Deck 30: Life in an Age of Globalization 1990 to the Present
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: Life in an Age of Globalization 1990 to the Present
1
What was a major reason for the decline of western European birthrates?
A)Married women entering careers and the related drive for gender equality
B)Increasing rates of homosexuality
C)State policies discouraging childbearing
D)The decline of religious belief
A)Married women entering careers and the related drive for gender equality
B)Increasing rates of homosexuality
C)State policies discouraging childbearing
D)The decline of religious belief
Married women entering careers and the related drive for gender equality
2
What was a characteristic of the multitiered society established by deindustrialization in the twenty-first century?
A)The top tier of society was a small, affluent group of highly paid experts, executives, and professionals.
B)Race or ethnicity seldom determined inclusion in the bottom tier of society.
C)The second tier of the middle class enjoyed rising incomes and an improved standard of living.
D)Workers in the second and third tiers were provided generous welfare and workplace benefits.
A)The top tier of society was a small, affluent group of highly paid experts, executives, and professionals.
B)Race or ethnicity seldom determined inclusion in the bottom tier of society.
C)The second tier of the middle class enjoyed rising incomes and an improved standard of living.
D)Workers in the second and third tiers were provided generous welfare and workplace benefits.
The top tier of society was a small, affluent group of highly paid experts, executives, and professionals.
3
Why did nationalists oppose the proposed European Union Constitution?
A)They refused to abandon their national militaries.
B)They believed other nations and people were inferior.
C)They feared losing political sovereignty and cultural identity.
D)They rejected the undemocratic nature of the EU.
A)They refused to abandon their national militaries.
B)They believed other nations and people were inferior.
C)They feared losing political sovereignty and cultural identity.
D)They rejected the undemocratic nature of the EU.
They feared losing political sovereignty and cultural identity.
4
In addition to the emergence of married career women, why else have European birthrates declined substantially?
A)Expanded availability of effective birth control
B)Decline in religious belief and practice
C)Uninspiring economic conditions
D)Growing infertility as a result of environmental pollution
A)Expanded availability of effective birth control
B)Decline in religious belief and practice
C)Uninspiring economic conditions
D)Growing infertility as a result of environmental pollution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the former Soviet bloc, who were the winners and losers in economic reconstruction?
A)Veterans and factory workers were losers; scholars and organized crime leaders were big winners.
B)Ordinary citizens and the elderly were losers; the young and ex-Communists were winners.
C)Ex-Communists and government officials were losers; skilled technicians and scientists were winners.
D)Corporate managers and bankers were losers; construction workers and the military were winners.
A)Veterans and factory workers were losers; scholars and organized crime leaders were big winners.
B)Ordinary citizens and the elderly were losers; the young and ex-Communists were winners.
C)Ex-Communists and government officials were losers; skilled technicians and scientists were winners.
D)Corporate managers and bankers were losers; construction workers and the military were winners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Persian Gulf War in 1991 clearly demonstrated
A)the disunity among the world community.
B)the lingering resentment of the Arab world against the United States.
C)the effort of the United States and western Europe to promote international consensus under U.S. guidance.
D)U)S. unwillingness to deploy troops in large numbers in the Middle East.
A)the disunity among the world community.
B)the lingering resentment of the Arab world against the United States.
C)the effort of the United States and western Europe to promote international consensus under U.S. guidance.
D)U)S. unwillingness to deploy troops in large numbers in the Middle East.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the consequence of globalization for national economies?
A)They are able to specialize in the production of a smaller range of products.
B)Their commercial wealth can be much more efficiently taxed.
C)They lose all distinctive regional variation.
D)They are much more vulnerable to worldwide economic panics.
A)They are able to specialize in the production of a smaller range of products.
B)Their commercial wealth can be much more efficiently taxed.
C)They lose all distinctive regional variation.
D)They are much more vulnerable to worldwide economic panics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Serbian president Slobodan Milošević's actions in 1990 hastened separatism and civil war in Yugoslavia. His ultimate goal was to establish
A)Greater Serbia.
B)the Muslim League of the Balkans.
C)the League of Communists States.
