Deck 26: Understanding Probability Distributions and Statistical Inference
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Understanding Probability Distributions and Statistical Inference
1
A P-value indicates
A) the probability that the null hypothesis is true
B) the probability that the alternative hypothesis is true
C) the probability of the observed statistic given that the null hypothesis is true
D) the probability of the observed statistic given that the alternative hypothesis is true
E) the probability of the null hypothesis
A) the probability that the null hypothesis is true
B) the probability that the alternative hypothesis is true
C) the probability of the observed statistic given that the null hypothesis is true
D) the probability of the observed statistic given that the alternative hypothesis is true
E) the probability of the null hypothesis
C
2
We have calculated a 95% confidence interval and would like our next confidence interval to have a smaller margin of error without losing any confidence. In order to do this, we can
I) change the z* value to a smaller number
II) take a larger sample
III) take a smaller sample
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) I and III
I) change the z* value to a smaller number
II) take a larger sample
III) take a smaller sample
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) I and III
B
3
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Insurance company records indicate that 10% of its policyholders file claims involving theft or robbery of personal property from their homes. Suppose a random sample of 400 policyholders is selected.
The probability that the sample proportion of policyholders filing claims involving theft or robbery from their homes is less than 8% is
A) 0.0918
B) 0.1333
C) 0.4082
D) 0.0517
E) 0.7892
Insurance company records indicate that 10% of its policyholders file claims involving theft or robbery of personal property from their homes. Suppose a random sample of 400 policyholders is selected.
The probability that the sample proportion of policyholders filing claims involving theft or robbery from their homes is less than 8% is
A) 0.0918
B) 0.1333
C) 0.4082
D) 0.0517
E) 0.7892
A
4
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Insurance company records indicate that 10% of its policyholders file claims involving theft or robbery of personal property from their homes. Suppose a random sample of 400 policyholders is selected.
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion of policyholders filing claims involving theft or robbery from their homes is
A) 0.000225
B) 0.25
C) 0.0455
D) 0.1667
E) 0.015
Insurance company records indicate that 10% of its policyholders file claims involving theft or robbery of personal property from their homes. Suppose a random sample of 400 policyholders is selected.
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion of policyholders filing claims involving theft or robbery from their homes is
A) 0.000225
B) 0.25
C) 0.0455
D) 0.1667
E) 0.015

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
In economic downturns companies attempt to downsize their workforces by offering early retirement incentives to older employees. A survey of 723 companies found that 195 engage in such downsizing practices.
The estimated proportion of companies that downsize their workforces by offering early retirement incentives is
A) 0.50
B) 0.73
C) 0.195
D) 0.27
E) 0.67
In economic downturns companies attempt to downsize their workforces by offering early retirement incentives to older employees. A survey of 723 companies found that 195 engage in such downsizing practices.
The estimated proportion of companies that downsize their workforces by offering early retirement incentives is
A) 0.50
B) 0.73
C) 0.195
D) 0.27
E) 0.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A men's clothing store has determined the following probability distribution for the number of special size orders placed per month. The distribution is as follows:
Number Ordered Probability
0 0.10
5 0.10
10 0.12
15 0.30
20 0.38
The number of special size orders this men's clothing store can expect per month is
A) 13.8
B) 20
C) 15
D) 14.2
E) 12.5
A men's clothing store has determined the following probability distribution for the number of special size orders placed per month. The distribution is as follows:
Number Ordered Probability
0 0.10
5 0.10
10 0.12
15 0.30
20 0.38
The number of special size orders this men's clothing store can expect per month is
A) 13.8
B) 20
C) 15
D) 14.2
E) 12.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
The weights of soy patties sold by Veggie Burgers Delight are normally distributed. A random sample of 15 patties yields a mean weight of 108 grams with a sample standard deviation of 14 grams. At the 0.05 level of significance, perform a hypothesis test to see if the true mean weight is less than 113 grams.
The correct null and alternative hypotheses are
A) H0: µ = 113; HA: µ > 113
B) H0: µ = 113; HA: µ < 113
C) H0: µ > 113; HA: µ = 113
D) H0: µ < 113; HA: µ = 113
E) H0: µ = 113; HA: µ ≠ 113
The weights of soy patties sold by Veggie Burgers Delight are normally distributed. A random sample of 15 patties yields a mean weight of 108 grams with a sample standard deviation of 14 grams. At the 0.05 level of significance, perform a hypothesis test to see if the true mean weight is less than 113 grams.
The correct null and alternative hypotheses are
A) H0: µ = 113; HA: µ > 113
B) H0: µ = 113; HA: µ < 113
C) H0: µ > 113; HA: µ = 113
D) H0: µ < 113; HA: µ = 113
E) H0: µ = 113; HA: µ ≠ 113

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
The weights of soy patties sold by Veggie Burgers Delight are normally distributed. A random sample of 15 patties yields a mean weight of 108 grams with a sample standard deviation of 14 grams. At the 0.05 level of significance, perform a hypothesis test to see if the true mean weight is less than 113 grams.
The correct calculated value of the test statistic is
A) -0.4
B) 0.4
C) -1.38
D) 1.38
E) 2.79
The weights of soy patties sold by Veggie Burgers Delight are normally distributed. A random sample of 15 patties yields a mean weight of 108 grams with a sample standard deviation of 14 grams. At the 0.05 level of significance, perform a hypothesis test to see if the true mean weight is less than 113 grams.
The correct calculated value of the test statistic is
A) -0.4
B) 0.4
C) -1.38
D) 1.38
E) 2.79

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A quality assurance manager is interested in determining the likelihood that more than 20 calls come in to a particular customer service centre per hour. What method would be most appropriate for assigning this probability?
A) Personal
B) Judgmental
C) Subjective
D) Relative Frequency
E) Classical
A) Personal
B) Judgmental
C) Subjective
D) Relative Frequency
E) Classical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A survey of investors finds that 60% use a full service brokerage firm to invest in stocks, 30% trade stocks online and 24% do both.
What is the probability that an investor selected at random neither uses a full service brokerage firm to invest in stocks nor trades online is
A) 90%
B) 66%
C) 34%
D) 10%
E) 60%
A survey of investors finds that 60% use a full service brokerage firm to invest in stocks, 30% trade stocks online and 24% do both.
What is the probability that an investor selected at random neither uses a full service brokerage firm to invest in stocks nor trades online is
A) 90%
B) 66%
C) 34%
D) 10%
E) 60%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
An advocacy group is investigating whether gender has an effect on job category in large investment firms. She surveyed a sample of firms with the following results:
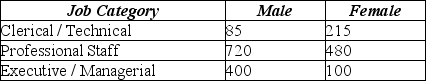
What is the probability that a randomly selected employee's job category is executive/managerial, given that she is female?
A) 0.13
B) 0.20
C) 0.80
D) 0.05
E) 0.45
An advocacy group is investigating whether gender has an effect on job category in large investment firms. She surveyed a sample of firms with the following results:

