Deck 20: Biochemistry-The Compounds of Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/168
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Biochemistry-The Compounds of Life
1
Isomers that cannot be superimposed on their mirror images are called ________
A)geometric isomers.
B)structural isomers.
C)functional isomers.
D)enantiomers.
E)constitutional isomers.
A)geometric isomers.
B)structural isomers.
C)functional isomers.
D)enantiomers.
E)constitutional isomers.
enantiomers.
2
At a physiological pH of 7.4,amino acids exist as zwitterions because the pKa of the -NH3+ group is ________ 7.4,and the pKa of the -COOH group is ________ 7.4.
A)greater than / less than
B)less than / greater than
C)greater than / greater than
D)less than / less than
E)equal to / equal to
A)greater than / less than
B)less than / greater than
C)greater than / greater than
D)less than / less than
E)equal to / equal to
greater than / less than
3
At a physiological pH of 7.4,amino acids exist as zwitterions.At a very low pH (in an acid solution),both the amine group and the carboxylic acid group on an amino acid are protonated.Therefore,the following must be true: the pKa of the ________ group is larger than the pKa of the ________ group.
A)protonated amine group / carboxylic acid group
B)carboxylic acid group / protonated amine group
C)amine group / carbonate group
D)hydronium ion group / hydroxyl ion group
E)carbonate group / amine group
A)protonated amine group / carboxylic acid group
B)carboxylic acid group / protonated amine group
C)amine group / carbonate group
D)hydronium ion group / hydroxyl ion group
E)carbonate group / amine group
protonated amine group / carboxylic acid group
4
Which statement regarding amino acids found in human proteins is NOT correct?
A)The -carbon is bonded to one of 20 different R groups.
B)Nearly half of the amino acids have side groups containing only carbon and hydrogen.
C)Several of the amino acids have side groups containing the carboxylic acid functional group.
D)Several of the amino acids have weakly basic side groups that contain nitrogen.
E)All -amino acids are nonpolar.
A)The -carbon is bonded to one of 20 different R groups.
B)Nearly half of the amino acids have side groups containing only carbon and hydrogen.
C)Several of the amino acids have side groups containing the carboxylic acid functional group.
D)Several of the amino acids have weakly basic side groups that contain nitrogen.
E)All -amino acids are nonpolar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An amino acid contains ________
A)an amide and a carboxylic acid group.
B)an amine and a carboxylic acid group.
C)an amine and an alcohol group.
D)an amine and a ether group.
E)an amide and a ester group.
A)an amide and a carboxylic acid group.
B)an amine and a carboxylic acid group.
C)an amine and an alcohol group.
D)an amine and a ether group.
E)an amide and a ester group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following,if any,should NOT be classified as an amino acid?
I.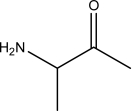
II.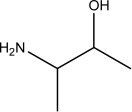
III.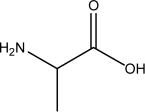
IV.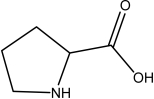
A)III and IV
B)I and II
C)I only
D)II only
E)III only
I.

II.

III.

IV.

A)III and IV
B)I and II
C)I only
D)II only
E)III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement about amino acid enantiomers is NOT correct?
A)An enantiomer cannot be superimposed on its mirror image.
B)Enantiomers are examples of stereoisomers.
C)A solution of an enantiomer rotates the plane of polarized light.
D)Enantiomers are designated by the prefixes D and L.
E)All the chiral amino acids in our bodies are mixtures of enantiomers.
A)An enantiomer cannot be superimposed on its mirror image.
B)Enantiomers are examples of stereoisomers.
C)A solution of an enantiomer rotates the plane of polarized light.
D)Enantiomers are designated by the prefixes D and L.
E)All the chiral amino acids in our bodies are mixtures of enantiomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
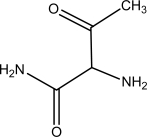
Which one of the following is NOT an amino acid?
A)
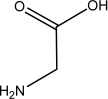
B)
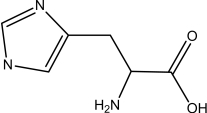
C)
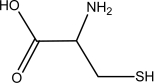
D)
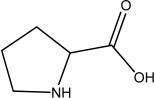
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An organic molecule present naturally in a living system is called a ________
A)hydrocarbon.
B)ribosome.
C)hormone.
D)porphyrin.
E)biomolecule.
A)hydrocarbon.
B)ribosome.
C)hormone.
D)porphyrin.
E)biomolecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following are NOT considered biopolymers?
A)proteins
B)polysaccharides
C)nucleic acids
D)lipids
E)all of these are biopolymers
A)proteins
B)polysaccharides
C)nucleic acids
D)lipids
E)all of these are biopolymers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
This molecule is ________ 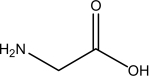
A)a lipid.
B)a fatty acid.
C)an amino acid.
D)a nucleic acid.
E)a saccharide.

