Deck 4: Gravity and Orbits
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/88
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Gravity and Orbits
1
The escape velocity on the Moon is less than that on Earth.
True
2
According to the scales in the figure, about how many times stronger is gravity on Earth than on the Moon? 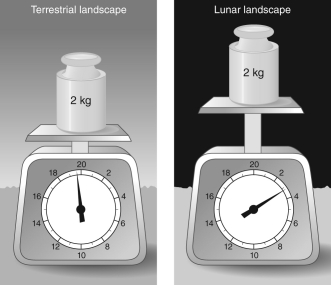
A) 20
B) 3
C) 2
D) 6
E) They are the same.

A) 20
B) 3
C) 2
D) 6
E) They are the same.
6
3
If you weighed 150 lbs on Earth, what would you weigh on Mars? For reference, Mars has a mass that is 0.1 times the Earth's mass and Mars has a radius that is 0.5 times the Earth's radius.
A) 30 lbs
B) 110 lbs
C) 75 lbs
D) 60 lbs
E) 15 lbs
A) 30 lbs
B) 110 lbs
C) 75 lbs
D) 60 lbs
E) 15 lbs
60 lbs
4
Because of the Moon's tidal effect on the oceans, the Moon's orbital distance is shrinking and eventually the Moon will collide with the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An unbound orbit results when a satellite has a velocity greater than the escape velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
More massive objects fall faster in the Earth's gravitational field than less massive objects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Moons that wander inside of a planet's Roche limit can be torn apart due to tidal forces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Once two objects are far enough away from each other, they no longer exert any gravitational attraction on each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
All objects on Earth, regardless of the size of their mass, fall with the same acceleration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The tidal force on the Earth due to the Moon is about two times stronger than that due to the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Ocean tides on Earth are caused primarily by the gravitational pull of the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose you are suddenly transported to a planet that had 1/4 the radius of Earth but the same mass as the Earth. Your weight would _________ by a factor of _________.
A) increase; 4
B) increase; 16
C) decrease; 4
D) decrease; 16
E) decrease; 8
A) increase; 4
B) increase; 16
C) decrease; 4
D) decrease; 16
E) decrease; 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If you weighed 100 lbs on Earth, what would you weigh at the upper atmosphere of Jupiter? For reference, Jupiter has a mass that is about 300 times the Earth's mass and a radius that is 10 times the Earth's radius.
A) 10,000 lbs
B) 3,000 lbs
C) 1,000 lbs
D) 300 lbs
E) 30 lbs
A) 10,000 lbs
B) 3,000 lbs
C) 1,000 lbs
D) 300 lbs
E) 30 lbs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The only acceleration you experience on a merry-go-round is when it starts or stops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Mass and weight are different names for the same physical property of matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Two rocks (call them S and T) are released at the same time from the same height and start from rest. Rock S has 20 times the mass of rock T. Which rock will fall faster if the only forces involved are each rock's mutual gravitational attraction with Earth?
A) Rock S
B) Rock T
C) Both rocks will fall at the same rate.
D) not enough information is available to answer
A) Rock S
B) Rock T
C) Both rocks will fall at the same rate.
D) not enough information is available to answer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose you are suddenly transported to a planet with 1/4 the mass of Earth but the same radius as the Earth. Your weight would _________ by a factor of _________.
A) increase; 4
B) increase; 16
C) decrease; 4
D) decrease; 16
E) increase; 2
A) increase; 4
B) increase; 16
C) decrease; 4
D) decrease; 16
E) increase; 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the absence of air friction, a 0.001-kg piece of paper and a 0.1-kg notebook are dropped from the same height and allowed to fall to the ground. How do their accelerations compare?
A) The accelerations are the same.
B) The notebook's acceleration is 100 times faster than the paper's acceleration.
C) The notebook's acceleration is 1,000 times faster than the paper's acceleration.
D) The paper's acceleration is 100 times faster than the notebook's acceleration.
