Deck 11: The Aggregate Expenditures Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/143
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: The Aggregate Expenditures Model
1
In the aggregate expenditure model, which of the following variables is assumed to be independent of real GDP?
A) Profit
B) Saving
C) Investment
D) Consumption
A) Profit
B) Saving
C) Investment
D) Consumption
Investment
2
A rightward shift of the investment demand curve will:
A) Shift the investment schedule downward
B) Shift the investment schedule upward
C) Decrease the quantity of investment
D) Decrease the real rate of interest
A) Shift the investment schedule downward
B) Shift the investment schedule upward
C) Decrease the quantity of investment
D) Decrease the real rate of interest
Shift the investment schedule upward
3
The data below are for a private (no government) closed economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 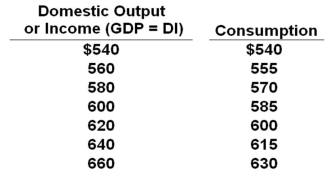 Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $15 billion, then at the $560 billion level of output, there will be a(n):
Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $15 billion, then at the $560 billion level of output, there will be a(n):
A) Unplanned increase in inventories of $5 billion
B) Unplanned increase in inventories of $10 billion
C) Unplanned decrease in inventories of $5 billion
D) Unplanned decrease in inventories of $10 billion
 Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $15 billion, then at the $560 billion level of output, there will be a(n):
Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $15 billion, then at the $560 billion level of output, there will be a(n):A) Unplanned increase in inventories of $5 billion
B) Unplanned increase in inventories of $10 billion
C) Unplanned decrease in inventories of $5 billion
D) Unplanned decrease in inventories of $10 billion
Unplanned decrease in inventories of $10 billion
4
Which of the following is graphed as a horizontal line across levels of real GDP in the aggregate expenditures model?
A) The saving schedule
B) The investment schedule
C) The consumption schedule
D) The investment demand curve
A) The saving schedule
B) The investment schedule
C) The consumption schedule
D) The investment demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When aggregate expenditure is greater than GDP, then there will be an:
A) Unplanned increase in inventories and GDP will increase
B) Unplanned decrease in inventories and GDP will increase
C) Unplanned increase in inventories and GDP will decrease
D) Unplanned decrease in inventories and GDP will decrease
A) Unplanned increase in inventories and GDP will increase
B) Unplanned decrease in inventories and GDP will increase
C) Unplanned increase in inventories and GDP will decrease
D) Unplanned decrease in inventories and GDP will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The data below are for a private (no government) closed economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 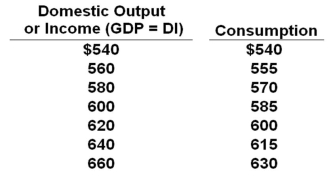 Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $25 billion, then aggregate expenditures at the income level of $560 billion will be:
Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $25 billion, then aggregate expenditures at the income level of $560 billion will be:
A) $565 billion
B) $580 billion
C) $585 billion
D) $595 billion
 Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $25 billion, then aggregate expenditures at the income level of $560 billion will be:
Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $25 billion, then aggregate expenditures at the income level of $560 billion will be:A) $565 billion
B) $580 billion
C) $585 billion
D) $595 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In a private closed economy, the two components of aggregate expenditures are:
A) Consumption and government spending
B) Consumption and net exports
C) Consumption, investment, and net exports
D) Consumption and investment
A) Consumption and government spending
B) Consumption and net exports
C) Consumption, investment, and net exports
D) Consumption and investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The investment schedule shows the:
A) Inverse relationship between the expected rate of return and the quantity of investment demanded
B) Positive relationship between the expected rate of return and the quantity of investment demanded
C) Amounts business firms collectively intend to invest at each possible level of GDP
D) Rate of interest that business firms must pay when they make investments in capital goods
A) Inverse relationship between the expected rate of return and the quantity of investment demanded
B) Positive relationship between the expected rate of return and the quantity of investment demanded
C) Amounts business firms collectively intend to invest at each possible level of GDP
D) Rate of interest that business firms must pay when they make investments in capital goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the real interest rate falls, then the:
A) Investment schedule will shift upward
B) Investment schedule will shift downward
C) Point moves along the investment schedule to the right
D) Consumption schedule will shift downward
A) Investment schedule will shift upward
B) Investment schedule will shift downward
C) Point moves along the investment schedule to the right
D) Consumption schedule will shift downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The difference between the investment demand curve and the investment schedule is that the former shows:
A) A direct relationship between investment and interest rate, while the latter shows no correlation between investment and income
B) An inverse relationship between investment and interest rate, while the latter shows no correlation between investment and income
C) A direct relationship between investment and income, while the latter shows no correlation between investment and interest rate
D) An inverse relationship between investment and income, while the latter shows no correlation between investment and interest rate
A) A direct relationship between investment and interest rate, while the latter shows no correlation between investment and income
B) An inverse relationship between investment and interest rate, while the latter shows no correlation between investment and income
C) A direct relationship between investment and income, while the latter shows no correlation between investment and interest rate
