investment spending by private sector firms
A) I only
B) II only
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The budget balance equals:
A) taxes plus government spending.
B) taxes minus government spending.
C) consumption plus investment.
D) imports minus exports.
A) taxes plus government spending.
B) taxes minus government spending.
C) consumption plus investment.
D) imports minus exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Most human capital is provided by: I. governments through public education
II) investment spending by private sector firms
A) I only
B) II only
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II
II) investment spending by private sector firms
A) I only
B) II only
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: Closed Economy S = I
GDP is $12 trillion this year in a closed economy. Consumption is $8 trillion and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion.
(Scenario: Closed Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Closed Economy S = I. How much is investment spending?
A) $3.5 trillion
B) $3 trillion
C) $2.5 trillion
D) $2 trillion
Scenario: Closed Economy S = I
GDP is $12 trillion this year in a closed economy. Consumption is $8 trillion and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion.
(Scenario: Closed Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Closed Economy S = I. How much is investment spending?
A) $3.5 trillion
B) $3 trillion
C) $2.5 trillion
D) $2 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Investment spending in macroeconomics refers to:
A) buying stocks.
B) buying newly issued shares of stock.
C) adding to physical capital.
D) adding to one's retirement account.
A) buying stocks.
B) buying newly issued shares of stock.
C) adding to physical capital.
D) adding to one's retirement account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Facebook's primary type of investment spending is the purchase of:
A) server farms, or arrays of linked computers.
B) health care for its employees.
C) stock in Yahoo and Google.
D) U.S. Treasury securities.
A) server farms, or arrays of linked computers.
B) health care for its employees.
C) stock in Yahoo and Google.
D) U.S. Treasury securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is considered to be investing in a physical asset?
A) purchasing stock in IBM
B) selling stock in IBM
C) buying a bond issued by IBM
D) buying a new factory that produces IBM handheld devices
A) purchasing stock in IBM
B) selling stock in IBM
C) buying a bond issued by IBM
D) buying a new factory that produces IBM handheld devices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The savings-investment spending identity says that savings and investment spending are:
A) always equal because private savings match government savings.
B) equal as long as there is no trade surplus or deficit.
C) always equal for the economy as a whole.
D) equal as long as there is no government budget deficit or surplus.
A) always equal because private savings match government savings.
B) equal as long as there is no trade surplus or deficit.
C) always equal for the economy as a whole.
D) equal as long as there is no government budget deficit or surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a closed economy, all investment spending must come from:
A) government.
B) national savings.
C) foreign savings.
D) government, domestic savings, and foreign savings.
A) government.
B) national savings.
C) foreign savings.
D) government, domestic savings, and foreign savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
National savings is the sum of private savings and:
A) private consumption.
B) government tax revenue.
C) the budget balance.
D) trade surplus.
A) private consumption.
B) government tax revenue.
C) the budget balance.
D) trade surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In a closed economy, national savings equals private savings:
A) minus consumption spending.
B) plus the budget balance.
C) minus investment spending.
D) minus tax receipts.
A) minus consumption spending.
B) plus the budget balance.
C) minus investment spending.
D) minus tax receipts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: Open Economy S = I
In an open economy GDP is $12 trillion this year. Consumption is $8 trillion, and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion. Exports are $1 trillion, and imports are $3 trillion.
(Scenario: Open Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Open Economy S = I. How much is national saving?
A) $4 trillion
B) $3.5 trillion
C) $2 trillion
D) $5.5 trillion
Scenario: Open Economy S = I
In an open economy GDP is $12 trillion this year. Consumption is $8 trillion, and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion. Exports are $1 trillion, and imports are $3 trillion.
(Scenario: Open Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Open Economy S = I. How much is national saving?
A) $4 trillion
B) $3.5 trillion
C) $2 trillion
D) $5.5 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
To help increase investment spending, the government can:
A) lower taxes on consumption, so that disposable income rises.
B) lower taxes on the returns from savings, so that total savings increase and the interest rate falls.
C) raise taxes on the returns from bonds while lowering taxes on stock dividends.
D) lower taxes on investment spending while raising taxes on savings, so that total tax revenue remains constant.
A) lower taxes on consumption, so that disposable income rises.
B) lower taxes on the returns from savings, so that total savings increase and the interest rate falls.
C) raise taxes on the returns from bonds while lowering taxes on stock dividends.
