Deck 30: Human Evolution
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: Human Evolution
1
Most researchers believed that modern humans evolved from
A) Australopithecus afarensis.
B) Australopithecus africanus.
C) Proconsul.
D) Homo ergaster.
E) Homo erectus.
A) Australopithecus afarensis.
B) Australopithecus africanus.
C) Proconsul.
D) Homo ergaster.
E) Homo erectus.
D
2
The earliest fossils of archaic humans known to have produced tools are
A) Homo ergaster.
B) Australopithecus.
C) Proconsul.
D) Homo habilis.
E) Homo erectus.
A) Homo ergaster.
B) Australopithecus.
C) Proconsul.
D) Homo habilis.
E) Homo erectus.
B
3
Modern humans are
A) hominoids.
B) hominids.
C) anthropoids.
D) primates.
E) All of the choices apply to humans.
A) hominoids.
B) hominids.
C) anthropoids.
D) primates.
E) All of the choices apply to humans.
E
4
The early evolution of higher apes and early ancestors of modern humans most closely resembles
A) a straight-line vine with one main trunk and many unsuccessful short branches, with only one or two forms coexisting at any one time.
B) two main trunks leading to apes or humans, and where each newly advanced species of Homo immediately eliminated any coexisting hominids.
C) a many-branched tree with all modern forms extending back relatively unchanged until reaching the common "missing link" at an origin about 33 million years ago.
D) a complex bush with many branches and perhaps as many as ten species of hominins 2 million years ago.
E) two streams, Australopithecus and Homo, that merge into one lineage leading to humans.
A) a straight-line vine with one main trunk and many unsuccessful short branches, with only one or two forms coexisting at any one time.
B) two main trunks leading to apes or humans, and where each newly advanced species of Homo immediately eliminated any coexisting hominids.
C) a many-branched tree with all modern forms extending back relatively unchanged until reaching the common "missing link" at an origin about 33 million years ago.
D) a complex bush with many branches and perhaps as many as ten species of hominins 2 million years ago.
E) two streams, Australopithecus and Homo, that merge into one lineage leading to humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What were the tools of Cro-Magnon man made from?
A) stone
B) metal
C) wood
D) wood that had been hardened in a fire to increase it's strength
E) No answer choice is correct.
A) stone
B) metal
C) wood
D) wood that had been hardened in a fire to increase it's strength
E) No answer choice is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The main features that place Homo habilis in the genus Homo rather than Australopithecus are
A) human facial appearance and lack of hair.
B) advanced use of language and total carnivorous diet.
C) brain size, dentition, and tool use.
D) care of young and altruistic behavior.
E) hand grip, extensive use of tools, and house-building.
A) human facial appearance and lack of hair.
B) advanced use of language and total carnivorous diet.
C) brain size, dentition, and tool use.
D) care of young and altruistic behavior.
E) hand grip, extensive use of tools, and house-building.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Prosimians include
A) lemurs.
B) baboons.
C) gibbons.
D) All of the answer choices are correct.
E) No answer choice is correct.
A) lemurs.
B) baboons.
C) gibbons.
D) All of the answer choices are correct.
E) No answer choice is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements best describes the replacement model for the evolution of early humans?
A) Modern humans evolved from archaic humans in Africa and then migrated to Asia and Europe.
B) Modern humans evolved from archaic humans in Africa, Asia and Europe simultaneously.
C) Modern humans evolved from archaic humans in Asia and then migrated to Africa and Europe.
D) Modern humans evolved from Neanderthals in Europe and then migrated to Asia.
E) Modern humans evolved from apes in Africa and then migrated to Asia and Europe.
A) Modern humans evolved from archaic humans in Africa and then migrated to Asia and Europe.
B) Modern humans evolved from archaic humans in Africa, Asia and Europe simultaneously.
C) Modern humans evolved from archaic humans in Asia and then migrated to Africa and Europe.
D) Modern humans evolved from Neanderthals in Europe and then migrated to Asia.
