Deck 15: Scenarios
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/12
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Scenarios
1
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2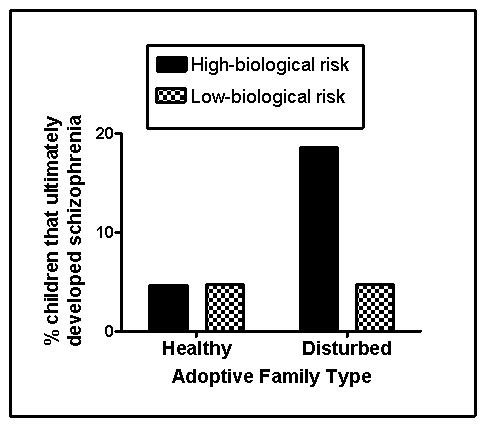
(Scenario II)Numerous studies have demonstrated enlarged ventricles in patients with schizophrenia,particularly those exhibiting the negative symptoms of the disease.Why would interpretation of this finding NOT be complicated?
A)Treatment drugs may produce ventricular enlargement.
B)The majority of people with schizophrenia do not show ventricular enlargement.
C)Identical twins of persons with schizophrenia do not usually exhibit enlarged ventricles.
D)Persons with enlarged ventricles may not exhibit symptoms of schizophrenia.
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2

(Scenario II)Numerous studies have demonstrated enlarged ventricles in patients with schizophrenia,particularly those exhibiting the negative symptoms of the disease.Why would interpretation of this finding NOT be complicated?
A)Treatment drugs may produce ventricular enlargement.
B)The majority of people with schizophrenia do not show ventricular enlargement.
C)Identical twins of persons with schizophrenia do not usually exhibit enlarged ventricles.
D)Persons with enlarged ventricles may not exhibit symptoms of schizophrenia.
Identical twins of persons with schizophrenia do not usually exhibit enlarged ventricles.
2
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1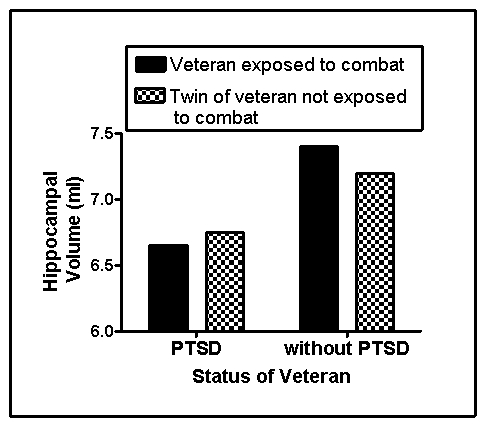
(Scenario I)For a number of years,psychologists with expertise in the stress response hypothesized that glucocorticoid release at and shortly after the time of trauma were neurotoxic and led to smaller hippocampi.The results of the study by Gilbertson and colleagues (2002):
A)provide no evidence as to the veracity of this hypothesis.
B)are consistent with but do not prove the theory.
C)demonstrate a cause and effect relation between hippocampal volume and PTSD.
D)are inconsistent with the hypothesis.
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1

(Scenario I)For a number of years,psychologists with expertise in the stress response hypothesized that glucocorticoid release at and shortly after the time of trauma were neurotoxic and led to smaller hippocampi.The results of the study by Gilbertson and colleagues (2002):
A)provide no evidence as to the veracity of this hypothesis.
B)are consistent with but do not prove the theory.
C)demonstrate a cause and effect relation between hippocampal volume and PTSD.
D)are inconsistent with the hypothesis.
are inconsistent with the hypothesis.
3
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1
(Scenario I)Which factor BEST distinguishes PTSD from a normal reaction to a traumatic event?
A)the release of stress hormones triggered by the trauma
B)recurrent unwanted thoughts about the trauma
C)anxiety when reminded of the trauma
D)symptom-related distress that does not lessen with time
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1

