Deck 6: Understanding Organic Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/43
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Understanding Organic Reactions
1
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Bond dissociation energies increase down a column of the periodic table.
B) When H° is positive, more energy is released in forming bonds than is needed to break bonds.
C) When H° is negative, more energy is needed to break bonds than is released in forming bonds.
D) Bond dissociation energies decrease down a column of the periodic table.
A) Bond dissociation energies increase down a column of the periodic table.
B) When H° is positive, more energy is released in forming bonds than is needed to break bonds.
C) When H° is negative, more energy is needed to break bonds than is released in forming bonds.
D) Bond dissociation energies decrease down a column of the periodic table.
Bond dissociation energies decrease down a column of the periodic table.
2
Which of the following statements about bond breaking is true?
A) Homolysis and heterolysis require energy.
B) In homolysis, the electrons in the bond are divided unequally.
C) In heterolysis, the electrons in the bond are divided equally.
D) Homolysis generates charged intermediates.
A) Homolysis and heterolysis require energy.
B) In homolysis, the electrons in the bond are divided unequally.
C) In heterolysis, the electrons in the bond are divided equally.
D) Homolysis generates charged intermediates.
Homolysis and heterolysis require energy.
3
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) Bond breaking is endothermic.
B) The bond dissociation energy for bond breaking is always negative.
C) Bond making is exothermic.
D) The bond dissociation energy for bond formation is always negative.
A) Bond breaking is endothermic.
B) The bond dissociation energy for bond breaking is always negative.
C) Bond making is exothermic.
D) The bond dissociation energy for bond formation is always negative.
The bond dissociation energy for bond breaking is always negative.
4
Which of the following statements about the equilibrium constant, Keq, is true?
A) When Keq > 1, the equilibrium favors the reactants.
B) When Keq < 1, the equilibrium favors the products.
C) The size of Keq tells about the position of equilibrium.
D) For a reaction to be useful, the equilibrium must favor the reactants.
A) When Keq > 1, the equilibrium favors the reactants.
B) When Keq < 1, the equilibrium favors the products.
C) The size of Keq tells about the position of equilibrium.
D) For a reaction to be useful, the equilibrium must favor the reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following expressions summarizes the correct relationship between the free energy change, G°, and the equilibrium constant, Keq?
A) Keq > 1 when G° > 0
B) Keq > 1 when G° < 0
C) Keq < 1 when G° < 0
D) Keq < 1 when G° = 0
A) Keq > 1 when G° > 0
B) Keq > 1 when G° < 0
C) Keq < 1 when G° < 0
D) Keq < 1 when G° = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Using the bond dissociation energies given, calculate H° for the following reaction.
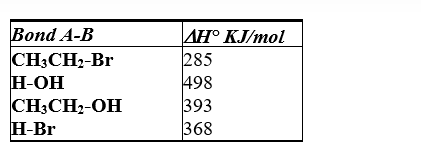
A) +108 KJ/mol
B) -130 KJ/mol
C) -22 KJ/mol
D) +22 KJ/mol

A) +108 KJ/mol
B) -130 KJ/mol
C) -22 KJ/mol
D) +22 KJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What kind of reaction does the conversion of A to B represent? 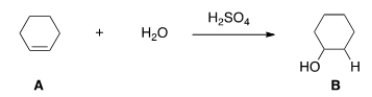
A) Acid-base reaction.
B) Elimination reaction.
C) Substitution reaction.
D) Addition reaction.

A) Acid-base reaction.
B) Elimination reaction.
C) Substitution reaction.
D) Addition reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the Keq corresponds to the lowest value of G°?
A) "Keq = 10-3"
B) "Keq = 10-2"
C) "Keq = 10-1"
D) " G° cannot be determined"
A) "Keq = 10-3"
B) "Keq = 10-2"
C) "Keq = 10-1"
D) " G° cannot be determined"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the Keq corresponds to the most negative value of G°?
A) Keq = 1
B) Keq = 101
C) Keq = 102
D) Keq = 103
A) Keq = 1
B) Keq = 101
C) Keq = 102
D) Keq = 103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Ionic intermediates are formed in radical reactions.
B) Radicals are intermediates in polar reactions.
C) Carbocations are electrophiles.
D) Radicals are nucleophiles.
A) Ionic intermediates are formed in radical reactions.
B) Radicals are intermediates in polar reactions.
C) Carbocations are electrophiles.
D) Radicals are nucleophiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Using the bond dissociation energies given, calculate H° for the following reaction. 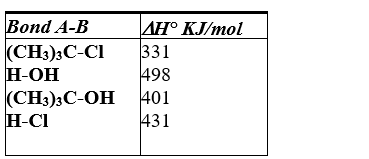
A) +3 KJ/mol
B) -3 KJ/mol
C) -67 KJ/mol
D) +70 KJ/mol