D) An inverse relationship between investment and income, while the latter shows no correlation between investment and interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the stock of available capital in the economy is running too low, then the:
A) Investment schedule will shift upward
B) Investment schedule will shift downward
C) Consumption schedule will shift upward
D) Consumption schedule will shift downward
A) Investment schedule will shift upward
B) Investment schedule will shift downward
C) Consumption schedule will shift upward
D) Consumption schedule will shift downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The data below are for a private (no government) closed economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 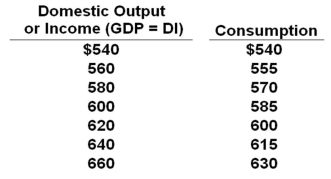 Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $25 billion, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $25 billion, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
A) $600 billion
B) $620 billion
C) $640 billion
D) $660 billion
 Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $25 billion, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $25 billion, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:A) $600 billion
B) $620 billion
C) $640 billion
D) $660 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The most basic premise of the aggregate expenditures model is that:
A) The total output produced in the economy depends directly on the level of total spending
B) The level of employment in the economy depends inversely on the real wage rate
C) The total output produced depends mostly on the total capacity of firms to produce
D) The unemployment level in the economy is inversely related to the inflation rate
A) The total output produced in the economy depends directly on the level of total spending
B) The level of employment in the economy depends inversely on the real wage rate
C) The total output produced depends mostly on the total capacity of firms to produce
D) The unemployment level in the economy is inversely related to the inflation rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the aggregate expenditures model, the consumption schedule is shown to be:
A) Directly related to real interest rates
B) Inversely related to real interest rates
C) Directly related to real income GDP
D) Inversely related to real income GDP
A) Directly related to real interest rates
B) Inversely related to real interest rates
C) Directly related to real income GDP
D) Inversely related to real income GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a private closed economy, the equilibrium condition for the economy is:
A) AE = C + Ig = GDP
B) AE = G + Ig = GDP
C) AE = C + Ig + G = GDP
D) C + Ig + G + NX = GDP
A) AE = C + Ig = GDP
B) AE = G + Ig = GDP
C) AE = C + Ig + G = GDP
D) C + Ig + G + NX = GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
John Maynard Keynes developed the aggregate expenditures model in order to understand the:
A) Second World War
B) Great Depression
C) Oil crises of the 1970s and 1980s
D) Great Recession of 2007-2009
A) Second World War
B) Great Depression
C) Oil crises of the 1970s and 1980s
D) Great Recession of 2007-2009

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
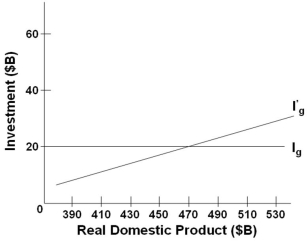 The graph above indicates that:
The graph above indicates that:A) I'g is an investment schedule that assumes that the investment plans of business are independent of the current level of income, whereas Ig does not
B) Ig is an investment schedule that assumes that the investment plans of business are independent of the current level of income, whereas I'g does not
C) The equilibrium level of investment is determined at the point where investment schedule I'g crosses the Ig investment schedule
D) Investment schedule I'g shows the inverse relationship between real domestic product and investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a private closed economy, there will be an unplanned increase in inventories when:
A) Aggregate expenditures exceed GDP
B) Aggregate expenditures exceed (C + Ig)
C) (C + Ig) exceeds aggregate expenditures
D) GDP exceeds aggregate expenditures
A) Aggregate expenditures exceed GDP
B) Aggregate expenditures exceed (C + Ig)
C) (C + Ig) exceeds aggregate expenditures
D) GDP exceeds aggregate expenditures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the expected rate of return on investment decreases, then most likely the:
A) Investment schedule will shift upward
B) Investment schedule will shift downward
C) Consumption schedule will shift upward
D) Consumption schedule will shift downward
A) Investment schedule will shift upward
B) Investment schedule will shift downward
C) Consumption schedule will shift upward
D) Consumption schedule will shift downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
One basic assumption of the aggregate expenditures model is that:
A) The economy is operating at full employment
B) There is inflation in the economy
C) There is no public sector in the economy
D) The average price level in the economy is fixed
A) The economy is operating at full employment
B) There is inflation in the economy
C) There is no public sector in the economy
D) The average price level in the economy is fixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
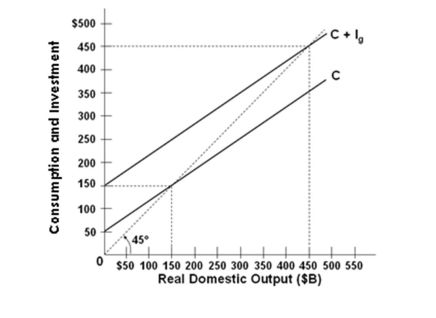 Refer to the graph above for a private closed economy. At the equilibrium level of GDP, saving will be:
Refer to the graph above for a private closed economy. At the equilibrium level of GDP, saving will be:A) $50 billion
B) $100 billion
C) $150 billion
D) Cannot be determined from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
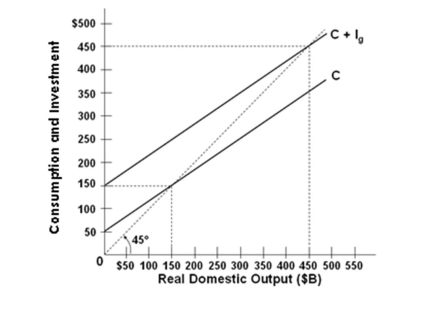 Refer to the graph above for a private closed economy. In this economy, investment is:
Refer to the graph above for a private closed economy. In this economy, investment is:A) $50 billion
B) $100 billion
C) $150 billion
D) $200 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The data below are for a private (no government) closed economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 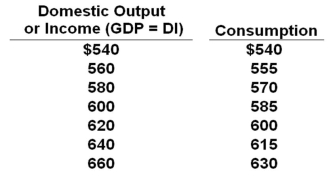 Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $18 billion, then at the $660 billion level of disposable income, there will be an:
Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $18 billion, then at the $660 billion level of disposable income, there will be an:
A) Unplanned increase in inventories of $12 billion