What is the probability that a randomly selected employee's job category is executive/managerial, given that she is female?
A) 0.13
B) 0.20
C) 0.80
D) 0.05
E) 0.45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
In economic downturns companies attempt to downsize their workforces by offering early retirement incentives to older employees. A survey of 723 companies found that 195 engage in such downsizing practices.
The 99% confidence interval for the proportion of companies that downsize their workforces by offering early retirement incentives is
A) 0.19 to 0.35
B) 0.65 to 0.81
C) 0.19 to 0.47
D) 0.69 to 0.77
E) 0.23 to 0.31
In economic downturns companies attempt to downsize their workforces by offering early retirement incentives to older employees. A survey of 723 companies found that 195 engage in such downsizing practices.
The 99% confidence interval for the proportion of companies that downsize their workforces by offering early retirement incentives is
A) 0.19 to 0.35
B) 0.65 to 0.81
C) 0.19 to 0.47
D) 0.69 to 0.77
E) 0.23 to 0.31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A truck company wants on-time delivery for 98% of the parts they order from a metal manufacturing plant. They have been ordering from Hudson Manufacturing but will switch to a new, cheaper manufacturer (Steel-R-Us) unless there is evidence that this new manufacturer cannot meet the 98% on-time goal. As a test the truck company purchases a random sample of metal parts from Steel-R-Us, and then determines if these parts were delivered on-time. Which hypotheses should they test?
A) H0: p < 0.98 HA: p > 0.98
B) H0: p > 0.98 HA: p = 0.98
C) H0: p = 0.98 HA: p < 0.98
D) H0: p = 0.98 HA: p ≠ 0.98
E) H0: p = 0.98 HA: p > 0.98
A) H0: p < 0.98 HA: p > 0.98
B) H0: p > 0.98 HA: p = 0.98
C) H0: p = 0.98 HA: p < 0.98
D) H0: p = 0.98 HA: p ≠ 0.98
E) H0: p = 0.98 HA: p > 0.98

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A survey of investors finds that 60% use a full service brokerage firm to invest in stocks, 30% trade stocks online and 24% do both.
The probability that an investor selected at random uses a full service brokerage firm to invest in stocks or trades stocks online is
A) 90%
B) 66%
C) 34%
D) 54%
E) 60%
A survey of investors finds that 60% use a full service brokerage firm to invest in stocks, 30% trade stocks online and 24% do both.
The probability that an investor selected at random uses a full service brokerage firm to invest in stocks or trades stocks online is
A) 90%
B) 66%
C) 34%
D) 54%
E) 60%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A men's clothing store has determined the following probability distribution for the number of special size orders placed per month. The distribution is as follows:
Number Ordered Probability
0 0.10
5 0.10
10 0.12
15 0.30
20 0.38
The standard deviation in the number of special size orders placed per month is
A) 24.516
B) 4.95
C) 15.345
D) 6.60
E) 3.88
A men's clothing store has determined the following probability distribution for the number of special size orders placed per month. The distribution is as follows:
Number Ordered Probability
0 0.10
5 0.10
10 0.12
15 0.30
20 0.38
The standard deviation in the number of special size orders placed per month is
A) 24.516
B) 4.95
C) 15.345
D) 6.60
E) 3.88

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A theorem that allows us to use the normal probability distribution to approximate the sampling distribution of the sample mean whenever the sample size is large (over 30) is the
A) approximation theorem
B) central normality theorem
C) central limit theorem
D) normal probability theorem
E) normal sampling theorem
A) approximation theorem
B) central normality theorem
C) central limit theorem
D) normal probability theorem
E) normal sampling theorem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose that a manufacturer is testing one of its machines to make sure that the machine is producing more than 97% good parts (H0: p = 0.97 and HA: p > 0.97). The test results in a P-value of 0.102. In reality, the machine is producing 99% good parts. What probably happens as a result of our testing?
A) We correctly fail to reject H0.
B) We correctly reject H0.
C) We reject H0, making a Type I error.
D) We fail to reject H0, making a Type I error.
E) We fail to reject H0, making a Type II error.
A) We correctly fail to reject H0.
B) We correctly reject H0.
C) We reject H0, making a Type I error.
D) We fail to reject H0, making a Type I error.
E) We fail to reject H0, making a Type II error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
We have created a 95% confidence interval for µ with the result (10, 15). What conclusion will we make if we test H0: µ = 16 versus HA: µ ≠ 16 at α = 0.05?
A) Reject the null hypothesis.
B) Accept the null hypothesis.
C) Fail to reject the null hypothesis.
D) Reject the alternative hypothesis.
E) No decision can made from the information given.
A) Reject the null hypothesis.
B) Accept the null hypothesis.
C) Fail to reject the null hypothesis.
D) Reject the alternative hypothesis.
E) No decision can made from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
An advocacy group is investigating whether gender has an effect on job category in large investment firms. She surveyed a sample of firms with the following results:

Which of the following statements is true about gender and job category?
A) Gender and job category are independent.
B) Gender and job category are not independent.
C) Gender and job category are mutually exclusive.
D) Gender and job category are independent and mutually exclusive.
E) There is not sufficient information to determine whether gender and job category are independent or mutually exclusive.
An advocacy group is investigating whether gender has an effect on job category in large investment firms. She surveyed a sample of firms with the following results:

Which of the following statements is true about gender and job category?
A) Gender and job category are independent.
B) Gender and job category are not independent.
C) Gender and job category are mutually exclusive.
D) Gender and job category are independent and mutually exclusive.
E) There is not sufficient information to determine whether gender and job category are independent or mutually exclusive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
An advocacy group is investigating whether gender has an effect on job category in large investment firms. She surveyed a sample of firms with the following results:

What is the probability that a randomly selected employee's job category is executive/managerial?
A) 0.20
B) 0.80
C) 0.13
D) 0.45
E) 0.25
An advocacy group is investigating whether gender has an effect on job category in large investment firms. She surveyed a sample of firms with the following results:

What is the probability that a randomly selected employee's job category is executive/managerial?
A) 0.20
B) 0.80
C) 0.13
D) 0.45
E) 0.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A government agency has 6000 employees. As an alternative to the traditional five day work week, employees were asked whether they preferred a four day work week (10 hours per day) or flexible hours. The table below shows the results by age category.

What is the probability that an employee prefers flex hours given that he/she is in the 30-45 age group?
A) 0.90
B) 0.56
C) 0.31
D) 0.80
E) 0.67
A government agency has 6000 employees. As an alternative to the traditional five day work week, employees were asked whether they preferred a four day work week (10 hours per day) or flexible hours. The table below shows the results by age category.

