Deck 2: Principles for Analyzing Government
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Principles for Analyzing Government
1
The market system is based upon _____.
A)money
B)voluntary exchange
C)capitalism
D)profits
A)money
B)voluntary exchange
C)capitalism
D)profits
B
2
The key difference between the Pareto optimality and Pareto superiority is that ______.
A)Pareto optimality is incompatible with utilitarianism,while Pareto superiority is compatible
B)Pareto superiority is superior to Pareto optimality
C)Pareto optimality requires interpersonal utility calculations,while Pareto superiority does not
D)Pareto optimality refers to a state of the world while Pareto superiority compares two states of the world
A)Pareto optimality is incompatible with utilitarianism,while Pareto superiority is compatible
B)Pareto superiority is superior to Pareto optimality
C)Pareto optimality requires interpersonal utility calculations,while Pareto superiority does not
D)Pareto optimality refers to a state of the world while Pareto superiority compares two states of the world
D
3
Employing utilitarianism as a measure of the public interest _____.
A)is inconsistent with the concept of a social welfare function
B)attempts to minimize the problems associated with market failure
C)attempts to maximize total utility in a society
D)avoids comparing individual's utilities
A)is inconsistent with the concept of a social welfare function
B)attempts to minimize the problems associated with market failure
C)attempts to maximize total utility in a society
D)avoids comparing individual's utilities
C
4
If government did not individual rights,the efficiency of a market economy_____.
A)would decline
B)would be about the same
C)would increase
D)could possibly decline or possibly increase
A)would decline
B)would be about the same
C)would increase
D)could possibly decline or possibly increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The idea that the public interest should be equated with those policies that produce the greatest good for the greatest number _____.
A)is the utilitarian criterion
B)is the Pareto optimality criterion
C)is the Hobbesian criterion
D)is a value free judgment
A)is the utilitarian criterion
B)is the Pareto optimality criterion
C)is the Hobbesian criterion
D)is a value free judgment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Government institutions that protect the rights of individuals are ______.
A)the executive,legislative,and judicial branches of government
B)federal,state,and local governments
C)federal agencies such as OSHA,FEC,and the FCC
D)police,military branches,and the court system
A)the executive,legislative,and judicial branches of government
B)federal,state,and local governments
C)federal agencies such as OSHA,FEC,and the FCC
D)police,military branches,and the court system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The Pareto optimality concept is _____.
A)equivalent to the concept of economic efficiency
B)equivalent to Pareto superiority
C)equivalent to utilitarianism
D)equivalent to cost-benefit analysis
A)equivalent to the concept of economic efficiency
B)equivalent to Pareto superiority
C)equivalent to utilitarianism
D)equivalent to cost-benefit analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not a drawback of utilitarianism?
A)There exists no valid way to make interpersonal utility comparisons.
B)Is incompatible with the Pareto criteria.
C)It is not directly compatible with economic efficiency.
D)It implies social arrangements that most people would find objectionable.
A)There exists no valid way to make interpersonal utility comparisons.
B)Is incompatible with the Pareto criteria.
C)It is not directly compatible with economic efficiency.
D)It implies social arrangements that most people would find objectionable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of these is not a valid reason for government intervention into mutually beneficial exchange?
A)The market system might not function at all without government protecting certain rights
B)The market system produces an efficient outcome that the majority does not like
C)The government might be able to undertake some activities more efficiently than the market outcome.
D)The market allocation might be viewed as inequitable,so redistribution might be desired to achieve equity goals.
A)The market system might not function at all without government protecting certain rights
B)The market system produces an efficient outcome that the majority does not like
C)The government might be able to undertake some activities more efficiently than the market outcome.
D)The market allocation might be viewed as inequitable,so redistribution might be desired to achieve equity goals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The market system is able to allocate resources efficiently because individuals have the right to the output they produce and _____.
A)freedom of the press
B)freedom of speech
C)freedom of movement
D)freedom of exchange
A)freedom of the press
B)freedom of speech
C)freedom of movement
D)freedom of exchange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
_____ a cornerstone of the market economy.
A)Mutually beneficial exchange is
B)A strong central bank
C)Monopoly rents are
D)Government regulation is
A)Mutually beneficial exchange is
B)A strong central bank
C)Monopoly rents are
D)Government regulation is

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
As long as the value of additional units of output exceed the opportunity cost of that output,_____.
A)it will not be produced
B)it likely will not be produced
C)it will be produced
D)it is likely to be produced
A)it will not be produced
B)it likely will not be produced
C)it will be produced
D)it is likely to be produced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Pareto superiority concept _____.
A)is equivalent to utilitarianism
B)is equivalent to equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market
C)compares two different states of the world
D)looks at a state of the world and judges its superiority
A)is equivalent to utilitarianism
B)is equivalent to equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market
C)compares two different states of the world
D)looks at a state of the world and judges its superiority