A)a lipid.
B)a fatty acid.
C)an amino acid.
D)a nucleic acid.
E)a saccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which statement about chirality is NOT correct?
A)An amino acid is chiral if it has a carbon atom bonded to four different groups.
B)An amino acid is chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image.
C)Almost all of the amino acids found in human proteins are chiral.
D)The -carbon in an amino acid is a chiral center.
E)Almost all the amino acids found in human proteins are dextrorotary enantiomers and rotate plane-polarized light to the right.
A)An amino acid is chiral if it has a carbon atom bonded to four different groups.
B)An amino acid is chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image.
C)Almost all of the amino acids found in human proteins are chiral.
D)The -carbon in an amino acid is a chiral center.
E)Almost all the amino acids found in human proteins are dextrorotary enantiomers and rotate plane-polarized light to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Aspartame exists as a zwitterion with a ________ amine group and a ________ carboxylic acid group.
A)deprotonated / protonated
B)protonated / deprotonated
C)protonated / protonated
D)deprotonated / deprotonated
E)functionalized / defunctionalized
A)deprotonated / protonated
B)protonated / deprotonated
C)protonated / protonated
D)deprotonated / deprotonated
E)functionalized / defunctionalized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which statement is NOT correct? A chiral amino acid ________
A)is an enantiomer.
B)can be superimposed on its mirror image.
C)has four different groups bonded to the same carbon atom.
D)has properties different from those of its mirror image.
E)rotates the plane of polarized light.
A)is an enantiomer.
B)can be superimposed on its mirror image.
C)has four different groups bonded to the same carbon atom.
D)has properties different from those of its mirror image.
E)rotates the plane of polarized light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
At a physiological pH of 7.4,amino acids exist as zwitterions.At a very low pH (in an acid solution),both the amine group and the carboxylic acid group on an amino acid are protonated.Which acid group is the stronger acid?
A)"-NH2"
B)"-NH3+"
C)"-COOH"
D)"-COO-"
E)"-H3O+"
A)"-NH2"
B)"-NH3+"
C)"-COOH"
D)"-COO-"
E)"-H3O+"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Amino acids that human cannot synthesize are called ________ amino acids.
A)animal
B)legume
C)essential
D)required
E)perfect
A)animal
B)legume
C)essential
D)required
E)perfect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identify the amino acid(s)among the following.
I.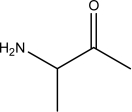
II.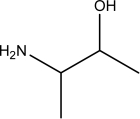
III.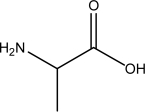
IV.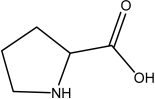
A)III and IV
B)I and II
C)I only
D)II only
E)III only
I.

II.

III.

IV.

A)III and IV
B)I and II
C)I only
D)II only
E)III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following compounds is an -amino acid?
A)
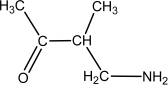
B)

C)

D)
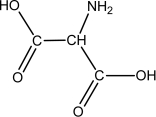
E)
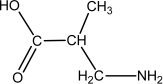
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An -amino acid is one in which the amine group and the carboxylic acid group are attached to ________
A)different carbon atoms.
B)different nitrogen atoms.
C)the same carbon atom.
D)the first and third carbon of the molecule.
E)neighboring carbon atoms.
A)different carbon atoms.
B)different nitrogen atoms.
C)the same carbon atom.
D)the first and third carbon of the molecule.
E)neighboring carbon atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
L-alanine has the molecular structure shown.Which of the choices given shows D-alanine?
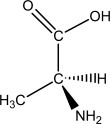
A)
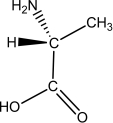
B)
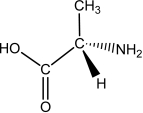
C)
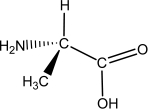
D)
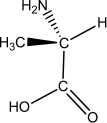
E)
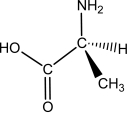

