Deck 17: Basic Multivarate Techniques
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/38
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Basic Multivarate Techniques
1
Multiple regression analysis attempts to:
A) predict independent variable variations from 2 or more dependent variable feedback effects
B) predict variation in a dependent variable from two or more control variables
C) predict variation in a dependent variable from two or more independent variables
D) to regress the means of the variables in a co-variant manner
A) predict independent variable variations from 2 or more dependent variable feedback effects
B) predict variation in a dependent variable from two or more control variables
C) predict variation in a dependent variable from two or more independent variables
D) to regress the means of the variables in a co-variant manner
C
2
When the source of spuriousness variable is controlled for, and the model turns out to be correct, then the original relationship between X and Y must have:
A) remained the same
B) disappeared
C) become mixed
D) b and c
E) a and b
A) remained the same
B) disappeared
C) become mixed
D) b and c
E) a and b
B
3
To demonstrate the causal order of a relationship, one must:
A) demonstrate that present variables do indeed influence the past
B) demonstrate the proposed cause precedes the effect in time
C) use a statistical rank ordering routine
D) cite evidence from a literature review
A) demonstrate that present variables do indeed influence the past
B) demonstrate the proposed cause precedes the effect in time
C) use a statistical rank ordering routine
D) cite evidence from a literature review
B
4
The dilemma of the sources of spuriousness model and the intervening variable model is that:
A) the models do not use the same methodology
B) the models are too complex for the beginning researcher
C) the models are not empirically distinguishable
D) the models do not yield similar results
A) the models do not use the same methodology
B) the models are too complex for the beginning researcher
C) the models are not empirically distinguishable
D) the models do not yield similar results

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
To accept a 4 variable causal model (A ► B ► C ► D),.which of the following conditions must be satisfied:
A) (rAB > rAC, rAD) and (rBC > rBD) and (rCD > rAC)
B) (rAC > rAB, rAD) and (rBA > rBE) and (rCD > rAC)
C) (rAB > rAD, raa) and (rBC > rBD) and (rCD > rAC)
D) (rAB > rAC, rAD) and (rBD > rBE) and (rCD > rAC)
A) (rAB > rAC, rAD) and (rBC > rBD) and (rCD > rAC)
B) (rAC > rAB, rAD) and (rBA > rBE) and (rCD > rAC)
C) (rAB > rAD, raa) and (rBC > rBD) and (rCD > rAC)
D) (rAB > rAC, rAD) and (rBD > rBE) and (rCD > rAC)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The simplest regression analysis, elaborated upon in the course text, involves:
A) non-linear relationship between variables
B) a parabolic relationship between variables
C) an additive, linear relationship between variables
D) the opposite methodology of correlational analysis
A) non-linear relationship between variables
B) a parabolic relationship between variables
C) an additive, linear relationship between variables
D) the opposite methodology of correlational analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When employing PARTIAL CORR to test an intervening variable, which of the following is not an indicator of a correct model:
A) the correlation between adjacent variables will be greater than between non-adjacent categories
B) the correlation between adjacent variables will be less than that between non-adjacent categories
C) rxy.I = 0
D) rxy < rxI or rIy
A) the correlation between adjacent variables will be greater than between non-adjacent categories
B) the correlation between adjacent variables will be less than that between non-adjacent categories
C) rxy.I = 0
D) rxy < rxI or rIy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
To state that two variables are associated is to state that:
A) they are statistically significant
B) they have a spurious connection
C) they vary together
D) the means of each are equally close to the standard deviation of the population
A) they are statistically significant
B) they have a spurious connection
C) they vary together
D) the means of each are equally close to the standard deviation of the population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is not a condition which must be satisfied in order to establish a causal relationship:
A) the variables are associated
B) the variables are in a plausible causal sequence
C) the relationship is to be statistically significant
D) the variables cannot be connected spuriously
A) the variables are associated
B) the variables are in a plausible causal sequence
C) the relationship is to be statistically significant
D) the variables cannot be connected spuriously