E) The paper's acceleration is 1,000 times faster than the notebook's acceleration.
A) The accelerations are the same.
B) The notebook's acceleration is 100 times faster than the paper's acceleration.
C) The notebook's acceleration is 1,000 times faster than the paper's acceleration.
D) The paper's acceleration is 100 times faster than the notebook's acceleration.
E) The paper's acceleration is 1,000 times faster than the notebook's acceleration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An astronaut orbiting the Earth in a circular orbit at a constant speed does not feel the force of gravity because his or her acceleration is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following properties of an astronaut changes when he or she is standing on the Moon, relative to when the astronaut is standing on Earth?
A) weight
B) mass
C) inertia
D) all of the above
E) Nothing changes.
A) weight
B) mass
C) inertia
D) all of the above
E) Nothing changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Titan, the largest moon of Saturn, has an orbital period of 16 days and a semimajor axis of 1.2 *109 m. Based on this information, what is Saturn's mass? For reference, the Earth's mass is 6 * 1024 kg.
A) 290 MEarth
B) 130 MEarth
C) 90 MEarth
D) 40 MEarth
E) 4 MEarth
A) 290 MEarth
B) 130 MEarth
C) 90 MEarth
D) 40 MEarth
E) 4 MEarth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Mercury orbits the Sun with an average distance of 0.4 AU, and its mass is 0.06 times that of the Earth. The gravitational force that the Sun exerts on Mercury is _______________ times the force of gravity that the Sun exerts on the Earth.
A) 20
B) 6
C) 4
D) 0.4
E) 0.1
A) 20
B) 6
C) 4
D) 0.4
E) 0.1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the escape velocity from a large asteroid if its mass is 6 * 1021 kg and its radius is 2,400 km?
A) 98 km/s
B) 210 km/s
C) 340 m/s
D) 580 m/s
E) 12,400 m/s
A) 98 km/s
B) 210 km/s
C) 340 m/s
D) 580 m/s
E) 12,400 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the distance between the Earth and Sun were cut in half, the gravitational force between these two objects would:
A) decrease by 4
B) decrease by 2
C) increase by 2
D) increase by 4
E) decrease by 8
A) decrease by 4
B) decrease by 2
C) increase by 2
D) increase by 4
E) decrease by 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Two rocks (call them S and T) are a distance of 50 km from one another. Rock S has 20 times the mass of rock T. Considering only their mutual gravitational force, which rock will accelerate faster in response to gravity?
A) rock S
B) rock T
C) Both rocks will have the same acceleration.
D) not enough information available to answer
A) rock S
B) rock T
C) Both rocks will have the same acceleration.
D) not enough information available to answer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How fast is the Moon moving as it orbits the Earth? For reference, the Moon's orbit is approximately circular with a radius equal to 400,000 km, and the Moon's orbital period is 27 days.
A) 1 km/s
B) 10 km/s
C) 50 km/
D) 100 km/s
E) 500 km/s
A) 1 km/s
B) 10 km/s
C) 50 km/
D) 100 km/s
E) 500 km/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If you found an exoplanet whose mass was the same as Jupiter's, but the planet orbited its star with a period of 2 years and a semimajor axis of 1 AU, what would be the mass of its star? For reference, Jupiter has a semimajor axis of 5.4 AU and an orbital period of 12 years.
A) 0.25 M
B) 0.5 M
C) 2.0 M
D) 1.5 M
E) not enough information available to answer
A) 0.25 M
B) 0.5 M
C) 2.0 M
D) 1.5 M
E) not enough information available to answer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the escape velocity from Mars if its mass is 6 * 1023 kg and its radius is 3,400 km?