D)the Commonwealth of Independent States.
A)Greater Serbia.
B)the Muslim League of the Balkans.
C)the League of Communists States.
D)the Commonwealth of Independent States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What was the consequence for European national governments in meeting the fiscal standards to join the monetary union?
A)Governments sparked considerable economic growth as they balanced their budgets.
B)Governments drastically reduced their borrowing, freeing more capital for business investment.
C)Governments had to reduce health and social benefits for their citizens.
D)Governments had to substantially increase taxes on service industries.
A)Governments sparked considerable economic growth as they balanced their budgets.
B)Governments drastically reduced their borrowing, freeing more capital for business investment.
C)Governments had to reduce health and social benefits for their citizens.
D)Governments had to substantially increase taxes on service industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following characterizes the presidency of Vladimir Putin in Russia?
A)He pursued strong free-market reforms that allowed Russia to break free of its socialist economic heritage.
B)He sought Russia's full admission into the European Union and its acceptance as a "normal" state.
C)He reasserted anti-Western Russian nationalism and centralized political authority in the Kremlin.
D)He worked to weed out corruption of Russia's political system in order to secure liberal political gains.
A)He pursued strong free-market reforms that allowed Russia to break free of its socialist economic heritage.
B)He sought Russia's full admission into the European Union and its acceptance as a "normal" state.
C)He reasserted anti-Western Russian nationalism and centralized political authority in the Kremlin.
D)He worked to weed out corruption of Russia's political system in order to secure liberal political gains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Why were Poland, the Czech Republic, and Hungary the most successful eastern European nations at economic modernization?
A)They provided the largest government subsidies to new industries and businesses and repealed most labor laws.
B)They quickly opened their economies to foreign investment and had no labor unions.
C)They had never collectivized agriculture.
D)They were flexible in the adoption of economic policies and had an enthusiastic entrepreneurial class.
A)They provided the largest government subsidies to new industries and businesses and repealed most labor laws.
B)They quickly opened their economies to foreign investment and had no labor unions.
C)They had never collectivized agriculture.
D)They were flexible in the adoption of economic policies and had an enthusiastic entrepreneurial class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What event finally galvanized NATO action against the Bosnian Serbs?
A)The discovery of ethnic-cleansing policies
B)The slaughter of thousands of citizens in Srebrenica
C)The invasion of Bosnia by the regular Serbian army
D)The fear of Russian intervention on the Bosnian Serb side
A)The discovery of ethnic-cleansing policies
B)The slaughter of thousands of citizens in Srebrenica
C)The invasion of Bosnia by the regular Serbian army
D)The fear of Russian intervention on the Bosnian Serb side

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What type of policies do the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, and the World Trade Organization pursue?
A)Socialist policies that promote economic equality
B)Environmental policies that encourage sustainable development
C)Monetary policies to create a single currency
D)Neoliberal economic policies promoting free markets and trade
A)Socialist policies that promote economic equality
B)Environmental policies that encourage sustainable development
C)Monetary policies to create a single currency
D)Neoliberal economic policies promoting free markets and trade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When the Russian government launched rapid privatization in the 1990s, it provided each citizen with a voucher worth
A)1,000 rubles.
B)10,000 rubles.
C)20,000 rubles.
D)100,000 rubles.
A)1,000 rubles.
B)10,000 rubles.
C)20,000 rubles.
D)100,000 rubles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following characterizes the daily life of most immigrants to Europe in the twenty-first century?
A)They live in separate city districts marked by poor housing and crowded conditions.
B)They work as highly trained technical specialists.
C)They refuse to become a part of European art, music, or culture.
D)They de-emphasize their cultural origins by adopting European consumer habits.
A)They live in separate city districts marked by poor housing and crowded conditions.
B)They work as highly trained technical specialists.
C)They refuse to become a part of European art, music, or culture.
D)They de-emphasize their cultural origins by adopting European consumer habits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
It is estimated that between 1993 and 2003, illegal immigration into the European Union
A)remained constant at about 50,000 persons annually.
B)dropped quickly from 50,000 to 10,000 persons per year.
