Deck 28: Translation of the Financial Statements of Foreign Entities
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Translation of the Financial Statements of Foreign Entities
1
If foreign currency denominated non-monetary items are measured using the fair value method, they must be translated into the functional currency using the:
A) exchange rate at the date when the value was determined;
B) exchange rate current at end of reporting period;
C) closing exchange rate for the financial year;
D) exchange rate at the transaction date.
A) exchange rate at the date when the value was determined;
B) exchange rate current at end of reporting period;
C) closing exchange rate for the financial year;
D) exchange rate at the transaction date.
A
2
Differences arise in relation to the treatment of which of the following when translating from the local to functional currency as opposed to the functional to presentation currency?
A) accounts receivable
B) cost of goods sold
C) depreciation expense
D) share capital
A) accounts receivable
B) cost of goods sold
C) depreciation expense
D) share capital
C
3
In order for the financial statements of a foreign operation to be included in the consolidated financial statements of the parent it is necessary to translate the foreign operation's financial statements into:
A) the presentation currency of the reporting entity;
B) the functional currency of the foreign operation;
C) the local currency of the foreign operation;
D) the domestic currency of the foreign operation;
A) the presentation currency of the reporting entity;
B) the functional currency of the foreign operation;
C) the local currency of the foreign operation;
D) the domestic currency of the foreign operation;
A
4
The following information relates to question 3 and 4
Aussie Ltd acquired 100% of Sing Sing Ltd (Sing Sing) on 1 July 20X0. The balance sheet of Sing Sing on that date was as follows:
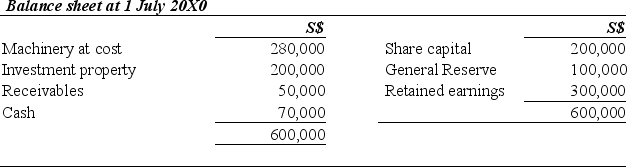
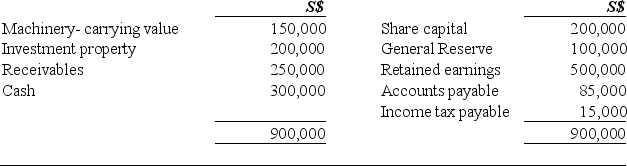
The balance sheet of Sing Sing as at is as follows:
Balance Sheet as at 30 June 20X1
Relevant exchange rates are as follows:

-If the functional currency of Sing Sing is Singapore dollars and the presentation currency is Australian dollars the total assets of S$900,000 would translate into Australian dollars as:
A) $703 125
B) $709 688
C) $1 141 500
D) $1 152 000
Aussie Ltd acquired 100% of Sing Sing Ltd (Sing Sing) on 1 July 20X0. The balance sheet of Sing Sing on that date was as follows:

The balance sheet of Sing Sing as at is as follows:
Balance Sheet as at 30 June 20X1

Relevant exchange rates are as follows:

-If the functional currency of Sing Sing is Singapore dollars and the presentation currency is Australian dollars the total assets of S$900,000 would translate into Australian dollars as:
A) $703 125
B) $709 688
C) $1 141 500
D) $1 152 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Aussie Ltd has an investment in Yankee Inc. The shares in Yankee were acquired on 15 August 20X4. Yankee uses the revaluation model to account for land & buildings. A building which was acquired by Yankee on 1 April 20X2 was revalued on 15 March 20X9. The exchange rate used to translate the building into the presentation currency at 30 June 20X9 is the rate that applied on:
A) 1 April 20X2
B) 15 August 20X4
C) 15 March 20X9
D) 30 June 20X9
A) 1 April 20X2
B) 15 August 20X4
C) 15 March 20X9
D) 30 June 20X9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When translating into the presentation currency the translation difference is recognised:
A) in profit or loss
B) as a separate component of equity
C) in retained earnings
D) as an asset or liability, depending on whether it is a debit or credit balance.
A) in profit or loss
B) as a separate component of equity
C) in retained earnings
D) as an asset or liability, depending on whether it is a debit or credit balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Indicators pointing towards the local overseas currency as the functional currency include, that the:
I) Parent's cash flows are directly affected on a current basis.
II) Cash flows are primarily in the local currency and do not affect the parent's cash flows.
III) Sales prices are primarily responsive to exchange rate changes in the short-term.
IV) Production costs are determined primarily by local conditions.
A) I and III only;
B) II and IV only;
C) I, III and IV only;
D) I, II and IV only.
I) Parent's cash flows are directly affected on a current basis.
II) Cash flows are primarily in the local currency and do not affect the parent's cash flows.
III) Sales prices are primarily responsive to exchange rate changes in the short-term.
IV) Production costs are determined primarily by local conditions.
A) I and III only;
B) II and IV only;
C) I, III and IV only;
D) I, II and IV only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When translating into the functional currency monetary liabilities are translated using the:
A) exchange rate current at the date the item was first recorded;
B) exchange rate prevailing at the end of the last reporting period;
C) closing exchange rate;
D) exchange rate current at end of reporting period.
A) exchange rate current at the date the item was first recorded;
B) exchange rate prevailing at the end of the last reporting period;
C) closing exchange rate;
D) exchange rate current at end of reporting period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When translating into the functional currency foreign currency denominated non-monetary items measured using historical cost must be translated using the:
A) rate current at end of reporting period;
B) average rate for the reporting period;
C) exchange rate at the date of the transaction;
D) rate prevailing at the end of the last financial year.
A) rate current at end of reporting period;
B) average rate for the reporting period;
C) exchange rate at the date of the transaction;
D) rate prevailing at the end of the last financial year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Post acquisition date retained earnings that are denominated in a foreign currency are:
A) translated into the functional currency using the rate current at the latest end of reporting period;
B) translated into the functional currency using the average rate since acquisition date;
C) translated into the functional currency using the rates at the end of each year since acquisition date;
D) balances carried forward from translation of previous statement of comprehensive income and do not need to be translated.
A) translated into the functional currency using the rate current at the latest end of reporting period;
B) translated into the functional currency using the average rate since acquisition date;
C) translated into the functional currency using the rates at the end of each year since acquisition date;
D) balances carried forward from translation of previous statement of comprehensive income and do not need to be translated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The following information relates to questions 20 to 22
Aussie Ltd has a controlling interest in Pommie Plc. On 1 June 20X5 Pommie sold inventory to Aussie for 10 000 pounds. The inventory was originally acquired by Pommie on 18 May 20X5 for 7000 pounds. The entire amount of inventory was held by Aussie at 30 June 20X5. The Australian tax rate is 30% and the British tax rate is 35%.
Exchange rates are as follows:

The credit to cost of goods sold to eliminate the intragroup sale (to the nearest whole dollar) is:
A) A$2 240
B) A$9 375
C) A$17 073
D) A$21 875
Aussie Ltd has a controlling interest in Pommie Plc. On 1 June 20X5 Pommie sold inventory to Aussie for 10 000 pounds. The inventory was originally acquired by Pommie on 18 May 20X5 for 7000 pounds. The entire amount of inventory was held by Aussie at 30 June 20X5. The Australian tax rate is 30% and the British tax rate is 35%.
Exchange rates are as follows:

The credit to cost of goods sold to eliminate the intragroup sale (to the nearest whole dollar) is:
A) A$2 240
B) A$9 375
C) A$17 073
D) A$21 875

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The general rule for translating liabilities denominated in a foreign currency into the functional currency is to:
A) translate all liabilities using the current rate existing at end of reporting period;
B) first classify the liabilities into current and non-current;
C) first classify the liabilities as monetary or non-monetary;
D) translate all liabilities using the rate current on entering into the transaction.
A) translate all liabilities using the current rate existing at end of reporting period;
B) first classify the liabilities into current and non-current;
C) first classify the liabilities as monetary or non-monetary;
D) translate all liabilities using the rate current on entering into the transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The following information relates to question 3 and 4
Aussie Ltd acquired 100% of Sing Sing Ltd (Sing Sing) on 1 July 20X0. The balance sheet of Sing Sing on that date was as follows:

The balance sheet of Sing Sing as at is as follows:
Balance Sheet as at 30 June 20X1

Relevant exchange rates are as follows:

-If the local currency of Sing Sing is Singapore dollars and the functional currency is Australian dollars the total assets of S$900,000 would translate into Australian dollars as:
A) $703 125
B) $709 688
C) $1 141 500
D) $1 152 000
Aussie Ltd acquired 100% of Sing Sing Ltd (Sing Sing) on 1 July 20X0. The balance sheet of Sing Sing on that date was as follows:

The balance sheet of Sing Sing as at is as follows:
Balance Sheet as at 30 June 20X1

Relevant exchange rates are as follows:

-If the local currency of Sing Sing is Singapore dollars and the functional currency is Australian dollars the total assets of S$900,000 would translate into Australian dollars as:
A) $703 125
B) $709 688
C) $1 141 500
D) $1 152 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Monetary items are best described as:
A) plant and equipment;
B) units of currency held and assets and liabilities to be received or paid in fixed numbers of currency units;
C) all intangible items including goodwill;
D) all items that are contingent in nature.
A) plant and equipment;
B) units of currency held and assets and liabilities to be received or paid in fixed numbers of currency units;
C) all intangible items including goodwill;
D) all items that are contingent in nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When translating the revenue and expenses in the statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income, theoretically each item of revenue and expense should be translated using the spot exchange rate between the:
A) functional currency and the foreign currency on the reporting date;
B) presentation currency and the functional currency on the reporting date;
C) functional currency and the foreign currency on the date the transaction occurred;
D) presentation currency and the local currency on the transaction date.
A) functional currency and the foreign currency on the reporting date;
B) presentation currency and the functional currency on the reporting date;
C) functional currency and the foreign currency on the date the transaction occurred;
D) presentation currency and the local currency on the transaction date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
By applying the definition provided in IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates, the following items will be regarded as a monetary item:
A) property, plant and equipment;
B) land and buildings;
C) inventory;
D) accounts receivable.
A) property, plant and equipment;
B) land and buildings;
C) inventory;
D) accounts receivable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Mortimer Limited has the following items in its statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income:
Revenue FC60 000,
Cost of goods sold FC25 000,
Interest expense FC8 000,
Income tax expense FC10 000.
All items arose evenly across the year. The following exchange rates applied:
End of reporting period FC1 = $0.80
Average rate for year FC1 = $0.75
The net profit after tax translated into the presentation currency is:
A) $12 750;
B) $13 600;
C) $21 250;
D) $26 667.
Revenue FC60 000,
Cost of goods sold FC25 000,
Interest expense FC8 000,
Income tax expense FC10 000.
All items arose evenly across the year. The following exchange rates applied:
End of reporting period FC1 = $0.80
Average rate for year FC1 = $0.75
The net profit after tax translated into the presentation currency is:
A) $12 750;
B) $13 600;
C) $21 250;
D) $26 667.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When an entity has an investment in a foreign domiciled entity it is necessary to translate the financial statements of the foreign operation to the currency used by the investor:
A) regardless of the ownership interest in the entity
B) only where the entity is a wholly owned subsidiary
C) where the investor has control over the foreign entity
D) where the investment is material to the investor
A) regardless of the ownership interest in the entity
B) only where the entity is a wholly owned subsidiary
C) where the investor has control over the foreign entity
D) where the investment is material to the investor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Where a change in the functional currency occurs, the translation procedures as outlined in IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rules, apply:
A) prospectively, from the date of the change;
B) prospectively, from the next reporting date;
C) retrospectively and must be adjusted in the opening balance of retained earnings;
D) retrospectively and must be adjusted directly into the current period profit or loss.
A) prospectively, from the date of the change;
B) prospectively, from the next reporting date;
C) retrospectively and must be adjusted in the opening balance of retained earnings;
D) retrospectively and must be adjusted directly into the current period profit or loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When translating foreign currency denominated financial statements into the functional currency, the exchange differences are recognised:
A) as an item of gain or loss in the statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income;
B) directly in the retained earnings account;
C) as a deferred asset or liability;
D) as a separate component of equity.
A) as an item of gain or loss in the statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income;
B) directly in the retained earnings account;
C) as a deferred asset or liability;