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following peptides is phenylalanylproline at a physiological pH of 7.4?
A)
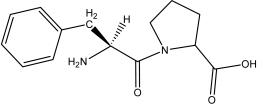
B)
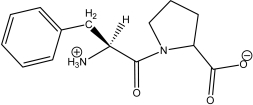
C)
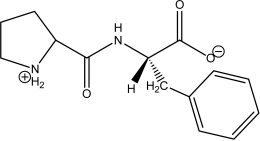
D)
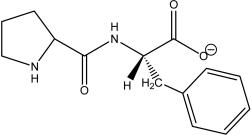
E)
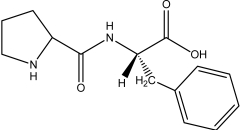
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which functional group links amino acids together to form proteins?
A)amide
B)ester
C)ether
D)amine
E)phosphate
A)amide
B)ester
C)ether
D)amine
E)phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An oligopeptide consists of up to ________ amino acids that bond together.
A)5
B)10
C)20
D)50
E)75
A)5
B)10
C)20
D)50
E)75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A peptide bond is the result of a condensation reaction between ________
A)two carboxylic acid groups on different amino acids.
B)an amino group on one amino acid and the carboxylic acid group on another.
C)two amino groups on different amino acids.
D)an amino group and a carboxylic acid group on the same amino acid.
E)an amino group and a carboxylic acid group producing a zwitterion.
A)two carboxylic acid groups on different amino acids.
B)an amino group on one amino acid and the carboxylic acid group on another.
C)two amino groups on different amino acids.
D)an amino group and a carboxylic acid group on the same amino acid.
E)an amino group and a carboxylic acid group producing a zwitterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Kyotorphin (tyrosylarginine)is a neuroactive dipeptide that plays a role in pain regulation in the brain.Which of the following shows its structure at a physiological pH of 7.4?
A)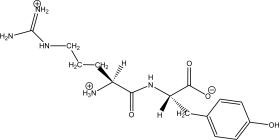
B)
C)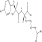
D)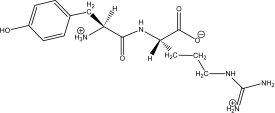
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Amino acids bond together via ________ bonds.
A)glycosidic
B)coordinate covalent
C)hydrogen
D)peptide
E)van der Waals
A)glycosidic
B)coordinate covalent
C)hydrogen
D)peptide
E)van der Waals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which one of the following is best associated with proteins?
A)trigylcerides
B)saccharides
C)hydrocarbon chains
D)amino acids
E)nucleotides
A)trigylcerides
B)saccharides
C)hydrocarbon chains
D)amino acids
E)nucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The ordering of subunits,such as amino acids,in a polymer,is called ________
A)the primary structure.
B)the secondary structure.
C)the tertiary structure.
D)the ordering structure.
E)the quaternary structure.
A)the primary structure.
B)the secondary structure.
C)the tertiary structure.
D)the ordering structure.
E)the quaternary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In an experiment,100 mL of a 0.1 M solution of methionine is titrated using 0.1 M NaOH.Using this information,along with the titration curve shown,which of the following statements is NOT correct?
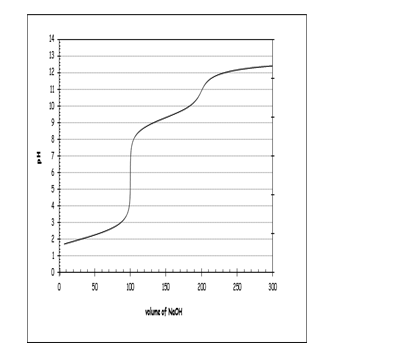
A)At low pHs,the majority of the amino acid present is fully protonated.
B)The pKa of the protonated amine group seems to be a little greater than 10.
C)When the pH reaches the physiological value of 7.4,the carboxylic acid group is essentially deprotonated.
D)The Ka of the -COOH group appears to be between 5 10-3 and 8 10-3.
E)Methionine appears to have a neutral side group,as there seem to be two equivalence points evident on the titration curve.