C)rose from 50,000 to about 500,000 persons per year.
D)disappeared entirely owing to tighter border security measures.
A)remained constant at about 50,000 persons annually.
B)dropped quickly from 50,000 to 10,000 persons per year.
C)rose from 50,000 to about 500,000 persons per year.
D)disappeared entirely owing to tighter border security measures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Who is Vladimir Putin?
A)Head of the KGB under Mikhail Gorbachev
B)Leader of the Chechen independence movement
C)President of Russia beginning in 2000
D)Yeltsin's chief economic adviser
A)Head of the KGB under Mikhail Gorbachev
B)Leader of the Chechen independence movement
C)President of Russia beginning in 2000
D)Yeltsin's chief economic adviser

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
At the end of the twentieth century, international trade was deeply affected by the development of the Internet and
A)the deregulation of financial systems.
B)the consolidation of merchant marine networks.
C)the formation of the International Monetary Fund.
D)the establishment of the World Trade Court.
A)the deregulation of financial systems.
B)the consolidation of merchant marine networks.
C)the formation of the International Monetary Fund.
D)the establishment of the World Trade Court.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In 1990, what percentage of the French population believed that there were "too many Arabs"?
A)Less than 5 percent
B)37 percent
C)10 percent
D)70 percent
A)Less than 5 percent
B)37 percent
C)10 percent
D)70 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Why did the rapid economic liberalization of Russia work poorly?
A)Production of many items was concentrated in one or two giant factories.
B)Russia depended too much on investment and management skills from abroad.
C)The government passed too many economic regulations, effectively repressing entrepreneurship.
D)Russia lost access to many raw materials as its empire collapsed.
A)Production of many items was concentrated in one or two giant factories.
B)Russia depended too much on investment and management skills from abroad.
C)The government passed too many economic regulations, effectively repressing entrepreneurship.
D)Russia lost access to many raw materials as its empire collapsed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The deindustrialization of Europe meant that by 2005, the once-booming manufacturing sector employed only about
A)one in two workers.
B)one in three workers.
C)one in eight workers.
D)one in ten workers.
A)one in two workers.
B)one in three workers.
C)one in eight workers.
D)one in ten workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What was the result of the Maastricht Treaty?
A)It established the process by which the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)was dissolved.
B)It provided the basis for the formation of the European Union (EU)and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
C)It outlined the role the World Trade Organization (WTO)would play in the management of trade and tariff agreements.
D)It made available the necessary international financial resources needed for the successful Doctors without Borders campaign against malaria.
A)It established the process by which the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)was dissolved.
B)It provided the basis for the formation of the European Union (EU)and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
C)It outlined the role the World Trade Organization (WTO)would play in the management of trade and tariff agreements.
D)It made available the necessary international financial resources needed for the successful Doctors without Borders campaign against malaria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Some scholars conclude that owing to European population declines, Europeans need to
A)award large government subsidies to Europeans who have large families.
B)recognize that Europe needs and should welcome talented newcomers.
C)promote birth-control methods among migrant communities.
D)tax migrant families for every child that they produce.
A)award large government subsidies to Europeans who have large families.
B)recognize that Europe needs and should welcome talented newcomers.
C)promote birth-control methods among migrant communities.
D)tax migrant families for every child that they produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Europe's Muslim population, estimated in 2010 at 20 million, appears likely to grow by 2025 to 35 million, which would be what percentage of Europe's projected population?
A)2 percent
B)4 percent
C)8 percent
D)10 percent
A)2 percent
B)4 percent
C)8 percent
D)10 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What was the goal of the Muslim Brotherhood when it was founded in Egypt in 1928?
A)A united Arab state in the Middle East
B)National liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law
C)A jihad (struggle)against all of Western society
D)An end to monarchy as a form of government in the Middle East
A)A united Arab state in the Middle East
B)National liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law
C)A jihad (struggle)against all of Western society
D)An end to monarchy as a form of government in the Middle East

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The United States invaded Iraq because American leaders asserted that Iraq
A)had offered sanctuary to Al Qaeda after the United States had driven it out of Afghanistan.