What is the probability that an employee prefers flex hours given that he/she is in the 30-45 age group?
A) 0.90
B) 0.56
C) 0.31
D) 0.80
E) 0.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A sample of 30 year fixed mortgage rates at 12 randomly chosen credit unions yields a mean rate of 6.65 % and a sample standard deviation of 0.39%. A sample of 30 year fixed mortgage rates at 16 randomly selected banks yields a mean rate of 7.05% and a sample standard deviation of 0.22%. Are the mean rates different between credit unions and banks? Relevant output is shown below.
At the 0.05 level of significance, the correct conclusion is
A) Reject the null hypothesis.
B) Do not reject the null hypothesis.
C) Evidence suggests that there is a significant difference in mean mortgage rates between credit unions and banks.
D) Reject the null hypothesis and evidence suggests that there is a significant difference in mean mortgage rates between credit unions and banks.
E) Do not reject the null hypothesis and evidence suggests that there is a significant difference in mean mortgage rates between credit unions and banks.
A sample of 30 year fixed mortgage rates at 12 randomly chosen credit unions yields a mean rate of 6.65 % and a sample standard deviation of 0.39%. A sample of 30 year fixed mortgage rates at 16 randomly selected banks yields a mean rate of 7.05% and a sample standard deviation of 0.22%. Are the mean rates different between credit unions and banks? Relevant output is shown below.

At the 0.05 level of significance, the correct conclusion is
A) Reject the null hypothesis.
B) Do not reject the null hypothesis.
C) Evidence suggests that there is a significant difference in mean mortgage rates between credit unions and banks.
D) Reject the null hypothesis and evidence suggests that there is a significant difference in mean mortgage rates between credit unions and banks.
E) Do not reject the null hypothesis and evidence suggests that there is a significant difference in mean mortgage rates between credit unions and banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is not an assumption or condition that needs to be checked for a paired t-interval?
A) Paired Data
B) Independent Groups
C) Randomization
D) 10% Condition
E) Nearly Normal Condition
A) Paired Data
B) Independent Groups
C) Randomization
D) 10% Condition
E) Nearly Normal Condition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
At the 0.05 level of significance, the correct conclusion is
A) Evidence suggests that the demand is the same for different types of boats.
B) Evidence suggests that the demand is not the same for different types of boats.
C) Reject the null hypothesis.
D) Evidence suggests that the demand is the same for different types of boats and that we should reject the null hypothesis
E) Evidence suggests that the demand is not the same for different types of boats and that we should reject the null hypothesis.
A) Evidence suggests that the demand is the same for different types of boats.
B) Evidence suggests that the demand is not the same for different types of boats.
C) Reject the null hypothesis.
D) Evidence suggests that the demand is the same for different types of boats and that we should reject the null hypothesis
E) Evidence suggests that the demand is not the same for different types of boats and that we should reject the null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A professor was interested in determining whether the prices of new textbooks in the bookstore were higher than if purchased online. She selected 6 textbooks and priced each at the bookstore and online. Which statement is true at 5% significance level? 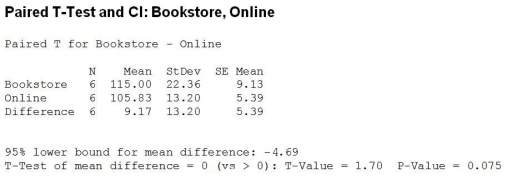
A) The online prices are at least as high as the prices in the bookstore.
B) The prices are higher in the bookstore.
C) The prices are higher online.
D) The prices are different in the bookstore and online.
E) The analysis is not conclusive.

A) The online prices are at least as high as the prices in the bookstore.
B) The prices are higher in the bookstore.
C) The prices are higher online.
D) The prices are different in the bookstore and online.
E) The analysis is not conclusive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A sample of 30 year fixed mortgage rates at 12 randomly chosen credit unions yields a mean rate of 6.65 % and a sample standard deviation of 0.39%. A sample of 30 year fixed mortgage rates at 16 randomly selected banks yields a mean rate of 7.05% and a sample standard deviation of 0.22%. Are the mean rates different between credit unions and banks? Relevant output is shown below.
Which of the following is true?
A) This is a paired design.
B) This is a test of two means from independent samples.
C) This is a one-tailed test.
D) This is a paired design and this is a one-tailed test.
E) This is a test of two means from independent samples and this is a one-tailed test.
A sample of 30 year fixed mortgage rates at 12 randomly chosen credit unions yields a mean rate of 6.65 % and a sample standard deviation of 0.39%. A sample of 30 year fixed mortgage rates at 16 randomly selected banks yields a mean rate of 7.05% and a sample standard deviation of 0.22%. Are the mean rates different between credit unions and banks? Relevant output is shown below.

Which of the following is true?
A) This is a paired design.
B) This is a test of two means from independent samples.
C) This is a one-tailed test.
D) This is a paired design and this is a one-tailed test.
E) This is a test of two means from independent samples and this is a one-tailed test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Three brands of AAA batteries are compared to determine if differences in lifetime exist. Each brand is tested in four devices (TV remote, hand-held game, flashlight and digital camera). The experiment is run once for each combination of brand and device. The twelve runs are ordered randomly. The time (in minutes) that each battery lasts under continuous usage is recorded. The partial ANOVA results are as follows: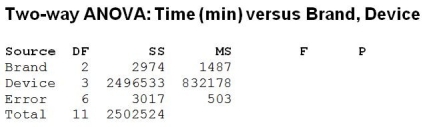
The F-statistic for testing whether the three brands of AAA batteries have equal mean lifetimes is
A) 2.96
B) 1654.89
C) 0.98
D) 827.49
E) 54.67
Three brands of AAA batteries are compared to determine if differences in lifetime exist. Each brand is tested in four devices (TV remote, hand-held game, flashlight and digital camera). The experiment is run once for each combination of brand and device. The twelve runs are ordered randomly. The time (in minutes) that each battery lasts under continuous usage is recorded. The partial ANOVA results are as follows:

The F-statistic for testing whether the three brands of AAA batteries have equal mean lifetimes is
A) 2.96
B) 1654.89
C) 0.98
D) 827.49
E) 54.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
The weights of soy patties sold by Veggie Burgers Delight are normally distributed. A random sample of 15 patties yields a mean weight of 108 grams with a sample standard deviation of 14 grams. At the 0.05 level of significance, perform a hypothesis test to see if the true mean weight is less than 113 grams.
The correct conclusion at the 0.05 level of significance is
A) Fail to reject the null hypothesis, and there is no evidence that the true mean weight is less than 113 grams.
B) Reject the null hypothesis.
C) Evidence suggests that the mean weight is less than 113 grams.
D) Do not reject the null hypothesis and evidence suggests that the mean weight is less than 113 grams.
E) Reject the null hypothesis and evidence suggests that the mean weight is less than 113 grams.
The weights of soy patties sold by Veggie Burgers Delight are normally distributed. A random sample of 15 patties yields a mean weight of 108 grams with a sample standard deviation of 14 grams. At the 0.05 level of significance, perform a hypothesis test to see if the true mean weight is less than 113 grams.
The correct conclusion at the 0.05 level of significance is
A) Fail to reject the null hypothesis, and there is no evidence that the true mean weight is less than 113 grams.
B) Reject the null hypothesis.
C) Evidence suggests that the mean weight is less than 113 grams.
D) Do not reject the null hypothesis and evidence suggests that the mean weight is less than 113 grams.
E) Reject the null hypothesis and evidence suggests that the mean weight is less than 113 grams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Three brands of AAA batteries are compared to determine if differences in lifetime exist. Each brand is tested in four devices (TV remote, hand-held game, flashlight and digital camera). The experiment is run once for each combination of brand and device. The twelve runs are ordered randomly. The time (in minutes) that each battery lasts under continuous usage is recorded. The partial ANOVA results are as follows:
The P-value associated with this F-statistic is 0.128. Based on this we can conclude that
A) We should reject the null hypothesis.
B) There is a difference in the mean lifetimes among the different brands.
C) There is a difference in the mean lifetimes among the different devices.
D) There is no significant interaction effect.
E) There is no difference in the mean lifetimes among the different brands.
Three brands of AAA batteries are compared to determine if differences in lifetime exist. Each brand is tested in four devices (TV remote, hand-held game, flashlight and digital camera). The experiment is run once for each combination of brand and device. The twelve runs are ordered randomly. The time (in minutes) that each battery lasts under continuous usage is recorded. The partial ANOVA results are as follows:

The P-value associated with this F-statistic is 0.128. Based on this we can conclude that
A) We should reject the null hypothesis.
B) There is a difference in the mean lifetimes among the different brands.
C) There is a difference in the mean lifetimes among the different devices.
D) There is no significant interaction effect.
E) There is no difference in the mean lifetimes among the different brands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A government agency has 6000 employees. As an alternative to the traditional five day work week, employees were asked whether they preferred a four day work week (10 hours per day) or flexible hours. The table below shows the results by age category.

What is the probability that an employee at this government agency prefers a four day work week?
A) 0.54
B) 0.15
C) 0.50
D) 0.35
E) 0.65
A government agency has 6000 employees. As an alternative to the traditional five day work week, employees were asked whether they preferred a four day work week (10 hours per day) or flexible hours. The table below shows the results by age category.

What is the probability that an employee at this government agency prefers a four day work week?
A) 0.54
B) 0.15
C) 0.50
D) 0.35
E) 0.65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Chris Columbus is responsible for controlling inventory levels for four types of sailboats sold by his company. Chris takes a sample of 48 boats sold over the past several months to determine if demand is the same for each type. His results are as follows:
Type of Boat Sales
Pirate's Revenge 15
Jolly Roger 11
Sails Delight 10
Cruiser Cove 12
The calculated value of the Chi Square statistic is
A) 7.815
B) 1.17
C) 22.35
D) -1.17
E) 12.56
Chris Columbus is responsible for controlling inventory levels for four types of sailboats sold by his company. Chris takes a sample of 48 boats sold over the past several months to determine if demand is the same for each type. His results are as follows:
Type of Boat Sales
Pirate's Revenge 15
Jolly Roger 11
Sails Delight 10
Cruiser Cove 12
The calculated value of the Chi Square statistic is
A) 7.815
B) 1.17
C) 22.35
D) -1.17
E) 12.56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Absorption rates into the body are important considerations when manufacturing a generic version of a brand-name drug. A pharmacist read that the absorption rate into the body of a new generic drug (G) is the same as its brand-name counterpart (B). She has a researcher friend of hers run a small experiment to test H0: μG - μB = 0 against the alternative HA: μG - μB ≠ 0. Which of the following would be a Type I error?
A) Deciding that the absorption rates are the same, when in fact they are.
B) Deciding that the absorption rates are different, when in fact they are.
C) Deciding that the absorption rates are the same, when in fact they are not.
D) Deciding that the absorption rates are different, when in fact they are not.
E) The researcher cannot make a Type I error, since he has run an experiment.
A) Deciding that the absorption rates are the same, when in fact they are.
B) Deciding that the absorption rates are different, when in fact they are.
C) Deciding that the absorption rates are the same, when in fact they are not.
D) Deciding that the absorption rates are different, when in fact they are not.
E) The researcher cannot make a Type I error, since he has run an experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Chris Columbus is responsible for controlling inventory levels for four types of sailboats sold by his company. Chris takes a sample of 48 boats sold over the past several months to determine if demand is the same for each type. His results are as follows:
Type of Boat Sales
Pirate's Revenge 15
Jolly Roger 11
Sails Delight 10
Cruiser Cove 12
The correct null hypothesis to be tested is
A) Type of boat and demand are related.
B) The demand differs for each type of boat.
C) The demand is the same for each type of boat.
D) Type of boat and demand are related and the demand differs for each type of boat.
E) Type of boat and demand are related and the demand is the same for each type of boat.
Chris Columbus is responsible for controlling inventory levels for four types of sailboats sold by his company. Chris takes a sample of 48 boats sold over the past several months to determine if demand is the same for each type. His results are as follows:
Type of Boat Sales
Pirate's Revenge 15
Jolly Roger 11
Sails Delight 10
Cruiser Cove 12
The correct null hypothesis to be tested is
A) Type of boat and demand are related.
B) The demand differs for each type of boat.
C) The demand is the same for each type of boat.
D) Type of boat and demand are related and the demand differs for each type of boat.
E) Type of boat and demand are related and the demand is the same for each type of boat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A publishing company conducted a survey of its readership and found that 60% subscribed to Food & Wine, 30% subscribed to Wine Spectator, and 25% subscribed to both.
The probability that a reader subscribes to Food & Wine or Wine Spectator is
A) 0.90
B) 0.65
C) 0.25
D) 0.50
E) 0.85
A publishing company conducted a survey of its readership and found that 60% subscribed to Food & Wine, 30% subscribed to Wine Spectator, and 25% subscribed to both.
The probability that a reader subscribes to Food & Wine or Wine Spectator is
A) 0.90
B) 0.65
C) 0.25
D) 0.50
E) 0.85

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose that 6 economists who work for the federal government and 7 university economists were asked to grade the effectiveness of an economic stimulus bill in terms of its ability to increase jobs over the next two years. What nonparametric method is appropriate for testing if the two groups differ in terms of their opinion?
A) Wilcoxon rank-sum test
B) Wilcoxon signed-rank test
C) Spearman's rho test
D) Kruskal-Wallis Test
E) Kendall's tau test
A) Wilcoxon rank-sum test
B) Wilcoxon signed-rank test
C) Spearman's rho test
D) Kruskal-Wallis Test
E) Kendall's tau test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A publishing company conducted a survey of its readership and found that 60% subscribed to Food & Wine, 30% subscribed to Wine Spectator, and 25% subscribed to both.
The probability that a reader does not subscribe to either is
A) 0.10
B) 0.65
C) 0.50
D) 0.45
E) 0.35
A publishing company conducted a survey of its readership and found that 60% subscribed to Food & Wine, 30% subscribed to Wine Spectator, and 25% subscribed to both.
The probability that a reader does not subscribe to either is
A) 0.10
B) 0.65
C) 0.50
D) 0.45
E) 0.35