B) Unplanned increase in inventories of $30 billion
C) Unplanned decrease in inventories of $12 billion
D) Unplanned decrease in inventories of $30 billion
 Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $18 billion, then at the $660 billion level of disposable income, there will be an:
Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $18 billion, then at the $660 billion level of disposable income, there will be an:A) Unplanned increase in inventories of $12 billion
B) Unplanned increase in inventories of $30 billion
C) Unplanned decrease in inventories of $12 billion
D) Unplanned decrease in inventories of $30 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When the economy is at its equilibrium GDP level, all of the following will occur, except:
A) Aggregate expenditures = GDP
B) Inventories will be zero
C) Saving equals planned investment
D) There are no unplanned changes in inventories
A) Aggregate expenditures = GDP
B) Inventories will be zero
C) Saving equals planned investment
D) There are no unplanned changes in inventories

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The table shows a private closed economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 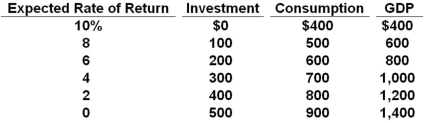 Refer to the table above. An increase in the real interest rate from 2% to 6% will:
Refer to the table above. An increase in the real interest rate from 2% to 6% will:
A) Decrease the equilibrium level of GDP by $200 billion
B) Decrease the equilibrium level of GDP by $300 billion
C) Decrease the equilibrium level of GDP by $400 billion
D) Increase the equilibrium level of GDP by $400 billion
 Refer to the table above. An increase in the real interest rate from 2% to 6% will:
Refer to the table above. An increase in the real interest rate from 2% to 6% will:A) Decrease the equilibrium level of GDP by $200 billion
B) Decrease the equilibrium level of GDP by $300 billion
C) Decrease the equilibrium level of GDP by $400 billion
D) Increase the equilibrium level of GDP by $400 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Saving is $15 billion at the $125 billion equilibrium level of output in a closed, private economy. Actual investment must be:
A) Less than saving
B) Greater than saving
C) Equal to $15 billion
D) Equal to $125 billion
A) Less than saving
B) Greater than saving
C) Equal to $15 billion
D) Equal to $125 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When saving is less than planned investment in the aggregate expenditures model of a private closed economy then:
A) Real GDP will decrease
B) The rate of interest will decline
C) There will be a decline in the price level
D) There will be a rise in real GDP
A) Real GDP will decrease
B) The rate of interest will decline
C) There will be a decline in the price level
D) There will be a rise in real GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The table shows a private closed economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 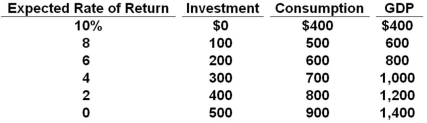 Refer to the table above. If the real rate of interest is 2%, then the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
Refer to the table above. If the real rate of interest is 2%, then the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
A) $800 billion
B) $1000 billion
C) $1200 billion
D) $1400 billion
 Refer to the table above. If the real rate of interest is 2%, then the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
Refer to the table above. If the real rate of interest is 2%, then the equilibrium level of GDP will be:A) $800 billion
B) $1000 billion
C) $1200 billion
D) $1400 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If GDP exceeds aggregate expenditures in a private closed economy:
A) Saving will exceed planned investment
B) Planned investment will exceed saving
C) Planned investment will exceed actual investment
D) Injections will exceed leakages
A) Saving will exceed planned investment
B) Planned investment will exceed saving
C) Planned investment will exceed actual investment
D) Injections will exceed leakages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In the flow of income and spending, saving and investment are, respectively:
A) An injection and a leakage
B) A leakage and an injection
C) Wealth and income
D) Income and wealth
A) An injection and a leakage
B) A leakage and an injection
C) Wealth and income
D) Income and wealth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
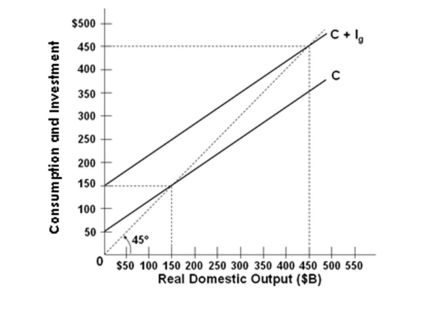 Refer to the graph above for a private closed economy. The equilibrium level of GDP in this economy is:
Refer to the graph above for a private closed economy. The equilibrium level of GDP in this economy is:A) $150 billion
B) $250 billion
C) $350 billion
D) $450 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
All figures below are in billions of dollars. 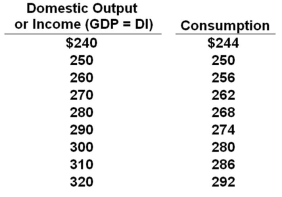 Refer to the table above. Suppose investment is $12 billion and the economy revises its saving plans so as to save $4 billion less at all levels of income. The new equilibrium GDP will be:
Refer to the table above. Suppose investment is $12 billion and the economy revises its saving plans so as to save $4 billion less at all levels of income. The new equilibrium GDP will be:
A) $260 billion
B) $270 billion
C) $280 billion
D) $290 billion
 Refer to the table above. Suppose investment is $12 billion and the economy revises its saving plans so as to save $4 billion less at all levels of income. The new equilibrium GDP will be:
Refer to the table above. Suppose investment is $12 billion and the economy revises its saving plans so as to save $4 billion less at all levels of income. The new equilibrium GDP will be:A) $260 billion
B) $270 billion
C) $280 billion
D) $290 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
All figures below are in billions of dollars. 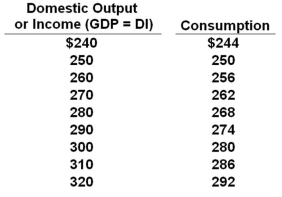 Refer to the table above. When there is no investment in this private closed economy, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
Refer to the table above. When there is no investment in this private closed economy, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
A) $240 billion
B) $250 billion
C) $260 billion
D) $270 billion
 Refer to the table above. When there is no investment in this private closed economy, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
Refer to the table above. When there is no investment in this private closed economy, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:A) $240 billion