A)At low pHs,the majority of the amino acid present is fully protonated.
B)The pKa of the protonated amine group seems to be a little greater than 10.
C)When the pH reaches the physiological value of 7.4,the carboxylic acid group is essentially deprotonated.
D)The Ka of the -COOH group appears to be between 5 10-3 and 8 10-3.
E)Methionine appears to have a neutral side group,as there seem to be two equivalence points evident on the titration curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements regarding the sequence of amino acids in proteins is NOT correct?
A)The solubility of proteins in water depends on their sequence of amino acids.
B)Sickle cell anemia is an example of the effect that the primary structure of a protein can have on its function.
C)The effect of substituting one amino acid for another in a protein can depend heavily on the polarity of the side groups involved.
D)Two proteins containing the same numbers and types of amino acids can have different functions.
E)Changing only one or two amino acids in a protein usually has little impact on its properties.
A)The solubility of proteins in water depends on their sequence of amino acids.
B)Sickle cell anemia is an example of the effect that the primary structure of a protein can have on its function.
C)The effect of substituting one amino acid for another in a protein can depend heavily on the polarity of the side groups involved.
D)Two proteins containing the same numbers and types of amino acids can have different functions.
E)Changing only one or two amino acids in a protein usually has little impact on its properties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is characteristic of an -helix?
A)Hydrogen bonds between -NH groups on one part of the chain and C=O groups on nearby amino acids cause the protein to coil with the amino acids' R groups pointing outward.
B)Dipole-dipole interactions between polar side groups in one part of the chain and C=O or -NH groups on nearby amino acids cause the protein to coil with the amino acids' R groups pointing outward.
C)London forces between hydrophobic regions in the amino acid sequence cause the protein to coil up in order to have hydrophilic regions of the chain point outward.
D)Single-strand proteins interact via hydrogen bonds,forming coils in which polar side groups point outward.
E)Side-by-side zigzag chains of amino acids held together by hydrogen bonds aggregate to form a coiled structure held together by intermolecular forces.
A)Hydrogen bonds between -NH groups on one part of the chain and C=O groups on nearby amino acids cause the protein to coil with the amino acids' R groups pointing outward.
B)Dipole-dipole interactions between polar side groups in one part of the chain and C=O or -NH groups on nearby amino acids cause the protein to coil with the amino acids' R groups pointing outward.
C)London forces between hydrophobic regions in the amino acid sequence cause the protein to coil up in order to have hydrophilic regions of the chain point outward.
D)Single-strand proteins interact via hydrogen bonds,forming coils in which polar side groups point outward.
E)Side-by-side zigzag chains of amino acids held together by hydrogen bonds aggregate to form a coiled structure held together by intermolecular forces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which functional group is NOT present in this tripeptide? 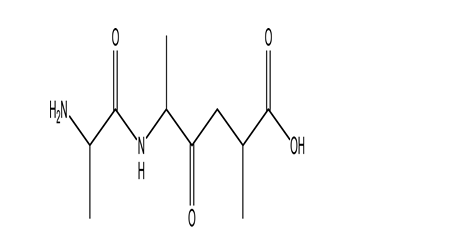
A)amide
B)alcohol
C)carbonyl
D)amine
E)methyl

A)amide
B)alcohol
C)carbonyl
D)amine
E)methyl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is NOT a description of the secondary structure of a protein?
A)" -helix"
B)" -pleated sheet"
C)"random coil"
D)"sequence of amino acids in the protein"
E)"geometric patterns formed by amino acids"
A)" -helix"
B)" -pleated sheet"
C)"random coil"
D)"sequence of amino acids in the protein"
E)"geometric patterns formed by amino acids"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The following reaction produces a peptide.Which statement about this reaction is NOT correct?
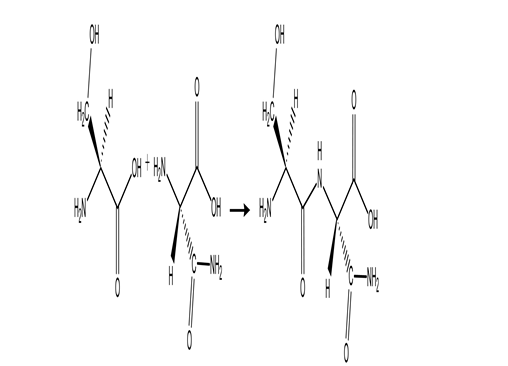
A)The peptide shown is the only product produced by this reaction.
B)This condensation reaction produces a peptide bond.
C)An amide group is formed in this reaction.
D)An amino group reacts with a carboxylic acid group.
E)Two amino acids are linked together by this reaction.

A)The peptide shown is the only product produced by this reaction.
B)This condensation reaction produces a peptide bond.
C)An amide group is formed in this reaction.
D)An amino group reacts with a carboxylic acid group.
E)Two amino acids are linked together by this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The -helix and -pleated sheet are examples of ________
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)arrangement structure.
E)quaternary structure.
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)arrangement structure.
E)quaternary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the name of the peptide shown? 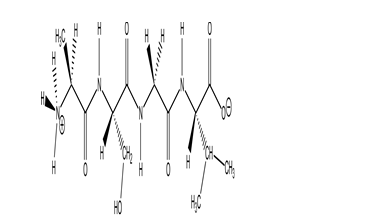
A)valylseylalanine
B)alaylserylvaline
C)alasergylvaline
D)valinylglycinylserinylalanine
E)alanylserylglycylvaline