D) as a separate component of equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Yandos Limited has made a loan of A$50 000 to a foreign subsidiary in Japan, Yamuchi Limited. The loan was made when the exchange rate was A$4 = Y1. By reporting date, the exchange rate had changed to A$5 = Y1. The Australian parent will need to recognise the following as part of the entry to revalue the loan:
A) DR Loan receivable $62 500;
B) DR Loan receivable $50 000
C) DR Loan receivable $12 500;
D) DR Loan receivable $2500.
A) DR Loan receivable $62 500;
B) DR Loan receivable $50 000
C) DR Loan receivable $12 500;
D) DR Loan receivable $2500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Under IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates, an entity must disclose which of the following items in particular?
I) The amount of exchange differences included in profit or loss of the period.
II) The amount of the exchange difference included directly in share capital during the period.
III) Whether a change in the functional currency has occurred.
IV) The reason for using a presentation currency that is different from the functional currency.
A) I, II, III and IV;
B) II and III only;
C) I, III and IV only;
D) I and IV only.
I) The amount of exchange differences included in profit or loss of the period.
II) The amount of the exchange difference included directly in share capital during the period.
III) Whether a change in the functional currency has occurred.
IV) The reason for using a presentation currency that is different from the functional currency.
A) I, II, III and IV;
B) II and III only;
C) I, III and IV only;
D) I and IV only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A Ltd has an 80% investment in B Inc. A Ltd lent $US500,000 to B Inc on 1 January 20X4. The loan is considered to form part of the net investment in B Inc. The functional currency of A Ltd is Australian dollars and for B Inc is US dollars.
The exchange rate on 1 January 20X4 was $A1.00 = $US0.875 and on 30 June 20X4 was $A1.00 = $US0.750.
The consolidation adjustment to the foreign currency translation reserve at 30 June 20X4 in relation to the loan (to the nearest whole dollar) is:
A) $62 500 credit
B) $62 500 debit
C) $95 238 credit
D) $95 238 debit
The exchange rate on 1 January 20X4 was $A1.00 = $US0.875 and on 30 June 20X4 was $A1.00 = $US0.750.
The consolidation adjustment to the foreign currency translation reserve at 30 June 20X4 in relation to the loan (to the nearest whole dollar) is:
A) $62 500 credit
B) $62 500 debit
C) $95 238 credit
D) $95 238 debit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The following information relates to questions 23 to 25
On 1 January 20X3, Claudia Ltd, an Australian company, acquired 80% of the shares of Saskia Ltd, a New Zealand company, for A$2 498 000. At that date the share capital of Saskia was NZ$2 million and the retained earnings were NZ$1 440 000.
All the assets and liabilities of Saskia were recorded at fair value except for land, for which the fair value was NZ$200 000 higher than the carrying amount and equipment, for which the fair value was NZ$80 000 higher than the carrying amount. The undervalued equipment had a further 4-year life. The tax rate in New Zealand is 25%.
Exchange rates are as follows:
1 January 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.20
31 December 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.40
Average for the year A$1.00 = NZ$1.30
The adjustment to the foreign currency translation reserve on 31 December 20X3 relating to the revaluation of the land if the functional currency of Saskia is Australian dollars dollars is:
A) 5 953 debit
B) 5 953 credit
C) 17 857 debit
D) 17 857 credit
On 1 January 20X3, Claudia Ltd, an Australian company, acquired 80% of the shares of Saskia Ltd, a New Zealand company, for A$2 498 000. At that date the share capital of Saskia was NZ$2 million and the retained earnings were NZ$1 440 000.
All the assets and liabilities of Saskia were recorded at fair value except for land, for which the fair value was NZ$200 000 higher than the carrying amount and equipment, for which the fair value was NZ$80 000 higher than the carrying amount. The undervalued equipment had a further 4-year life. The tax rate in New Zealand is 25%.
Exchange rates are as follows:
1 January 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.20
31 December 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.40
Average for the year A$1.00 = NZ$1.30
The adjustment to the foreign currency translation reserve on 31 December 20X3 relating to the revaluation of the land if the functional currency of Saskia is Australian dollars dollars is:
A) 5 953 debit
B) 5 953 credit
C) 17 857 debit
D) 17 857 credit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The following information relates to questions 20 to 22
Aussie Ltd has a controlling interest in Pommie Plc. On 1 June 20X5 Pommie sold inventory to Aussie for 10 000 pounds. The inventory was originally acquired by Pommie on 18 May 20X5 for 7000 pounds. The entire amount of inventory was held by Aussie at 30 June 20X5. The Australian tax rate is 30% and the British tax rate is 35%.
Exchange rates are as follows:

The debit to the deferred tax asset account in relation to the elimination of the intragroup sale (to the nearest whole dollar) is:
A) A$2 813
B) A$3 281
C) A$6 563
D) A$7 656
Aussie Ltd has a controlling interest in Pommie Plc. On 1 June 20X5 Pommie sold inventory to Aussie for 10 000 pounds. The inventory was originally acquired by Pommie on 18 May 20X5 for 7000 pounds. The entire amount of inventory was held by Aussie at 30 June 20X5. The Australian tax rate is 30% and the British tax rate is 35%.
Exchange rates are as follows:

The debit to the deferred tax asset account in relation to the elimination of the intragroup sale (to the nearest whole dollar) is:
A) A$2 813
B) A$3 281
C) A$6 563
D) A$7 656

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The following information relates to questions 23 to 25
On 1 January 20X3, Claudia Ltd, an Australian company, acquired 80% of the shares of Saskia Ltd, a New Zealand company, for A$2 498 000. At that date the share capital of Saskia was NZ$2 million and the retained earnings were NZ$1 440 000.
All the assets and liabilities of Saskia were recorded at fair value except for land, for which the fair value was NZ$200 000 higher than the carrying amount and equipment, for which the fair value was NZ$80 000 higher than the carrying amount. The undervalued equipment had a further 4-year life. The tax rate in New Zealand is 25%.
Exchange rates are as follows:
1 January 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.20
31 December 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.40
Average for the year A$1.00 = NZ$1.30
The goodwill arising on Claudia's acquisition of Saskia is:
A) NZ$77 600;
B) NZ$88 800;
C) A$93 120;
D) A$422 000.
On 1 January 20X3, Claudia Ltd, an Australian company, acquired 80% of the shares of Saskia Ltd, a New Zealand company, for A$2 498 000. At that date the share capital of Saskia was NZ$2 million and the retained earnings were NZ$1 440 000.
All the assets and liabilities of Saskia were recorded at fair value except for land, for which the fair value was NZ$200 000 higher than the carrying amount and equipment, for which the fair value was NZ$80 000 higher than the carrying amount. The undervalued equipment had a further 4-year life. The tax rate in New Zealand is 25%.
Exchange rates are as follows:
1 January 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.20
31 December 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.40
Average for the year A$1.00 = NZ$1.30
The goodwill arising on Claudia's acquisition of Saskia is:
A) NZ$77 600;
B) NZ$88 800;
C) A$93 120;
D) A$422 000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The following information relates to questions 23 to 25
On 1 January 20X3, Claudia Ltd, an Australian company, acquired 80% of the shares of Saskia Ltd, a New Zealand company, for A$2 498 000. At that date the share capital of Saskia was NZ$2 million and the retained earnings were NZ$1 440 000.
All the assets and liabilities of Saskia were recorded at fair value except for land, for which the fair value was NZ$200 000 higher than the carrying amount and equipment, for which the fair value was NZ$80 000 higher than the carrying amount. The undervalued equipment had a further 4-year life. The tax rate in New Zealand is 25%.
Exchange rates are as follows:
1 January 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.20
31 December 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.40
Average for the year A$1.00 = NZ$1.30
The adjustment to the foreign currency translation reserve on 31 December 20X3 relating to the revaluation of the land if the functional currency of Saskia is New Zealand dollars is:
A) 5 953 debit
B) 5 953 credit
C) 17 857 debit
D) 17 857 credit
On 1 January 20X3, Claudia Ltd, an Australian company, acquired 80% of the shares of Saskia Ltd, a New Zealand company, for A$2 498 000. At that date the share capital of Saskia was NZ$2 million and the retained earnings were NZ$1 440 000.
All the assets and liabilities of Saskia were recorded at fair value except for land, for which the fair value was NZ$200 000 higher than the carrying amount and equipment, for which the fair value was NZ$80 000 higher than the carrying amount. The undervalued equipment had a further 4-year life. The tax rate in New Zealand is 25%.
Exchange rates are as follows:
1 January 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.20
31 December 20X3 A$1.00 = NZ$1.40
Average for the year A$1.00 = NZ$1.30
The adjustment to the foreign currency translation reserve on 31 December 20X3 relating to the revaluation of the land if the functional currency of Saskia is New Zealand dollars is:
A) 5 953 debit
B) 5 953 credit
C) 17 857 debit
D) 17 857 credit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The following information relates to questions 20 to 22
Aussie Ltd has a controlling interest in Pommie Plc. On 1 June 20X5 Pommie sold inventory to Aussie for 10 000 pounds. The inventory was originally acquired by Pommie on 18 May 20X5 for 7000 pounds. The entire amount of inventory was held by Aussie at 30 June 20X5. The Australian tax rate is 30% and the British tax rate is 35%.
Exchange rates are as follows:

The credit to inventory in relation to the elimination of the intragroup sale (to the nearest whole dollar) is:
A) A$7 317
B) A$8 108
C) A$8 333
D) A$9 375
Aussie Ltd has a controlling interest in Pommie Plc. On 1 June 20X5 Pommie sold inventory to Aussie for 10 000 pounds. The inventory was originally acquired by Pommie on 18 May 20X5 for 7000 pounds. The entire amount of inventory was held by Aussie at 30 June 20X5. The Australian tax rate is 30% and the British tax rate is 35%.
Exchange rates are as follows:

The credit to inventory in relation to the elimination of the intragroup sale (to the nearest whole dollar) is:
A) A$7 317
B) A$8 108
C) A$8 333
D) A$9 375

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