A) +3 KJ/mol
B) -3 KJ/mol
C) -67 KJ/mol
D) +70 KJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements about bond breaking is not true?
A) Homolysis generates uncharged reactive intermediates with unpaired electrons.
B) Homolysis require energy but heterolysis does not require energy.
C) Heterolysis generates charged intermediates.
D) Heterolysis involves unequal sharing of bonding electrons by atoms.
A) Homolysis generates uncharged reactive intermediates with unpaired electrons.
B) Homolysis require energy but heterolysis does not require energy.
C) Heterolysis generates charged intermediates.
D) Heterolysis involves unequal sharing of bonding electrons by atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements about addition reactions is true?
A) Two bonds are formed.
B) Two bonds are broken.
C) Two bonds are formed.
D) One bond is formed.
A) Two bonds are formed.
B) Two bonds are broken.
C) Two bonds are formed.
D) One bond is formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements about substitution reactions is true?
A) Substitution reactions involve bonds.
B) Substitution reactions involve bonds.
C) One bond breaks and another forms at a different carbon atom.
D) One bond breaks and another forms at the same carbon atom.
A) Substitution reactions involve bonds.
B) Substitution reactions involve bonds.
C) One bond breaks and another forms at a different carbon atom.
D) One bond breaks and another forms at the same carbon atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What kind of reaction does the conversion of A to B represent? 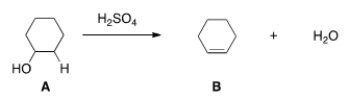
A) Addition reaction.
B) Elimination reaction.
C) Substitution reaction.
D) Oxidation-reduction reaction.

A) Addition reaction.
B) Elimination reaction.
C) Substitution reaction.
D) Oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) In polar reactions, a nucleophile reacts with an electrophile.
B) Carbocations are electrophiles.
C) Carbanions are nucleophiles.
D) A half-headed curved arrow shows the movement of an electron pair.
A) In polar reactions, a nucleophile reacts with an electrophile.
B) Carbocations are electrophiles.
C) Carbanions are nucleophiles.
D) A half-headed curved arrow shows the movement of an electron pair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the Keq corresponds to the highest value of G°?
A) Keq = 10-1
B) Keq = 10-2
C) Keq = 10-3
D) Keq = 10-5
A) Keq = 10-1
B) Keq = 10-2
C) Keq = 10-3
D) Keq = 10-5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements about equilibrium is true?
A) Equilibrium favors the products when the energy of the products is higher than the energy of the reactants.
B) Equilibrium favors the reactants when the energy of the product is lower than the energy of the reactants.
C) Equilibrium favors the products when they are less stable than the starting material of a reaction
D) Equilibrium favors the products when they are more stable than the starting material of a reaction.
A) Equilibrium favors the products when the energy of the products is higher than the energy of the reactants.
B) Equilibrium favors the reactants when the energy of the product is lower than the energy of the reactants.
C) Equilibrium favors the products when they are less stable than the starting material of a reaction
D) Equilibrium favors the products when they are more stable than the starting material of a reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements about elimination reactions is true?
A) Two bonds are broken.
B) Two bonds are formed.
C) Two bonds are broken.
D) Two bonds are formed.
A) Two bonds are broken.
B) Two bonds are formed.
C) Two bonds are broken.
D) Two bonds are formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What kind of reaction does the conversion of A to B represent? 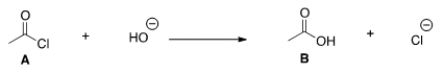
A) Addition reaction.
B) Substitution reaction.
C) Elimination reaction.
D) Acid-base reaction.

A) Addition reaction.
B) Substitution reaction.
C) Elimination reaction.
D) Acid-base reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements about a two-step reaction mechanism is true?
A) The transition states are located at energy minima.
B) Each step is characterized by its own value of H° and Ea.
C) The rate-determining step has the lower energy transition state.
D) The reactive intermediate is located at an energy maximum.
A) The transition states are located at energy minima.
B) Each step is characterized by its own value of H° and Ea.
C) The rate-determining step has the lower energy transition state.
D) The reactive intermediate is located at an energy maximum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What kind of reaction does the conversion of A to D represent? 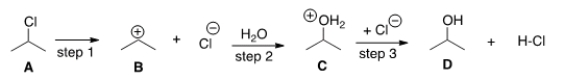
A) Addition reaction
B) Substitution reaction
C) Elimination reaction
D) Oxidation-reduction reaction

