Deck 30: How Animals Move
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/72
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: How Animals Move
1
If you inflate a balloon and then let it go, the air rushing out moves the balloon in a way that is similar to the way that a ________ moves.
A) snake
B) kangaroo
C) squid
D) shark
A) snake
B) kangaroo
C) squid
D) shark
C
2
Which structure constitutes part of the axial skeleton?
A) skull
B) pelvic girdle
C) pectoral girdle
D) radius
A) skull
B) pelvic girdle
C) pectoral girdle
D) radius
A
3
An important function of the bones in the skeleton is to
A) provide a source of ATP.
B) generate hormones.
C) add weight.
D) support the body.
A) provide a source of ATP.
B) generate hormones.
C) add weight.
D) support the body.
D
4
The way the tendons in the legs of a kangaroo aid in locomotion is most like
A) stepping in mud and the mud spreading out as your foot sinks in.
B) stretching and contracting a rubber band.
C) the circular movements of the wheels of an automobile.
D) smashing an apple to make applesauce.
A) stepping in mud and the mud spreading out as your foot sinks in.
B) stretching and contracting a rubber band.
C) the circular movements of the wheels of an automobile.
D) smashing an apple to make applesauce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement about hydrostatic skeletons is true?
A) Hydrostatic skeletons are nonflexible.
B) Hydrostatic skeletons provide little support for muscle action.
C) Hydrostatic skeletons produce rigid animals that maintain one shape.
D) Hydrostatic skeletons can protect internal organs.
A) Hydrostatic skeletons are nonflexible.
B) Hydrostatic skeletons provide little support for muscle action.
C) Hydrostatic skeletons produce rigid animals that maintain one shape.
D) Hydrostatic skeletons can protect internal organs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which animal has an endoskeleton made entirely of cartilage and reinforced with cartilage?
A) bullfrog
B) mackerel
C) shark
D) robin
A) bullfrog
B) mackerel
C) shark
D) robin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why is a newly molted crab unusually slow and clumsy?
A) Its new exoskeleton cannot support the forces that its muscles generate.
B) It temporarily lacks an exoskeleton.
C) Its muscles are still forming their connections with the new exoskeleton.
D) Its neurons are still forming their connections with the new muscles.
A) Its new exoskeleton cannot support the forces that its muscles generate.
B) It temporarily lacks an exoskeleton.
C) Its muscles are still forming their connections with the new exoskeleton.
D) Its neurons are still forming their connections with the new muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which is most like an exoskeleton?
A) springs in a mattress
B) a water balloon
C) a suit of armor
D) the hair covering the surface of a bear
A) springs in a mattress
B) a water balloon
C) a suit of armor
D) the hair covering the surface of a bear

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which statement about locomotion is true?
A) Locomotion requires energy to overcome friction and gravity.
B) Gravity is a greater locomotion problem for animals in water than for those on land.
C) Overcoming friction is a greater locomotion problem for land animals than for those that live in water.
D) Bone strength is more important than body shape in the locomotion of land animals.
A) Locomotion requires energy to overcome friction and gravity.
B) Gravity is a greater locomotion problem for animals in water than for those on land.
C) Overcoming friction is a greater locomotion problem for land animals than for those that live in water.
D) Bone strength is more important than body shape in the locomotion of land animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which provides a base of support for the bones of the forelimbs and hind limbs to the axial skeleton in a human?
A) pectoral girdle
B) pelvic girdle
C) cervical vertebrae
D) appendicular skeleton
A) pectoral girdle
B) pelvic girdle
C) cervical vertebrae
D) appendicular skeleton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which object is most like a hydrostatic skeleton?
A) a water balloon
B) a hot-air balloon
C) a piece of M&M candy
D) a bowling ball
A) a water balloon
B) a hot-air balloon
C) a piece of M&M candy
D) a bowling ball

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which animal has an exoskeleton?
A) human
B) trout
C) shark
D) clam
A) human
B) trout
C) shark
D) clam