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A telecommunications company is interested in determining the likelihood of a new breakthrough technology being developed in the next ten years. What type of probability would they estimate?
A) Relative Frequency
B) Classical
C) Personal
D) Mathematical
E) Empirical
A) Relative Frequency
B) Classical
C) Personal
D) Mathematical
E) Empirical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Based on the scatterplot shown below, what makes a nonparametric method more appropriate than the Pearson correlation for measuring the association between the two variables? 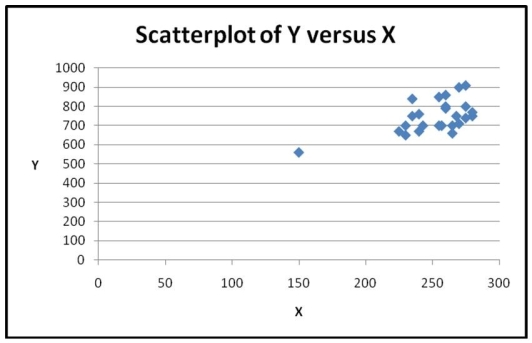
A) Nonlinearity
B) These variables are not quantitative.
C) The presence of an outlier
D) Nonlinearity and the fact that these variables are not quantitative
E) Nonlinearity, the fact that these variables are not quantitative as well as the presence of an outlier

A) Nonlinearity
B) These variables are not quantitative.
C) The presence of an outlier
D) Nonlinearity and the fact that these variables are not quantitative
E) Nonlinearity, the fact that these variables are not quantitative as well as the presence of an outlier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Based on the following plot, what can you say about the conditions for ANOVA? 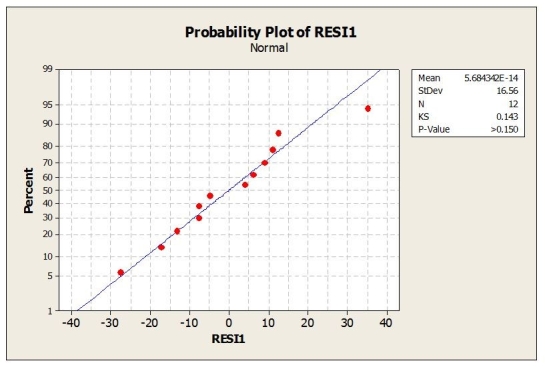
A) The equal variance assumption is satisfied.
B) The linearity assumption is satisfied.
C) The nearly normal assumption is satisfied.
D) The nearly normal assumption is not satisfied.
E) The additive assumption is satisfied.

A) The equal variance assumption is satisfied.
B) The linearity assumption is satisfied.
C) The nearly normal assumption is satisfied.
D) The nearly normal assumption is not satisfied.
E) The additive assumption is satisfied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Three brands of AAA batteries are compared to determine if differences in lifetime exist. Each brand is tested in four devices (TV remote, hand-held game, flashlight and digital camera). The experiment is run once for each combination of brand and device. The twelve runs are ordered randomly. The time (in minutes) that each battery lasts under continuous usage is recorded. The partial ANOVA results are as follows:
Which of the following statements is true about this design?
A) This is a completely randomized design in one factor.
B) The devices serve as blocks to account for the variability between the lengths of time batteries last in different devices.
C) The interaction effect between brand of battery and type of device is significant.
D) This is an observational study.
E) This is a retrospective study.
Three brands of AAA batteries are compared to determine if differences in lifetime exist. Each brand is tested in four devices (TV remote, hand-held game, flashlight and digital camera). The experiment is run once for each combination of brand and device. The twelve runs are ordered randomly. The time (in minutes) that each battery lasts under continuous usage is recorded. The partial ANOVA results are as follows:

Which of the following statements is true about this design?
A) This is a completely randomized design in one factor.
B) The devices serve as blocks to account for the variability between the lengths of time batteries last in different devices.
C) The interaction effect between brand of battery and type of device is significant.
D) This is an observational study.
E) This is a retrospective study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A human resources manager at a large company wants to estimate the proportion of employees that would be interested in reimbursement for college courses. If she wishes to be 95% confident that her estimate is within 5% of the true proportion, how many employees would need to be sampled?
A) 271
B) 385
C) 543
D) 646
E) 1234
A) 271
B) 385
C) 543
D) 646
E) 1234

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A manufacturer of cordless electric shavers sampled 13 from a day's production and found the mean time of continuous usage without recharging to be 410 minutes with a sample standard deviation of 30 minutes. We can assume that times are normally distributed. We wish to test if the true mean operating time without recharging is more than 400 minutes.
The correct calculated value of the test statistic is
A) 1.20
B) -0.333
C) -2.52
D) -1.20
E) 2.79
A manufacturer of cordless electric shavers sampled 13 from a day's production and found the mean time of continuous usage without recharging to be 410 minutes with a sample standard deviation of 30 minutes. We can assume that times are normally distributed. We wish to test if the true mean operating time without recharging is more than 400 minutes.
The correct calculated value of the test statistic is
A) 1.20
B) -0.333
C) -2.52
D) -1.20
E) 2.79

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Shape-Up-By-Susie claims that participating in her exercise program will result in guaranteed weight loss in just 6 weeks. Five clients weighed themselves before and then again after participating in her program and the differences "weight after - weight before" were analyzed. Below is the relevant computer output.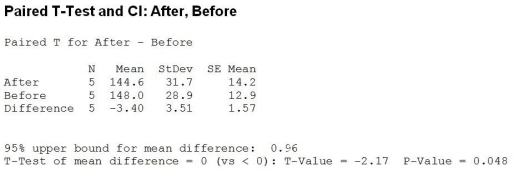
Which of the following statement is true?
A) This is a paired design.
B) This is a two-tailed test.
C) This is a one-tailed test.
D) This is a paired design, and it is a two-tailed test.
E) This is a paired design, and it is a one-tailed test.
Shape-Up-By-Susie claims that participating in her exercise program will result in guaranteed weight loss in just 6 weeks. Five clients weighed themselves before and then again after participating in her program and the differences "weight after - weight before" were analyzed. Below is the relevant computer output.