A) 2,400 m/s
B) 4,900 m/s
C) 8,600 km/s
D) 12,000 m/s
E) 25,000 km/s
A) 2,400 m/s
B) 4,900 m/s
C) 8,600 km/s
D) 12,000 m/s
E) 25,000 km/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Astronauts orbiting Earth in the space shuttle feel weightless in space because:
A) they are farther away from the Earth
B) they eat less food while in orbit
C) the gravitational pull of the Moon counteracts the Earth's gravitational pull
D) they are in constant free fall around the Earth
E) they are in space where there is no gravity
A) they are farther away from the Earth
B) they eat less food while in orbit
C) the gravitational pull of the Moon counteracts the Earth's gravitational pull
D) they are in constant free fall around the Earth
E) they are in space where there is no gravity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If an object is moving in a circular orbit at a constant speed, which of the following is FALSE?
A) Its acceleration is not zero.
B) Its acceleration is zero.
C) Its velocity is not zero.
D) There is an unbalanced force acting on it.
E) All the above statements are true.
A) Its acceleration is not zero.
B) Its acceleration is zero.
C) Its velocity is not zero.
D) There is an unbalanced force acting on it.
E) All the above statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Hubble Space Telescope orbits at an altitude of 600 km above the Earth's surface. Assuming it is in a stable circular orbit, what is its velocity? For reference, the Earth's radius is 6,400 km and Earth's mass is 6 *1024 kg.
A) 240,000 m/s
B) 7,500 m/s
C) 51,000 m/s
D) 64,000 m/s
E) You also must know the mass of the Hubble Space Telescope to determine its speed.
A) 240,000 m/s
B) 7,500 m/s
C) 51,000 m/s
D) 64,000 m/s
E) You also must know the mass of the Hubble Space Telescope to determine its speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If we wanted to increase the Hubble Space Telescope's altitude above the Earth and keep it in a stable orbit, we also would need to:
A) increase its orbital speed
B) increase its weight
C) decrease its weight
D) decrease its orbital speed
E) increase its mass
A) increase its orbital speed
B) increase its weight
C) decrease its weight
D) decrease its orbital speed
E) increase its mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
_________ hypothesized that planetary motions could be explained by a force arising from the attraction between the mass of the planet and Sun that decreased with the square of the distance between them.
A) Johannes Kepler
B) Isaac Newton
C) Tycho Brahe
D) Nicolaus Copernicus
E) Galileo Galilei
A) Johannes Kepler
B) Isaac Newton
C) Tycho Brahe
D) Nicolaus Copernicus
E) Galileo Galilei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a satellite sent to Mars is designed to return a rock sample to Earth, how fast must the satellite be launched from its surface in order to escape Mars's gravity? For reference, Mars has a mass of 6 * 1023 kg and a radius of 3,400 km.
A) 100 m/s
B) 5,000 m/s
C) 20 m/s
D) 20,000 m/s
E) You must know the mass of the satellite to determine the answer.
A) 100 m/s
B) 5,000 m/s
C) 20 m/s
D) 20,000 m/s
E) You must know the mass of the satellite to determine the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The force of gravity that an object has is directly proportional to its:
A) inertia
B) size
C) mass
D) density
E) distance
A) inertia
B) size
C) mass
D) density
E) distance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The force of gravity between the Earth and the Sun is _________ the force of gravity between the Earth and the Moon. For reference, the average distance between the Earth and the Moon is 0.003 AU, the mass of the Moon is 7 * 1022 kg, and the mass of the Sun is 2 *1030 kg.
A) 86,000 times larger than
B) 260 times larger than
C) 140 times smaller than
D) 6,400 times smaller than
E) the same as
A) 86,000 times larger than
B) 260 times larger than
C) 140 times smaller than
D) 6,400 times smaller than
E) the same as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
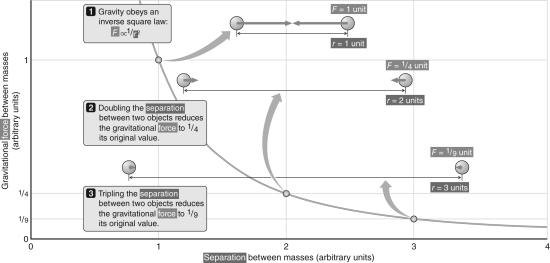
According to the progression shown in the figure above, if the distance between two objects is increased to four times its original value, the gravitational force between the two objects would be _________ times its original value.
