Deck 10: Real GDP and the Price Level in the Long Run
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/298
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Real GDP and the Price Level in the Long Run
1
The total of all planned production for the entire economy is known as
A) aggregate expenditures.
B) aggregate demand.
C) aggregate supply.
D) aggregate inflation.
A) aggregate expenditures.
B) aggregate demand.
C) aggregate supply.
D) aggregate inflation.
C
2
All of the following would shift the LRAS curve to the right EXCEPT
A) an increase in the size of the labor force.
B) a net inflow of human capital.
C) an increase in the overall price level.
D) an improvement in technology.
A) an increase in the size of the labor force.
B) a net inflow of human capital.
C) an increase in the overall price level.
D) an improvement in technology.
C
3
The long-run aggregate supply curve is
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
C
4
The long-run aggregate supply curve
A) shifts to the right when there is a tax increase.
B) indicates the level of output (GDP) that occurs when resources are fully employed.
C) indicates that an increase in the overall price level will cause an increase in production.
D) shifts to the right when the Federal Reserve increases the money supply.
A) shifts to the right when there is a tax increase.
B) indicates the level of output (GDP) that occurs when resources are fully employed.
C) indicates that an increase in the overall price level will cause an increase in production.
D) shifts to the right when the Federal Reserve increases the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a nation's production possibilities curve shifts outward, we should expect its long-run aggregate supply curve to
A) have an upward movement along the curve.
B) have a downward movement along the curve.
C) have a rightward shift.
D) have a leftward shift.
A) have an upward movement along the curve.
B) have a downward movement along the curve.
C) have a rightward shift.
D) have a leftward shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The long-run aggregate supply curve is
A) horizontal at the full-employment level of real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
B) vertical at the full-employment level of real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
C) sloping upward due to the effects of price level changes on real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
D) the same as the short run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve.
A) horizontal at the full-employment level of real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
B) vertical at the full-employment level of real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
C) sloping upward due to the effects of price level changes on real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
D) the same as the short run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Long-run aggregate supply is
A) the sum of planned expenditures by consumers and firms.
B) the level of output that occurs when the economy is operating on the production possibilities curve.
C) downward sloping.
D) upward sloping.
A) the sum of planned expenditures by consumers and firms.
B) the level of output that occurs when the economy is operating on the production possibilities curve.
C) downward sloping.
D) upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because
A) the economy has yet to use all its available resources.
B) the economy has reached its potential real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and is at full employment.
C) the economy has contracted.
D) the economy has large numbers of unemployed.
A) the economy has yet to use all its available resources.
B) the economy has reached its potential real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and is at full employment.
C) the economy has contracted.
D) the economy has large numbers of unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The long run aggregate supply curve (LRAS) also represents
A) the full-information level of output.
B) the full-employment level of output.
C) the full-adjustment level of output.
D) all of the above.
A) the full-information level of output.
B) the full-employment level of output.
C) the full-adjustment level of output.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is measured on the vertical axis of the aggregate demand/aggregate supply model?
A) real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
B) nominal income
C) the price level
D) the interest rate
A) real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
B) nominal income
C) the price level
D) the interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The aggregate supply curve
A) shows what each producer is willing and able to produce at each income level.
B) relates planned aggregate production to price level.
C) is the sum of all supply curves of natural resources.
D) shows a negative relationship between the price level and real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
A) shows what each producer is willing and able to produce at each income level.
B) relates planned aggregate production to price level.
C) is the sum of all supply curves of natural resources.
D) shows a negative relationship between the price level and real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) The long-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.
B) The long-run aggregate demand curve is upward sloping.
C) The short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
A) The long-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.
B) The long-run aggregate demand curve is upward sloping.
C) The short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Long-run aggregate supply reflects
A) total production in the economy at full employment.
B) total spending in the economy at full employment.
C) both production and spending in the economy.
D) only foreign production from U.S. subsidiaries.
A) total production in the economy at full employment.
B) total spending in the economy at full employment.
C) both production and spending in the economy.
D) only foreign production from U.S. subsidiaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The full-employment and full-adjustment level of real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in the economy is represented by
A) the LRAS curve.
B) the horizontal line at the price level.
C) the AD curve.