B) $250 billion
C) $260 billion
D) $270 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When planned investment exceeds saving in a private closed economy:
A) Aggregate expenditures will equal GDP
B) Aggregate expenditures will exceed GDP
C) Aggregate expenditures will be less than GDP
D) Consumption plus investment will equal GDP
A) Aggregate expenditures will equal GDP
B) Aggregate expenditures will exceed GDP
C) Aggregate expenditures will be less than GDP
D) Consumption plus investment will equal GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
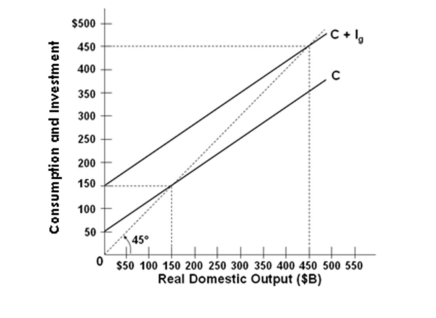 Refer to the graph above for a private closed economy. At the $150-billion level of GDP:
Refer to the graph above for a private closed economy. At the $150-billion level of GDP:A) Aggregate expenditures are less than real GDP, so GDP will rise
B) Aggregate expenditures are more than real GDP, so GDP will fall
C) Aggregate expenditures are more than real GDP, so GDP will rise
D) Aggregate expenditures will be equal to GDP, so there will be no change in GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If actual investment exceeds planned investment in a private closed economy, then:
A) Real GDP will decrease
B) Real GDP will increase
C) Saving exceeds planned investment
D) There is an unplanned decrease in inventories
A) Real GDP will decrease
B) Real GDP will increase
C) Saving exceeds planned investment
D) There is an unplanned decrease in inventories

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
All figures below are in billions of dollars. 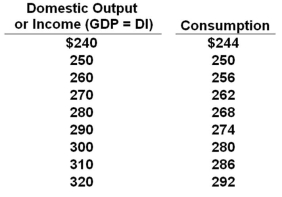 Refer to the table above. If gross investment is $12 billion, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
Refer to the table above. If gross investment is $12 billion, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
A) $260 billion
B) $270 billion
C) $280 billion
D) $290 billion
 Refer to the table above. If gross investment is $12 billion, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:
Refer to the table above. If gross investment is $12 billion, the equilibrium level of GDP will be:A) $260 billion
B) $270 billion
C) $280 billion
D) $290 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
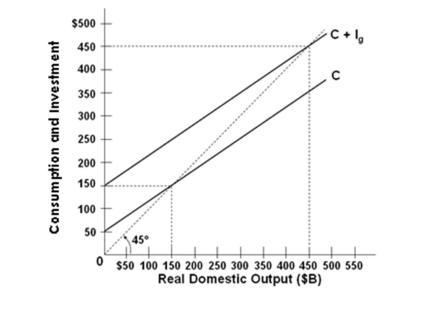 Refer to the graph above for a private closed economy. When output or income is $350 billion there will be:
Refer to the graph above for a private closed economy. When output or income is $350 billion there will be:A) Equilibrium GDP
B) Saving exceeding planned investment
C) Unplanned increases in inventories
D) Unplanned decreases in inventories

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Planned investment is $20 billion and saving is $15 billion when GDP in the economy is $180 billion. The economy is:
A) At the equilibrium level of GDP
B) In disequilibrium and its GDP will increase
C) In disequilibrium and its GDP will decrease
D) Having a GDP level that is greater than its aggregate expenditures
A) At the equilibrium level of GDP
B) In disequilibrium and its GDP will increase
C) In disequilibrium and its GDP will decrease
D) Having a GDP level that is greater than its aggregate expenditures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
All of the following are true when there is an unplanned decrease in inventories, except:
A) GDP is less than aggregate expenditures
B) Saving is less than planned investment
C) Actual investment is greater than planned investment
D) Real GDP will be rising
A) GDP is less than aggregate expenditures
B) Saving is less than planned investment
C) Actual investment is greater than planned investment
D) Real GDP will be rising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Recently, the level of GDP has declined by $60 billion in an economy where the marginal propensity to consume is 0.75. Aggregate expenditures must have fallen by:
A) $45 billion
B) $30 billion
C) $15 billion
D) $60 billion
A) $45 billion
B) $30 billion
C) $15 billion
D) $60 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The table shows a private open economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 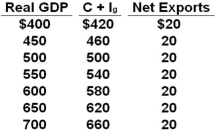 Refer to the above table. The equilibrium real GDP is:
Refer to the above table. The equilibrium real GDP is:
A) $550
B) $600
C) $650
D) $700
 Refer to the above table. The equilibrium real GDP is:
Refer to the above table. The equilibrium real GDP is:A) $550
B) $600
C) $650
D) $700

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the MPC in an economy is 0.75 and aggregate expenditures increase by $5 billion, then equilibrium GDP will increase by:
A) $3.75 billion
B) $6.7 billion
C) $8.75 billion
D) $20 billion
A) $3.75 billion
B) $6.7 billion
C) $8.75 billion
D) $20 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The marginal propensity to save is 0.2. Equilibrium GDP will decrease by $50 billion if aggregate expenditures schedule decrease by:
A) $10 billion
B) $15 billion
C) $16 billion
D) $40 billion
A) $10 billion
B) $15 billion
C) $16 billion
D) $40 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A newspaper story states: "For the fourth straight quarter, the nation purchased more goods from abroad than ever before." The event described would:
A) Increase the equilibrium level of GDP
B) Decrease the equilibrium level of GDP
C) Make no change in the equilibrium level of GDP
D) Increase, decrease, or make no change in the equilibrium level of GDP; we cannot tell from the information given
A) Increase the equilibrium level of GDP
B) Decrease the equilibrium level of GDP
C) Make no change in the equilibrium level of GDP
D) Increase, decrease, or make no change in the equilibrium level of GDP; we cannot tell from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Saving is $40 billion and planned investment is $28 billion at the $175 billion level of output in a private closed economy. At this level:
A) Consumption will be $147 billion
B) Actual investment will be $28 billion
C) Unplanned investment will be positive $12 billion
D) Unplanned investment will be negative $12 billion
A) Consumption will be $147 billion
B) Actual investment will be $28 billion
C) Unplanned investment will be positive $12 billion
D) Unplanned investment will be negative $12 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The table shows a private open economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 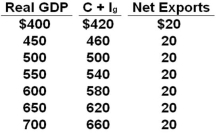 Refer to the above table. If net exports increased by $10 billion at each level of GDP, the equilibrium real GDP would be:
Refer to the above table. If net exports increased by $10 billion at each level of GDP, the equilibrium real GDP would be:
A) Not determinate in the table
B) $610
C) $650
D) $700
 Refer to the above table. If net exports increased by $10 billion at each level of GDP, the equilibrium real GDP would be:
Refer to the above table. If net exports increased by $10 billion at each level of GDP, the equilibrium real GDP would be:A) Not determinate in the table
B) $610
C) $650
D) $700

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
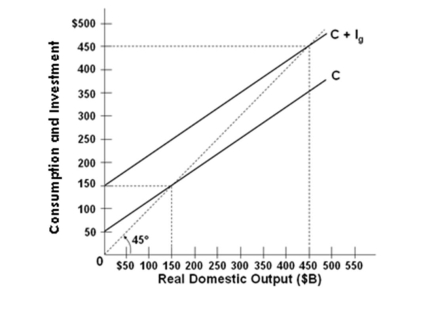 Refer to the above graph for a private closed economy. The multiplier for the above economy is:
Refer to the above graph for a private closed economy. The multiplier for the above economy is:A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Actual investment is $28 billion and saving is $15 billion at the $166 billion level of output in a private closed economy. At this level:
A) Consumption will be $151 billion
B) Planned investment will be $13 billion
C) Unplanned investment will be $15 billion
D) Planned investment minus saving will be $38 billion
A) Consumption will be $151 billion
B) Planned investment will be $13 billion
C) Unplanned investment will be $15 billion
D) Planned investment minus saving will be $38 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
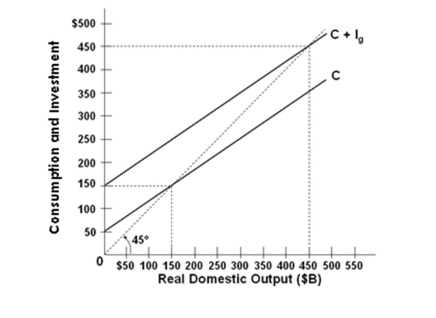 Refer to the above graph for a private closed economy. If the consumption schedule shifts up by $50 B at all levels of income or output, then the equilibrium GDP will increase to:
Refer to the above graph for a private closed economy. If the consumption schedule shifts up by $50 B at all levels of income or output, then the equilibrium GDP will increase to:A) $550 B
B) $300 B
C) $600 B
D) $150 B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
All figures in the table below are in billions. 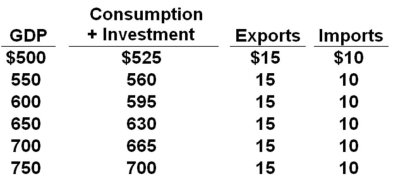 Refer to the above data. The equilibrium level of GDP in this private open economy is:
Refer to the above data. The equilibrium level of GDP in this private open economy is:
A) $550 billion
B) $600 billion
C) $650 billion
D) $700 billion
 Refer to the above data. The equilibrium level of GDP in this private open economy is:
Refer to the above data. The equilibrium level of GDP in this private open economy is:A) $550 billion
B) $600 billion
C) $650 billion
D) $700 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In a private closed economy where MPC = 0.8, if consumers reduce their spending by $10 billion and firms cut investments by $5 billion, then equilibrium GDP will decrease by:
A) $75 billion
B) $25 billion
C) $18.8 billion
D) $15 billion
A) $75 billion
B) $25 billion
C) $18.8 billion
D) $15 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Other things being equal, the effect of a downward shift of the economy's net export schedule on equilibrium GDP will be similar to a(n):
A) Rightward shift in the investment-demand schedule
B) Downward shift in the consumption schedule
C) Upward shift in the consumption schedule
D) Upward shift in the investment schedule
A) Rightward shift in the investment-demand schedule
B) Downward shift in the consumption schedule
C) Upward shift in the consumption schedule
D) Upward shift in the investment schedule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The table shows a private open economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 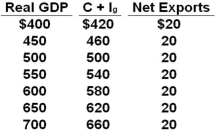 Refer to the above table. If the investment Ig in this economy is independent of income GDP, then a $10 increase in its net exports would increase its equilibrium real GDP by:
Refer to the above table. If the investment Ig in this economy is independent of income GDP, then a $10 increase in its net exports would increase its equilibrium real GDP by:
A) $25
B) $50
C) $100
D) $200
 Refer to the above table. If the investment Ig in this economy is independent of income GDP, then a $10 increase in its net exports would increase its equilibrium real GDP by:
Refer to the above table. If the investment Ig in this economy is independent of income GDP, then a $10 increase in its net exports would increase its equilibrium real GDP by:A) $25
B) $50
C) $100
D) $200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) An increase in exports will tend to increase, and an increase in imports will tend to decrease, the equilibrium GDP
B) An increase in exports and an increase in imports will both tend to increase the equilibrium GDP
C) An increase in exports and an increase in imports will both tend to decrease the equilibrium GDP
D) An increase in exports will tend to decrease, and an increase in imports will tend to increase, the equilibrium GDP
A) An increase in exports will tend to increase, and an increase in imports will tend to decrease, the equilibrium GDP
B) An increase in exports and an increase in imports will both tend to increase the equilibrium GDP
C) An increase in exports and an increase in imports will both tend to decrease the equilibrium GDP
D) An increase in exports will tend to decrease, and an increase in imports will tend to increase, the equilibrium GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Net exports are negative when:
A) Net exports exceed imports
B) Depreciation exceeds exports
C) Exports exceed imports
D) Imports exceed exports
A) Net exports exceed imports
B) Depreciation exceeds exports
C) Exports exceed imports
D) Imports exceed exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Consumption is $141 billion, planned investment is $15 billion, and saving is $15 billion in a private, closed economy. At this level:
A) Actual investment does not equal planned investment
B) There will be unplanned increases in inventories
C) There will be unplanned decreases in inventories
D) The economy is in equilibrium
A) Actual investment does not equal planned investment
B) There will be unplanned increases in inventories
C) There will be unplanned decreases in inventories
D) The economy is in equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Other things constant, if domestic consumers purchase fewer foreign goods at each level of GDP in the short run:
A) GDP will rise
B) GDP will fall
C) Foreign countries' GDP will rise
D) There will be no change in GDP in this country
A) GDP will rise
B) GDP will fall
C) Foreign countries' GDP will rise
D) There will be no change in GDP in this country