(Scenario I)Which factor BEST distinguishes PTSD from a normal reaction to a traumatic event?
A)the release of stress hormones triggered by the trauma
B)recurrent unwanted thoughts about the trauma
C)anxiety when reminded of the trauma
D)symptom-related distress that does not lessen with time
symptom-related distress that does not lessen with time
4
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2
(Scenario II)Which symptom is positive of schizophrenia?
A)inability to maintain eye contact
B)blunted emotional affect
C)poverty of speech
D)masturbating in public
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2

(Scenario II)Which symptom is positive of schizophrenia?
A)inability to maintain eye contact
B)blunted emotional affect
C)poverty of speech
D)masturbating in public

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2
(Scenario II)The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia was developed in large part due to research on the effects of psychoactive drugs in the brain.Which statement does that research NOT support?
A)Drugs that cause excessive dopamine release,such as methamphetamine,mimic some of the symptoms of schizophrenia.
B)Drugs that block the reuptake of dopamine,such as cocaine,mimic some of the symptoms of schizophrenia.
C)Drugs that block the functions of dopamine,such as chlorpromazine,may reduce some symptoms of schizophrenia.
D)Drugs that begin reducing dopamine levels immediately quickly reduce symptoms of schizophrenia more quickly than do drugs with more delayed onsets of action.
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2

(Scenario II)The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia was developed in large part due to research on the effects of psychoactive drugs in the brain.Which statement does that research NOT support?
A)Drugs that cause excessive dopamine release,such as methamphetamine,mimic some of the symptoms of schizophrenia.
B)Drugs that block the reuptake of dopamine,such as cocaine,mimic some of the symptoms of schizophrenia.
C)Drugs that block the functions of dopamine,such as chlorpromazine,may reduce some symptoms of schizophrenia.
D)Drugs that begin reducing dopamine levels immediately quickly reduce symptoms of schizophrenia more quickly than do drugs with more delayed onsets of action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1
(Scenario I)The results of the study by Gilbertson and colleagues (2002)suggest that:
A)among veterans,smaller hippocampi probably are due to trauma-induced glucocorticoid release.
B)smaller hippocampi may make people more susceptible to PTSD if exposed to a traumatic event.
C)soldiers with smaller hippocampi probably will develop PTSD.
D)PTSD is largely genetically determined.
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1

(Scenario I)The results of the study by Gilbertson and colleagues (2002)suggest that:
A)among veterans,smaller hippocampi probably are due to trauma-induced glucocorticoid release.
B)smaller hippocampi may make people more susceptible to PTSD if exposed to a traumatic event.
C)soldiers with smaller hippocampi probably will develop PTSD.
D)PTSD is largely genetically determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2
(Scenario II)The results shown in Figure 15.2 demonstrate that:
A)children at genetic risk for schizophrenia are less sensitive to family-related problems.
B)the environment and genetics tend to work in opposition with respect to the development of schizophrenia.
C)neither genetic nor environmental factors alone predict the development of schizophrenia.
D)stressful home situations are a greater predictor of schizophrenia than are genetics.
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2

(Scenario II)The results shown in Figure 15.2 demonstrate that:
A)children at genetic risk for schizophrenia are less sensitive to family-related problems.
B)the environment and genetics tend to work in opposition with respect to the development of schizophrenia.
C)neither genetic nor environmental factors alone predict the development of schizophrenia.
D)stressful home situations are a greater predictor of schizophrenia than are genetics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2
(Scenario II)Which prediction is CONSISTENT with the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia?
A)Persons with schizophrenia have a reduced number of dopamine receptors in the brain.
B)Persons with Parkinson's disease have a greater than 1% chance of also being schizophrenic.
C)Amphetamines,which increase dopamine levels,can exacerbate symptoms of schizophrenia.
D)Dopamine antagonists used to treat schizophrenia require several weeks to begin working.
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2