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The intervening variable model is of interest in understanding:
A) the mechanism which connects the independent variable to the dependent one
B) the relationship of the control variable in relation to the standardized coefficients of X and Y
C) how X and Y are both influence by a third variable
D) all of the above
A) the mechanism which connects the independent variable to the dependent one
B) the relationship of the control variable in relation to the standardized coefficients of X and Y
C) how X and Y are both influence by a third variable
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
To support a proposed intervening variable model, the relationship must:
A) disappear in at least one category
B) disappear and decrease in each category respectively
C) stay the same in at least one category
D) stay the same in both categories
E) a and c
A) disappear in at least one category
B) disappear and decrease in each category respectively
C) stay the same in at least one category
D) stay the same in both categories
E) a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The source of spuriousness model suggests that:
A) a third variable is influencing the dependent variable
B) a third variable is influencing the independent variable
C) a third variable is influencing both the dependent variable and the independent variable
D) a fourth variable is influencing the independent variable
E) none of the above
A) a third variable is influencing the dependent variable
B) a third variable is influencing the independent variable
C) a third variable is influencing both the dependent variable and the independent variable
D) a fourth variable is influencing the independent variable
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
To test an intervening variable model with PARTIAL CORR, which of the following must also be employed:
A) CROSSTABS
B) MEANS
C) ANOVA
D) MANOVA
E) none of the above
A) CROSSTABS
B) MEANS
C) ANOVA
D) MANOVA
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Within Jackson's Rule of Thirds, if the difference remains within 1/3, the relationship can be said to have:
A) disappeared
B) stayed the same
C) increased
D) become mixed
A) disappeared
B) stayed the same
C) increased
D) become mixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When employing Jackson's Rule of Thirds, a relationship increase refers to:
A) the original difference between categories increasing by 1/2 or more
B) the original difference between categories increasing by 1/3 or more
C) the original difference between categories increasing by 1/4 or more
D) the original difference actually decreasing by 1/3 or more
A) the original difference between categories increasing by 1/2 or more
B) the original difference between categories increasing by 1/3 or more
C) the original difference between categories increasing by 1/4 or more
D) the original difference actually decreasing by 1/3 or more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A source of spuriousness model posits that a statistically significant relationship between X and Y:
A) is also a causal relationship
B) is necessarily a causal relationship
C) is not a causal relationship
D) is a relationship within which X influences some third variable
A) is also a causal relationship
B) is necessarily a causal relationship
C) is not a causal relationship
D) is a relationship within which X influences some third variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Before testing a source of spuriousness model, the original relationship between X and Y must have been demonstrated as being:
A) an associated one
B) statistically significant
C) one of co-variance
D) all of the above
A) an associated one
B) statistically significant
C) one of co-variance
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A first-order partial takes into account:
A) one additional variable
B) two additional variables
C) three additional variables
D) all of the above when properly modified
A) one additional variable
B) two additional variables
C) three additional variables
D) all of the above when properly modified

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
To fully demonstrate that a relationship is not spurious is:
A) impossible
B) a formidable challenge
C) to demonstrate that the obvious sources have been eliminated
D) to employ advanced statistical methods
A) impossible
B) a formidable challenge
C) to demonstrate that the obvious sources have been eliminated
D) to employ advanced statistical methods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In choosing the appropriate statistical procedure to test a causal model, one must:
A) determine the standard deviation for the sample population
B) determine the type of model to be tested
C) determine the levels of measurement of the key variables
D) compute the mean of each key variable and then compare
A) determine the standard deviation for the sample population
B) determine the type of model to be tested
C) determine the levels of measurement of the key variables
D) compute the mean of each key variable and then compare

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When techniques designed to include ordinal level variables in regression analysis, the price one pays is:
A) a weakened ability to predict independent variable values
B) a weakened ability to predict dependent variable values
C) minimal, ordinal level variables are sufficient
D) none of the above
A) a weakened ability to predict independent variable values
B) a weakened ability to predict dependent variable values
C) minimal, ordinal level variables are sufficient
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is an expression of the relationship between a dependent variable and several independent ones:
A) Y = a + Bx
B) Y = a + b1X1 + b2X2 + ... BkXk
C) Y = a1 + a2 = ... ak + BkXk
D)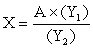
A) Y = a + Bx
B) Y = a + b1X1 + b2X2 + ... BkXk
C) Y = a1 + a2 = ... ak + BkXk
D)
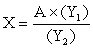