B)was still developing weapons of mass destruction despite a 1991 promise to end all such programs.
C)was threatening to declare war on the United States.
D)was planning to invade Israel.
A)had offered sanctuary to Al Qaeda after the United States had driven it out of Afghanistan.
B)was still developing weapons of mass destruction despite a 1991 promise to end all such programs.
C)was threatening to declare war on the United States.
D)was planning to invade Israel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the average number of children families must have to maintain a stable population?
A)1)2 children
B)1)8 children
C)2)1 children
D)2)4 children
A)1)2 children
B)1)8 children
C)2)1 children
D)2)4 children

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
During the recession that began in 2008, which country struggled to implement an austerity plan in order to receive financial aid from the International Monetary Fund, the European Central Bank, and the European Union?
A)France
B)The Czech Republic
C)Germany
D)Greece
A)France
B)The Czech Republic
C)Germany
D)Greece

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What happened to Czechoslovakia four years after the Velvet Revolution in 1989?
A)It became a member of NATO.
B)It became a member of the European Union.
C)It formed a union with Hungary.
D)It split into the Czech Republic and the Republic of Slovakia.
A)It became a member of NATO.
B)It became a member of the European Union.
C)It formed a union with Hungary.
D)It split into the Czech Republic and the Republic of Slovakia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How did the European response to terrorism differ from the American response?
A)Americans emphasized the need for warfare, while Europeans emphasized that terrorism was best resolved through police and intelligence measures.
B)Americans favored the strong use of force to resist terrorism, while the Europeans favored appeasement.
C)Americans believed that terrorism could be controlled through immigration, while Europeans believed that terrorists had to be attacked in their own countries.
D)Europeans supported strong punishments for terrorists, such as the death penalty, while Americans preferred indefinite incarceration.
A)Americans emphasized the need for warfare, while Europeans emphasized that terrorism was best resolved through police and intelligence measures.
B)Americans favored the strong use of force to resist terrorism, while the Europeans favored appeasement.
C)Americans believed that terrorism could be controlled through immigration, while Europeans believed that terrorists had to be attacked in their own countries.
D)Europeans supported strong punishments for terrorists, such as the death penalty, while Americans preferred indefinite incarceration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following characterizes the support in Great Britain for the war with Iraq that began in 2003?
A)The minority conservative party, the Tories, favored the war, but Labour Party leader Tony Blair refused to involve British troops.
B)British Prime Minister Tony Blair supported the war, but the majority of the population was opposed.
C)The majority of the population favored the war, but the military broadly opposed entrance into the war.
D)The majority Labour Party broadly favored entering the war, but the queen publicly counseled caution and turned the public against the war.
A)The minority conservative party, the Tories, favored the war, but Labour Party leader Tony Blair refused to involve British troops.
B)British Prime Minister Tony Blair supported the war, but the majority of the population was opposed.
C)The majority of the population favored the war, but the military broadly opposed entrance into the war.
D)The majority Labour Party broadly favored entering the war, but the queen publicly counseled caution and turned the public against the war.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What was the Arab Spring event that took place in 2011?
A)An unexpected series of revolts in the Middle East
B)Western economic recession owing to the war in Iraq
C)The rise of the Muslim population in Europe
D)The fusion of Western and Arab music as a result of multiculturalism
A)An unexpected series of revolts in the Middle East
B)Western economic recession owing to the war in Iraq
C)The rise of the Muslim population in Europe
D)The fusion of Western and Arab music as a result of multiculturalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What did the new, pro-Western Serbian government do to Slobodan Milošević in July 2001?
A)Put him on trial in the Serbian capital
B)Turned him over to a war crimes tribunal in the Netherlands to stand trial
C)Allowed him to go into exile in Russia
D)Placed him under indefinite house arrest
A)Put him on trial in the Serbian capital
B)Turned him over to a war crimes tribunal in the Netherlands to stand trial
C)Allowed him to go into exile in Russia
D)Placed him under indefinite house arrest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which country was most troubled by the idea of providing financial aid to nearly bankrupt Eurozone countries in 2012?