D) the distance between the LRAS curve and the AD curve.
A) the LRAS curve.
B) the horizontal line at the price level.
C) the AD curve.
D) the distance between the LRAS curve and the AD curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The long-run aggregate supply curve
A) shows that at higher prices, potential real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increases.
B) slopes up and to the right.
C) shows that long-run aggregate supply equals potential real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
D) is very sensitive to changes in the price level.
A) shows that at higher prices, potential real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increases.
B) slopes up and to the right.
C) shows that long-run aggregate supply equals potential real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
D) is very sensitive to changes in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The long-run aggregate supply curve of an economy corresponds to
A) a point inside the production possibilities curve.
B) a point outside the production possibilities curve.
C) a point on the production possibilities curve.
D) none of the above: there is no relationship between the long-run aggregate supply curve and the production possibilities curve.
A) a point inside the production possibilities curve.
B) a point outside the production possibilities curve.
C) a point on the production possibilities curve.
D) none of the above: there is no relationship between the long-run aggregate supply curve and the production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the aggregate demand/aggregate supply model, the vertical axis shows the values of ________ and the horizontal axis shows the values of ________.
A) the unemployment rate; the inflation rate
B) real Gross Domestic Product (GDP); the price level
C) the price level; real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
D) the inflation rate; the unemployment rate
A) the unemployment rate; the inflation rate
B) real Gross Domestic Product (GDP); the price level
C) the price level; real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
D) the inflation rate; the unemployment rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following will NOT cause a leftward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve?
A) a net outflow of human capital
B) an increase in the costs of obtaining energy resources
C) a reduction in the amount of capital
D) a reduction in government spending
A) a net outflow of human capital
B) an increase in the costs of obtaining energy resources
C) a reduction in the amount of capital
D) a reduction in government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is measured on the horizontal axis of the aggregate demand/aggregate supply model?
A) real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
B) nominal income
C) the price level
D) the interest rate
A) real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
B) nominal income
C) the price level
D) the interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A human resource such as ingenuity can be thought of as
A) a positive for imports.
B) part of a country's endowment.
C) part of government spending programs.
D) a causal factor for aggregate supply shifting left.
A) a positive for imports.
B) part of a country's endowment.
C) part of government spending programs.
D) a causal factor for aggregate supply shifting left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The real output of the economy under conditions of full employment
A) is long-run aggregate supply.
B) is long-run aggregate demand.
C) happens only when there is no inflation.
D) is determined by the real-balance effect.
A) is long-run aggregate supply.
B) is long-run aggregate demand.
C) happens only when there is no inflation.
D) is determined by the real-balance effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
As the capital stock reduces , we would expect the long-run aggregate supply curve to
A) shift left.
B) shift right.
C) remain the same.
D) first shift right, then shift left.
A) shift left.
B) shift right.
C) remain the same.
D) first shift right, then shift left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The full-employment level of GDP is
A) endowments.
B) long-run aggregate demand.
C) long-run aggregate supply.
D) economic growth.
A) endowments.
B) long-run aggregate demand.
C) long-run aggregate supply.
D) economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following will cause the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift? I. Changes in the amount of capital
II) Changes in the price level
III) Changes in the money supply
A) I only
B) II only
C) I, II, and III
D) only I and II
II) Changes in the price level
III) Changes in the money supply
A) I only
B) II only
C) I, II, and III
D) only I and II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A country's long-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left when there is (are)
A) fewer regulatory impediments to business.
B) a discovery of new oil reserves in that country.
C) a reduction in the labor force.
D) a reduction in the money supply.
A) fewer regulatory impediments to business.
B) a discovery of new oil reserves in that country.
C) a reduction in the labor force.
D) a reduction in the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The total of all planned production for the economy is
A) aggregate supply.
B) aggregate demand.
C) endowments.
D) real-balance effect.
A) aggregate supply.
B) aggregate demand.
C) endowments.
D) real-balance effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Economic growth can be depicted as
A) a shift of the LRAS curve to the left.
B) an inward shift of the production possibilities curve.
C) a shift of the LRAS curve to the right.
D) a movement along the production possibilities curve.
A) a shift of the LRAS curve to the left.
B) an inward shift of the production possibilities curve.