E) Modern humans evolved from apes in Africa and then migrated to Asia and Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What geographic region does the "Replacement Model" propose that modern humans arose in?
A) Africa
B) Asia
C) Europe
D) Africa, Asia and Europe simultaneously
E) None of these choices.
A) Africa
B) Asia
C) Europe
D) Africa, Asia and Europe simultaneously
E) None of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The evolutionary trends in primates include all of the following EXCEPT
A) mobile limbs.
B) stereoscopic vision.
C) a rounded, protruding face.
D) large, complex brain.
E) reduced reproductive rate.
A) mobile limbs.
B) stereoscopic vision.
C) a rounded, protruding face.
D) large, complex brain.
E) reduced reproductive rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is not an anthropoid?
A) chimpanzee
B) human
C) New World monkey
D) lemur
A) chimpanzee
B) human
C) New World monkey
D) lemur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The fossil called Lucy is a member of the species __________ that lived over 3 million years ago.
A) Australopithecus afarensis
B) Australopithecus africanus
C) Proconsul
D) Homo habilis
E) Homo erectus
A) Australopithecus afarensis
B) Australopithecus africanus
C) Proconsul
D) Homo habilis
E) Homo erectus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The probable transitional link between the hominoids and the monkeys is
A) Australopithecus afarensis.
B) Australopithecus africanus.
C) Proconsul.
D) Homo habilis.
E) Homo erectus.
A) Australopithecus afarensis.
B) Australopithecus africanus.
C) Proconsul.
D) Homo habilis.
E) Homo erectus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The stone tools and the dentition of Homo habilis indicate that early humans were
A) strictly herbivores.
B) strictly carnivores.
C) strictly scavengers.
D) omnivores that could either scavenge or hunt for meat.
A) strictly herbivores.
B) strictly carnivores.
C) strictly scavengers.
D) omnivores that could either scavenge or hunt for meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
It is proposed that Cro-Magnons were responsible for the extinction of many large mammals during the Pleistocene epoch. How could this feat have been accomplished?
A) Cro-Magnon man had an increase in tool technology that enabled them to kill animals from a distance.
B) Cro-Magnon man was the first species of hominid to use fire. This would have increased their success during hunting.
C) Cro-Magnon man was the most efficient bipedal species. They would have been able to run after prey species more efficiently than any of their predecessors.
D) Cro-Magnon man was the first species of hominids to hunt in groups. This would have increased their chance of killing larger animals.
A) Cro-Magnon man had an increase in tool technology that enabled them to kill animals from a distance.
B) Cro-Magnon man was the first species of hominid to use fire. This would have increased their success during hunting.
C) Cro-Magnon man was the most efficient bipedal species. They would have been able to run after prey species more efficiently than any of their predecessors.
D) Cro-Magnon man was the first species of hominids to hunt in groups. This would have increased their chance of killing larger animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
People often refer to chimpanzees as monkeys. What characteristic(s) do chimpanzees lack that monkeys have?
A) a tail
B) protruding noses
C) nails
D) binocular vision
A) a tail
B) protruding noses
C) nails
D) binocular vision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What are the advantages of bipedalism?
A) Allows the hands to be free for tool use.
B) Enables an adult to carry an offspring easier.
C) Would have allowed males to forage for food more efficiently.
D) Would allow the individual to spot danger further away.
E) All of these are advantages of bipedalism.
A) Allows the hands to be free for tool use.
B) Enables an adult to carry an offspring easier.
C) Would have allowed males to forage for food more efficiently.
D) Would allow the individual to spot danger further away.
E) All of these are advantages of bipedalism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
All of the following are characteristics of primates EXCEPT the
A) five long dexterous digits on hands and feet.
B) three-dimensional binocular vision.
C) well-developed brain.
D) opposable thumb.
E) rapid postnatal maturation.
A) five long dexterous digits on hands and feet.
B) three-dimensional binocular vision.
C) well-developed brain.
D) opposable thumb.
E) rapid postnatal maturation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following species, in the human evolutionary line, are believed to have been bipedal but still spent time living in the trees?