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Vertebrae are differentiated during embryonic development by the
A) amount of spongy bone present.
B) length of the backbone.
C) degree of structural support needed.
D) pattern of homeotic gene expression.
A) amount of spongy bone present.
B) length of the backbone.
C) degree of structural support needed.
D) pattern of homeotic gene expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The evolution of the vertebrate skeleton system
A) originated from a snake-like animal with limbs.
B) enabled tetrapods to colonize land.
C) made animals significantly taller.
A) originated from a snake-like animal with limbs.
B) enabled tetrapods to colonize land.
C) made animals significantly taller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Earthworms have a(n)
A) exoskeleton.
B) endoskeleton.
C) hydrostatic skeleton.
A) exoskeleton.
B) endoskeleton.
C) hydrostatic skeleton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An airfoil provides lift because air moving over a wing must travel
A) a greater distance than air moving under the wing, creating a lower pressure system above the wing.
B) a greater distance than air moving under the wing, creating a higher pressure system above the wing.
C) a lesser distance than air moving under the wing, creating a lower pressure system above the wing.
D) a lesser distance than air moving under the wing, creating a higher pressure system above the wing.
A) a greater distance than air moving under the wing, creating a lower pressure system above the wing.
B) a greater distance than air moving under the wing, creating a higher pressure system above the wing.
C) a lesser distance than air moving under the wing, creating a lower pressure system above the wing.
D) a lesser distance than air moving under the wing, creating a higher pressure system above the wing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Earthworms crawl by
A) undulating from side to side.
B) peristalsis.
C) extending their belly scales.
D) pushing themselves forward from the tail.
A) undulating from side to side.
B) peristalsis.
C) extending their belly scales.
D) pushing themselves forward from the tail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
You are cleaning out an old lab freezer and find a tube that contains the ground-up remains of an unknown animal. Your research advisor suggests that you perform chemical assays to determine what molecules made up the animal. After analyzing the data, you determine that the animal contained a large amount of chitin. What type of animal was in the tube?
A) mollusc
B) reptile
C) arthropod
A) mollusc
B) reptile
C) arthropod