A) Addition reaction
B) Substitution reaction
C) Elimination reaction
D) Oxidation-reduction reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the name given to the reaction species that lies at an energy minimum between steps on a reaction energy diagram?
A) Transition state
B) Activation energy
C) Reactive intermediate
D) Equilibrium product
A) Transition state
B) Activation energy
C) Reactive intermediate
D) Equilibrium product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The G° (free energy change) for the conversion of A to B is predicted to be which of the following? 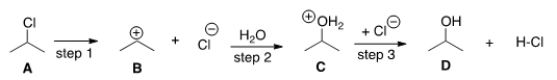
A) " G° = 0"
B) " G° < 0"
C) " G° > 0"
D) "Cannot be determined from the information provided"

A) " G° = 0"
B) " G° < 0"
C) " G° > 0"
D) "Cannot be determined from the information provided"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How many transition states and intermediates would the reaction profile have for the reaction shown below? 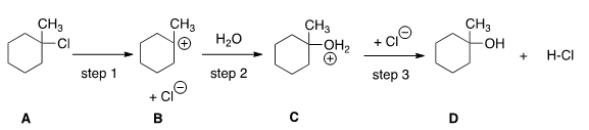
A) Three transition states and three intermediates
B) Two transition states and two intermediates
C) Three transition states and two intermediates
D) Two transition states and three intermediates

A) Three transition states and three intermediates
B) Two transition states and two intermediates
C) Three transition states and two intermediates
D) Two transition states and three intermediates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The product is favored in reaction in which H° is a positive value.
B) Entropy decreases when an acyclic compound forms a ring.
C) In homolytic bond cleavage, entropy decreases and favors formation of products.
D) The starting material is favored in a reaction in which H° is a negative value.
A) The product is favored in reaction in which H° is a positive value.
B) Entropy decreases when an acyclic compound forms a ring.
C) In homolytic bond cleavage, entropy decreases and favors formation of products.
D) The starting material is favored in a reaction in which H° is a negative value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A decrease in which of the following results in an increase in the rate of a chemical reaction?
A) Energy of activation
B) Concentration
C) Temperature
D) Kinetic energy
A) Energy of activation
B) Concentration
C) Temperature
D) Kinetic energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The equilibrium constant for the conversion of A to D is predicted to be which of the following? 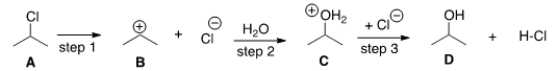
A) Keq = 1
B) Keq < 1
C) Keq > 1
D) Cannot be determined from the information provided

A) Keq = 1
B) Keq < 1
C) Keq > 1
D) Cannot be determined from the information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which reaction is slowest? 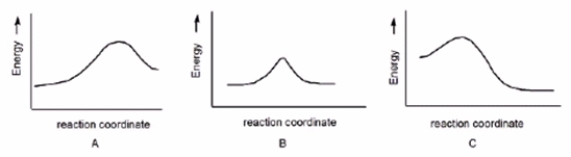
A) A
B) B
C) C

A) A
B) B
C) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Fast reactions have small rate constants.
B) Slow reactions have large rate constants.
C) A rate equation contains concentration terms for all reactants involved in a one-step mechanism.
D) A rate equation contains concentration terms for all the reactants involved in a multi-step reaction.
A) Fast reactions have small rate constants.
B) Slow reactions have large rate constants.
C) A rate equation contains concentration terms for all reactants involved in a one-step mechanism.
D) A rate equation contains concentration terms for all the reactants involved in a multi-step reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How many transition states are present in the reaction in the energy diagram? 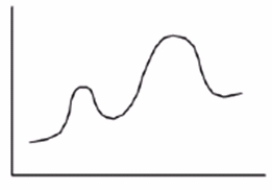
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3

A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which reaction has a positive G°, assuming that entropy changes are negligible compared to enthalpy changes? 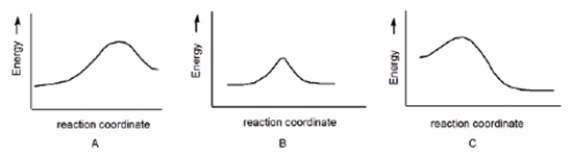
A) A
B) B
C) C

A) A
B) B
C) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which step would most likely have the largest energy of activation? 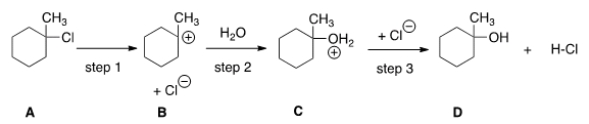
A) Step one
B) Step two
C) Step three
D) It cannot be determined from the information provided