A) Australopithecus afarensis
B) Homo habilis
C) Ardipithecus ramidus
D) Australopithecus africanus
E) Dryopithecus
A) Australopithecus afarensis
B) Homo habilis
C) Ardipithecus ramidus
D) Australopithecus africanus
E) Dryopithecus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Mistakenly, it is sometimes said that "man comes from monkeys." A more correct way to explain the apparent sequence of human evolution is
A) monkeys have evolved less than humans.
B) humans and monkeys share a common ancestor.
C) humans and monkeys are biologically identical.
D) evolution leads toward more perfect forms and humans therefore came after modern monkeys.
A) monkeys have evolved less than humans.
B) humans and monkeys share a common ancestor.
C) humans and monkeys are biologically identical.
D) evolution leads toward more perfect forms and humans therefore came after modern monkeys.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
All hominoids walk upright.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The reduced reproductive rate in primate evolution involves
A) a reduction in the number of offspring.
B) extended life spans.
C) lengthy gestation periods with one birth at a time.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) a reduction in the number of offspring.
B) extended life spans.
C) lengthy gestation periods with one birth at a time.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which features enabled Homo erectus to be successful in Asia?
A) They were able to control fire.
B) They were able to incorporate meat into their diet.
C) Higher degree of intellectual abilities.
D) All of these made Homo erectus succesful.
A) They were able to control fire.
B) They were able to incorporate meat into their diet.
C) Higher degree of intellectual abilities.
D) All of these made Homo erectus succesful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The most widely accepted model for the evolution of modern humans is pictured here. What is this model called? 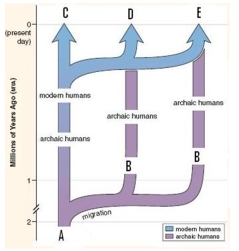
A) Out-of-Africa
B) Replacement Model
C) Multiregional continuity
D) Hardy-Weinberg
E) Out-of-Africa and Replacement Model

A) Out-of-Africa
B) Replacement Model
C) Multiregional continuity
D) Hardy-Weinberg
E) Out-of-Africa and Replacement Model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Australopithecines were apelike above the waist and humanoid below the waist. This is an example of
A) quadripedalism.
B) mosaic evolution.
C) multiregional continuity.
D) None of the choices are correct.
A) quadripedalism.
B) mosaic evolution.
C) multiregional continuity.
D) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
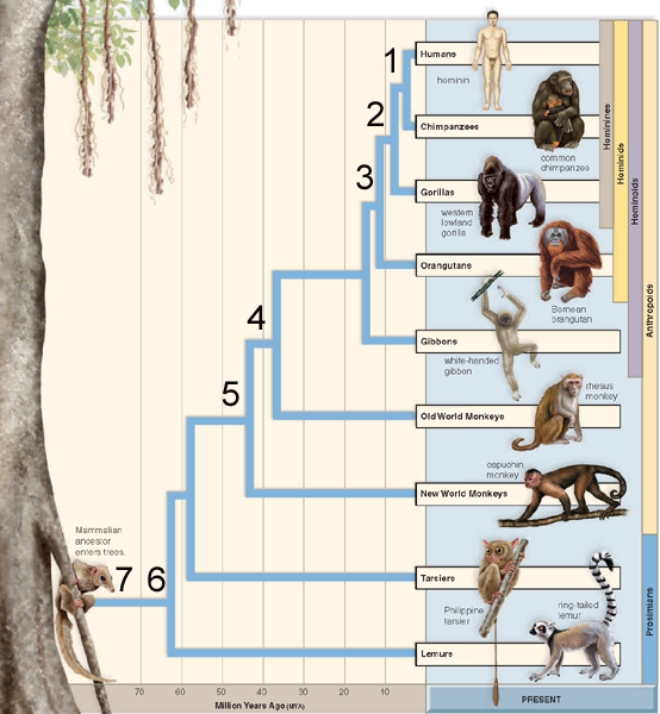
On the phylogenetic tree of primate evolution, where do you find the first primates to diverge from the common ancestor of the primates?