Which of the following statement is true?
A) This is a paired design.
B) This is a two-tailed test.
C) This is a one-tailed test.
D) This is a paired design, and it is a two-tailed test.
E) This is a paired design, and it is a one-tailed test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
IT staff for a large corporation has developed the following probability distribution for the number of calls requiring troubleshooting problems per day.
Number of Calls Probability
0 0.32
1 0.35
2 0.18
3 0.10
4 0.05
The expected number of calls per day is
A) 2.77
B) 1.56
C) 1.21
D) 1.31
E) 1.0
IT staff for a large corporation has developed the following probability distribution for the number of calls requiring troubleshooting problems per day.
Number of Calls Probability
0 0.32
1 0.35
2 0.18
3 0.10
4 0.05
The expected number of calls per day is
A) 2.77
B) 1.56
C) 1.21
D) 1.31
E) 1.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Suppose the time it takes for a purchasing agent to complete an online ordering process is normally distributed with a mean of 8 minutes and a standard deviation of 2 minutes. Suppose a random sample of 25 ordering processes is selected.
What is the probability that the sample mean will be less than 7.5 minutes?
A) 0.3944
B) 0.1056
C) 0.2114
D) 0.4013
E) 0.8944
Suppose the time it takes for a purchasing agent to complete an online ordering process is normally distributed with a mean of 8 minutes and a standard deviation of 2 minutes. Suppose a random sample of 25 ordering processes is selected.
What is the probability that the sample mean will be less than 7.5 minutes?
A) 0.3944
B) 0.1056
C) 0.2114
D) 0.4013
E) 0.8944

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Shape-Up-By-Susie claims that participating in her exercise program will result in guaranteed weight loss in just 6 weeks. Five clients weighed themselves before and then again after participating in her program and the differences "weight after - weight before" were analyzed. Below is the relevant computer output.
At the 0.05 level of significance, the correct conclusion is
A) Reject the null hypothesis.
B) Do not reject the null hypothesis.
C) Susie's claim is supported by the sample evidence.
D) Reject the null hypothesis and find that Susie's claim is supported by the sample evidence.
E) Do not reject the null hypothesis and find that Susie's claim is supported by the sample evidence.
Shape-Up-By-Susie claims that participating in her exercise program will result in guaranteed weight loss in just 6 weeks. Five clients weighed themselves before and then again after participating in her program and the differences "weight after - weight before" were analyzed. Below is the relevant computer output.

At the 0.05 level of significance, the correct conclusion is
A) Reject the null hypothesis.
B) Do not reject the null hypothesis.
C) Susie's claim is supported by the sample evidence.
D) Reject the null hypothesis and find that Susie's claim is supported by the sample evidence.
E) Do not reject the null hypothesis and find that Susie's claim is supported by the sample evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which is true about a 99% confidence interval based on a given sample?
I) The interval contains 99% of the population.
II) Results from 99% of all samples will lie in this interval.
III) The interval is wider than a 95% confidence interval would be.
A) None
B) I only
C) II only
D) III only
E) I and III
I) The interval contains 99% of the population.
II) Results from 99% of all samples will lie in this interval.
III) The interval is wider than a 95% confidence interval would be.
A) None
B) I only
C) II only
D) III only
E) I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
After computing a confidence interval, the investigator believes that the results are meaningless because the width of the interval is too large. In reconstructing the interval, the investigator should
A) decrease the sample size
B) increase the level of confidence
C) increase the sample size
D) reduce the population variance
E) decrease the sample size and increase the level of confidence
A) decrease the sample size
B) increase the level of confidence
C) increase the sample size
D) reduce the population variance
E) decrease the sample size and increase the level of confidence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An urban planning group is interested in estimating the difference in mean household income between two neighbourhoods. They obtain the following 95% confidence interval: 95% CI for difference: (-5693, -4107).
Which of the following is true?
A) This is a paired design.
B) There is no significant difference in the mean household incomes between the two neighbourhoods.
C) There is a significant difference in the mean household incomes between the two neighbourhoods.
D) This is a paired design and there is no significant difference in the mean household incomes between the two neighbourhoods.
E) This is a paired design and there is a significant difference in the mean household incomes between the two neighbourhoods.
Which of the following is true?
A) This is a paired design.
B) There is no significant difference in the mean household incomes between the two neighbourhoods.
C) There is a significant difference in the mean household incomes between the two neighbourhoods.
D) This is a paired design and there is no significant difference in the mean household incomes between the two neighbourhoods.
E) This is a paired design and there is a significant difference in the mean household incomes between the two neighbourhoods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A newspaper poll asked respondents if they trusted "eco friendly" labels on cleaning products. Out of 1000 adults surveyed, 498 responded "yes." We would like to test if the proportion of respondents that trust these labels is at least 50%.
The correct alternative hypothesis is
A) p = 0.50
B) p ≤ 0.50
C) p ≥ 0.50
D) p > 0.50
E) p < 0.50
A newspaper poll asked respondents if they trusted "eco friendly" labels on cleaning products. Out of 1000 adults surveyed, 498 responded "yes." We would like to test if the proportion of respondents that trust these labels is at least 50%.
The correct alternative hypothesis is
A) p = 0.50
B) p ≤ 0.50
C) p ≥ 0.50
D) p > 0.50
E) p < 0.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements is true about work week preferences and age category?
A) Work week preferences are independent of age category.
B) Work week preferences are mutually exclusive.
C) Work week preferences are not independent of age category.
D) Work week preferences are independent and mutually exclusive.
E) There is insufficient information to determine whether work week preferences and age category are independent or mutually exclusive.
A) Work week preferences are independent of age category.
B) Work week preferences are mutually exclusive.
C) Work week preferences are not independent of age category.
D) Work week preferences are independent and mutually exclusive.
E) There is insufficient information to determine whether work week preferences and age category are independent or mutually exclusive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A manufacturer of cordless electric shavers sampled 13 from a day's production and found the mean time of continuous usage without recharging to be 410 minutes with a sample standard deviation of 30 minutes. We can assume that times are normally distributed. We wish to test if the true mean operating time without recharging is more than 400 minutes.
The correct null and alternative hypotheses are
A) H0: µ = 400; HA: µ < 400
B) H0: µ = 400; HA: µ > 400
C) H0: µ > 400; HA: µ = 400
D) H0: µ < 400; HA: µ = 400
E) H0: µ = 400; HA: µ ≠ 400
A manufacturer of cordless electric shavers sampled 13 from a day's production and found the mean time of continuous usage without recharging to be 410 minutes with a sample standard deviation of 30 minutes. We can assume that times are normally distributed. We wish to test if the true mean operating time without recharging is more than 400 minutes.
The correct null and alternative hypotheses are
A) H0: µ = 400; HA: µ < 400
B) H0: µ = 400; HA: µ > 400
C) H0: µ > 400; HA: µ = 400
D) H0: µ < 400; HA: µ = 400
E) H0: µ = 400; HA: µ ≠ 400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A contact lens wearer read that the producer of a new contact lens boasts that their lenses are cheaper than contact lenses from another popular company. The null hypothesis H0: μold -μnew = 0 is tested against the alternative HA: μold -μnew > 0 . Which of the following would be a Type II error?
A) Deciding that the new lenses are cheaper, when in fact they really are
B) Deciding that the new lenses are cheaper, when in fact they are not
C) Deciding that the new lenses are not really cheaper, when in fact they are
D) Deciding that the new lenses are not really cheaper, when in fact they are not
E) It does not matter.
A) Deciding that the new lenses are cheaper, when in fact they really are
B) Deciding that the new lenses are cheaper, when in fact they are not
C) Deciding that the new lenses are not really cheaper, when in fact they are
D) Deciding that the new lenses are not really cheaper, when in fact they are not
E) It does not matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A newspaper poll asked respondents if they trusted "eco friendly" labels on cleaning products. Out of 1000 adults surveyed, 498 responded "yes." We would like to test if the proportion of respondents that trust these labels is at least 50%.
The calculated test statistic value is
A) -0.126
B) -2.45
C) 1.27
D) -1.89
E) 0.139
A newspaper poll asked respondents if they trusted "eco friendly" labels on cleaning products. Out of 1000 adults surveyed, 498 responded "yes." We would like to test if the proportion of respondents that trust these labels is at least 50%.
The calculated test statistic value is
A) -0.126
B) -2.45
C) 1.27
D) -1.89
E) 0.139