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
All figures in the table below are in billions. 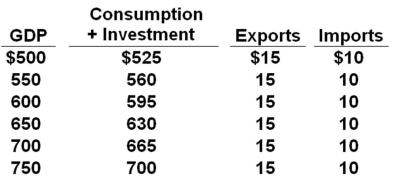 Refer to the above data. If exports increased by $15 billion at each level of GDP, all other factors constant, then the equilibrium level of GDP would be:
Refer to the above data. If exports increased by $15 billion at each level of GDP, all other factors constant, then the equilibrium level of GDP would be:
A) $550 billion
B) $600 billion
C) $650 billion
D) $700 billion
 Refer to the above data. If exports increased by $15 billion at each level of GDP, all other factors constant, then the equilibrium level of GDP would be:
Refer to the above data. If exports increased by $15 billion at each level of GDP, all other factors constant, then the equilibrium level of GDP would be:A) $550 billion
B) $600 billion
C) $650 billion
D) $700 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Other things being equal, a decrease in an economy's exports will:
A) Increase domestic aggregate expenditures and the equilibrium level of GDP
B) Decrease domestic aggregate expenditures and the equilibrium level of GDP
C) Have no effect on domestic GDP because imports will offset the change in exports
D) Increase the amount of imports consumed by the private sector
A) Increase domestic aggregate expenditures and the equilibrium level of GDP
B) Decrease domestic aggregate expenditures and the equilibrium level of GDP
C) Have no effect on domestic GDP because imports will offset the change in exports
D) Increase the amount of imports consumed by the private sector

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The table shows a consumption schedule. All figures are in billions of dollars. 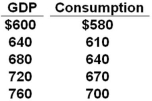 Refer to the above information. If lump-sum taxes were $20 billion, planned investment $45 billion, net exports zero, and government purchases $20 billion, then equilibrium GDP would be:
Refer to the above information. If lump-sum taxes were $20 billion, planned investment $45 billion, net exports zero, and government purchases $20 billion, then equilibrium GDP would be:
A) $640 billion
B) $680 billion
C) $720 billion
D) $760 billion
 Refer to the above information. If lump-sum taxes were $20 billion, planned investment $45 billion, net exports zero, and government purchases $20 billion, then equilibrium GDP would be:
Refer to the above information. If lump-sum taxes were $20 billion, planned investment $45 billion, net exports zero, and government purchases $20 billion, then equilibrium GDP would be:A) $640 billion
B) $680 billion
C) $720 billion
D) $760 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The data below is the consumption schedule in an economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 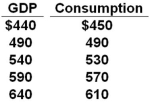 Refer to the above table. If gross investment is $34 billion, net exports are zero, and there is a lump-sum tax of $30 billion at all levels of GDP, then the after-tax equilibrium level of GDP will be:
Refer to the above table. If gross investment is $34 billion, net exports are zero, and there is a lump-sum tax of $30 billion at all levels of GDP, then the after-tax equilibrium level of GDP will be:
A) $490 billion
B) $540 billion
C) $590 billion
D) $640 billion
 Refer to the above table. If gross investment is $34 billion, net exports are zero, and there is a lump-sum tax of $30 billion at all levels of GDP, then the after-tax equilibrium level of GDP will be:
Refer to the above table. If gross investment is $34 billion, net exports are zero, and there is a lump-sum tax of $30 billion at all levels of GDP, then the after-tax equilibrium level of GDP will be:A) $490 billion
B) $540 billion
C) $590 billion
D) $640 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
All figures in the table below are in billions of dollars.  Refer to the above data. If this economy were closed to international trade, then the equilibrium GDP and the multiplier would be:
Refer to the above data. If this economy were closed to international trade, then the equilibrium GDP and the multiplier would be:
A) $500 billion and 5
B) $500 billion and 4
C) $600 billion and 5
D) $600 billion and 4
 Refer to the above data. If this economy were closed to international trade, then the equilibrium GDP and the multiplier would be:
Refer to the above data. If this economy were closed to international trade, then the equilibrium GDP and the multiplier would be:A) $500 billion and 5
B) $500 billion and 4
C) $600 billion and 5
D) $600 billion and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The data below is the consumption schedule in an economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 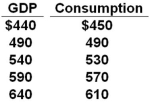 Refer to the above table. Given the level of investment at $34 billion, zero net exports, and a lump-sum tax of $30 billion, the addition of government expenditures of $20 billion at each level of GDP will result in an equilibrium GDP of:
Refer to the above table. Given the level of investment at $34 billion, zero net exports, and a lump-sum tax of $30 billion, the addition of government expenditures of $20 billion at each level of GDP will result in an equilibrium GDP of:
A) $490 billion
B) $540 billion
C) $590 billion
D) $640 billion
 Refer to the above table. Given the level of investment at $34 billion, zero net exports, and a lump-sum tax of $30 billion, the addition of government expenditures of $20 billion at each level of GDP will result in an equilibrium GDP of:
Refer to the above table. Given the level of investment at $34 billion, zero net exports, and a lump-sum tax of $30 billion, the addition of government expenditures of $20 billion at each level of GDP will result in an equilibrium GDP of:A) $490 billion
B) $540 billion
C) $590 billion
D) $640 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the aggregate expenditures model, we note that an increase in government purchases G and an increase in lump-sum taxes T of the same amount will have:
A) The same magnitudes of impact on equilibrium GDP, though in opposite directions
B) Different effects on GDP, with the change in G having a larger impact than the change in T
C) Different effects on GDP, with the change in T having a larger impact than the change in G
D) Essentially the same effect on equilibrium GDP, both in magnitude and in direction
A) The same magnitudes of impact on equilibrium GDP, though in opposite directions