A) Step one
B) Step two
C) Step three
D) It cannot be determined from the information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the conversion of A to B is slow and B to C is fast, what is the rate equation for this reaction? ![<strong>If the conversion of A to B is slow and B to C is fast, what is the rate equation for this reaction? </strong> A) Rate = k[(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>CHCl][H<sub>2</sub>O] B) Rate = k[(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>CHCl] C) Rate = k[(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>CH]<sup>+</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O] D) Rate = k[(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>CH]<sup>+</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5871/11ea9088_7001_598f_aec7_65c0854a64c4_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00.jpg)
A) Rate = k[(CH3)2CHCl][H2O]
B) Rate = k[(CH3)2CHCl]
C) Rate = k[(CH3)2CH]+[H2O]
D) Rate = k[(CH3)2CH]+
![<strong>If the conversion of A to B is slow and B to C is fast, what is the rate equation for this reaction? </strong> A) Rate = k[(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>CHCl][H<sub>2</sub>O] B) Rate = k[(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>CHCl] C) Rate = k[(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>CH]<sup>+</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O] D) Rate = k[(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>CH]<sup>+</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5871/11ea9088_7001_598f_aec7_65c0854a64c4_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00.jpg)
A) Rate = k[(CH3)2CHCl][H2O]
B) Rate = k[(CH3)2CHCl]
C) Rate = k[(CH3)2CH]+[H2O]
D) Rate = k[(CH3)2CH]+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The size of the activation energy tells us about the reaction mechanism.
B) The size of the activation energy tells us about the reaction rate.
C) A slow reaction has low activation energy.
D) A fast reaction has large activation energy.
A) The size of the activation energy tells us about the reaction mechanism.
B) The size of the activation energy tells us about the reaction rate.
C) A slow reaction has low activation energy.
D) A fast reaction has large activation energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following letters represents H° for the forward reaction in the following energy diagram? 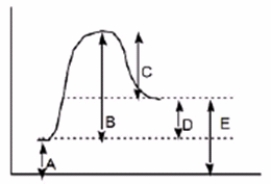
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In which reaction is Keq > 1? 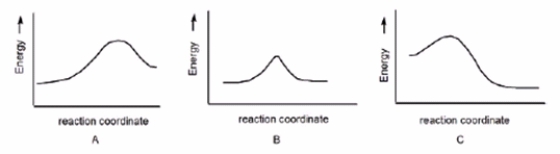
A) A
B) B
C) C

A) A
B) B
C) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which reaction is fast and has Keq= 1? 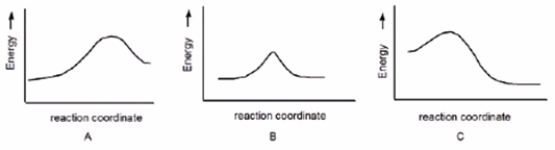
A) A
B) B
C) C

A) A
B) B
C) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) "Two reactions can have identical values for H° but very different Ea values."
B) "The larger the activation energy, the slower the reaction."
C) " H° determines the height of the energy barrier."
D) "The lower the activation energy, the faster the reaction."
A) "Two reactions can have identical values for H° but very different Ea values."
B) "The larger the activation energy, the slower the reaction."
C) " H° determines the height of the energy barrier."
D) "The lower the activation energy, the faster the reaction."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following reaction quantities will have an effect on reaction rate?
A) " G°"
B) " H°"
C) "Keq"
D) "Ea"
A) " G°"
B) " H°"
C) "Keq"
D) "Ea"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which compound would you predict to be highest in energy? 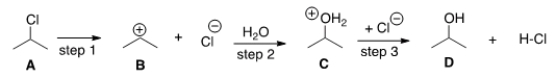
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements about a catalyst is true?
A) A catalyst accelerates a reaction by changing the amount of reactant and product at equilibrium.
B) A catalyst accelerates a reaction by lowering the energy of activation.
C) A catalyst accelerates a reaction by raising the energy of activation.
D) A catalyst accelerates a reaction by lowering the equilibrium constant.
A) A catalyst accelerates a reaction by changing the amount of reactant and product at equilibrium.
B) A catalyst accelerates a reaction by lowering the energy of activation.
C) A catalyst accelerates a reaction by raising the energy of activation.
D) A catalyst accelerates a reaction by lowering the equilibrium constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements about enzymes is true?
A) Enzymes increase the activation energy for a reaction.
B) Enzymes decrease the equilibrium constant.
C) Enzymes shift the equilibrium to favor the product.
D) Enzymes lower the transition state for the rate-determining step.
A) Enzymes increase the activation energy for a reaction.
B) Enzymes decrease the equilibrium constant.
C) Enzymes shift the equilibrium to favor the product.
D) Enzymes lower the transition state for the rate-determining step.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