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A type I error is committed when
A) We don't reject a null hypothesis that is true.
B) We reject a null hypothesis that is false.
C) We reject a null hypothesis that is true.
D) We don't reject a null hypothesis that is false.
E) The null hypothesis is not properly constructed.
A) We don't reject a null hypothesis that is true.
B) We reject a null hypothesis that is false.
C) We reject a null hypothesis that is true.
D) We don't reject a null hypothesis that is false.
E) The null hypothesis is not properly constructed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
At the 0.01 level of significance, the correct conclusion is
A) Do not reject the null hypothesis.
B) Reject the null hypothesis.
C) Evidence suggests that at least 50% of respondents trust "eco-friendly" labels.
D) Do not reject the null hypothesis and find that evidence suggests that at least 50% of respondents trust "eco-friendly" labels.
E) Reject the null hypothesis and find that evidence suggests that at least 50% of respondents trust "eco-friendly" labels.
A) Do not reject the null hypothesis.
B) Reject the null hypothesis.
C) Evidence suggests that at least 50% of respondents trust "eco-friendly" labels.
D) Do not reject the null hypothesis and find that evidence suggests that at least 50% of respondents trust "eco-friendly" labels.
E) Reject the null hypothesis and find that evidence suggests that at least 50% of respondents trust "eco-friendly" labels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A manufacturer of cordless electric shavers sampled 13 from a day's production and found the mean time of continuous usage without recharging to be 410 minutes with a sample standard deviation of 30 minutes. We can assume that times are normally distributed. We wish to test if the true mean operating time without recharging is more than 400 minutes.
The correct conclusion at the 0.05 level of significance is
A) Reject the null hypothesis.
B) Fail to reject the null hypothesis, and there is no evidence that true mean operating time without recharging is more than 400 minutes.
C) Evidence suggests that the mean operating time is more than 400 minutes.
D) Reject the null hypothesis and find that evidence suggests that the mean operating time is more than 400 minutes.
E) Do not reject the null hypothesis and find that evidence suggests that the mean operating time is more than 400 minutes.
A manufacturer of cordless electric shavers sampled 13 from a day's production and found the mean time of continuous usage without recharging to be 410 minutes with a sample standard deviation of 30 minutes. We can assume that times are normally distributed. We wish to test if the true mean operating time without recharging is more than 400 minutes.
The correct conclusion at the 0.05 level of significance is
A) Reject the null hypothesis.
B) Fail to reject the null hypothesis, and there is no evidence that true mean operating time without recharging is more than 400 minutes.
C) Evidence suggests that the mean operating time is more than 400 minutes.
D) Reject the null hypothesis and find that evidence suggests that the mean operating time is more than 400 minutes.
E) Do not reject the null hypothesis and find that evidence suggests that the mean operating time is more than 400 minutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
IT staff for a large corporation has developed the following probability distribution for the number of calls requiring troubleshooting problems per day.
Number of Calls Probability
0 0.32
1 0.35
2 0.18
3 0.10
4 0.05
The standard deviation in the number of calls per day is
A) 1.31
B) 1.14
C) 2.77
D) 1.56
E) 1.21
IT staff for a large corporation has developed the following probability distribution for the number of calls requiring troubleshooting problems per day.
Number of Calls Probability
0 0.32
1 0.35
2 0.18
3 0.10
4 0.05
The standard deviation in the number of calls per day is
A) 1.31
B) 1.14
C) 2.77
D) 1.56
E) 1.21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Suppose the time it takes for a purchasing agent to complete an online ordering process is normally distributed with a mean of 8 minutes and a standard deviation of 2 minutes. Suppose a random sample of 25 ordering processes is selected.
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution of mean times is
A) 0.4 minutes
B) 2 minutes
C) 0.08 minutes
D) 1.6 minutes
E) 0.12 minutes
Suppose the time it takes for a purchasing agent to complete an online ordering process is normally distributed with a mean of 8 minutes and a standard deviation of 2 minutes. Suppose a random sample of 25 ordering processes is selected.
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution of mean times is
A) 0.4 minutes
B) 2 minutes
C) 0.08 minutes
D) 1.6 minutes
E) 0.12 minutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If a population is normally distributed with µ = 500 and σ = 50, and a sample of size 20 is selected, the probability that the sample mean falls between 450 and 550 will be ________ the probability that an individual value falls between 450 and 550.
A) the same as
B) less than
C) greater than
D) less than or the same as
E) not enough information given
A) the same as
B) less than
C) greater than
D) less than or the same as
E) not enough information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is not an assumption or condition that needs to be checked for a two-sample t-test for the difference between two means?
A) Independent Groups
B) Randomization
C) 10% Condition
D) Nearly Normal Condition
E) 90% Condition
A) Independent Groups
B) Randomization
C) 10% Condition
D) Nearly Normal Condition
E) 90% Condition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A local politician was interested in determining whether income level affects opinion regarding the governments' bailout bill of the auto industry during the 2008 financial crisis. He surveyed a sample of his constituents and got the following results.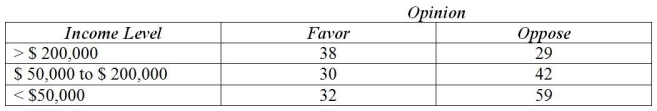
The calculated value of the Chi Square statistic is
A) 7.433
B) 29.13
C) 40.70
D) 5.999
E) 2.347
A local politician was interested in determining whether income level affects opinion regarding the governments' bailout bill of the auto industry during the 2008 financial crisis. He surveyed a sample of his constituents and got the following results.