A) No. 1
B) No. 4
C) No. 5
D) No. 6
E) No. 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The evolution of genus Homo began about
A) 4.6 BYA (billion years ago).
B) 7 MYA (million years ago).
C) 2.0 MYA (million years ago).
D) 55 MYA (million years ago).
A) 4.6 BYA (billion years ago).
B) 7 MYA (million years ago).
C) 2.0 MYA (million years ago).
D) 55 MYA (million years ago).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Explain how mitochondrial DNA studies of Africans and Europeans support the replacement model for the evolution of modern humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which species of Homo is most closely related to the Australopithecines?
A) erectus
B) habilis
C) sapiens
D) ergaster
A) erectus
B) habilis
C) sapiens
D) ergaster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which species is believed to have been the first ones to develop stone tool technology?
A) Homo erectus
B) Homo habilis
C) Cro-Magnon man
D) Neanderthal man
A) Homo erectus
B) Homo habilis
C) Cro-Magnon man
D) Neanderthal man

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A major development in the evolution of primates is stereoscopic vision. This development is associated with
A) a decline in the importance of smell.
B) eyes in front of the head.
C) a binocular field of vision.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) a decline in the importance of smell.
B) eyes in front of the head.
C) a binocular field of vision.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

Where on this phylogenetic tree of primate evolution do you find evolution of the hominines?201
A) No. 1
B) No. 2
C) No. 3
D) No. 4
E) No. 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Explain how mitochondrial DNA studies of Africans and Europeans support the replacement model for the evolution of modern humans.
A) a fossil must have an anatomy consistent with standing erect and bipedalism.
B) the individual would have a broader pelvis and hip joint to prevent swaying when walking.
C) the individual would have an arch instead of an opposable toe.
D) All of the choices are qualifications.
A) a fossil must have an anatomy consistent with standing erect and bipedalism.
B) the individual would have a broader pelvis and hip joint to prevent swaying when walking.
C) the individual would have an arch instead of an opposable toe.
D) All of the choices are qualifications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The most widely accepted model for the evolution of modern humans is pictured here. What is this model called?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The proposed advantages of bipedalism, which characterizes hominin evolution, include making it easier to
A) collect food from overhead.
B) travel and move about.
C) carry food back to their camp or their young.
D) carry their young from place to place.
E) All of these are correct.
A) collect food from overhead.
B) travel and move about.
C) carry food back to their camp or their young.
D) carry their young from place to place.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

Where on this phylogenetic tree of primate evolution do you find evolution of the anthropoids?13
A) No. 2
B) No. 6
C) No. 5
D) No. 4
E) No. 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A shortened snout and a relatively flat face are associated with
A) a decline in the importance of vision and an increase in reliance on smell.
B) bilateral symmetry and aquatic reproduction.
C) a decline in the importance of smell and an increase in reliance on vision.
D) a terrestrial life style.
A) a decline in the importance of vision and an increase in reliance on smell.
B) bilateral symmetry and aquatic reproduction.
C) a decline in the importance of smell and an increase in reliance on vision.
D) a terrestrial life style.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38

Where on this phylogenetic tree of primate evolution do you find the evolution of humans and species very closely related to humans?1
A) No. 1
B) No. 2
C) No. 3
D) No. 4
E) No. 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Fossils are considered to belong to the genus Homo if which of the following is true?
A) The brain size is 600cc or larger.
B) The jaw and teeth are human like.
C) Tool use is evident.
D) All of the choices are characteristics of this group
A) The brain size is 600cc or larger.
B) The jaw and teeth are human like.
C) Tool use is evident.
D) All of the choices are characteristics of this group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What were the major disadvantages of our early ancestors becoming bipedal?
A) Lower back problems developed.
B) Increased predation by faster predators.
C) Decrease in speed and mobility.
D) Decreased protection of the abdominal region.
A) Lower back problems developed.
B) Increased predation by faster predators.
