Deck 23: Pleural Diseases
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Pleural Diseases
1
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Distal airway and alveolar weakening
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Distal airway and alveolar weakening
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
2
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Distal Airway and Alveolar Weakening Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Distal Airway and Alveolar Weakening Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.
NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.
3
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Atelectasis
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Atelectasis
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
4
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Fibrotic thickening of the alveoli (parenchymal fibrosis)
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Fibrotic thickening of the alveoli (parenchymal fibrosis)
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Excessive Bronchial Secretions Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Excessive Bronchial Secretions Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Alveolar hyperinflation (air-trapping)
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Alveolar hyperinflation (air-trapping)
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Destruction of pulmonary capillaries
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Destruction of pulmonary capillaries
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Increased Alveolar-Capillary Membrane Thickness Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Increased Alveolar-Capillary Membrane Thickness Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Interstitial edema
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Interstitial edema
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Alveolar rupture
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Alveolar rupture
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Increased surface tension of pulmonary surfactant
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Increased surface tension of pulmonary surfactant
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Lung compression
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Lung compression
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Atelectasis Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Atelectasis Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Bronchospasm (smooth muscle constriction of bronchial airways)
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Bronchospasm (smooth muscle constriction of bronchial airways)
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Granulomas
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Granulomas
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Pulmonary capillary congestion
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Pulmonary capillary congestion
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Alveolar consolidation
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Alveolar consolidation
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Alveolar Consolidation Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Alveolar Consolidation Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Chronic dilation and distortion of bronchial airway
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Chronic dilation and distortion of bronchial airway
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Bronchospasm Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory disease result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pleural Effusions.
Bronchospasm Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pleural effusions.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural effusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Excessive bronchial secretions
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Excessive bronchial secretions
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur in a small pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
PaCO2
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
PaCO2
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Next to the pulmonary function studies listed below, match the findings that typically develop in the patient with a pleural disease. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
VT
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
VT
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Permanent enlargement and deterioration of alveoli
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Permanent enlargement and deterioration of alveoli
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Next to the pulmonary function studies listed below, match the findings that typically develop in the patient with a pleural disease. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
VC
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
VC
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Next to the pulmonary function studies listed below, match the findings that typically develop in the patient with a pleural disease. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
IC
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
IC
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Next to the pulmonary function studies listed below, match the findings that typically develop in the patient with a pleural disease. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
TLC
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
TLC
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Cavity formation
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Cavity formation
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur in a small pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
HCO3-
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
HCO3-
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Chronic inflammation and swelling of airways
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Chronic inflammation and swelling of airways
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Next to the pulmonary function studies listed below, match the findings that typically develop in the patient with a pleural disease. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
RV%
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
RV%
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Next to the pulmonary function studies listed below, match the findings that typically develop in the patient with a pleural disease. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
RV/TLC %
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
RV/TLC %
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur in a small pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
pH
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
pH
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Compression of the great veins and decreased cardiac venous return
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Compression of the great veins and decreased cardiac venous return
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pleural disease.
Bronchial airway obstruction
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.
Bronchial airway obstruction
A)YES-This is associated with pleural disease.
B)NO-This is not associated with pleural disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Next to the pulmonary function studies listed below, match the findings that typically develop in the patient with a pleural disease. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
FRC
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
FRC
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur in a large pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
HCO3-
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
HCO3-
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur in a large pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
PaCO2
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
PaCO2
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur in a large pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
pH
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
pH
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Next to the pulmonary function studies listed below, match the findings that typically develop in the patient with a pleural disease. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
FRC
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
FRC
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
C(a-v)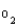
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
C(a-v)
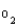
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
PCWP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
PCWP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
O2ER
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
O2ER
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
 S/
S/  T
T
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
 S/
S/  T
TA)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
RVSWI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
RVSWI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
CI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
CI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
SVO2
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
SVO2
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
SVI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
SVI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
SV
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
SV
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
SVR
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
SVR
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
PA
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
PA
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The clinical manifestations associated with pleural effusion are based on the clinical scenarios activated by distal airway and alveolar weakening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
DO2
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
DO2
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
LVSWI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
LVSWI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The most common cause of a pleural effusion is pneumonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
PVR
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
PVR
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
CO
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
CO
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
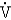 O2
O2
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
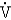 O2
O2A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
CVP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
CVP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in a patient with a severe pleural effusion to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
RAP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
RAP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is/are associated with transudative pleural effusion? 
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
E) I and IV only

A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
E) I and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity is called empyema.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An exudative pleural effusion has a low protein content.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Congestive heart failure is a common cause of an exudative pleural effusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A tracheal shift is commonly associated with a pleural effusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A major cause of a transudative pleural effusion is a complication of hepatic cirrhosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Fluid samples from a thoracentesis may be examined for which of the following? 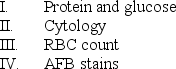
A) I and III only
B) II and IV only
C) II, III, and IV only
D) I, II, III, and IV
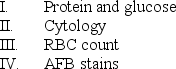
A) I and III only
B) II and IV only
C) II, III, and IV only
D) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is/are major causes of an exudative pleural effusion? 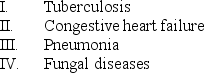
A) II only
B) III only
C) I and IV only
D) I, III, and IV only
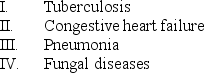
A) II only
B) III only
C) I and IV only
D) I, III, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Trauma to the neck commonly causes what is called a chylothorax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Pulmonary emboli are often associated with pleural effusions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A hemothorax is said to be present when the hematocrit of the pleural fluid is at least 25% of the peripheral blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Trauma to the neck commonly causes which of the following?
A) Hemothorax
B) Chylothorax
C) Empyema
D) Hydrothorax
E) None of the above
A) Hemothorax
B) Chylothorax
C) Empyema
D) Hydrothorax
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A pleural effusion commonly demonstrates which of the following findings during a chest assessment? 
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and IV only
E) I, III, and IV only

A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and IV only
E) I, III, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