D) lower taxes on investment spending while raising taxes on savings, so that total tax revenue remains constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
National savings in a closed economy is all of the following EXCEPT:
A) the sum of private savings plus the government budget balance.
B) the total savings in the economy.
C) GDP - C - G.
D) government spending minus consumption.
A) the sum of private savings plus the government budget balance.
B) the total savings in the economy.
C) GDP - C - G.
D) government spending minus consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The savings-investment spending identity says that:
A) each person in the economy must invest as much as he or she saves.
B) savings and investment spending are always equal for the economy as a whole.
C) savings must equal government investment for the economy as a whole.
D) each person in the economy must save as much as he or she invests.
A) each person in the economy must invest as much as he or she saves.
B) savings and investment spending are always equal for the economy as a whole.
C) savings must equal government investment for the economy as a whole.
D) each person in the economy must save as much as he or she invests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: Open Economy S = I
In an open economy GDP is $12 trillion this year. Consumption is $8 trillion, and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion. Exports are $1 trillion, and imports are $3 trillion.
(Scenario: Open Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Open Economy S = I. What is the government budget balance?
A) a surplus of $1.5 trillion
B) a deficit of $1.5 trillion
C) a deficit of $0.5 trillion
D) a surplus of $3.5 trillion
Scenario: Open Economy S = I
In an open economy GDP is $12 trillion this year. Consumption is $8 trillion, and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion. Exports are $1 trillion, and imports are $3 trillion.
(Scenario: Open Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Open Economy S = I. What is the government budget balance?
A) a surplus of $1.5 trillion
B) a deficit of $1.5 trillion
C) a deficit of $0.5 trillion
D) a surplus of $3.5 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: Open Economy S = I
In an open economy GDP is $12 trillion this year. Consumption is $8 trillion, and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion. Exports are $1 trillion, and imports are $3 trillion.
(Scenario: Open Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Open Economy S = I. How much is the net capital inflow?
A) $1 trillion
B) $2 trillion
C) $3 trillion
D) $4 trillion
Scenario: Open Economy S = I
In an open economy GDP is $12 trillion this year. Consumption is $8 trillion, and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion. Exports are $1 trillion, and imports are $3 trillion.
(Scenario: Open Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Open Economy S = I. How much is the net capital inflow?
A) $1 trillion
B) $2 trillion
C) $3 trillion
D) $4 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In a closed economy government spending was $30 billion, consumption was $70 billion, taxes were $20 billion, and GDP was $110 billion this year. Investment spending was $10 billion. As a result:
A) private savings were $10 billion.
B) the government's budget balance was a surplus of $10 billion.
C) there was no net savings.
D) private savings were $20 billion.
A) private savings were $10 billion.
B) the government's budget balance was a surplus of $10 billion.
C) there was no net savings.
D) private savings were $20 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In a closed economy, the savings-investment spending identity is:
A) I = GDP - C - G + (IM - NX).
B) NS = GDP + I.
C) NS = GDP + (C - T + TR) + (T - TR -G).
D) I = GDP - C - G.
A) I = GDP - C - G + (IM - NX).
B) NS = GDP + I.
C) NS = GDP + (C - T + TR) + (T - TR -G).
D) I = GDP - C - G.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In an open economy, total investment equals:
A) national savings plus capital inflow.
B) private savings plus national savings plus capital inflow.
C) private savings plus capital inflow.
D) national savings minus private savings minus capital inflow.
A) national savings plus capital inflow.
B) private savings plus national savings plus capital inflow.
C) private savings plus capital inflow.
D) national savings minus private savings minus capital inflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: Open Economy S = I
In an open economy GDP is $12 trillion this year. Consumption is $8 trillion, and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion. Exports are $1 trillion, and imports are $3 trillion.
(Scenario: Open Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Open Economy S = I. How much is private saving?
A) $4 trillion
B) $2.5 trillion
C) $3.5 trillion
D) $1.5 trillion
Scenario: Open Economy S = I
In an open economy GDP is $12 trillion this year. Consumption is $8 trillion, and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion. Exports are $1 trillion, and imports are $3 trillion.
(Scenario: Open Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Open Economy S = I. How much is private saving?
A) $4 trillion
B) $2.5 trillion
C) $3.5 trillion
D) $1.5 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In a closed economy, national savings equals:
A) (disposable income minus consumption spending) minus (tax receipts minus government spending).
B) (disposable income minus consumption spending) plus (government spending minus tax receipts).
C) (disposable income minus consumption spending) plus (tax receipts minus government spending).