C) Decrease in speed and mobility.
D) Decreased protection of the abdominal region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which two species are believed to have evolved from Homo ergaster?
A) Homo erectus & Homo floresiensis
B) Homo erectus & Homo rudolfensis
C) Homo rudolfensis & Homo floresiensis
D) Homo habilis & Cro Magnon man
A) Homo erectus & Homo floresiensis
B) Homo erectus & Homo rudolfensis
C) Homo rudolfensis & Homo floresiensis
D) Homo habilis & Cro Magnon man

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which group of primates has the closest evolutionary relatedness to the lemurs?
A) Tarsiers
B) Gibbons
C) Gorillas
D) Old World Monkeys
E) Chimpanzees
A) Tarsiers
B) Gibbons
C) Gorillas
D) Old World Monkeys
E) Chimpanzees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Apes walk on their feet and knuckles, which have opposable thumbs and big toes, like the ancestral form from which apes and humans evolved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
All primates have thumbs, but only Old World monkeys, great apes, and humans have truly opposable thumbs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which species shows the first solid evidence of bipedalism?
A) Ardipithecus ramidus
B) Sahelanthropus tchadensis
C) Homo habilis
D) Australopithecus afarensis
A) Ardipithecus ramidus
B) Sahelanthropus tchadensis
C) Homo habilis
D) Australopithecus afarensis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Old World monkeys have a prehensile tail and a flattened nose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Identify which of the following scenarios is most probable for the evolution of members of genus Homo.
A) Australopithecus afarensis gave rise to Homo habilis who gave rise to Homo ergaster who gave rise to Homo erectus
B) Australopithecus afarensis gave rise to Homo erectus who gave rise to Homo ergaster who gave rise to Homo habilis
C) Ardipithecus ramidis gave rise to Homo habilis who gave rise to Homo ergaster who gave rise to Homo erectus
D) Australopithecus afarensis gave rise to Homo habilis who gave rise to Homo sapiens who gave rise to Homo erectus
A) Australopithecus afarensis gave rise to Homo habilis who gave rise to Homo ergaster who gave rise to Homo erectus
B) Australopithecus afarensis gave rise to Homo erectus who gave rise to Homo ergaster who gave rise to Homo habilis
C) Ardipithecus ramidis gave rise to Homo habilis who gave rise to Homo ergaster who gave rise to Homo erectus
D) Australopithecus afarensis gave rise to Homo habilis who gave rise to Homo sapiens who gave rise to Homo erectus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Explain the features that would have enabled Homo ergaster to have migrated out of Africa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Explain how becoming a more bipedal organism increased the chances of survival among the genus Homo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which European species is believed to have evolved from Homo ergaster?
A) Homo heidelbergensis
B) Homo erectus
C) Homo floresiensis
D) Homo sapiens
E) Australopithecus africanus
A) Homo heidelbergensis
B) Homo erectus
C) Homo floresiensis
D) Homo sapiens
E) Australopithecus africanus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In what order did these organisms diverge from the lineage of the common ancestral primate?
A) H. neandertalensis, H. ergaster, H. habilis, gorillas and chimpanzees, hominins
B) prosimians, monkeys, gibbons, orangutans, gorillas and chimpanzees, hominins
C) monkeys, gibbons, prosimians, orangutans, H. habilis, H. ergaster, humans
D) gibbons, lemurs, tarsiers, H. habilis, monkeys, H. neandertalensis, hominins
A) H. neandertalensis, H. ergaster, H. habilis, gorillas and chimpanzees, hominins
B) prosimians, monkeys, gibbons, orangutans, gorillas and chimpanzees, hominins
C) monkeys, gibbons, prosimians, orangutans, H. habilis, H. ergaster, humans
D) gibbons, lemurs, tarsiers, H. habilis, monkeys, H. neandertalensis, hominins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52

Where on this phylogenetic tree of primate evolution do you find evolution of the hominids?
A) No. 1
B) No. 2
C) No. 3
D) No. 4
E) No. 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