A)valylseylalanine
B)alaylserylvaline
C)alasergylvaline
D)valinylglycinylserinylalanine
E)alanylserylglycylvaline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The primary structure of a protein is ________
A)the -helix structure of the protein.
B)the -pleated sheet structure of the protein.
C)the sequence of amino acids in the protein.
D)a list of the amino acids in the protein along with the number of times each occurs.
E)the arrangement of -helices and -pleated sheets in the protein.
A)the -helix structure of the protein.
B)the -pleated sheet structure of the protein.
C)the sequence of amino acids in the protein.
D)a list of the amino acids in the protein along with the number of times each occurs.
E)the arrangement of -helices and -pleated sheets in the protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When the number of amino acids linked together in a peptide reaches about 50 to 75,its classification usually transitions from ________ to ________.
A)peptide / oligopeptide
B)oligopeptide / polypeptide
C)minipeptide / megapeptide
D)polypeptide / protein
E)hypoprotein / hyperprotein
A)peptide / oligopeptide
B)oligopeptide / polypeptide
C)minipeptide / megapeptide
D)polypeptide / protein
E)hypoprotein / hyperprotein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The molecule drawn below is an example of ________ 
A)a nucleic acid base.
B)a peptide.
C)a carbohydrate.
D)a fatty acid.
E)an amino acid.

A)a nucleic acid base.
B)a peptide.
C)a carbohydrate.
D)a fatty acid.
E)an amino acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How many amino acids are in the following peptide? 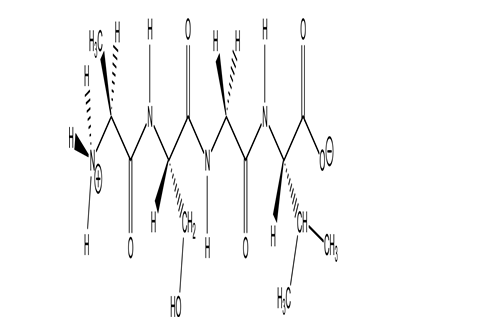
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)5
E)6

A)2
B)3
C)4
D)5
E)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A carbohydrate might have a molecular formula of ________
A)CH2O.
B)C6H12O6.
C)C6H10O2.
D)C2H4O2.
E)C3H6O3.
A)CH2O.
B)C6H12O6.
C)C6H10O2.
D)C2H4O2.
E)C3H6O3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following chemical formulas is probably that of a disaccharide?
A)CH2O
B)C6H10O5
C)C12H22O11
D)C2H4O2
E)C3H6O3
A)CH2O
B)C6H10O5
C)C12H22O11
D)C2H4O2
E)C3H6O3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is characteristic of a -pleated sheet?
A)Hydrogen bonds between -NH groups on one part of the chain and C=O groups on nearby amino acids cause the protein to fold up on itself with the amino acids' R groups pointing outward.
B)Ion-ion interactions between side groups on different parts of the chain cause the protein to fold up on itself to forms sheets of amino acid chains.
C)London forces between hydrophobic regions in the amino acid sequence cause the protein to fold up on itself in order to have hydrophilic regions of the chain point outward.
D)Side-by-side zigzag chains of amino acids held together by hydrogen bonds aggregate to form a continuous sheet.
E)Single-strand proteins form peptide linkages between chains that cause the chains to fold on top of one another,forming a continuous sheet.
A)Hydrogen bonds between -NH groups on one part of the chain and C=O groups on nearby amino acids cause the protein to fold up on itself with the amino acids' R groups pointing outward.
B)Ion-ion interactions between side groups on different parts of the chain cause the protein to fold up on itself to forms sheets of amino acid chains.
C)London forces between hydrophobic regions in the amino acid sequence cause the protein to fold up on itself in order to have hydrophilic regions of the chain point outward.
D)Side-by-side zigzag chains of amino acids held together by hydrogen bonds aggregate to form a continuous sheet.
E)Single-strand proteins form peptide linkages between chains that cause the chains to fold on top of one another,forming a continuous sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The assembly and interaction of coils and sheets in a polypeptide to produce the overall three-dimensional shape are described by the term ________
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)long-range structure.
E)quaternary structure.
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)long-range structure.
E)quaternary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which statement is NOT correct? Sucrose is ________
A)used for table sugar.
B)a disaccharide.
C)consists of glucose and fructose with a glycosidic bond.
D)a synonym for glucose.
E)formed in a condensation reaction that eliminates water.
A)used for table sugar.
B)a disaccharide.
C)consists of glucose and fructose with a glycosidic bond.
D)a synonym for glucose.
E)formed in a condensation reaction that eliminates water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Table sugar is ________
A)glucose.
B)fructose.
C)cellobiose.
D)a monosaccharide.
E)a disaccharide.
A)glucose.
B)fructose.
C)cellobiose.
D)a monosaccharide.
E)a disaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is a monosaccharide?
A)sucrose
B)glucose
C)starch
D)cellulose
E)cellobiose
A)sucrose
B)glucose
C)starch
D)cellulose
E)cellobiose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
This molecule is ________
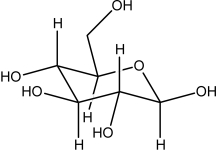
A)a lipid.
B)a fatty acid.
C)an amino acid.
D)a saccharide.
E)a nucleic acid base.