B) Different effects on GDP, with the change in G having a larger impact than the change in T
C) Different effects on GDP, with the change in T having a larger impact than the change in G
D) Essentially the same effect on equilibrium GDP, both in magnitude and in direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
All figures in the table below are in billions of dollars. 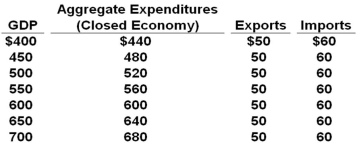 Refer to the above data. If this economy were an open economy, the equilibrium GDP will be:
Refer to the above data. If this economy were an open economy, the equilibrium GDP will be:
A) $650 billion
B) $600 billion
C) $550 billion
D) $500 billion
 Refer to the above data. If this economy were an open economy, the equilibrium GDP will be:
Refer to the above data. If this economy were an open economy, the equilibrium GDP will be:A) $650 billion
B) $600 billion
C) $550 billion
D) $500 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
All figures in the table below are in billions of dollars. 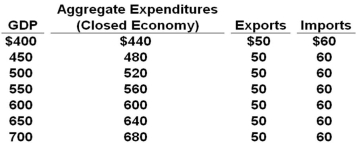 Refer to the above data. If exports should decrease by $20 billion at each level of GDP, other factors constant, then the equilibrium GDP for the economy will be:
Refer to the above data. If exports should decrease by $20 billion at each level of GDP, other factors constant, then the equilibrium GDP for the economy will be:
A) $650 billion
B) $550 billion
C) $500 billion
D) $450 billion
 Refer to the above data. If exports should decrease by $20 billion at each level of GDP, other factors constant, then the equilibrium GDP for the economy will be:
Refer to the above data. If exports should decrease by $20 billion at each level of GDP, other factors constant, then the equilibrium GDP for the economy will be:A) $650 billion
B) $550 billion
C) $500 billion
D) $450 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which event would most likely decrease an economy's exports?
A) A decline in the tariff on products imported from abroad
B) An increase the prosperity of trading partners for this economy
C) An appreciation of the nation's currency relative to foreign currencies
D) A depreciation of the nation's currency relative to foreign currencies
A) A decline in the tariff on products imported from abroad
B) An increase the prosperity of trading partners for this economy
C) An appreciation of the nation's currency relative to foreign currencies
D) A depreciation of the nation's currency relative to foreign currencies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
All figures in the table below are in billions of dollars. 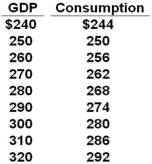 Refer to the above data. Gross investment is $8 billion, net exports are $4 billion, and government collects a lump-sum tax of $30 billion and spends $30 billion. Assume all taxes are personal taxes and that government spending does not entail shifts in the consumption and investment schedules. The equilibrium GDP will be:
Refer to the above data. Gross investment is $8 billion, net exports are $4 billion, and government collects a lump-sum tax of $30 billion and spends $30 billion. Assume all taxes are personal taxes and that government spending does not entail shifts in the consumption and investment schedules. The equilibrium GDP will be:
A) $280 billion
B) $290 billion
C) $300 billion
D) $310 billion
 Refer to the above data. Gross investment is $8 billion, net exports are $4 billion, and government collects a lump-sum tax of $30 billion and spends $30 billion. Assume all taxes are personal taxes and that government spending does not entail shifts in the consumption and investment schedules. The equilibrium GDP will be:
Refer to the above data. Gross investment is $8 billion, net exports are $4 billion, and government collects a lump-sum tax of $30 billion and spends $30 billion. Assume all taxes are personal taxes and that government spending does not entail shifts in the consumption and investment schedules. The equilibrium GDP will be:A) $280 billion
B) $290 billion
C) $300 billion
D) $310 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a lump-sum tax of $40 billion is levied at each level of income and the MPC is 0.75, then the saving schedule will shift:
A) Upward by $10 billion
B) Upward by $25 billion
C) Downward by $10 billion
D) Downward by $25 billion
A) Upward by $10 billion
B) Upward by $25 billion
C) Downward by $10 billion
D) Downward by $25 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the aggregate expenditures model of the economy, a downward shift in aggregate expenditures can be caused by a:
A) Decrease in government spending or an increase in taxes
B) Decrease in taxes or an increase in government spending
C) Decrease in interest rates or a decrease in taxes
D) Decrease in saving or an increase in government spending
A) Decrease in government spending or an increase in taxes
B) Decrease in taxes or an increase in government spending
C) Decrease in interest rates or a decrease in taxes
D) Decrease in saving or an increase in government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The data below is the consumption schedule in an economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 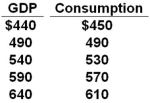 Refer to the above table. If a government sector is introduced and a lump-sum tax of $30 billion is imposed at all levels of GDP, then the consumption column in the table becomes:
Refer to the above table. If a government sector is introduced and a lump-sum tax of $30 billion is imposed at all levels of GDP, then the consumption column in the table becomes:
A) $420, 460, 500, 540, 580
B) $426, 466, 506, 546, 586
C) $430, 470, 510, 550, 590
D) $432, 472, 512, 552, 592
 Refer to the above table. If a government sector is introduced and a lump-sum tax of $30 billion is imposed at all levels of GDP, then the consumption column in the table becomes:
Refer to the above table. If a government sector is introduced and a lump-sum tax of $30 billion is imposed at all levels of GDP, then the consumption column in the table becomes:A) $420, 460, 500, 540, 580
B) $426, 466, 506, 546, 586
C) $430, 470, 510, 550, 590
D) $432, 472, 512, 552, 592

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
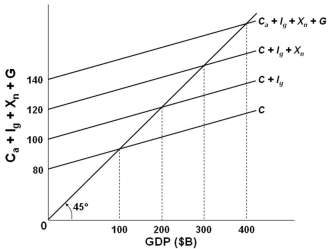 In the above graph it is assumed that investment, net exports, and government expenditures:
In the above graph it is assumed that investment, net exports, and government expenditures:A) Are all increasing
B) Vary directly with GDP
C) Vary inversely with GDP