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A racehorse cannot stand on one leg, but when it runs it rarely has more than one leg on the ground. Why is a running horse more stable than a standing one?
A) Its legs tilt so the hooves fall in line with its center of gravity.
B) Its momentum gives it stability.
C) It uses its neck for balance the way a tightrope walker uses a pole.
A) Its legs tilt so the hooves fall in line with its center of gravity.
B) Its momentum gives it stability.
C) It uses its neck for balance the way a tightrope walker uses a pole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose that the circular muscles in an earthworm have become selectively paralyzed such that they are not able to contract. How will this affect the earthworm's locomotion?
A) The earthworm will be able to elongate, but not get thicker.
B) The earthworm will be able to get thicker, but not elongate.
C) The earthworm will not be able to elongate or get thicker.
D) The earthworm will be able to crawl as normal.
A) The earthworm will be able to elongate, but not get thicker.
B) The earthworm will be able to get thicker, but not elongate.
C) The earthworm will not be able to elongate or get thicker.
D) The earthworm will be able to crawl as normal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A thick filament consists of
A) actin molecules.
B) myosin molecules.
C) actin and myosin molecules.
A) actin molecules.
B) myosin molecules.
C) actin and myosin molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Bone is composed of
A) living cells that secrete a surrounding matrix.
B) a hard composite of phosphate and sodium ions.
C) channels containing lymphoid tissue.
D) hardened cartilage.
A) living cells that secrete a surrounding matrix.
B) a hard composite of phosphate and sodium ions.
C) channels containing lymphoid tissue.
D) hardened cartilage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Functionally, the muscle fiber's fundamental unit of contraction is the
A) thick filament.
B) myofibril.
C) sarcomere.
D) Z line.
A) thick filament.
B) myofibril.
C) sarcomere.
D) Z line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Osteoporosis is characterized by
A) hairline cracks in long bones, such as the femur.
B) low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue.
C) low phosphate levels in bone.
D) lack of vitamin E in bone tissue.
A) hairline cracks in long bones, such as the femur.
B) low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue.
C) low phosphate levels in bone.
D) lack of vitamin E in bone tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which part of a bone contains mostly stored fat?
A) red bone marrow
B) fibrous connective tissue
C) spongy bone
D) yellow bone marrow
A) red bone marrow
B) fibrous connective tissue
C) spongy bone
D) yellow bone marrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Skeletal muscles
A) are found in and around internal organs.
B) get longer when they contract.
C) work in antagonistic pairs.
D) push on bones to make them move.
A) are found in and around internal organs.
B) get longer when they contract.
C) work in antagonistic pairs.
D) push on bones to make them move.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which list of muscle components is in the correct order from smallest to largest?
A) muscle, sarcomeres, myofibrils, muscle fibers
B) sarcomeres, myofibrils, muscle fibers, muscle
C) sarcomeres, myofibrils, muscle, muscle fibers
D) myofibrils, muscle, sarcomeres, muscle fibers
A) muscle, sarcomeres, myofibrils, muscle fibers
B) sarcomeres, myofibrils, muscle fibers, muscle
C) sarcomeres, myofibrils, muscle, muscle fibers
D) myofibrils, muscle, sarcomeres, muscle fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Muscles are connected to bones by
A) cartilage.
B) ligaments.
C) tendons.
D) myofibrils.
A) cartilage.
B) ligaments.
C) tendons.
D) myofibrils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
To treat a broken bone, physicians will
A) graft new bone to the region.
B) exercise the area of the broken bone.
C) prescribe bed rest and calcium supplements.
D) reshape broken bone parts to their natural position.
A) graft new bone to the region.
B) exercise the area of the broken bone.
C) prescribe bed rest and calcium supplements.
D) reshape broken bone parts to their natural position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Structurally, a sarcomere is
A) the region between two thick filaments.