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Pareto optimality and Pareto superiority _____.
A)concern only monetary gains and losses
B)compare utility gains with utility losses
C)do not require interpersonal utility comparisons
D)are equivalent to the concept of economic efficiency
A)concern only monetary gains and losses
B)compare utility gains with utility losses
C)do not require interpersonal utility comparisons
D)are equivalent to the concept of economic efficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The right of people to receive the value of their output as determined by the market _____.
A)leads to people pursuing their own selfish ends,with little regard for others
B)leads individuals to produce only goods that will appeal to the masses
C)provides strong incentives to produce goods that will make themselves happy
D)provides incentive to produce goods that others find valuable
A)leads to people pursuing their own selfish ends,with little regard for others
B)leads individuals to produce only goods that will appeal to the masses
C)provides strong incentives to produce goods that will make themselves happy
D)provides incentive to produce goods that others find valuable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The subject matter of public economics falls into the two general categories of _____ and _____.
A)public interest;private interest
B)coercion action;individual liberty
C)revenue generation;government spending
D)civilian activities;military duties
A)public interest;private interest
B)coercion action;individual liberty
C)revenue generation;government spending
D)civilian activities;military duties

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Utilitarianism is inconsistent with _____.
A)the social welfare function
B)cost-benefit analysis
C)the Pareto criteria
D)slavery
A)the social welfare function
B)cost-benefit analysis
C)the Pareto criteria
D)slavery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
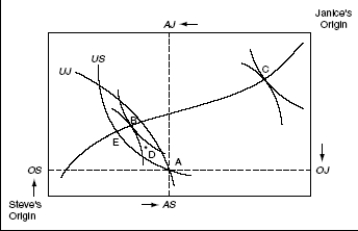
Using the above figure and the Pareto criteria to determine the public interest,would a move from point A to point C be in the public interest?
A)yes
B)no
C)possible,depending upon other factors
D)cannot say using the Pareto criteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the below statements is true?
A)It is efficient to produce beyond the equilibrium output level as long as costs are low.
B)The level of output that maximizes the value of an economy's output is found at the intersection of supply and demand in a competitive market.
C)Production and exchange is beneficial as long as the demand curve lies below the supply curve.
D)Mutually beneficial exchange is mostly harmful unless regulated.
A)It is efficient to produce beyond the equilibrium output level as long as costs are low.
B)The level of output that maximizes the value of an economy's output is found at the intersection of supply and demand in a competitive market.
C)Production and exchange is beneficial as long as the demand curve lies below the supply curve.
D)Mutually beneficial exchange is mostly harmful unless regulated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of these is not true?
A)Government uses its powers of coercion and force to collect taxes
B)Government uses its powers of coercion and force to protect rights
C)Government uses its powers of coercion and force to violate rights
D)Government uses its powers of coercion and force only to improve the general welfare
A)Government uses its powers of coercion and force to collect taxes
B)Government uses its powers of coercion and force to protect rights
C)Government uses its powers of coercion and force to violate rights
D)Government uses its powers of coercion and force only to improve the general welfare