A) 1/2
B) 1/32
C) 1/4
D) 1/16
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The force of gravity between Saturn and the Sun is _________ the force of gravity between the Earth and the Sun. For reference, Saturn is approximately 100 times more massive than Earth, and the semimajor axis of Saturn's orbit is 10 AU.
A) 10 times smaller than
B) 1,000 times larger than
C) 1,000 times smaller than
D) 100 times larger than
E) approximately equal to
A) 10 times smaller than
B) 1,000 times larger than
C) 1,000 times smaller than
D) 100 times larger than
E) approximately equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If you measured the orbital period of the Moon and the distance between the Earth and the Moon then you could calculate:
A) the mass of the Moon
B) the sum of the masses of the Earth and the Moon
C) the average distance between the Earth and Sun
D) the radius of the Earth
E) the radius of the Moon
A) the mass of the Moon
B) the sum of the masses of the Earth and the Moon
C) the average distance between the Earth and Sun
D) the radius of the Earth
E) the radius of the Moon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If you have two moons that have the same radius, but Moon A is denser and has 2 times the mass of Moon B, how do their escape velocities compare?
A) Moon A has an escape velocity that is 1.4 times larger than Moon B.
B) Moon A has an escape velocity that is 1.4 times smaller than Moon B.
C) Moon A has an escape velocity that is 2 times smaller than Moon B.
D) Moon A has an escape velocity that is 2 times larger than Moon B.
E) Because gravity affects all masses the same, the escape velocities are the same.
A) Moon A has an escape velocity that is 1.4 times larger than Moon B.
B) Moon A has an escape velocity that is 1.4 times smaller than Moon B.
C) Moon A has an escape velocity that is 2 times smaller than Moon B.
D) Moon A has an escape velocity that is 2 times larger than Moon B.
E) Because gravity affects all masses the same, the escape velocities are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Assume that a planet just like Earth orbits the bright star named Sirius. If this Earth-like planet orbits with a semimajor axis of 1 AU and an orbital period of 7 months, what is the mass of Sirius?
A) 3 M
B) 12 M
C) 8 M
D) 5 M
E) 17 M
A) 3 M
B) 12 M
C) 8 M
D) 5 M
E) 17 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Moon always keeps the same face toward Earth because of:
A) tidal locking
B) tidal forces from the Sun
C) tidal forces from Earth
D) tidal forces from the Earth and Sun
E) all sides of the moon face Earth at one time or another
A) tidal locking
B) tidal forces from the Sun
C) tidal forces from Earth
D) tidal forces from the Earth and Sun
E) all sides of the moon face Earth at one time or another

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
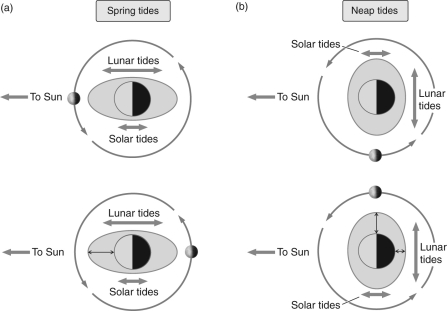 Figure 2
Figure 2According to Figure 2, neap tides occur when the lunar and solar tides _________, resulting in _________ tides.
A) add; above average
B) partially cancel out; above average
C) add; below average
D) partially cancel out; below average
E) completely cancel out; no

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If you discovered a planet orbiting another star, and the planet had an orbital period of 2 years and a semimajor axis of 1 AU, what would be the mass of its parent star? You can assume the planet's mass is much less than the star's mass.
A) 0.25 M
B) 0.5 M
C) 1.0 M
D) 1.25 M
E) 2.0 M
A) 0.25 M
B) 0.5 M
C) 1.0 M
D) 1.25 M
E) 2.0 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
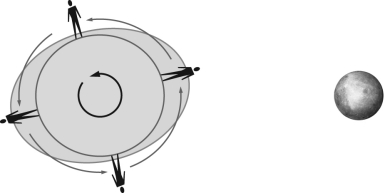 Figure 1
Figure 1According to Figure 1, a high tide at a given location will occur ____ time(s) a day.