D) Are independent of GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The table shows the consumption schedule for a hypothetical economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 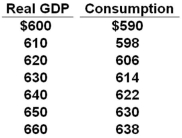 Refer to the above table. If planned investments were fixed at $16, taxes were zero, government purchases of goods and services were zero, and net exports were zero, then equilibrium real GDP would be $630 initially. If government purchases were then raised from $0 to $10, and lump-sum taxes also increased from $0 to $10, other things constant, then the equilibrium real GDP would become:
Refer to the above table. If planned investments were fixed at $16, taxes were zero, government purchases of goods and services were zero, and net exports were zero, then equilibrium real GDP would be $630 initially. If government purchases were then raised from $0 to $10, and lump-sum taxes also increased from $0 to $10, other things constant, then the equilibrium real GDP would become:
A) $660
B) $630
C) $640
D) $650
 Refer to the above table. If planned investments were fixed at $16, taxes were zero, government purchases of goods and services were zero, and net exports were zero, then equilibrium real GDP would be $630 initially. If government purchases were then raised from $0 to $10, and lump-sum taxes also increased from $0 to $10, other things constant, then the equilibrium real GDP would become:
Refer to the above table. If planned investments were fixed at $16, taxes were zero, government purchases of goods and services were zero, and net exports were zero, then equilibrium real GDP would be $630 initially. If government purchases were then raised from $0 to $10, and lump-sum taxes also increased from $0 to $10, other things constant, then the equilibrium real GDP would become:A) $660
B) $630
C) $640
D) $650

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
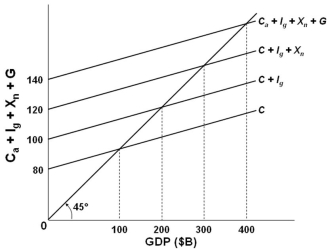 Refer to the above graph. If this economy was an open economy without a government sector, the level of GDP would be:
Refer to the above graph. If this economy was an open economy without a government sector, the level of GDP would be:A) $100 billion
B) $200 billion
C) $300 billion
D) $400 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The table shows the consumption schedule for a hypothetical economy. All figures are in billions of dollars. 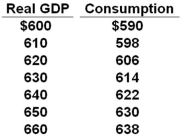 Refer to the above table. If planned investments were fixed at $16, taxes were zero, government purchases of goods and services were zero, and net exports were zero, then equilibrium real GDP would be $630 initially. If government purchases were then raised from $0 to $4, other things constant, then the equilibrium real GDP would become:
Refer to the above table. If planned investments were fixed at $16, taxes were zero, government purchases of goods and services were zero, and net exports were zero, then equilibrium real GDP would be $630 initially. If government purchases were then raised from $0 to $4, other things constant, then the equilibrium real GDP would become:
A) $660
B) $630
C) $640
D) $650
 Refer to the above table. If planned investments were fixed at $16, taxes were zero, government purchases of goods and services were zero, and net exports were zero, then equilibrium real GDP would be $630 initially. If government purchases were then raised from $0 to $4, other things constant, then the equilibrium real GDP would become:
Refer to the above table. If planned investments were fixed at $16, taxes were zero, government purchases of goods and services were zero, and net exports were zero, then equilibrium real GDP would be $630 initially. If government purchases were then raised from $0 to $4, other things constant, then the equilibrium real GDP would become:A) $660
B) $630
C) $640
D) $650

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Over time, an increase in the real output and incomes of the trading partners of the United States will most likely:
A) Increase U.S. exports
B) Decrease U.S. exports
C) Increase imports of the U.S.
D) Decrease imports of the U.S.
A) Increase U.S. exports
B) Decrease U.S. exports
C) Increase imports of the U.S.
D) Decrease imports of the U.S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A tax-cut will have a greater effect on equilibrium GDP if the:
A) Marginal propensity to consume is smaller
B) Marginal propensity to save is smaller
C) Marginal propensity to save is larger
D) Average propensity to consume is larger
A) Marginal propensity to consume is smaller
B) Marginal propensity to save is smaller
C) Marginal propensity to save is larger
D) Average propensity to consume is larger

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the likely result from a depreciation of a nation's currency when its economy is already operating at its full-employment level of output?
A) Net exports fall and contribute to demand-pull inflation
B) Net exports rise and contribute to demand-pull inflation
C) Net exports fall, but equilibrium GDP rises
D) Net exports rise, but equilibrium GDP falls
A) Net exports fall and contribute to demand-pull inflation
B) Net exports rise and contribute to demand-pull inflation
C) Net exports fall, but equilibrium GDP rises
D) Net exports rise, but equilibrium GDP falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The table shows a consumption schedule. All figures are in billions of dollars. 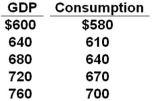 Refer to the above information. If planned investment was $20 billion, government purchases of goods and services were $20 billion, and taxes and net exports were zero, then the equilibrium level of GDP would be:
Refer to the above information. If planned investment was $20 billion, government purchases of goods and services were $20 billion, and taxes and net exports were zero, then the equilibrium level of GDP would be:
A) $600 billion
B) $640 billion
C) $680 billion
D) $720 billion
 Refer to the above information. If planned investment was $20 billion, government purchases of goods and services were $20 billion, and taxes and net exports were zero, then the equilibrium level of GDP would be:
Refer to the above information. If planned investment was $20 billion, government purchases of goods and services were $20 billion, and taxes and net exports were zero, then the equilibrium level of GDP would be:A) $600 billion
B) $640 billion
C) $680 billion
D) $720 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



