Deck 20: Pulmonary Embolism and Infarction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/63
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Pulmonary Embolism and Infarction
1
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Excessive Bronchial Secretions Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Excessive Bronchial Secretions Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
2
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Alveolar consolidation
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Alveolar consolidation
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
3
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Alveolar hyperinflation (air-trapping)
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Alveolar hyperinflation (air-trapping)
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
4
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Interstitial edema
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Interstitial edema
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Increased Alveolar-Capillary Membrane Thickness Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Increased Alveolar-Capillary Membrane Thickness Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Atelectasis Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Atelectasis Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Fibrotic thickening of the alveoli (parenchymal fibrosis)
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Fibrotic thickening of the alveoli (parenchymal fibrosis)
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Hyaline membrane formation
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Hyaline membrane formation
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Granulomas
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Granulomas
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Distal Airway and Alveolar Weakening Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Distal Airway and Alveolar Weakening Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Blockage of pulmonary vascular system
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Blockage of pulmonary vascular system
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Distal airway and alveolar weakening
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Distal airway and alveolar weakening
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Chronic dilation and distortion of bronchial airway
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Chronic dilation and distortion of bronchial airway
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Alveolar Consolidation Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Alveolar Consolidation Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Bronchospasm (smooth muscle constriction of bronchial airways)
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Bronchospasm (smooth muscle constriction of bronchial airways)
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Atelectasis
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Atelectasis
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
MATCHING
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Bronchospasm Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
The clinical scenarios associated with respiratory diseases result from the pathophysiologic mechanisms caused (or activated) by the anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with the disorder. Using the "Yes" or "No" items, match the major anatomic alterations of the lungs, listed below, that cause the clinical scenario associated with Pulmonary Embolism.
Bronchospasm Clinical Scenario
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Compression of great vessels and decreased cardiac return
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Compression of great vessels and decreased cardiac return
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Destruction of pulmonary capillaries
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Destruction of pulmonary capillaries
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary capillary congestion
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary capillary congestion
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Permanent enlargement and deterioration of alveoli
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Permanent enlargement and deterioration of alveoli
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur during extensive pulmonary embolism and infarction to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
PaCO2
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
PaCO2
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur during extensive pulmonary embolism and infarction to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
pH
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
pH
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
 S/
S/  T
T
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
 S/
S/  T
TA)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
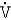 O2
O2
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
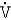 O2
O2A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
DO2
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
DO2
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Frothy white (or pink) bronchial secretions
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Frothy white (or pink) bronchial secretions
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
RAP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
RAP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary infarction
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary infarction
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
O2ER
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
O2ER
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Excessive thick, whitish bronchial secretions
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Excessive thick, whitish bronchial secretions
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur during a mild to moderate pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
pH
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
pH
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur during a mild to moderate pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
HCO3-
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
HCO3-
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Mucus plugging
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Mucus plugging
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
C(a-v)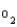
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
C(a-v)
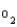
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
CVP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
CVP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur during a mild to moderate pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
PaCO2
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
PaCO2
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Match what develops in the oxygen indices of a patient with a pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
SvO2
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased
SvO2
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Normal or decreased
E)Normal or increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Identify the major anatomic alterations of the lungs associated with pulmonary embolism.
Chronic inflammation and swelling of airways
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.
Chronic inflammation and swelling of airways
A)YES-This is associated with pulmonary embolism.
B)NO-This is not associated with pulmonary embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Match the arterial blood gas changes that occur during extensive pulmonary embolism and infarction to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
HCO3-
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal
HCO3-
A)Increases
B)Decreases
C)Normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
PA
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
PA
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The term syncope is defined as a loss of consciousness resulting from insufficient blood flow to the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
CO
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
CO
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Blood clots are the most common source of pulmonary embolus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
LVSWI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
LVSWI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
PVR
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
PVR
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A large embolus that lodges in the bifurcation of the pulmonary artery is called a saddle embolus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An angiogram procedure generally poses no risk to a patient with a pulmonary embolus, unless the mean pulmonary artery pressure is greater than 25 mm Hg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
One of the consequences of pulmonary embolism is the reduction of certain humoral agents, primarily serotonin and prostaglandin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
As a result of the decreased systemic blood pressure associated with a pulmonary embolism, reflexes from the aortic and carotid sinus baroreceptors cause a decreased heart rate and a decreased ventilatory rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
SVI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
SVI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A large pulmonary embolus causes the systemic blood pressure to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
SV
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
SV
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For a ventilation lung scan, the patient inhales a gas mixture containing a small amount of radioactive gas. This radioactive mixture is usually Xenon-133.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
CI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
CI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Heparin is a thrombolytic agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
SVR
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
SVR
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
PCWP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
PCWP
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Match what hemodynamic indices develop in patients with an extensive pulmonary embolism to the items listed below. Items may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
RVSWI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal
RVSWI
A)Normal
B)Decreases
C)Increases
D)Decrease/normal
E)Increase/normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
It is not the pulmonary embolism but rather the decreased 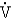 /
/  ratio that develops that causes the patient's PaO2 to decrease.
ratio that develops that causes the patient's PaO2 to decrease.
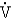 /
/  ratio that develops that causes the patient's PaO2 to decrease.
ratio that develops that causes the patient's PaO2 to decrease.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is/are major mechanisms that contribute to the pulmonary hypertension commonly seen in the patients with pulmonary embolism? 
A) I and III only
B) II and IV only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) I, II, III, and IV

A) I and III only
B) II and IV only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following thrombolytic agents is/are used to treat pulmonary embolism? 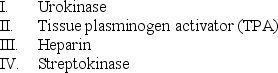
A) III only
B) IV only
C) II and IV only
D) I, II, and IV only
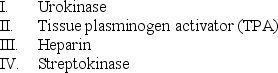
A) III only
B) IV only
C) II and IV only
D) I, II, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Most patients with a pulmonary embolus have a mean pulmonary artery pressure in excess of:
A) 20 mm Hg.
B) 30 mm Hg.
C) 40 mm Hg.
D) 50 mm Hg.
E) 60 mm Hg.
A) 20 mm Hg.
B) 30 mm Hg.
C) 40 mm Hg.
D) 50 mm Hg.
E) 60 mm Hg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