C) a shift of the LRAS curve to the right.
D) a movement along the production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The long-run aggregate supply curve occurs at the level of real GDP consistent with
A) individuals' tastes and preferences.
B) the natural rate of unemployment.
C) no inflation.
D) low levels of inflation.
A) individuals' tastes and preferences.
B) the natural rate of unemployment.
C) no inflation.
D) low levels of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The position of the long-run aggregate supply curve is determined by
A) the long-run aggregate demand curve.
B) the production possibilities curve.
C) the open economy effect.
D) the interest rate effect.
A) the long-run aggregate demand curve.
B) the production possibilities curve.
C) the open economy effect.
D) the interest rate effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An assumption on the LRAS curve is
A) technology remains unchanged.
B) an increase in the average price level occurs.
C) the economy is operating to the right of the production possibilities curve.
D) labor productivity is increasing.
A) technology remains unchanged.
B) an increase in the average price level occurs.
C) the economy is operating to the right of the production possibilities curve.
D) labor productivity is increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The total of all planned production for the economy is
A) determined only by individuals and firms.
B) determined only by the government.
C) aggregate demand.
D) aggregate supply.
A) determined only by individuals and firms.
B) determined only by the government.
C) aggregate demand.
D) aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The long-run aggregate supply curve is
A) horizontal.
B) vertical.
C) upward sloping.
D) downward sloping.
A) horizontal.
B) vertical.
C) upward sloping.
D) downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The long run aggregate supply curve is vertical because
A) the production possibilities curve is vertical.
B) the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.
C) technology increases at a constant rate.
D) a change in the level of prices will have no effect on real output in the long-run.
A) the production possibilities curve is vertical.
B) the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.
C) technology increases at a constant rate.
D) a change in the level of prices will have no effect on real output in the long-run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following does NOT affect the long-run aggregate supply curve?
A) technology
B) production possibilities curve
C) endowments of resources
D) price level
A) technology
B) production possibilities curve
C) endowments of resources
D) price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Aggregate supply is
A) the summation of all product supply curves.
B) the horizontal summation of all supply curves for services.
C) the stock of all goods in the economy.
D) the sum of all planned production in the economy.
A) the summation of all product supply curves.
B) the horizontal summation of all supply curves for services.
C) the stock of all goods in the economy.
D) the sum of all planned production in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The long-run aggregate supply when resources are fully employed
A) has no relationship with the production possibilities curve.
B) will always be associated with a point outside the production possibilities curve.
C) will always be associated with a point on the production possibilities curve.
D) is determined by demand.
A) has no relationship with the production possibilities curve.
B) will always be associated with a point outside the production possibilities curve.
C) will always be associated with a point on the production possibilities curve.
D) is determined by demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When talking about aggregate supply, it is necessary to
A) focus on the short run.
B) focus on the long run.
C) distinguish between the long-run aggregate supply curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) distinguish between the long-run aggregate supply curve and the long run aggregate demand curve when all adjustments to price level changes have been made.
A) focus on the short run.
B) focus on the long run.
C) distinguish between the long-run aggregate supply curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) distinguish between the long-run aggregate supply curve and the long run aggregate demand curve when all adjustments to price level changes have been made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The long-run aggregate supply will increase when
A) labor supply decreases.
B) international trade barriers are removed.
C) the price level increases.
D) tax rates increase.
A) labor supply decreases.
B) international trade barriers are removed.
C) the price level increases.
D) tax rates increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Over time in a growing economy, the long run aggregate supply curve will
A) move so as to match the short run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve.
B) shift outward to the right.
C) shift inward to the left.
D) become increasingly steep.
A) move so as to match the short run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve.
B) shift outward to the right.
C) shift inward to the left.
D) become increasingly steep.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An increase in the level of prices of goods and services will do what to the long-run aggregate supply curve?
A) shift it to the right
B) shift it to the left
C) a movement along the curve
D) make the curve flat
A) shift it to the right
B) shift it to the left
C) a movement along the curve
D) make the curve flat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The level of real GDP identified by the long-run aggregate supply curve is
A) the full-employment level of real GDP.
B) the level of GDP at which each business firm is experiencing growth in sales.
C) the level of GDP at which each industry is experiencing growth in sales.