The calculated value of the Chi Square statistic is
A) 7.433
B) 29.13
C) 40.70
D) 5.999
E) 2.347

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The best tasting ice creams are generally high in fat content, which gives them a creamy texture. Four brands of ice cream (two national and two local) were tested by consumers who graded their level of creaminess (A = very creamy to F = not creamy). Each brand was rated by a different group of consumers (the data are shown below). 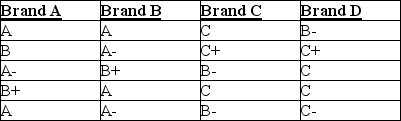 Using the Kruskal-Wallis test, at α = 0.10 we would conclude that
Using the Kruskal-Wallis test, at α = 0.10 we would conclude that
A) The null hypothesis should be rejected.
B) The null hypothesis should be accepted.
C) There is no difference in creaminess among the brands.
D) The null hypothesis should be rejected and that there is no difference in creaminess among the brands.
E) The null hypothesis should be accepted and find that there is no difference in creaminess among the brands.
 Using the Kruskal-Wallis test, at α = 0.10 we would conclude that
Using the Kruskal-Wallis test, at α = 0.10 we would conclude thatA) The null hypothesis should be rejected.
B) The null hypothesis should be accepted.
C) There is no difference in creaminess among the brands.
D) The null hypothesis should be rejected and that there is no difference in creaminess among the brands.
E) The null hypothesis should be accepted and find that there is no difference in creaminess among the brands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
At the 0.01 level of significance, the correct conclusion is
A) Income level affects opinion.
B) There is a relationship between income level and opinion.
C) Opinion and income level are independent.
D) Reject the null hypothesis.
E) Reject the null hypothesis and find that there is a relationship between income level and opinion.
A) Income level affects opinion.
B) There is a relationship between income level and opinion.
C) Opinion and income level are independent.
D) Reject the null hypothesis.
E) Reject the null hypothesis and find that there is a relationship between income level and opinion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Preparing wheat for use in bread and pasta products generally involves both milling and bleaching. A company that processes wheat is interested in determining the best combination of milling and bleaching that results in a desirable wheat product without sacrificing fibre content. They vary the milling time (short, medium and long) and bleaching (no bleaching and bleaching) and measure fibre content (gms/100 grams) of the resulting wheat product. The partial ANOVA results apply.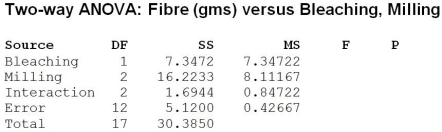
The F-statistic for testing whether bleaching has an effect on fibre content is
A) 17.22
B) 19.01
C) 1.99
D) 1.43
E) 45.22
Preparing wheat for use in bread and pasta products generally involves both milling and bleaching. A company that processes wheat is interested in determining the best combination of milling and bleaching that results in a desirable wheat product without sacrificing fibre content. They vary the milling time (short, medium and long) and bleaching (no bleaching and bleaching) and measure fibre content (gms/100 grams) of the resulting wheat product. The partial ANOVA results apply.

The F-statistic for testing whether bleaching has an effect on fibre content is
A) 17.22
B) 19.01
C) 1.99
D) 1.43
E) 45.22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is true about this study?
A) It is an observational study.
B) It is a completely randomized design in one factor.
C) The different levels of milling time act as blocks in the design.
D) It is an experimental study.
E) The different levels of bleaching act as blocks in the design.
A) It is an observational study.
B) It is a completely randomized design in one factor.
C) The different levels of milling time act as blocks in the design.
D) It is an experimental study.
E) The different levels of bleaching act as blocks in the design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
Preparing wheat for use in bread and pasta products generally involves both milling and bleaching. A company that processes wheat is interested in determining the best combination of milling and bleaching that results in a desirable wheat product without sacrificing fibre content. They vary the milling time (short, medium and long) and bleaching (no bleaching and bleaching) and measure fibre content (gms/100 grams) of the resulting wheat product. The partial ANOVA results apply.
The F-statistic for testing whether milling has an effect on fibre content is
A) 17.22
B) 19.01
C) 1.99
D) 1.43
E) 45.22
Preparing wheat for use in bread and pasta products generally involves both milling and bleaching. A company that processes wheat is interested in determining the best combination of milling and bleaching that results in a desirable wheat product without sacrificing fibre content. They vary the milling time (short, medium and long) and bleaching (no bleaching and bleaching) and measure fibre content (gms/100 grams) of the resulting wheat product. The partial ANOVA results apply.

The F-statistic for testing whether milling has an effect on fibre content is
A) 17.22
B) 19.01
C) 1.99
D) 1.43
E) 45.22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer the question(s) below.
A local politician was interested in determining whether income level affects opinion regarding the governments' bailout bill of the auto industry during the 2008 financial crisis. He surveyed a sample of his constituents and got the following results.
The correct null hypothesis to be tested is
A) There is no relationship between income level and opinion.
B) There is a relationship between income level and opinion.
C) Opinion depends on income level.
D) Opinion and income level are not independent
E) There is a relationship between income level and opinion and, and opinion and income level are not independent.
A local politician was interested in determining whether income level affects opinion regarding the governments' bailout bill of the auto industry during the 2008 financial crisis. He surveyed a sample of his constituents and got the following results.

The correct null hypothesis to be tested is
A) There is no relationship between income level and opinion.
B) There is a relationship between income level and opinion.
C) Opinion depends on income level.
D) Opinion and income level are not independent
E) There is a relationship between income level and opinion and, and opinion and income level are not independent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The P-value associated with the F-statistic for the interaction effect is 0.180. Based on this we can conclude that
A) There is a significant interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) The significance of the interaction effect will not affect the interpretation of the main effects on fibre content due to milling and bleaching.
D) There is a significant interaction effect, and it is not appropriate to interpret the main effects on fibre content due to milling and bleaching separately.
E) There is not a significant interaction effect, and it is appropriate to interpret the main effects on fibre content due to milling and bleaching separately.
A) There is a significant interaction effect.
B) There is an interaction effect.
C) The significance of the interaction effect will not affect the interpretation of the main effects on fibre content due to milling and bleaching.
D) There is a significant interaction effect, and it is not appropriate to interpret the main effects on fibre content due to milling and bleaching separately.
E) There is not a significant interaction effect, and it is appropriate to interpret the main effects on fibre content due to milling and bleaching separately.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The best tasting ice creams are generally high in fat content, which gives them a creamy texture. Four brands of ice cream were tested by consumers who graded their level of creaminess (A = very creamy to F = not creamy). Each brand was rated by a different group of consumers (the data are shown below). 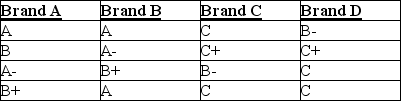 A A- B- C-
A A- B- C-
Using the Kruskal-Wallis test, the value of H is
A) 14.51
B) 22.10
C) 6.351
D) 5.999
E) Indeterminate with the information that is given.
 A A- B- C-
A A- B- C-Using the Kruskal-Wallis test, the value of H is
A) 14.51
B) 22.10
C) 6.351
D) 5.999
E) Indeterminate with the information that is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