D) (consumption spending minus disposable income) plus (government spending minus tax receipts).
A) (disposable income minus consumption spending) minus (tax receipts minus government spending).
B) (disposable income minus consumption spending) plus (government spending minus tax receipts).
C) (disposable income minus consumption spending) plus (tax receipts minus government spending).
D) (consumption spending minus disposable income) plus (government spending minus tax receipts).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The government saves when it:
A) has a balanced budget.
B) has a budget deficit.
C) has a budget surplus.
D) borrows by selling bonds.
A) has a balanced budget.
B) has a budget deficit.
C) has a budget surplus.
D) borrows by selling bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
One difference between a closed and an open economy is that:
A) in the latter, foreign savings complement domestic savings in financing investment spending.
B) in the latter, the government is more open to the idea of financing investment spending than in the former.
C) in the former, foreign savings complement domestic savings in financing investment spending.
D) in the former, foreign savings finance more investment spending than in the latter.
A) in the latter, foreign savings complement domestic savings in financing investment spending.
B) in the latter, the government is more open to the idea of financing investment spending than in the former.
C) in the former, foreign savings complement domestic savings in financing investment spending.
D) in the former, foreign savings finance more investment spending than in the latter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
According to the savings-investment spending identity:
A) savings equals investment spending.
B) government spending equals tax receipts.
C) total income equals consumption spending plus savings.
D) savings equals investment spending plus consumption spending.
A) savings equals investment spending.
B) government spending equals tax receipts.
C) total income equals consumption spending plus savings.
D) savings equals investment spending plus consumption spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The government saves when:
A) tax revenue is less than government spending.
B) tax revenue is more than government spending.
C) tax revenue equals government spending.
D) tax revenue is positive.
A) tax revenue is less than government spending.
B) tax revenue is more than government spending.
C) tax revenue equals government spending.
D) tax revenue is positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In a closed economy, investment spending, I, must equal:
A) GDP - C - G.
B) GDP - C.
C) GDP - C - G - X.
D) GDP - [C × G].
A) GDP - C - G.
B) GDP - C.
C) GDP - C - G - X.
D) GDP - [C × G].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In an open economy, savings can come from all of the following EXCEPT:
A) domestic sources.
B) foreign sources.
C) government sources.
D) consumption.
A) domestic sources.
B) foreign sources.
C) government sources.
D) consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
National savings equals:
A) private savings plus consumption spending.
B) trade balance plus the budget balance.
C) private savings plus the budget balance.
D) government spending plus taxes.
A) private savings plus consumption spending.
B) trade balance plus the budget balance.
C) private savings plus the budget balance.
D) government spending plus taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Net capital inflow equals:
A) national savings.
B) imports minus exports.
C) consumption.
D) consumption plus government spending.
A) national savings.
B) imports minus exports.
C) consumption.
D) consumption plus government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In an open economy government spending was $30 billion, consumption was $70 billion, taxes were $20 billion, GDP was $100 billion, and investment spending was $10 billion. As a result, there was:
A) a net capital inflow of $10 billion.
B) capital inflows of $10 billion and capital outflows of $20 billion.
C) a trade surplus of $20 billion and a financial deficit of $20 billion.
D) a net capital outflow of $10 billion.
A) a net capital inflow of $10 billion.
B) capital inflows of $10 billion and capital outflows of $20 billion.
C) a trade surplus of $20 billion and a financial deficit of $20 billion.
D) a net capital outflow of $10 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the following to answer questions : 
(Table: Investment Spending, Private Spending, and Capital Inflows) Northlandia has a _____, while Southlandia has a _____.
A) balanced budget; budget deficit
B) budget deficit; balanced budget
C) budget surplus; balanced budget
D) balanced budget; balanced budget

(Table: Investment Spending, Private Spending, and Capital Inflows) Northlandia has a _____, while Southlandia has a _____.
A) balanced budget; budget deficit
B) budget deficit; balanced budget
C) budget surplus; balanced budget
D) balanced budget; balanced budget

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which statement is CORRECT?
A) The budget deficit equals tax revenues plus transfer payments.
B) Government spending equals private savings plus the budget deficit.
C) Tax revenues equal national savings plus the budget deficit.
D) The budget deficit equals government spending minus tax revenues.
A) The budget deficit equals tax revenues plus transfer payments.
B) Government spending equals private savings plus the budget deficit.
C) Tax revenues equal national savings plus the budget deficit.