A)France
B)The United States
C)Germany
D)The United Kingdom
A)France
B)The United States
C)Germany
D)The United Kingdom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Why did Russia invade Georgia in 2008?
A)To punish Georgia for its support of Chechnya
B)To stop Georgian criticism of Vladimir Putin's domestic policies
C)To support a separatist movement in South Ossetia
D)To intimidate Ukraine and Belarus
A)To punish Georgia for its support of Chechnya
B)To stop Georgian criticism of Vladimir Putin's domestic policies
C)To support a separatist movement in South Ossetia
D)To intimidate Ukraine and Belarus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Some Europeans warned that Europe's rapidly growing Muslim population was not only a security danger but also threatened
A)the West's military power as Muslims joined national armies.
B)the West's fundamental foundation in the Christian faith.
C)the West's social structure as Muslims took middle-class jobs but rejected middle-class values.
D)the West's tradition of freedoms, representative government, and toleration for difference.
A)the West's military power as Muslims joined national armies.
B)the West's fundamental foundation in the Christian faith.
C)the West's social structure as Muslims took middle-class jobs but rejected middle-class values.
D)the West's tradition of freedoms, representative government, and toleration for difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the twenty-first century, which resource could Russia use to assert political influence?
A)Coal
B)Water
C)Oil
D)Natural Gas
A)Coal
B)Water
C)Oil
D)Natural Gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The European promotion of human rights has led the European Union to do which of the following?
A)Intervene militarily in the Balkan War
B)Reinstate the death penalty
C)Insist on the importance of national sovereignty
D)Adopt increasingly socialist economic policies
A)Intervene militarily in the Balkan War
B)Reinstate the death penalty
C)Insist on the importance of national sovereignty
D)Adopt increasingly socialist economic policies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What aspect of American foreign policy under President George W. Bush most troubled leaders of the European Union?
A)The United States increasingly ignored international opinion and pursued its own interests unilaterally.
B)The United States persistently attacked Islamic nations, which created considerable domestic problems in Europe among the large Muslim populations.
C)The United States constantly demonstrated its military superiority to all other nations, leading smaller nations to seek U.S. support rather than maintain European alliances.
D)The United States lacked detailed knowledge about the nations that it was invading.
A)The United States increasingly ignored international opinion and pursued its own interests unilaterally.
B)The United States persistently attacked Islamic nations, which created considerable domestic problems in Europe among the large Muslim populations.
C)The United States constantly demonstrated its military superiority to all other nations, leading smaller nations to seek U.S. support rather than maintain European alliances.
D)The United States lacked detailed knowledge about the nations that it was invading.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In his public calls for jihad (struggle) against the United States and the West, what grievances did Osama bin Laden list?
A)The American way of life, which he saw as an affront to Muslim ideas of morality
B)American domination of the world economy
C)U)S. support for Israel in the Israeli-Palestinian crisis and U.S. military bases in Saudi Arabia
D)Discrimination against Muslims in the United States and western Europe
A)The American way of life, which he saw as an affront to Muslim ideas of morality
B)American domination of the world economy
C)U)S. support for Israel in the Israeli-Palestinian crisis and U.S. military bases in Saudi Arabia
D)Discrimination against Muslims in the United States and western Europe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
On Map 30.1: Russia and the Successor States, 1991-2015, including the inset map, which area declared its independence in 1991 and fought with the Russian Republic to try to maintain independence? 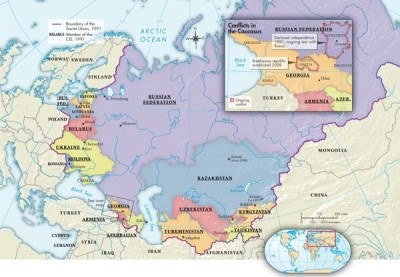
A)Latvia
B)Georgia
C)Chechnya
D)South Ossetia

A)Latvia
B)Georgia
C)Chechnya
D)South Ossetia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
As shown on Map 30.3: The European Union, 2016, which new members joined in 2007? 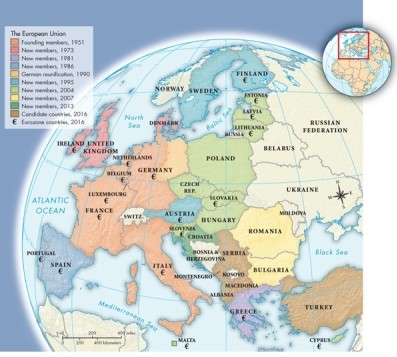
A)Romania and Bulgaria
B)Austria and Sweden
C)Portugal and Spain
D)Slovenia and Hungary

A)Romania and Bulgaria
B)Austria and Sweden
C)Portugal and Spain
D)Slovenia and Hungary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Delegates to the annual United Nations Climate Change Conference in 2012 voted to extend which protocol on climate change?