A) one
B) three
C) two
D) four
E) eight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the figure shown below, the person on the Moon is standing at the same location on the Moon as the Moon rotates around the Earth. Based on this, we see that the Moon's rotational period is equal to: 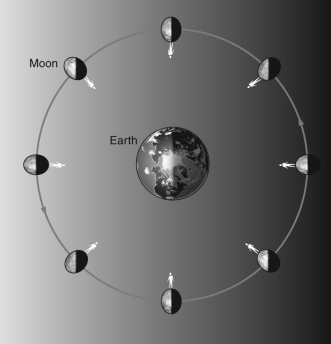
A) the Earth's rotational period
B) half the Earth's rotational period
C) the Moon's orbital period
D) half the Moon's orbital period
E) the Earth's orbital period around the Sun

A) the Earth's rotational period
B) half the Earth's rotational period
C) the Moon's orbital period
D) half the Moon's orbital period
E) the Earth's orbital period around the Sun

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When the Sun and Moon are separated by 90 degrees in the sky, _________ tides occur on Earth when the strength of the tides are _________ than normal.
A) spring; smaller
B) spring; larger
C) lunar; smaller
D) neap; smaller
E) neap; larger
A) spring; smaller
B) spring; larger
C) lunar; smaller
D) neap; smaller
E) neap; larger

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
 Figure 2
Figure 2According to Figure 2, neap tides occur at which phases of the Moon?
A) new and full
B) third quarter
C) first quarter and third quarter
D) full
E) new

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
 Figure 1
Figure 1According to Figure 1, the approximate amount of time between a high tide and a low tide at a given location is:
A) 3 hours
B) 8 hours
C) 6 hours
D) 12 hours
E) 24 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
You find a moon orbiting a planet. The moon has a period of 10 days, and the average distance between the moon and planet is 106 km. What is the planet's mass? Note that the mass of Jupiter is 1.9 * 1027 kg.
A) 0.1 MJupiter
B) 0.4 MJupiter
C) 1 MJupiter
D) 4 MJupiter
E) 10 MJupiter
A) 0.1 MJupiter
B) 0.4 MJupiter
C) 1 MJupiter
D) 4 MJupiter
E) 10 MJupiter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Tidal forces are caused by:
A) the weight of the water in the oceans on the ocean floor
B) the strength of the gravitation pull of the Moon on Earth
C) the difference between the weight of the water on the ocean floor at high and low tide
D) the difference between the strength of the gravitiational pull of the Moon and Sun on either side of Earth
E) the strength of the gravitation pull of the Moon and the Sun on Earth
A) the weight of the water in the oceans on the ocean floor
B) the strength of the gravitation pull of the Moon on Earth
C) the difference between the weight of the water on the ocean floor at high and low tide
D) the difference between the strength of the gravitiational pull of the Moon and Sun on either side of Earth
E) the strength of the gravitation pull of the Moon and the Sun on Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The moon keeps the same hemisphere facing the Earth because the _________ is equal to the _________.
A) rotational period of the Earth;
Orbital period of the Moon around the Earth
B) orbital period of the Earth;
Orbital period of the Moon around the Earth
C) orbital period of the Moon around the Earth;
Rotational period of the Earth
D) rotational period of the Moon;
Orbital period of the Moon around the Earth
E) rotational period of the Earth;
Orbital period of the Earth
A) rotational period of the Earth;
Orbital period of the Moon around the Earth
B) orbital period of the Earth;
Orbital period of the Moon around the Earth
C) orbital period of the Moon around the Earth;
Rotational period of the Earth
D) rotational period of the Moon;
Orbital period of the Moon around the Earth
E) rotational period of the Earth;
Orbital period of the Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
 Figure 2
Figure 2According to Figure 2, when the Moon is in between Earth and the Sun, _________ tides occur.