D) the level of GDP at which no one is below the poverty line.
A) the full-employment level of real GDP.
B) the level of GDP at which each business firm is experiencing growth in sales.
C) the level of GDP at which each industry is experiencing growth in sales.
D) the level of GDP at which no one is below the poverty line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The long-run aggregate supply curve will shift outward to the right when
A) there is economic growth.
B) the price level decreases.
C) government spending increases.
D) the amount of labor decreases.
A) there is economic growth.
B) the price level decreases.
C) government spending increases.
D) the amount of labor decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The aggregate supply curve cannot tell us
A) anything about the quantity demanded of all commodities and the price level.
B) what the effect of changes in interest rates will be on real GDP.
C) how the total dollar values of spending will ultimately be divided between output and prices.
D) how changes in the price level affect quantity demanded of all commodities.
A) anything about the quantity demanded of all commodities and the price level.
B) what the effect of changes in interest rates will be on real GDP.
C) how the total dollar values of spending will ultimately be divided between output and prices.
D) how changes in the price level affect quantity demanded of all commodities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The long-run aggregate supply curve is determined by all of the following EXCEPT
A) aggregate demand.
B) human capital.
C) technology.
D) the amount of resources that exist in the economy.
A) aggregate demand.
B) human capital.
C) technology.
D) the amount of resources that exist in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Economic growth can be thought of as
A) an increase in the price level.
B) a decrease in the price level.
C) an increase in long-run aggregate supply.
D) an increase in aggregate demand.
A) an increase in the price level.
B) a decrease in the price level.
C) an increase in long-run aggregate supply.
D) an increase in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The natural rate of unemployment will help determine
A) the open economy effect.
B) the position of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
C) the level of economic growth in the economy.
D) the slope of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
A) the open economy effect.
B) the position of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
C) the level of economic growth in the economy.
D) the slope of the long-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Aggregate supply
A) is the total amount of raw materials available in an economy.
B) is the overall wealth within an economy.
C) is the total amount of money circulating in an economy.
D) is the total amount of planned production in an economy.
A) is the total amount of raw materials available in an economy.
B) is the overall wealth within an economy.
C) is the total amount of money circulating in an economy.
D) is the total amount of planned production in an economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Real GDP will increase over the long run if
A) prices continually go up.
B) the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts continually to the right.
C) the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts continually to the left.
D) the long-run aggregate demand curve shifts continually to the left.
A) prices continually go up.
B) the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts continually to the right.
C) the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts continually to the left.
D) the long-run aggregate demand curve shifts continually to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
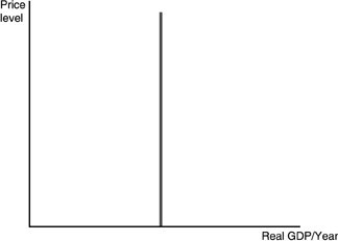
The above figure shows a
A) short-run aggregate demand curve.
B) short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) long-run aggregate demand curve.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The aggregate supply curve shows
A) the total amount of planned production for an economy.
B) the various quantities of goods consumers will purchase.
C) that real GDP can only increase when the price level increases.
D) what an economy can produce if resource prices are constant.
A) the total amount of planned production for an economy.
B) the various quantities of goods consumers will purchase.
C) that real GDP can only increase when the price level increases.
D) what an economy can produce if resource prices are constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
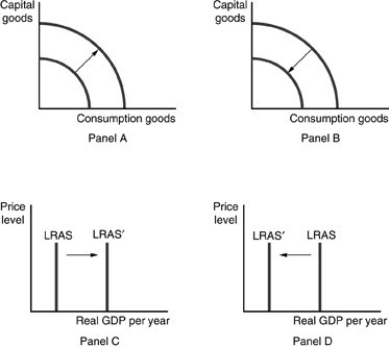
Refer to the above figures. Which panel(s) represent economic growth?
A) Panel A only
B) Panels A and C only
C) Panel D only
D) Panels B and D only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Refer to the above figures. Which panel(s) represent the effect of a decrease in labor productivity?