D) The budget deficit equals government spending minus tax revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: A Small Economy
Suppose there is no trade and no government in a small economy. GDP is $25 trillion, and consumption spending is $18 trillion this year.
(Scenario: A Small Economy) Look at the scenario A Small Economy. There is a new government, and it imposes taxes on its citizens to spend on infrastructure. Taxes and government spending are both $2 trillion. What is the level of private saving now?
A) $11 trillion
B) $7 trillion
C) $5 trillion
D) $18 trillion
Scenario: A Small Economy
Suppose there is no trade and no government in a small economy. GDP is $25 trillion, and consumption spending is $18 trillion this year.
(Scenario: A Small Economy) Look at the scenario A Small Economy. There is a new government, and it imposes taxes on its citizens to spend on infrastructure. Taxes and government spending are both $2 trillion. What is the level of private saving now?
A) $11 trillion
B) $7 trillion
C) $5 trillion
D) $18 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: A Small Economy
Suppose there is no trade and no government in a small economy. GDP is $25 trillion, and consumption spending is $18 trillion this year.
(Scenario: A Small Economy) Look at the scenario A Small Economy. What is the level of investment spending?
A) $18 trillion
B) $7 trillion
C) $25 trillion
D) -$7 trillion
Scenario: A Small Economy
Suppose there is no trade and no government in a small economy. GDP is $25 trillion, and consumption spending is $18 trillion this year.
(Scenario: A Small Economy) Look at the scenario A Small Economy. What is the level of investment spending?
A) $18 trillion
B) $7 trillion
C) $25 trillion
D) -$7 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The budget balance equals:
A) taxes minus government spending.
B) transfers minus government spending.
C) taxes plus government spending.
D) savings plus taxes.
A) taxes minus government spending.
B) transfers minus government spending.
C) taxes plus government spending.
D) savings plus taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the following to answer questions : 
(Table: Investment Spending, Private Spending, and Capital Inflows) What is the budget balance as a percentage of GDP in Southlandia?
A) -10%
B) 0%
C) 10%
D) 20%

(Table: Investment Spending, Private Spending, and Capital Inflows) What is the budget balance as a percentage of GDP in Southlandia?
A) -10%
B) 0%
C) 10%
D) 20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If a country has a trade surplus, we can conclude that it also has:
A) a budget surplus.
B) a net capital outflow.
C) a net capital inflow.
D) a budget deficit.
A) a budget surplus.
B) a net capital outflow.
C) a net capital inflow.
D) a budget deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Capital inflow equals:
A) GDP plus exports minus imports.
B) the growth in capital stock minus investment spending.
C) foreign direct investment.
D) the total inflow of foreign funds minus the total outflow of domestic funds.
A) GDP plus exports minus imports.
B) the growth in capital stock minus investment spending.
C) foreign direct investment.
D) the total inflow of foreign funds minus the total outflow of domestic funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: Open Economy S = I
In an open economy GDP is $12 trillion this year. Consumption is $8 trillion, and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion. Exports are $1 trillion, and imports are $3 trillion.
(Scenario: Open Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Open Economy S = I. How much is investment spending?
A) $2 trillion
B) $3 trillion
C) $3.5 trillion
D) $4 trillion
Scenario: Open Economy S = I
In an open economy GDP is $12 trillion this year. Consumption is $8 trillion, and government spending is $2 trillion. Taxes are $0.5 trillion. Exports are $1 trillion, and imports are $3 trillion.
(Scenario: Open Economy S = I) Look at the scenario Open Economy S = I. How much is investment spending?
A) $2 trillion
B) $3 trillion
C) $3.5 trillion
D) $4 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Taxes equal:
A) government spending plus private savings.
B) total spending minus consumption minus investment minus private savings.
C) total income minus consumption minus private savings.
D) consumption plus private savings plus total income.
A) government spending plus private savings.
B) total spending minus consumption minus investment minus private savings.
C) total income minus consumption minus private savings.
D) consumption plus private savings plus total income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Capital inflow is:
A) the net inflow of funds into a country.
B) the net outflow of funds from a country.
C) the amount by which domestic savings exceeds foreign savings.
D) physical capital exported minus physical capital imported.
A) the net inflow of funds into a country.
B) the net outflow of funds from a country.
C) the amount by which domestic savings exceeds foreign savings.