A)The Rio de Janeiro Protocol
B)The Copenhagen Protocol
C)The Kyoto Protocol
D)The Shanghai Protocol
A)The Rio de Janeiro Protocol
B)The Copenhagen Protocol
C)The Kyoto Protocol
D)The Shanghai Protocol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The following is an excerpt from William Pfaff's analysis of the 2005 French riots (Evaluating the Evidence 30.2): "Their grandfathers came to France, mostly from North Africa, to do the hard labor in France's industrial reconstruction after the Second World War. Their fathers saw the work gradually dry up as Europe's economies slowed, following the first oil shock in the early 1970s. After that came unemployment. The unemployment rate in the zones where there has been the most violence is nearly 40 percent and among young people it is higher. Many of the young men in these places have never been offered a job. When they applied, their names often excluded them."
In this passage, Pfaff suggested that ____________ was a key underlying cause of the riots.
A)religion
B)unemployment
C)education
D)ideology
In this passage, Pfaff suggested that ____________ was a key underlying cause of the riots.
A)religion
B)unemployment
C)education
D)ideology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How have European leaders envisioned a new, heroic mission for Europe?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The following is an excerpt from a 2007 speech in which Vladimir Putin outlined his views on global security, emphasizing the undesirability of a "unipolar world" (Evaluating the Evidence 30.1): "What is a unipolar world? However one might embellish this term, at the end of the day it . . . is [a] world in which there is one master, one sovereign. And at the end of the day this is pernicious not only for all those within this system, but also for the sovereign itself because it destroys itself from within. . . .
I consider that the unipolar model is not only unacceptable but also impossible in today's world. . . . The model itself is flawed because at its basis there is and can be no moral foundations for modern civilization. . . ."
In Putin's view, a unipolar world was incompatible with
A)social progress.
B)centralized decision making.
C)modern civilization.
D)economic growth.
I consider that the unipolar model is not only unacceptable but also impossible in today's world. . . . The model itself is flawed because at its basis there is and can be no moral foundations for modern civilization. . . ."
In Putin's view, a unipolar world was incompatible with
A)social progress.
B)centralized decision making.
C)modern civilization.
D)economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How did European Union leadership react to the failed European Union Constitution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
As shown on Map 30.3: The European Union, 2016, which states are the original members? 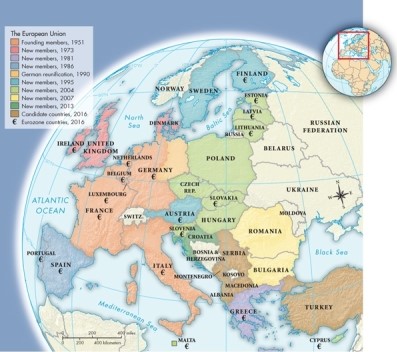
A)Ireland, United Kingdom, and Denmark
B)France, Italy, Germany, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands
C)Spain, Portugal, Austria, Sweden, and Finland
D)Norway, Denmark, Germany, Switzerland, Austria, and Italy.