A) Panel A only
B) Panels A and C only
C) Panel D only
D) Panels B and D only
A) Panel A only
B) Panels A and C only
C) Panel D only
D) Panels B and D only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
We draw the long-run aggregate supply curve as a vertical line to reflect the fact that
A) the productive capacity of the economy never changes after full adjustment has occurred.
B) changes in the price level do not alter the level of long-run real GDP after full adjustment has occurred.
C) technology and resource endowments do not affect long-run real GDP after full adjustment has occurred.
D) an accurate depiction of the production possibilities curve is vertical after full adjustment has occurred.
A) the productive capacity of the economy never changes after full adjustment has occurred.
B) changes in the price level do not alter the level of long-run real GDP after full adjustment has occurred.
C) technology and resource endowments do not affect long-run real GDP after full adjustment has occurred.
D) an accurate depiction of the production possibilities curve is vertical after full adjustment has occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The curve in the above figure will shift to the right when
A) the price level falls.
B) labor productivity increases.
C) population falls.
D) the proportion of the population that is elderly increases.
A) the price level falls.
B) labor productivity increases.
C) population falls.
D) the proportion of the population that is elderly increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following would cause the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the left?
A) an increase in wages
B) a decrease in aggregate demand
C) a decrease in labor productivity
D) a decrease in taxes on profits
A) an increase in wages
B) a decrease in aggregate demand
C) a decrease in labor productivity
D) a decrease in taxes on profits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following will NOT lead to a rightward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve?
A) increase in labor productivity
B) increase in aggregate spending
C) increase in capital
D) increase in labor
A) increase in labor productivity
B) increase in aggregate spending
C) increase in capital
D) increase in labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The long-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left when
A) population decreases.
B) the price level increases.
C) technology improves.
D) new sources of natural resources are discovered.
A) population decreases.
B) the price level increases.
C) technology improves.
D) new sources of natural resources are discovered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The long-run aggregate supply curve can be thought of as the
A) level of output that the nation is currently producing.
B) full-employment level of real GDP.
C) level of real GDP associated with a constant price level.
D) level of output for which real GDP equals nominal GDP.
A) level of output that the nation is currently producing.
B) full-employment level of real GDP.
C) level of real GDP associated with a constant price level.
D) level of output for which real GDP equals nominal GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If our economy is growing at a constant rate of 2 percent per year, then over a period of 20 years we would expect to see which of the following?
A) nice, steady flat-line growth
B) an upward sloping growth path
C) a downward sloping growth path
D) It is impossible to say what kind of growth path we would see.
A) nice, steady flat-line growth
B) an upward sloping growth path
C) a downward sloping growth path
D) It is impossible to say what kind of growth path we would see.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Refer to the above figures. Which panel(s) represent the effect of an increase in the price level?
A) Panel A only
B) Panels A and C only
C) Panel D only
D) none of the panels
A) Panel A only
B) Panels A and C only
C) Panel D only
D) none of the panels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Long-run aggregate supply and a country's production possibility curve (PPC)
A) are closely related.
B) are inversely related.
C) have no relationship.
D) are examples of microeconomic models.
A) are closely related.
B) are inversely related.
C) have no relationship.
D) are examples of microeconomic models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Long-run aggregate supply curve corresponds to
A) real GDP when the economy is above full employment.
B) real GDP when the economy is at full employment.
C) the economy outside its production possibilities curve.
D) the economy inside its production possibilities curve.
A) real GDP when the economy is above full employment.
B) real GDP when the economy is at full employment.
C) the economy outside its production possibilities curve.
D) the economy inside its production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is measured on the vertical axis when we draw a graph of long-run aggregate supply?
A) production of capital goods
B) spending on goods and services in an economy
C) the price level
D) real GDP
A) production of capital goods
B) spending on goods and services in an economy
C) the price level
D) real GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What causes the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift right?
A) economic growth
B) inflation
C) unemployment
D) scarcity
A) economic growth
B) inflation
C) unemployment
D) scarcity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The values on the axes of the long-run aggregate supply diagram are
A) real GDP per year and the price level.
B) nominal GDP and the price level.
C) real GDP and interest rates.
D) real GDP and nominal GDP.
A) real GDP per year and the price level.
B) nominal GDP and the price level.
C) real GDP and interest rates.
D) real GDP and nominal GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When the production possibilities curve shifts outward,
A) the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
B) the long-run aggregate supply curve is unchanged.