A) spring
B) no
C) neap
D) high
E) low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
 Figure 2
Figure 2According to Figure 2, spring tides occur when the lunar and solar tides _________ resulting in _________ tides.
A) add; above average
B) partially cancel out; above average
C) add; below average
D) partially cancel out; below average
E) completely cancel out; no

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The distance between Earth and the Moon:
A) will never change
B) is slowly decreasing
C) is slowly increasing
D) will increase or decrease depending on future changes in the tides on the Moon due to the Earth
E) will increase or decrease depending on future changes in the tides on the Earth due to the Moon
A) will never change
B) is slowly decreasing
C) is slowly increasing
D) will increase or decrease depending on future changes in the tides on the Moon due to the Earth
E) will increase or decrease depending on future changes in the tides on the Earth due to the Moon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
 Figure 2
Figure 2According to Figure 2, when Earth is in between the Moon and the Sun, _________ tides occur.
A) spring
B) no
C) neap
D) high
E) low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
 Figure 1
Figure 1According to Figure 1, the approximate amount of time between two high tides at a given location is:
A) 3 hours
B) 8 hours
C) 6 hours
D) 12 hours
E) 24 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Because of the tidal force between the Earth and Moon:
A) the Earth's rotation rate is decreasing
B) the Moon's distance from Earth is increasing
C) the Moon's orbital period is increasing
D) the Moon's rotational period is increasing
E) All of the above are true.
A) the Earth's rotation rate is decreasing
B) the Moon's distance from Earth is increasing
C) the Moon's orbital period is increasing
D) the Moon's rotational period is increasing
E) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
 Figure 2
Figure 2According to Figure 2, spring tides occur at which phases of the Moon?
A) third quarter
B) new and full
C) first and third quarter
D) full
E) new

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Lunar tides are approximately _________ solar tides.
A) 2 times weaker than
B) 2 times stronger than
C) 200 times weaker than
D) 200 times stronger than
E) the same strength as
A) 2 times weaker than
B) 2 times stronger than
C) 200 times weaker than
D) 200 times stronger than
E) the same strength as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the velocity one would need to give a satellite in order for it to escape from the Solar System (meaning escape the Sun's gravity) if it was launched from the Earth at a distance of 1 AU from the Sun? Give your answer in units of m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Because of tidal forces, for every _________ time(s) it rotates on its axis, Mercury revolves around the Sun _________ time(s).
A) 1; 1
B) 2; 3
C) 3; 2
D) 10; 1
E) 20; 1
A) 1; 1
B) 2; 3
C) 3; 2
D) 10; 1
E) 20; 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Tidal forces can affect:
A) moons
B) galaxies
C) planets
D) satellites
E) all of the above
A) moons
B) galaxies
C) planets
D) satellites
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How does the force of gravity between the Sun and Mercury compare to the gravitational force between the Sun and the Earth? Note that the semimajor axis of Mercury's orbit is 0.4 AU, and Mercury's mass is 0.06 times the mass of the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The International Space Station orbits at an altitude of 400 km above the Earth's surface. Assuming it is in a stable circular orbit, what is its velocity? For reference, the Earth's radius is 6,400 km, and Earth's mass is 6 * 1024 kg and G = 6.7 * 10-11 N m2/kg2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How would the acceleration due to gravity on a planet that is 16 times as massive as Earth and 4 times its radius compared to the acceleration of gravity on the Earth?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The distance between Earth and the Moon is increasing because of:
A) the expansion of the Universe
B) the expansion of the Solar System
C) tidal forces from the Moon
D) tidal forces from the Moon and Sun
E) dark energy
A) the expansion of the Universe
B) the expansion of the Solar System
C) tidal forces from the Moon
D) tidal forces from the Moon and Sun
E) dark energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Mars has about one tenth the mass of Earth and half the Earth's radius. How does the acceleration of gravity on Mars compare to that on Earth?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Is there a difference in your weight between when you are on top of a mountain at 1,000 meters above sea level compared to when you are sitting in a classroom at 10 meters above sea level?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Explain the difference between being weightless and being in free fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The Earth's rotation rate is slowing because of:
A) radioactive decays in its core
B) relativistic effects of gravity
C) tidal forces from the Moon
D) the gravitational force of the Sun
E) gravitational drag from dark matter
A) radioactive decays in its core
B) relativistic effects of gravity
C) tidal forces from the Moon
D) the gravitational force of the Sun
E) gravitational drag from dark matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In a system with three gravitating bodies, there are _________ stable locations called _________ points for the third object to orbit in lockstep with the two more massive objects.