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Outcomes are likely to be Pareto superior if they were _____.
A)approved of by a unanimous vote
B)enacted by a bureaucrat
C)decreed by a judge
D)enacted by bipartisan legislation
A)approved of by a unanimous vote
B)enacted by a bureaucrat
C)decreed by a judge
D)enacted by bipartisan legislation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Positive economic analysis _____.
A)evaluates policy changes and determines whether it is a good idea
B)seeks to understand the outcome of a policy change
C)cannot be proven incorrect
D)is a statement about "what ought to be"
A)evaluates policy changes and determines whether it is a good idea
B)seeks to understand the outcome of a policy change
C)cannot be proven incorrect
D)is a statement about "what ought to be"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Normative analysis is very important to public finance because _____.
A)public policy enacted by government is the result of voting by individuals
B)positive analysis is full of value judgments
C)we should be concerned with how the world works
D)voluntary exchanges are economically efficient
A)public policy enacted by government is the result of voting by individuals
B)positive analysis is full of value judgments
C)we should be concerned with how the world works
D)voluntary exchanges are economically efficient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Every market exchange is a Pareto superior move.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the Pareto criteria are taken literally,_____ percent of United States residents must agree for a policy change to be a move towards efficiency.
A)25
B)50
C)75
D)100
A)25
B)50
C)75
D)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Normative economic analysis _____.
A)is concerned only with the facts
B)is a statement about the relationship between a policy change an outcome
C)judges the desirability of a policy change
D)does not involve value judgments
A)is concerned only with the facts
B)is a statement about the relationship between a policy change an outcome
C)judges the desirability of a policy change
D)does not involve value judgments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Coercion and force underlie government activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When comparing public and private schools,the voluntary choice of going to a private school _____.
A)is a Pareto optimal move
B)is a Pareto superior move
C)is neither Pareto optimal nor Pareto superior
D)cannot be evaluated according to the Pareto criteria
A)is a Pareto optimal move
B)is a Pareto superior move
C)is neither Pareto optimal nor Pareto superior
D)cannot be evaluated according to the Pareto criteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Production and exchange is beneficial as long as the demand curve lies below the supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is a normative economics statement?
A)An increase in the minimum wage will reduce teenage employment.
B)Increasing the minimum wage will result in more votes for progressive candidates.
C)Raising the minimum wage would greatly increase labor costs in certain industries.
D)Raising the minimum wage is a poor idea because living wage laws are better.
A)An increase in the minimum wage will reduce teenage employment.
B)Increasing the minimum wage will result in more votes for progressive candidates.
C)Raising the minimum wage would greatly increase labor costs in certain industries.
D)Raising the minimum wage is a poor idea because living wage laws are better.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of these is an argument for using the potential compensation criterion?
A)If the winners can compensate the losers,no one is harmed by employing the criterion.
B)The criterion does not employ interpersonal utility calculations.
C)If employed over a large number of policy changes,everyone should enjoy a net gain in the long run.
D)It is easy to determine the magnitude of the wins and losses.
A)If the winners can compensate the losers,no one is harmed by employing the criterion.
B)The criterion does not employ interpersonal utility calculations.
C)If employed over a large number of policy changes,everyone should enjoy a net gain in the long run.
D)It is easy to determine the magnitude of the wins and losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If compared against other criteria for evaluating the public interest,the social welfare function is most comparable to _____.
A)utilitarianism
B)the Pareto criteria
C)the potential compensation criterion
D)cost-benefit analysis
A)utilitarianism
B)the Pareto criteria
C)the potential compensation criterion
D)cost-benefit analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A government strong enough to protect individual rights is also strong enough to violate them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Using the utilitarian criterion,it is possible that slavery could be in the public interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements about the social welfare function is not true?
A)It can be thought of as a set of indifference curves that depict the wealth of the entire society.
B)It does not employ interpersonal utility comparisons.
C)It is one possible method for evaluating the public interest/
D)It allows for the rankings of possible outcomes.
A)It can be thought of as a set of indifference curves that depict the wealth of the entire society.
B)It does not employ interpersonal utility comparisons.
C)It is one possible method for evaluating the public interest/
D)It allows for the rankings of possible outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is not a limitation of the Pareto criteria?
A)Almost any policy change will make at least one person worse off.
B)The status quo is lent legitimacy from being the starting point for evaluating social welfare.
C)The criteria cannot tell us if a particular policy change will make all participants better off.
D)The criteria do not allow for the ranking of all possible states of the world.
A)Almost any policy change will make at least one person worse off.
B)The status quo is lent legitimacy from being the starting point for evaluating social welfare.
C)The criteria cannot tell us if a particular policy change will make all participants better off.
D)The criteria do not allow for the ranking of all possible states of the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements about economic efficiency is not true?
A)Economic efficiency is equivalent to Pareto optimality.
B)Economic efficiency can be determined normatively.
C)Economic efficiency is superior to equity.
D)Economic efficiency can be evaluated positively.
A)Economic efficiency is equivalent to Pareto optimality.
B)Economic efficiency can be determined normatively.
C)Economic efficiency is superior to equity.
D)Economic efficiency can be evaluated positively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following would not satisfy the potential compensation criterion?
A)The winners from a policy change could compensate the losers so everyone would be better off.
B)The policy change was approved by a unanimous vote.
C)The policy change was a Pareto superior move
D)The policy change moved from a Pareto optimal position to a non-Pareto optimal position.
A)The winners from a policy change could compensate the losers so everyone would be better off.
B)The policy change was approved by a unanimous vote.
C)The policy change was a Pareto superior move
D)The policy change moved from a Pareto optimal position to a non-Pareto optimal position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Equity and efficiency _____.Thus,_____.
A)are always consistent with each other;trade-offs between the two are necessary
B)are never consistent with each other;trade-offs between the two are unnecessary
C)might be consistent in certain situations;trade-offs between the two might be necessary
D)might be consistent in certain situations,trade-offs between cannot be made
A)are always consistent with each other;trade-offs between the two are necessary
B)are never consistent with each other;trade-offs between the two are unnecessary
C)might be consistent in certain situations;trade-offs between the two might be necessary
D)might be consistent in certain situations,trade-offs between cannot be made

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If everyone agrees to a change,then the change will be a Pareto Superior move.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Public finance economists should only concern themselves with positive economic analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Compare and contrast Pareto optimality and Pareto superiority and provide a brief discussion of the advantages of the Pareto criteria in assessing the public interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Cost-benefit analysis does not employ interpersonal utility calculations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The goal of equity is fundamentally a positive issue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When acting upon the potential compensation criterion,the winners must compensate the losers to the exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
While limited in their practical applications,the real value of the Pareto criteria is in allowing the public interest to be judged without making interpersonal utility calculations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is cost-benefit analysis? Suppose that you were asked to do a cost benefit analysis of tearing down an elderly woman's ancestral home to provide space to expand a local high school.What difficulties might you encounter?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Briefly list and discuss in turn the three limitations of the Pareto criteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Draw a demand and supply curve for a competitive product,making sure to clearly label the axis.Give a brief explanation for why the resulting equilibrium is economically efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Suppose that a particular policy would result in a $100 gain for Gwen but a $20 loss for Sabrina.Everyone else in the economy remains the same.Is this policy change in the public interest according to the potential compensation criterion? Explain and justify your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