A)a lipid.
B)a fatty acid.
C)an amino acid.
D)a saccharide.
E)a nucleic acid base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The molecule drawn below is an example of ________ 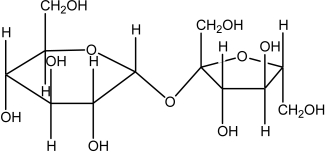
A)a nucleic acid base.
B)an amino acid.
C)a carbohydrate.
D)a fatty acid.
E)a lipid.

A)a nucleic acid base.
B)an amino acid.
C)a carbohydrate.
D)a fatty acid.
E)a lipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A carbohydrate has an empirical formula of ________
A)CH2O.
B)C6H12O6.
C)C12H22O11.
D)C2H4O2.
E)C3H6O3.
A)CH2O.
B)C6H12O6.
C)C12H22O11.
D)C2H4O2.
E)C3H6O3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements regarding enzymes is NOT correct?
A)An enzyme is a biological catalyst that is usually a protein.
B)The active site of an enzyme cannot accept or act on any molecule besides its intended substrate.
C)The ability of an enzyme to act effectively is heavily dependent on environmental factors,such as temperature and pH.
D)Most biological enzymes are highly specific,catalyzing one reaction only.
E)When the substrate binds to an enzyme,the enzyme's three-dimensional structure may change as the reaction proceeds.
A)An enzyme is a biological catalyst that is usually a protein.
B)The active site of an enzyme cannot accept or act on any molecule besides its intended substrate.
C)The ability of an enzyme to act effectively is heavily dependent on environmental factors,such as temperature and pH.
D)Most biological enzymes are highly specific,catalyzing one reaction only.
E)When the substrate binds to an enzyme,the enzyme's three-dimensional structure may change as the reaction proceeds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The three-dimensional structure of a multi-subunit protein,including how the subunits fit together,is described by the term ________
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)long-range structure.
E)quaternary structure.
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)long-range structure.
E)quaternary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The molecule drawn below is an example of ________ 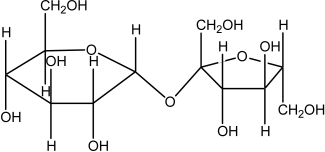
A)a nucleic acid base.
B)a dipeptide.
C)a disaccharide.
D)a fatty acid.
E)a lipid.

A)a nucleic acid base.
B)a dipeptide.
C)a disaccharide.
D)a fatty acid.
E)a lipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following chemical formulas is probably that of a monosaccharide?
A)CH2O
B)C6H10O2
C)C12H22O11
D)C2H4O2
E)C6H12O6
A)CH2O
B)C6H10O2
C)C12H22O11
D)C2H4O2
E)C6H12O6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Sucralose,the active ingredient in an artificial sweetener,Splenda,is shown below.Sucralose is advertised as being made from table sugar.What is the main difference between sucrose (table sugar)and sucralose? 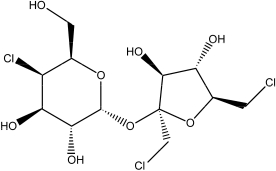
A)Sucralose is a disaccharide,whereas sucrose is a monosaccharide.
B)Sucralose has a six-membered and a five-membered ring,unlike the two six-membered rings in sucrose.
C)Sucralose has a glycosidic bond between the two saccharide units,unlike the C-C bond in sucrose.
D)Some hydroxyl groups in sucrose are replaced by chlorine atoms in sucralose.
E)Sucralose has a six-membered and a five-membered ring,unlike the two five-membered rings in sucrose.