B) the region between two Z lines.
C) an array of Z units.
D) the region between a thick filament and the next thin filament.
A) the region between two thick filaments.
B) the region between two Z lines.
C) an array of Z units.
D) the region between a thick filament and the next thin filament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The shoulder joint where the humerus meets the pectoral girdle is an example of a
A) hinge joint.
B) ligament.
C) pivot joint.
D) ball-and-socket joint.
A) hinge joint.
B) ligament.
C) pivot joint.
D) ball-and-socket joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which part of a bone contains red bone marrow?
A) compact bone
B) fibrous connective tissue
C) spongy bone
D) yellow bone marrow
A) compact bone
B) fibrous connective tissue
C) spongy bone
D) yellow bone marrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
During muscle contraction,
A) only the thin filaments shorten.
B) only the sarcomere shortens.
C) only the thick filaments shorten.
D) both the thick filaments and the sarcomere shorten.
A) only the thin filaments shorten.
B) only the sarcomere shortens.
C) only the thick filaments shorten.
D) both the thick filaments and the sarcomere shorten.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which statement about skeletal muscle fibers is true?
A) Each muscle fiber is composed of many cells.
B) Each muscle fiber is composed of globular proteins.
C) Each muscle fiber contains one sarcomere.
D) Each muscle fiber contains actin and myosin.
A) Each muscle fiber is composed of many cells.
B) Each muscle fiber is composed of globular proteins.
C) Each muscle fiber contains one sarcomere.
D) Each muscle fiber contains actin and myosin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which statement best describes the molecular basis of muscle shortening?
A) Individual filamentous proteins contract.
B) Individual filamentous proteins shorten by coiling.
C) Rod-shaped protein polymers shorten by losing subunits from their ends.
D) Protein filaments ratchet along other protein filaments.
A) Individual filamentous proteins contract.
B) Individual filamentous proteins shorten by coiling.
C) Rod-shaped protein polymers shorten by losing subunits from their ends.
D) Protein filaments ratchet along other protein filaments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Osteoporosis has long been recognized as a problem for women after menopause, but it is also emerging as a health concern for
A) women and men ages 20-30.
B) women ages 16-18.
C) men over the age of 65.
D) men and younger people in general.
A) women and men ages 20-30.
B) women ages 16-18.
C) men over the age of 65.
D) men and younger people in general.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If you lay your forearm along a table, you can rotate it so that your hand changes from a palm-down to a palm-up position. This is possible because your radius and ulna join at a
A) ball-and-socket joint.
B) hinge joint.
C) pivot joint.
D) ligament.
A) ball-and-socket joint.
B) hinge joint.
C) pivot joint.
D) ligament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
One change that occurs within a sarcomere during muscle contraction is that the
A) thin filaments get thicker.
B) thick filaments move closer together.
C) Z lines move closer together.
D) thick filaments get thicker.
A) thin filaments get thicker.
B) thick filaments move closer together.
C) Z lines move closer together.
D) thick filaments get thicker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
According to the sliding filament model of muscle contraction, a sarcomere contracts when its
A) thick filaments slide across its Z lines.
B) thin filaments slide across its Z lines.
C) thin filaments slide along its thick filaments.
D) thick filaments move closer together.
A) thick filaments slide across its Z lines.
B) thin filaments slide across its Z lines.
C) thin filaments slide along its thick filaments.
D) thick filaments move closer together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Thin sheets of ________ form a cushion-like surface for moving joints
A) red bone marrow.
B) cartilage.
C) spongy bone.
D) compact bone.
A) red bone marrow.
B) cartilage.
C) spongy bone.
D) compact bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which part of this figure depicts the thoracic vertebrae? 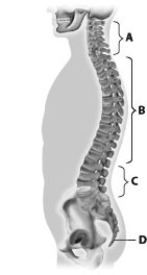
A) part A
B) part B
C) part C
D) part D