D) physical capital exported minus physical capital imported.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Use the following to answer questions : 
(Table: Investment Spending, Private Spending, and Capital Inflows) Look at the table Investment Spending, Private Spending, and Capital Inflows. What is the budget balance as a percentage of GDP in Northlandia?
A) -10%
B) 0%
C) 10%
D) 20%

(Table: Investment Spending, Private Spending, and Capital Inflows) Look at the table Investment Spending, Private Spending, and Capital Inflows. What is the budget balance as a percentage of GDP in Northlandia?
A) -10%
B) 0%
C) 10%
D) 20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Capital inflow into a country is associated with:
A) imports exceeding exports.
B) a small amount of funds available for domestic investment.
C) imports equaling exports.
D) exports exceeding imports.
A) imports exceeding exports.
B) a small amount of funds available for domestic investment.
C) imports equaling exports.
D) exports exceeding imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Assume that I = SPrivate + SGovernment + (IM - X). Furthermore, let's say that imports are equal to exports. In this case, private savings:
A) plus government savings exceed investment.
B) exceed investment.
C) plus government saving are less than investment.
D) plus government saving are equal to investment.
A) plus government savings exceed investment.
B) exceed investment.
C) plus government saving are less than investment.
D) plus government saving are equal to investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: A Small Economy
Suppose there is no trade and no government in a small economy. GDP is $25 trillion, and consumption spending is $18 trillion this year.
(Scenario: A Small Economy) Look at the scenario A Small Economy. There is a new government and it imposes taxes on its citizens to spend on infrastructure. Taxes and government spending are both $2 trillion. What is the level of investment spending now?
A) $7 trillion
B) $5 trillion
C) $18 trillion
D) -$4 trillion
Scenario: A Small Economy
Suppose there is no trade and no government in a small economy. GDP is $25 trillion, and consumption spending is $18 trillion this year.
(Scenario: A Small Economy) Look at the scenario A Small Economy. There is a new government and it imposes taxes on its citizens to spend on infrastructure. Taxes and government spending are both $2 trillion. What is the level of investment spending now?
A) $7 trillion
B) $5 trillion
C) $18 trillion
D) -$4 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario: A Small Economy
Suppose there is no trade and no government in a small economy. GDP is $25 trillion, and consumption spending is $18 trillion this year.
(Scenario: A Small Economy) Look at the scenario A Small Economy. What is the level of private saving?
A) $7 trillion
B) $18 trillion
C) $43 trillion
D) -$7 trillion
Scenario: A Small Economy
Suppose there is no trade and no government in a small economy. GDP is $25 trillion, and consumption spending is $18 trillion this year.
(Scenario: A Small Economy) Look at the scenario A Small Economy. What is the level of private saving?
A) $7 trillion
B) $18 trillion
C) $43 trillion
D) -$7 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The government can increase savings by:
A) taxing more than it spends.
B) spending more than it taxes.
C) increasing inflation.
D) increasing the deficit.
A) taxing more than it spends.
B) spending more than it taxes.
C) increasing inflation.
D) increasing the deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer questions
Figure: Loanable Funds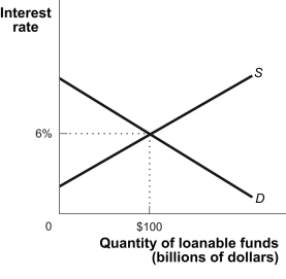
(Figure: Loanable Funds) Look at the figure Loanable Funds. Which of the following might produce a new equilibrium interest rate of 8% and a new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds of $75 billion?
A) Capital inflows from foreign citizens decline.
B) The federal government runs a budget deficit rather than a surplus.
C) Profit expectations for business investments become less optimistic.
D) The government eliminates taxes on income from interest earned.
Figure: Loanable Funds

(Figure: Loanable Funds) Look at the figure Loanable Funds. Which of the following might produce a new equilibrium interest rate of 8% and a new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds of $75 billion?
A) Capital inflows from foreign citizens decline.
B) The federal government runs a budget deficit rather than a surplus.
C) Profit expectations for business investments become less optimistic.
D) The government eliminates taxes on income from interest earned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The sources of financing of physical capital include:
A) domestic consumption.
B) foreign borrowing from the home country.
C) foreign investment in the home country.
D) domestic consumption, foreign borrowing from the home country, and foreign investment in the home country.
A) domestic consumption.
B) foreign borrowing from the home country.
C) foreign investment in the home country.