(Scenario II)Which prediction is CONSISTENT with the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia?
A)Persons with schizophrenia have a reduced number of dopamine receptors in the brain.
B)Persons with Parkinson's disease have a greater than 1% chance of also being schizophrenic.
C)Amphetamines,which increase dopamine levels,can exacerbate symptoms of schizophrenia.
D)Dopamine antagonists used to treat schizophrenia require several weeks to begin working.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1
(Scenario I)Which conclusion is STRONGEST,justified solely on the basis that comorbidity exists between PTSD and alcoholism?
A)PTSD and alcoholism tend to co-occur in the same individuals.
B)Trauma-induced changes leave the brain particularly sensitive to the effects of alcohol.
C)The two disorders have the same underlying cause.
D)Trauma survivors drink because it reduces their stress levels.
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1

(Scenario I)Which conclusion is STRONGEST,justified solely on the basis that comorbidity exists between PTSD and alcoholism?
A)PTSD and alcoholism tend to co-occur in the same individuals.
B)Trauma-induced changes leave the brain particularly sensitive to the effects of alcohol.
C)The two disorders have the same underlying cause.
D)Trauma survivors drink because it reduces their stress levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1
(Scenario I)The purpose of studying monozygotic twins of combat veterans in the Gilbertson and colleagues (2002)study was to:
A)demonstrate that combat exposure causes PTSD.
B)demonstrate that combat exposure is associated with PTSD.
C)determine if smaller hippocampi are the causes or consequences of PTSD.
D)control for all other third variables related to genetics other than hippocampal volume.
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1

(Scenario I)The purpose of studying monozygotic twins of combat veterans in the Gilbertson and colleagues (2002)study was to:
A)demonstrate that combat exposure causes PTSD.
B)demonstrate that combat exposure is associated with PTSD.
C)determine if smaller hippocampi are the causes or consequences of PTSD.
D)control for all other third variables related to genetics other than hippocampal volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1
(Scenario I)The results of the study by Gilbertson and colleagues (2002)are MOST consistent with which model of mental disorders?
A)medical
B)diathesis-stress
C)biopsychosocial
D)psychodynamic
Scenario I
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002).Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1

(Scenario I)The results of the study by Gilbertson and colleagues (2002)are MOST consistent with which model of mental disorders?
A)medical
B)diathesis-stress
C)biopsychosocial
D)psychodynamic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2
(Scenario II)The fabricated results consistent with those obtained by Tienari and colleagues (2004)and shown in Figure 15.2 suggest that:
A)overall,the home environment is not associated with schizophrenia.
B)a healthy home environment may serve as a protective factor in children at risk for developing schizophrenia.
C)a disturbed home environment increases the likelihood of schizophrenia in low-risk children.
D)in healthy home environments,biological risk factors are the best predictor of schizophrenia.
Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari,P. ,Wynne,L.C. ,Sorri,A. ,Lahti,I. ,Läksy,K. ,Moring,J. ,& ...Wahlberg,K.(2004).Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees.The British Journal of Psychiatry,184(3),216-222.doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes;a distorted perception of reality;altered or blunted emotional affect;and disturbances in thought,motivation,and behavior.The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative.Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs),hallucinations (false perceptual experiences),and disorganized speech.Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors,such as social withdrawal.Cognitive deficits in executive functioning,attention span,and working memory may also be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component.Over the years,a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia,although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder.One such example is the dopamine hypothesis,which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity.Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia.Although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles,this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease,and dopamine antagonists may also produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment,psychological and social factors also contribute.Tienari and colleagues (2004)compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families,the latter characterized by extreme conflict,volatile relationships,and communication deficits.Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic.The remainder were classified at low risk.The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2

(Scenario II)The fabricated results consistent with those obtained by Tienari and colleagues (2004)and shown in Figure 15.2 suggest that:
A)overall,the home environment is not associated with schizophrenia.
B)a healthy home environment may serve as a protective factor in children at risk for developing schizophrenia.
C)a disturbed home environment increases the likelihood of schizophrenia in low-risk children.
D)in healthy home environments,biological risk factors are the best predictor of schizophrenia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