C) the price level rises in the long run.
D) the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.
A) the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
B) the long-run aggregate supply curve is unchanged.
C) the price level rises in the long run.
D) the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Economic growth is demonstrated by the LRAS as it
A) shifts to the right.
B) shifts to the left.
C) becomes more horizontal.
D) becomes more vertical.
A) shifts to the right.
B) shifts to the left.
C) becomes more horizontal.
D) becomes more vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The slope of the long-run aggregate supply curve is
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) zero.
D) undefined.
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) zero.
D) undefined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The long-run aggregate supply curve assumes that
A) the unemployment rate is more than 9 percent.
B) all factors of production are fully employed.
C) only laborers are fully employed.
D) there is no government purchasing of goods and services.
A) the unemployment rate is more than 9 percent.
B) all factors of production are fully employed.
C) only laborers are fully employed.
D) there is no government purchasing of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Long-run aggregate supply is
A) the possible combinations of real GDP and inputs after full adjustments have been made.
B) the extraction of natural resources.
C) the real production of goods and services after full adjustments have been made.
D) all of the physical and human resources in the economy.
A) the possible combinations of real GDP and inputs after full adjustments have been made.
B) the extraction of natural resources.
C) the real production of goods and services after full adjustments have been made.
D) all of the physical and human resources in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is measured on the horizontal axis when we draw a graph of the long-run aggregate supply curve?
A) production of capital goods
B) production of consumer goods
C) the price level
D) real GDP
A) production of capital goods
B) production of consumer goods
C) the price level
D) real GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Economic growth is represented on the aggregate supply model by a
A) shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
B) shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
C) shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
D) shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
A) shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
B) shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
C) shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
D) shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A long-run aggregate supply curve may graphically be represented as a
A) vertical line.
B) horizontal line.
C) an upward sloping line.
D) a downward sloping line.
A) vertical line.
B) horizontal line.
C) an upward sloping line.
D) a downward sloping line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the shape of the long-run aggregate supply curve? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A rightward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve is caused by
A) an increase in the minimum wage.
B) an increase in the average duration of unemployment.
C) improvements in technology.
D) an increase in the GDP deflator.
A) an increase in the minimum wage.
B) an increase in the average duration of unemployment.
C) improvements in technology.
D) an increase in the GDP deflator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts right at the same time as
A) wages increase.
B) the production possibilities curve shifts outward.
C) the production possibilities curve shifts inward.
D) the inflation rate increases.
A) wages increase.
B) the production possibilities curve shifts outward.
C) the production possibilities curve shifts inward.
D) the inflation rate increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Economic growth causes the
A) production possibilities curve to shift rightward and the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift rightward.
B) production possibilities curve to shift leftward and the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift rightward.
C) production possibilities curve to shift rightward and the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift leftward.
D) production possibilities curve to shift leftward and the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift leftward.
A) production possibilities curve to shift rightward and the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift rightward.
B) production possibilities curve to shift leftward and the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift rightward.
C) production possibilities curve to shift rightward and the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift leftward.
D) production possibilities curve to shift leftward and the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift leftward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Why is the long-run aggregate supply curve a vertical line?
A) At that level of real GDP, the unemployment rate is 0 percent.
B) At that level of real GDP, the inflation rate is 0 percent.
C) At that level of real GDP, the production costs are at their lowest level.
D) At that level of real GDP, production costs have fully adjusted to price changes.
A) At that level of real GDP, the unemployment rate is 0 percent.
B) At that level of real GDP, the inflation rate is 0 percent.
C) At that level of real GDP, the production costs are at their lowest level.
D) At that level of real GDP, production costs have fully adjusted to price changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Economic growth can be shown by
A) a leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
B) no change in the aggregate supply curve.
C) a rightward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
D) a leftward shift in the production possibilities curve.
A) a leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
B) no change in the aggregate supply curve.
C) a rightward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
D) a leftward shift in the production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The long-run aggregate supply curve is
A) U-shaped.
B) horizontal.
C) upward sloping.
D) vertical.
A) U-shaped.
B) horizontal.
C) upward sloping.
D) vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