D) domestic consumption, foreign borrowing from the home country, and foreign investment in the home country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following to answer questions
Figure: Loanable Funds
(Figure: Loanable Funds) Look at the figure Loanable Funds. Which of the following might produce a new equilibrium interest rate of 8% and a new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds of $150 billion?
A) Consumption as a fraction of disposable income increases.
B) Businesses become more optimistic about the return on investment spending.
C) The federal government has a budget surplus rather than a budget deficit.
D) There is an increase in capital inflows from other nations.
Figure: Loanable Funds

(Figure: Loanable Funds) Look at the figure Loanable Funds. Which of the following might produce a new equilibrium interest rate of 8% and a new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds of $150 billion?
A) Consumption as a fraction of disposable income increases.
B) Businesses become more optimistic about the return on investment spending.
C) The federal government has a budget surplus rather than a budget deficit.
D) There is an increase in capital inflows from other nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The United States is a net recipient of foreign savings.
A) This has never happened before.
B) This is bad because we are borrowing money from overseas.
C) This is bad because we are losing control over our own destiny.
D) This has been true throughout much of our history.
A) This has never happened before.
B) This is bad because we are borrowing money from overseas.
C) This is bad because we are losing control over our own destiny.
D) This has been true throughout much of our history.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A firm does NOT want to borrow money for a project when:
A) the interest rate is higher than the rate of return on the project.
B) the interest rate is lower than the rate of return on the project.
C) the interest rate is positive.
D) the rate of return on the project is positive.
A) the interest rate is higher than the rate of return on the project.
B) the interest rate is lower than the rate of return on the project.
C) the interest rate is positive.
D) the rate of return on the project is positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following to answer question
Figure: Demand for Loanable Funds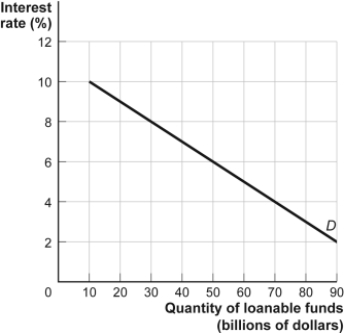
(Figure: Demand for Loanable Funds) Look at the figure Demand for Loanable Funds. When the interest rate is 6%, the quantity demanded of loanable funds will equal:
A) $30 billion.
B) $40 billion.
C) $50 billion.
D) $60 billion.
Figure: Demand for Loanable Funds

(Figure: Demand for Loanable Funds) Look at the figure Demand for Loanable Funds. When the interest rate is 6%, the quantity demanded of loanable funds will equal:
A) $30 billion.
B) $40 billion.
C) $50 billion.
D) $60 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If there is an increase in the government budget deficit, the _____ loanable funds will _____, interest rates will _____, and the amount of borrowing will _____.
A) demand for; increase; increase; increase
B) demand for; decrease; decrease; decrease
C) supply of; increase; decrease; increase
D) supply of; decrease; increase; decrease
A) demand for; increase; increase; increase
B) demand for; decrease; decrease; decrease
C) supply of; increase; decrease; increase
D) supply of; decrease; increase; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following to answer questions
Figure: Loanable Funds
(Figure: Loanable Funds) Look at the figure Loanable Funds. Which of the following might produce a new equilibrium interest rate of 4% and a new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds of $75 billion?
A) Profit expectations for business investments become less optimistic.
B) Capital inflows from foreign citizens decline.
C) The federal government runs a budget deficit rather than a surplus.
D) The government eliminates taxes on income from interest earned.
Figure: Loanable Funds

(Figure: Loanable Funds) Look at the figure Loanable Funds. Which of the following might produce a new equilibrium interest rate of 4% and a new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds of $75 billion?
A) Profit expectations for business investments become less optimistic.
B) Capital inflows from foreign citizens decline.
C) The federal government runs a budget deficit rather than a surplus.
D) The government eliminates taxes on income from interest earned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The interest rate is 5% in the market for loanable funds. Investors wish to borrow $100 million and savers wish to save $125 million at this interest rate. We would expect the interest rate to _____, as there is a _____ of loanable funds.
A) fall; shortage
B) rise; surplus
C) rise; shortage
D) fall; surplus
A) fall; shortage
B) rise; surplus
C) rise; shortage
D) fall; surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer question : 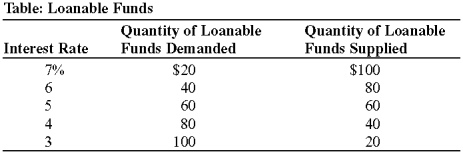
(Table: Loanable Funds) Look at the table Loanable Funds. At what interest rate will the market for loanable funds be in equilibrium?