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Beta weight comparisons make which of the following irrelevant:
A) differential dependent variable ranges
B) differential independent variable ranges
C) differential control variable values
D) all of the above
A) differential dependent variable ranges
B) differential independent variable ranges
C) differential control variable values
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Discriminant analysis is employed where:
A) the level of measurement of the dependent variable is nominal
B) the dependent variable does not constitute a normal distribution
C) the level of measurement of the independent variable(s) is other than ratio
D) the distributions of the independent variables are normal
A) the level of measurement of the dependent variable is nominal
B) the dependent variable does not constitute a normal distribution
C) the level of measurement of the independent variable(s) is other than ratio
D) the distributions of the independent variables are normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The pure researcher, as opposed to the applied researcher, will be interested in:
A) the b coefficients
B) beta weights
C) the overall R2 measure
D) all of the above
A) the b coefficients
B) beta weights
C) the overall R2 measure
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Regression analysis allows the researcher to:
A) establish which variable should be treated as independent and which one as a dependent variable
B) determine causal associations between all variables
C) determine a mathematical equation which expresses the relationship between the independent and dependent variables
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) establish which variable should be treated as independent and which one as a dependent variable
B) determine causal associations between all variables
C) determine a mathematical equation which expresses the relationship between the independent and dependent variables
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
As the number of actual, as opposed to missing, cases nears the number of variables, which of the following may occur:
A) the R2 will decrease substantially
B) the R2 will increase substantially
C) a or b on a random basis
D) all of the above
A) the R2 will decrease substantially
B) the R2 will increase substantially
C) a or b on a random basis
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Beta weights can be profitably thought of as:
A) standardized slopes
B) standardized means
C) equal in all respects to z-scores
D) standardized constants
A) standardized slopes
B) standardized means
C) equal in all respects to z-scores
D) standardized constants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
R2 is a measure of the:
A) variation within the independent variable(s)
B) variation of the dependent variable(s)
C) variation in the dependent variable explained by the combination of the independent variables
D) variation in the independent variable explained by the combination of the dependent variables
A) variation within the independent variable(s)
B) variation of the dependent variable(s)
C) variation in the dependent variable explained by the combination of the independent variables
D) variation in the independent variable explained by the combination of the dependent variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When variables are converted to log function variables, the new equation becomes:
A) multiplicative power function
B) a divisicatory power function
C) equal to its former function, but now more powerful
D) a multidimensional fractal
A) multiplicative power function
B) a divisicatory power function
C) equal to its former function, but now more powerful
D) a multidimensional fractal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The log function variable equation form is:
A) log y = log ab + log x1 + log x2 + log xk
B) log y = log a + log x1 + log x2 + log xk
C) Log y = (s - s2 + xy(c)) - y2
D) none of the above
A) log y = log ab + log x1 + log x2 + log xk
B) log y = log a + log x1 + log x2 + log xk
C) Log y = (s - s2 + xy(c)) - y2
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
With respect to regression analysis, the applied researcher will be interested in independent variables which:
A) vary significantly from the highest to the lowest value
B) are manipulatable through policy changes
C) have a more theoretical importance
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) vary significantly from the highest to the lowest value
B) are manipulatable through policy changes
C) have a more theoretical importance
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The importance of defining a mathematical equation to describe the relationship between an independent and dependent variable is:
A) the ability to substantiate findings to other scientists
B) the interdisciplinary approach of sociology and mathematics
C) to predict values for a dependent variable given independent variable values
D) to more effectively facilitate comparison of cross-cultural analyses
A) the ability to substantiate findings to other scientists
B) the interdisciplinary approach of sociology and mathematics
C) to predict values for a dependent variable given independent variable values
D) to more effectively facilitate comparison of cross-cultural analyses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
To execute regression analysis, the optimum level of measurement is:
A) ratio
B) ordinal
C) nominal
D) interval
A) ratio
B) ordinal
C) nominal
D) interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
By using the BACKWARD option within regression analysis, whereby all variables are included in the analysis and the least important ones are dropped, the advantage is:
A) variables of little importance are dropped
B) variables important in combination with others are included
C) only significant variables remain in the final analysis
D) all of the above
A) variables of little importance are dropped
B) variables important in combination with others are included
C) only significant variables remain in the final analysis
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Discriminant function analysis attempts to:
A) predict the categories of the independent variables which will influence the dependent variable(s)
B) predict the categories of the independent variables which will influence the control variable(s) and vice versa
C) predict the category of the dependent variable which in each case falls using the combined information of the independent variables
D) isolate the causal components of the dependent variable, thus, the reverse of regression analysis
A) predict the categories of the independent variables which will influence the dependent variable(s)
B) predict the categories of the independent variables which will influence the control variable(s) and vice versa
C) predict the category of the dependent variable which in each case falls using the combined information of the independent variables
D) isolate the causal components of the dependent variable, thus, the reverse of regression analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In ensuring that variables are theoretically independent, a researcher is really:
A) ensuring that independent variables are potential causes of the dependent variable's variation, not alternative measures of it
B) ensuring that independent variables are not highly correlates with one another
C) minimizing multicollinearity
D) ensuring that raw data is used in analyses
A) ensuring that independent variables are potential causes of the dependent variable's variation, not alternative measures of it
B) ensuring that independent variables are not highly correlates with one another
C) minimizing multicollinearity
D) ensuring that raw data is used in analyses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The MEANS solution (regression analysis):
A) exclusively analyzes means during regression analysis
B) substitutes the mean of a variable for missing cases
C) computes correlations of all pairs of data for which cases are available
D) repeats the analysis with only significant variables
A) exclusively analyzes means during regression analysis
B) substitutes the mean of a variable for missing cases
C) computes correlations of all pairs of data for which cases are available
D) repeats the analysis with only significant variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