A) part A
B) part B
C) part C
D) part D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which muscle(s) would have the greatest number of muscle cells per motor unit?
A) muscles controlling the movement of our hands
B) facial muscles
C) a thigh muscle
D) muscles controlling the movement of an eyeball
A) muscles controlling the movement of our hands
B) facial muscles
C) a thigh muscle
D) muscles controlling the movement of an eyeball

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements best describes the power stroke of muscle contraction?
A) The myosin head bends, pulling the thick filament toward the center of the sarcomere.
B) The myosin head bends, pulling the thin filament toward the center of the sarcomere.
C) The actin head bends, pulling the thin filament toward the center of the sarcomere.
D) The actin head bends, pulling the thick filament toward the center of the sarcomere.
A) The myosin head bends, pulling the thick filament toward the center of the sarcomere.
B) The myosin head bends, pulling the thin filament toward the center of the sarcomere.
C) The actin head bends, pulling the thin filament toward the center of the sarcomere.
D) The actin head bends, pulling the thick filament toward the center of the sarcomere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Muscles that are constantly active, such as those maintaining our body posture, have a high proportion of
A) fast, fatigue-resistant fibers.
B) fast, fatigue-susceptible fibers.
C) slow, fatigue-resistant fibers.
D) slow, fatigue-susceptible fibers.
A) fast, fatigue-resistant fibers.
B) fast, fatigue-susceptible fibers.
C) slow, fatigue-resistant fibers.
D) slow, fatigue-susceptible fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A motor unit is
A) the bundle of axons that goes from the spinal cord to a muscle.
B) one of the connective tissue-wrapped bundles of muscle fibers in a muscle.
C) a motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it controls.
D) the muscle or group of muscles that accomplishes a specific movement.
A) the bundle of axons that goes from the spinal cord to a muscle.
B) one of the connective tissue-wrapped bundles of muscle fibers in a muscle.
C) a motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it controls.
D) the muscle or group of muscles that accomplishes a specific movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Your friend is complaining of back pain. She also says that she hurts the most near her neck. What part of her back may have been injured?
A) cervical vertebrae
B) thoracic vertebrae
C) sacrum
D) coccyx
A) cervical vertebrae
B) thoracic vertebrae
C) sacrum
D) coccyx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The calcium that triggers muscle contraction is stored in the
A) motor neuron.
B) plasma membrane of cells.
C) endoplasmic reticulum.
D) mitochondria.
A) motor neuron.
B) plasma membrane of cells.
C) endoplasmic reticulum.
D) mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A tennis player serving the ball uses fast muscle fibers. The ATP needed to accomplish this comes from
A) anaerobic fermentation.
B) aerobic respiration.
C) conversion of lactic acid to ATP.
D) conversion of Ca2+ to ATP.
A) anaerobic fermentation.
B) aerobic respiration.
C) conversion of lactic acid to ATP.
D) conversion of Ca2+ to ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which statement regarding exercise is true?
A) Most of the ATP for aerobic exercise comes from aerobic respiration.
B) During a short burst of activity such as a sprint, the main source of energy is aerobic respiration.
C) If the demand for ATP outstrips oxygen supply, muscles switch to aerobic fermentation.
A) Most of the ATP for aerobic exercise comes from aerobic respiration.
B) During a short burst of activity such as a sprint, the main source of energy is aerobic respiration.
C) If the demand for ATP outstrips oxygen supply, muscles switch to aerobic fermentation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Fast muscle fibers contain a high proportion of myofibrils, which allows the fibers to generate high amounts of force. However, this leaves little room in the fibers for other cellular components, including mitochondria. The opposite is true for slow muscle fibers. Does this information support or refute what you know about the fatigue-susceptibility of fast and slow fibers? Why or why not?
A) It supports it because if fast fibers have less room for mitochondria than slow fibers do, they cannot produce as much ATP and thus are less fatigue-resistant than slow fibers.
B) It supports it because if fast fibers have less room for mitochondria than slow fibers do, they can produce more ATP than slow fibers and thus are more fatigue-resistant than slow fibers.
C) It refutes it because if fast fibers have less room for mitochondria than slow fibers do, they can produce more ATP than slow fibers and thus are less fatigue-resistant than slow fibers.
D) It refutes it because if fast fibers have less room for mitochondria than slow fibers do, they cannot produce as much ATP and thus are more fatigue-resistant than slow fibers.
A) It supports it because if fast fibers have less room for mitochondria than slow fibers do, they cannot produce as much ATP and thus are less fatigue-resistant than slow fibers.
B) It supports it because if fast fibers have less room for mitochondria than slow fibers do, they can produce more ATP than slow fibers and thus are more fatigue-resistant than slow fibers.
C) It refutes it because if fast fibers have less room for mitochondria than slow fibers do, they can produce more ATP than slow fibers and thus are less fatigue-resistant than slow fibers.
D) It refutes it because if fast fibers have less room for mitochondria than slow fibers do, they cannot produce as much ATP and thus are more fatigue-resistant than slow fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The role of calcium in muscle contraction is to
A) release ADP and phosphate from myosin.
B) make it possible for ATP to bind to actin.
C) make it possible for myosin to bind to actin.
D) make it possible for ATP to bind to myosin.
A) release ADP and phosphate from myosin.
B) make it possible for ATP to bind to actin.
C) make it possible for myosin to bind to actin.
D) make it possible for ATP to bind to myosin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A muscle fiber from the latissimus dorsi (one of the back muscles) of a chimpanzee has a lot of mitochondria and myoglobin and can generate relatively little force. Which type of muscle fiber is being described?
A) a fast, fatigue-resistant fiber
B) a fast, fatigue-susceptible fiber
C) a slow, fatigue-resistant fiber
D) a slow, fatigue-susceptible fiber
A) a fast, fatigue-resistant fiber
B) a fast, fatigue-susceptible fiber
C) a slow, fatigue-resistant fiber
D) a slow, fatigue-susceptible fiber