A)Ireland, United Kingdom, and Denmark
B)France, Italy, Germany, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands
C)Spain, Portugal, Austria, Sweden, and Finland
D)Norway, Denmark, Germany, Switzerland, Austria, and Italy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the World Trade Organization (WTO)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What are the potential consequences of Europe's population decline?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The following is an excerpt from an interview with the German politician Thilo Sarrazin, an outspoken critic of immigration into Germany (Thinking Like a Historian). In it, he explains what he would do to stop further immigration: "First: change the benefits system-immigrants receive no benefits for at least ten years. Second: change the permanent residency law-only those able and willing to make a long-term, highly skilled contribution to Germany receive residency rights. Third: social and family benefits in Germany should be dependent on adequate knowledge of the language and efforts at integration. Fourth: we must clearly say to the Muslim immigrants who are already here: at some point you become German, even if you obviously continue to cook Turkish food and go to the mosque, and if you don't want to do that, it's best you return home. Opinion polls show that more than 60 percent of Turks in Germany speak no German at all or cannot speak it well, and a third would leave Germany immediately if there were no German welfare benefits."
Sarrazin believed that a majority of Turks in Germany
A)were as German as he was.
B)made important contributions to the nation.
C)were criminals.
D)had a poor command of the German language.
Sarrazin believed that a majority of Turks in Germany
A)were as German as he was.
B)made important contributions to the nation.
C)were criminals.
D)had a poor command of the German language.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The following is an excerpt from an interview with the German politician Thilo Sarrazin, an outspoken critic of immigration into Germany (Thinking Like a Historian). In it, he explains what he would do to stop further immigration: "First: change the benefits system-immigrants receive no benefits for at least ten years. Second: change the permanent residency law-only those able and willing to make a long-term, highly skilled contribution to Germany receive residency rights. Third: social and family benefits in Germany should be dependent on adequate knowledge of the language and efforts at integration. Fourth: we must clearly say to the Muslim immigrants who are already here: at some point you become German, even if you obviously continue to cook Turkish food and go to the mosque, and if you don't want to do that, it's best you return home. Opinion polls show that more than 60 percent of Turks in Germany speak no German at all or cannot speak it well, and a third would leave Germany immediately if there were no German welfare benefits."
As part of a strategy to limit the flow of immigrants into Germany, Sarrazin advocated
A)setting racial quotas.
B)changing the benefit system.
C)establishing means tests for immigrants.
D)establishing literacy tests for entry visas.
As part of a strategy to limit the flow of immigrants into Germany, Sarrazin advocated
A)setting racial quotas.
B)changing the benefit system.
C)establishing means tests for immigrants.
D)establishing literacy tests for entry visas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What was economic shock therapy as applied in Russia? How well did it work?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What was the outcome of the last chapter of Yugoslav disintegration, the struggle by the Albanian Muslims of Kosovo for self-rule?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
To what extent has Poland succeeded in moving away from its Communist past?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
On Map 30.1: Russia and the Successor States, 1991-2015, which of the republics of the former Soviet Union did not join the Commonwealth of Independent States in 1991? 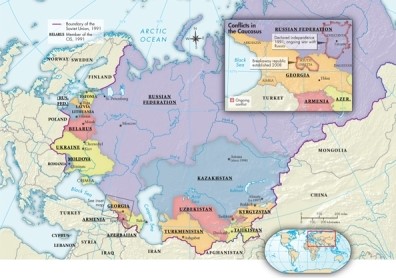
A)Ukraine, Moldova, and Turkmenistan
B)Belarus and Ukraine
C)Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania
D)Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan

A)Ukraine, Moldova, and Turkmenistan
B)Belarus and Ukraine
C)Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania
D)Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The following is an excerpt from William Pfaff's analysis of the 2005 French riots (Evaluating the Evidence 30.2): "The rioting in France's ghetto suburbs is a phenomenon of futility-but a revelation nonetheless. It has no ideology and no purpose other than to make a statement of distress and anger. It is beyond politics. It broke out spontaneously and spread in the same way, communicated by televised example, ratified by the huge attention it won from the press and television and the politicians, none of whom had any idea what to do.
It has been an immensely pathetic spectacle, whose primary meaning has been that it happened. It has been the most important popular social phenomenon in France since the student uprisings of 1968. But those uprisings . . . had consequences for power. The new riots have nothing to do with power."
In Pfaff's view, how were the 2005 riots different than the 1968 riots?