A) 3; tidal
B) 2; tidal
C) 4; Roche
D) 2; Lagrange
E) 5; Lagrange
A) 3; tidal
B) 2; tidal
C) 4; Roche
D) 2; Lagrange
E) 5; Lagrange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Show that the gravitational pull on Earth from the Sun is about 200 times the gravitational pull on Earth from the Moon. For reference, Moon's mass is 7.3 * 10 22 kg, the Sun's mass is 2 * 1030 kg, the Earth-Moon distance is 3.8 * 105 km, and the Earth-Sun distance is 1.5 * 108 km.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
How much stronger is the gravitational force of the Sun on the Earth compared to the gravitational force of the Sun on Pluto? Note that Pluto's semimajor axis is 40, AU, and Pluto's mass is 0.002 times the mass of the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
How does the force of gravity between the Sun and Jupiter compare to the gravitational force between the Sun and the Earth? Note that the semimajor axis of Jupiter's orbit is 5.2 AU, and Jupiter's mass is 320 times the mass of the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Explain what the terms circular velocity and escape velocity mean. Give the formula for each and explain what each mathematical symbol represents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
_________ may have been instrumental in shaping the interface between Earth's land and oceans where the chemistry needed to develop life may have occurred.
A) Meteor showers
B) Collisions with comets
C) Earth's Moon
D) Techtonic activity
E) A collision with a Mars-sized object
A) Meteor showers
B) Collisions with comets
C) Earth's Moon
D) Techtonic activity
E) A collision with a Mars-sized object

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the statements below are TRUE about the Roche limit of a giant planet?
A) It is about equal to the radius of the planet.
B) It is the closest to the planet that moons normally are found.
C) It is the closest to the planet that rings will be found.
D) It is the farthest from the planet that moons normally are found.
E) Because they have no solid surfaces, giant planets do not have a Roche limit.
A) It is about equal to the radius of the planet.
B) It is the closest to the planet that moons normally are found.
C) It is the closest to the planet that rings will be found.
D) It is the farthest from the planet that moons normally are found.
E) Because they have no solid surfaces, giant planets do not have a Roche limit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which one of the statements below about a planet's Roche limit is FALSE?
A) The Roche limit is about 2.5 times the radius of gaseous planets.
B) Objects orbiting closer to a planet than the Roche limit are likely to be ripped apart by tidal forces.
C) The Roche limit is where tidal forces from an orbiting object are equal to its internal self-gravity.
D) Orbiting objects beyond the Roche limit from the planet do not get ripped apart by tidal forces.
E) The ring systems around giant planets are located beyond the Roche limit.
A) The Roche limit is about 2.5 times the radius of gaseous planets.
B) Objects orbiting closer to a planet than the Roche limit are likely to be ripped apart by tidal forces.
C) The Roche limit is where tidal forces from an orbiting object are equal to its internal self-gravity.
D) Orbiting objects beyond the Roche limit from the planet do not get ripped apart by tidal forces.
E) The ring systems around giant planets are located beyond the Roche limit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Saturn has 95 times the mass of Earth, and its atmosphere extends outward 9.5 times the Earth's radius. How does the acceleration due to gravity at the edge of Saturn's atmosphere compare to that on the Earth?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