A)Sucralose is a disaccharide,whereas sucrose is a monosaccharide.
B)Sucralose has a six-membered and a five-membered ring,unlike the two six-membered rings in sucrose.
C)Sucralose has a glycosidic bond between the two saccharide units,unlike the C-C bond in sucrose.
D)Some hydroxyl groups in sucrose are replaced by chlorine atoms in sucralose.
E)Sucralose has a six-membered and a five-membered ring,unlike the two five-membered rings in sucrose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Table sugar is ________
A)sucrose.
B)fructose.
C)glucose.
D)sucralose.
E)maltose.
A)sucrose.
B)fructose.
C)glucose.
D)sucralose.
E)maltose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which one of the following statements about biomolecules is NOT correct?
A)Table sugar (sucrose)is a disaccharide made of glucose and fructose.
B)Starch and cellulose are polysaccharides made from glucose.
C)A glycosidic linkage in polysaccharides is an ether group.
D)Cellobiose is a disaccharide composed of two glucose monomers.
E)Maltose is a disaccharide composed of two fructose monomers.
A)Table sugar (sucrose)is a disaccharide made of glucose and fructose.
B)Starch and cellulose are polysaccharides made from glucose.
C)A glycosidic linkage in polysaccharides is an ether group.
D)Cellobiose is a disaccharide composed of two glucose monomers.
E)Maltose is a disaccharide composed of two fructose monomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Compounds that diminish or destroy the effectiveness of an enzyme are called ________
A)inhibitors.
B)decomposers.
C)deactivators.
D)disablers.
E)negators.
A)inhibitors.
B)decomposers.
C)deactivators.
D)disablers.
E)negators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Table sugar is ________
A)glucose.
B)lactose.
C)a disaccharide of glucose and fructose.
D)a glucose-glucose disccharide.
E)cellobiose.
A)glucose.
B)lactose.
C)a disaccharide of glucose and fructose.
D)a glucose-glucose disccharide.
E)cellobiose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which one of the following is best associated with carbohydrates?
A)amino acids
B)saccharides
C)hydrocarbon chains
D)phosphate linkages
E)hydrocarbon rings
A)amino acids
B)saccharides
C)hydrocarbon chains
D)phosphate linkages
E)hydrocarbon rings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The cyclization of fructose forms a ________
A)four-membered ring.
B)five-membered ring.
C)six-membered ring.
D)seven-membered ring.
E)double ring.
A)four-membered ring.
B)five-membered ring.
C)six-membered ring.
D)seven-membered ring.
E)double ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In its linear form,which functional groups are present in glucose?
A)aldehyde and alcohol
B)aldehyde and carboxyl
C)alcohol and ketone
D)amino and alcohol
E)ether and alcohol
A)aldehyde and alcohol
B)aldehyde and carboxyl
C)alcohol and ketone
D)amino and alcohol
E)ether and alcohol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following disaccharides illustrates the -1,4 glycosidic linkages present in starch?
A)
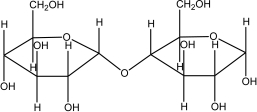
B)
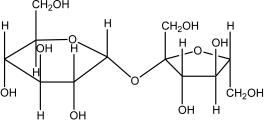
C)
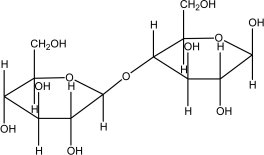
D)
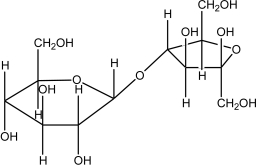
E)
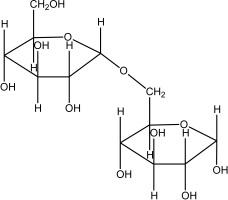
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A glycosidic bond links two sugar molecules in carbohydrates.This linkage could also be called an ________
A)alcohol.
B)amide.
C)ether.
D)aldehyde.
E)ester.
A)alcohol.
B)amide.
C)ether.
D)aldehyde.
E)ester.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Hydrolysis is ________
A)any reaction involving water.
B)always endothermic.
C)the process that forms a glycosidic linkage.
D)breaking a bond to produce hydrogen gas.
E)breaking a bond by the addition of water.
A)any reaction involving water.
B)always endothermic.
C)the process that forms a glycosidic linkage.
D)breaking a bond to produce hydrogen gas.
E)breaking a bond by the addition of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In its ring structure,which functional groups are present in glucose?
A)aldehyde and alcohol
B)aldehyde and carboxyl
C)alcohol and ketone
D)amino and alcohol
E)ether and alcohol
A)aldehyde and alcohol
B)aldehyde and carboxyl
C)alcohol and ketone
D)amino and alcohol
E)ether and alcohol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the linkage that forms between two monosaccharides in a polysaccharide?
A)C - CH2 - C
B)C - O - O - C
C)C - O - C
D)C - C =C - C
E)C - N - C
A)C - CH2 - C
B)C - O - O - C
C)C - O - C
D)C - C =C - C
E)C - N - C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
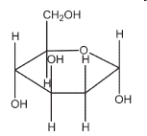
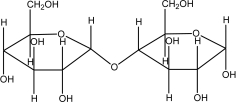
68
Which of the following sugars is glucose?
A)
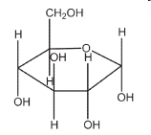
B)
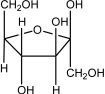
C)
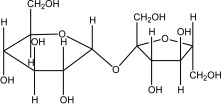
D)
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Fructose is shown below.Number the carbon atoms 1-6 from top to bottom.In the cyclization reaction,a bond is formed by an oxygen lone pair on the OH bonded to C5 to ________
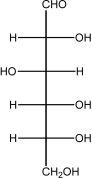
A)C1.
B)C2.
C)C3.
D)C4.
E)C6.