A) 7%
B) 6%
C) 5%
D) 4%

(Table: Loanable Funds) Look at the table Loanable Funds. At what interest rate will the market for loanable funds be in equilibrium?
A) 7%
B) 6%
C) 5%
D) 4%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
According to the savings-investment spending identity:
A) savings and investment spending are always equal for the economy as a whole.
B) for long-run economic growth savings must be more than investment spending.
C) for long-run economic growth savings must be less than investment spending.
D) the identity of savers and investors is important for encouraging long-run economic growth.
A) savings and investment spending are always equal for the economy as a whole.
B) for long-run economic growth savings must be more than investment spending.
C) for long-run economic growth savings must be less than investment spending.
D) the identity of savers and investors is important for encouraging long-run economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A relatively low saving rate affects productivity growth by:
A) causing a shortage of funds for investment in physical capital.
B) decreasing consumption spending and increasing investment in human capital.
C) reducing the tax base and preventing the government from providing public goods.
D) stimulating imports and increasing the trade deficit.
A) causing a shortage of funds for investment in physical capital.
B) decreasing consumption spending and increasing investment in human capital.
C) reducing the tax base and preventing the government from providing public goods.
D) stimulating imports and increasing the trade deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Economists use _____ as a model to explain how savers and borrowers come together to determine the equilibrium rate of interest.
A) the money market
B) the market for loanable funds
C) aggregate demand and aggregate supply
D) the financial system
A) the money market
B) the market for loanable funds
C) aggregate demand and aggregate supply
D) the financial system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The demand for loanable funds is _____ sloping because _____ respond to lower interest rates by _____ their quantity demanded of loanable funds.
A) downward; investors; increasing
B) downward; savers; increasing
C) upward; investors; decreasing
D) upward; savers; decreasing
A) downward; investors; increasing
B) downward; savers; increasing
C) upward; investors; decreasing
D) upward; savers; decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The supply of loanable funds is _____ sloping because _____ respond to lower interest rates by _____ their quantity supplied of loanable funds.
A) upward; savers; increasing
B) upward; investors; decreasing
C) upward; savers; decreasing
D) downward; investors; increasing
A) upward; savers; increasing
B) upward; investors; decreasing
C) upward; savers; decreasing
D) downward; investors; increasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If private savings increase, the _____ loanable funds will _____, interest rates will _____, and the amount of borrowing will _____.
A) demand for; increase; increase; increase
B) demand for; decrease; decrease; decrease
C) supply of; increase; decrease; increase
D) supply of; decrease; increase; decrease
A) demand for; increase; increase; increase
B) demand for; decrease; decrease; decrease
C) supply of; increase; decrease; increase
D) supply of; decrease; increase; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
GDP is the value of consumption spending _____ investment spending _____ government purchases _____ the value of exports _____ spending on imports.
A) plus; plus; plus; plus
B) plus; plus; plus; minus
C) plus; minus; minus; plus
D) minus; minus; plus; plus
A) plus; plus; plus; plus
B) plus; plus; plus; minus
C) plus; minus; minus; plus
D) minus; minus; plus; plus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Use the following to answer questions
Figure: Loanable Funds
(Figure: Loanable Funds) Look at the figure Loanable Funds. Which of the following might produce a new equilibrium interest rate of 5% and a new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds of $150 billion?
A) Consumption as a fraction of disposable income increases.
B) Businesses become more optimistic about the return on investment spending.
C) The federal government has a budget surplus rather than a budget deficit.
D) There is an increase in capital inflows from other nations.
Figure: Loanable Funds

(Figure: Loanable Funds) Look at the figure Loanable Funds. Which of the following might produce a new equilibrium interest rate of 5% and a new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds of $150 billion?
A) Consumption as a fraction of disposable income increases.
B) Businesses become more optimistic about the return on investment spending.
C) The federal government has a budget surplus rather than a budget deficit.
D) There is an increase in capital inflows from other nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A business will want to borrow to undertake an investment project when the rate of return on that project is _____ rate.
A) lower than the interest
B) higher than the interest
C) higher than the exchange
D) equal to the inflation
A) lower than the interest
B) higher than the interest
C) higher than the exchange
D) equal to the inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 398 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