A)The 2005 riots had nothing to do with power.
B)The 1968 riots were much less important.
C)The 1968 riots were about distress and anger.
D)The 2005 riots were organized well in advance.
It has been an immensely pathetic spectacle, whose primary meaning has been that it happened. It has been the most important popular social phenomenon in France since the student uprisings of 1968. But those uprisings . . . had consequences for power. The new riots have nothing to do with power."
In Pfaff's view, how were the 2005 riots different than the 1968 riots?
A)The 2005 riots had nothing to do with power.
B)The 1968 riots were much less important.
C)The 1968 riots were about distress and anger.
D)The 2005 riots were organized well in advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How have Europeans reacted to Europe's rapidly growing Muslim population?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What explains the growing gap between the United States and Europe?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What key factors help explain the emergence of a new era of globalization?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In your opinion, does the al-Qaeda attack of September 11, 2001, represent a fundamental turning point in Western history? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Answer the following questions :
diasporas
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
diasporas
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Answer the following questions :
Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA)
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA)
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Answer the following questions :
war on terror
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
war on terror
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Answer the following questions :
World Trade Organization (WTO)
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
World Trade Organization (WTO)
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Has the leadership of Vladimir Putin in Russia led to a reemergence of authoritarianism? Discuss his actions to support your conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The most disturbing consequence of the collapse of the Soviet Union has been the resurgence of ardent nationalism in central and eastern Europe and the border states of the former Soviet Union. Trace nationalistic developments in the former Soviet empire. What signs are there of a peaceful resolution to this problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Answer the following questions :
ethnic cleansing
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
ethnic cleansing
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Answer the following questions :
multiculturalism
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
multiculturalism
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Answer the following questions :
Maastricht Treaty
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
Maastricht Treaty
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Answer the following questions :
European Union (EU)
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
European Union (EU)
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Answer the following questions :
globalization
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
globalization
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Answer the following questions :
Arab Spring
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
Arab Spring
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The recent past has seen a quickening of the pace of European integration and unification. Describe this process since 1985. What are the key issues? How have Europeans reacted to the new Europe?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Answer the following questions :
climate change
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
climate change
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Answer the following questions :
nongovernmental organizations (NGOs)
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
nongovernmental organizations (NGOs)
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In what ways have immigration flows begun to transform Europe?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Answer the following questions :
Muslim Brotherhood
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
Muslim Brotherhood
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Answer the following questions :
Color Revolutions
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.
Color Revolutions
A)A series of popular revolts and insurrections that challenged regional politicians and Russian interests in the former Soviet republics during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
B)The attempt to establish ethnically homogeneous territories by intimidation, forced deportation, and killing.
C)Military organization formed in 1998 by militants who sought independence from Serbia.
D)The emergence of a freer, more technologically connected global economy, accompanied by a worldwide exchange of cultural, political, and religious ideas.
E)The economic, cultural, and political alliance of twenty-seven European nations.
F)The basis for the formation of the European Union, which set financial and cultural standards for potential member states and defined criteria for membership in the monetary union.
G)A powerful supranational financial institution that sets trade and tariff agreements for more than 150 member countries and so helps manage a large percentage of the world's import-export policies. Like the IMF and the World Bank, it promotes neoliberal policies around the world.
H)Independent organizations with specific agendas, such as humanitarian aid or environmental protection, that conduct international programs and activities.
I)Enclaves of ethnic groups settled outside of their homelands.
J)The mixing of ethnic styles in daily life and in cultural works such as film, music, art, and literature.
K)American policy under President George W. Bush to fight global terrorism in all its forms.
L)Islamic social and political reform group founded in Egypt in 1928 that called for national liberation from European control and a return to shari'a law (based on Muslim legal codes), and demanded land reform, extensive social welfare programs, and economic independence.
M)A series of popular revolts in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa that bought an end to authoritarian, often Western-supported regimes.
N)Changes in longstanding weather patterns caused primarily by carbon dioxide emissions from the burning of fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The collapse of the Soviet Union led quickly to the declaration that the Cold War was over. What have been the consequences of this historic event?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