A)C1.
B)C2.
C)C3.
D)C4.
E)C6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The cyclization of glucose forms a ________
A)four-membered ring.
B)five-membered ring.
C)six-membered ring.
D)seven-membered ring.
E)double ring.
A)four-membered ring.
B)five-membered ring.
C)six-membered ring.
D)seven-membered ring.
E)double ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
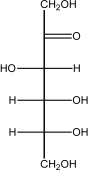
Which of the following shows the most stable form of glucose in aqueous solutions?
A)
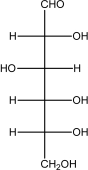
B)
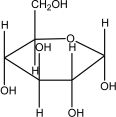
C)
D)
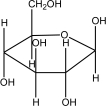
E)
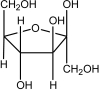
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The cyclization reaction of fructose is different from that of glucose because ________
A)a ketone is formed.
B)a bond is formed to a carbonyl carbon instead of to a methyl carbon.
C)the aldehyde group migrates to a new position.
D)a five-membered ring instead of a six-membered ring is formed.
E)fructose has only five carbon atoms total instead of six,as in sucrose.
A)a ketone is formed.
B)a bond is formed to a carbonyl carbon instead of to a methyl carbon.
C)the aldehyde group migrates to a new position.
D)a five-membered ring instead of a six-membered ring is formed.
E)fructose has only five carbon atoms total instead of six,as in sucrose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An ether linkage connects monomers in ________
A)carbohydrates.
B)nucleic acids.
C)proteins.
D)lipids.
E)steroids.
A)carbohydrates.
B)nucleic acids.
C)proteins.
D)lipids.
E)steroids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following statements regarding carbohydrates is NOT correct?
A)Most organisms use mono- and disaccharides for short-term energy storage.
B)Many plants use cellulose as structural support.
C)Carbohydrates and carbohydrate derivatives aid in molecular recognition,particularly at the surface of cells.
D)Starch is the most abundant energy-storage molecule in plants.
E)Humans can use starch as an energy source but not cellulose,even though both molecules contain glucose monomers.
A)Most organisms use mono- and disaccharides for short-term energy storage.
B)Many plants use cellulose as structural support.
C)Carbohydrates and carbohydrate derivatives aid in molecular recognition,particularly at the surface of cells.
D)Starch is the most abundant energy-storage molecule in plants.
E)Humans can use starch as an energy source but not cellulose,even though both molecules contain glucose monomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Glucose is to cellulose as ________
A)pure gold is to 14 karat gold.
B)a link is to a chain.
C)a leaf is to a tree.
D)a trumpet is to a tuba.
E)a tomato is to a potato.
A)pure gold is to 14 karat gold.
B)a link is to a chain.
C)a leaf is to a tree.
D)a trumpet is to a tuba.
E)a tomato is to a potato.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Glucose is to starch as ________
A)pure gold is to 14 karat gold.
B)a trumpet is to a tuba.
C)a leaf is to a tree.
D)a link is to a chain.
E)a tomato is to a potato.
A)pure gold is to 14 karat gold.
B)a trumpet is to a tuba.
C)a leaf is to a tree.
D)a link is to a chain.
E)a tomato is to a potato.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Glucose is shown below.Number the carbon atoms 1-6 from top to bottom.In the cyclization reaction,a bond is formed to C1 by an oxygen lone pair on the OH bonded to ________
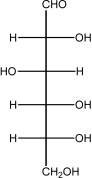
A)C2.
B)C3.
C)C4.
D)C5.
E)C6.

A)C2.
B)C3.
C)C4.
D)C5.
E)C6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Glucose and fructose undergo a ________ reaction in the formation of sucrose.
A)sugarization
B)precipitation
C)neutralization
D)condensation
E)addition
A)sugarization
B)precipitation
C)neutralization
D)condensation
E)addition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following is -glucose?
A)
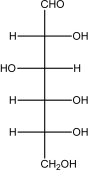
B)
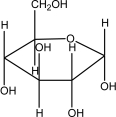
C)
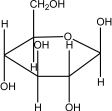
D)
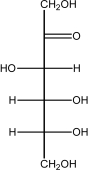
E)
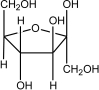
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which statement is NOT correct? Starch and cellulose ________
A)are polysaccharides.
B)have monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds.
C)are a major source of biomass.
D)are stereoisomers made from glucose monomers.
E)are equally easily hydrolyzed to produce glucose.
A)are polysaccharides.
B)have monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds.
C)are a major source of biomass.
D)are stereoisomers made from glucose monomers.
E)are equally easily hydrolyzed to produce glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