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which part of this figure depicting a bone shows spongy bone tissue? 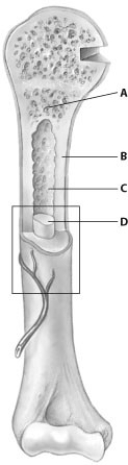
A) part A
B) part B
C) part C
D) part D

A) part A
B) part B
C) part C
D) part D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The sequence of events that cause a sarcomere to contract can be summed up in the correct order as
A) detach, extend, contract, attach.
B) attach, pull, extend, contract.
C) detach, extend, attach, pull.
D) attach, contract, detach, recoil.
A) detach, extend, contract, attach.
B) attach, pull, extend, contract.
C) detach, extend, attach, pull.
D) attach, contract, detach, recoil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Rickets is a softening of the bones that can lead to frequent fractures and skeletal deformities. The legs of a person with rickets tend to bow outward under the force exerted by body weight and movement. British scientists found a serious increase in the incidence of rickets and other bone deficiencies among women in Middle Eastern countries who cover their bodies completely to express a form of religious belief, as well as among their breast-fed children.
Most of the body's vitamin D, which is necessary for calcium absorption by bone tissue, is obtained through sunlight acting on the skin. Doctors warn that women who completely cover their skin do not get enough sunlight to produce the vitamin D necessary for bone health. This lack of sun exposure also lowers the level of vitamin D in their breast milk, which means that their children may develop the same vitamin D deficiencies. Lack of calcium and phosphorous, which are needed for bone repair and replacement, can also lead to rickets. Rickets caused by a dietary lack of these minerals is more common in developing countries because dairy products and green vegetables, the best sources of calcium, are not commonly eaten.
As a physician caring for a nursing woman who has chosen to dress in a way that covers her skin but who is concerned about rickets developing in her baby, you might advise her to
A) exercise more.
B) eats lots of meat and potatoes.
C) take vitamin D and calcium supplements.
D) give up smoking.
Rickets is a softening of the bones that can lead to frequent fractures and skeletal deformities. The legs of a person with rickets tend to bow outward under the force exerted by body weight and movement. British scientists found a serious increase in the incidence of rickets and other bone deficiencies among women in Middle Eastern countries who cover their bodies completely to express a form of religious belief, as well as among their breast-fed children.
Most of the body's vitamin D, which is necessary for calcium absorption by bone tissue, is obtained through sunlight acting on the skin. Doctors warn that women who completely cover their skin do not get enough sunlight to produce the vitamin D necessary for bone health. This lack of sun exposure also lowers the level of vitamin D in their breast milk, which means that their children may develop the same vitamin D deficiencies. Lack of calcium and phosphorous, which are needed for bone repair and replacement, can also lead to rickets. Rickets caused by a dietary lack of these minerals is more common in developing countries because dairy products and green vegetables, the best sources of calcium, are not commonly eaten.
As a physician caring for a nursing woman who has chosen to dress in a way that covers her skin but who is concerned about rickets developing in her baby, you might advise her to
A) exercise more.
B) eats lots of meat and potatoes.
C) take vitamin D and calcium supplements.
D) give up smoking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Mutations in the gene for troponin can result in the production of the troponin protein, which has varying affinities for Ca2+ ions. Suppose that in a muscle cell a mutant troponin is expressed that has such a high affinity for Ca2+ ions that once they bind to troponin they cannot unbind. What will likely happen in this muscle cell?
A) Myosin heads will not bind to actin after action potentials stop being received.
B) Myosin heads will bind to actin after action potentials stop being received.
C) Tropomyosin will not move to expose myosin binding sites.
D) Cross-bridges will form between myosin and tropomyosin.
A) Myosin heads will not bind to actin after action potentials stop being received.
B) Myosin heads will bind to actin after action potentials stop being received.
C) Tropomyosin will not move to expose myosin binding sites.
D) Cross-bridges will form between myosin and tropomyosin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An animal's locomotor (relates to locomotion) muscle was dissected and the percentages of fast and slow fibers were determined and plotted in the accompanying figure. Which muscle is the likely source for this data? 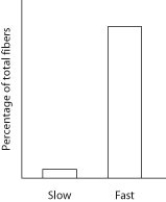
A) flight muscles of a migratory bird
B) thigh muscles of a marathon runner
C) neck muscles of a chimpanzee
D) jumping muscles of a frog

A) flight muscles of a migratory bird
B) thigh muscles of a marathon runner
C) neck muscles of a chimpanzee
D) jumping muscles of a frog

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The neurotransmitter found at the synapse between nerves and human skeletal muscle cells is
A) acetylcholine.
B) epinephrine.
C) dopamine.
D) serotonin.
A) acetylcholine.
B) epinephrine.
C) dopamine.
D) serotonin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which treatment could possibly help to transform the bone on the right to the bone on the left? 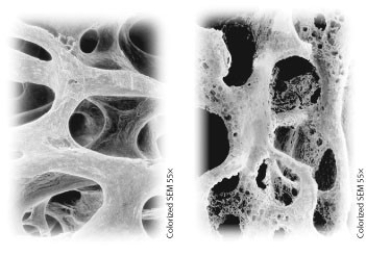
A) wearing long sleeves while out in the sun
B) swimming for 30 minutes a day
C) removing calcium from the diet
D) taking vitamin D supplements

A) wearing long sleeves while out in the sun
B) swimming for 30 minutes a day
C) removing calcium from the diet
D) taking vitamin D supplements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Acetylcholine (ACh) is released by motor neurons and binds to receptors on muscle cells to initiate action potentials. Some snake venom contains specific toxins that bind irreversibly to these receptors and block acetylcholine's ability to bind. If an animal is bitten by a snake with these toxins in its venom, what do you predict would happen?
A) The animal's muscle cells would increase production of myoglobin.
B) The animal's muscles would contract uncontrollably.
C) The animal's muscles would not be able to contract.
D) The animal's muscle cells would show shrinkage in mitochondria.
A) The animal's muscle cells would increase production of myoglobin.
B) The animal's muscles would contract uncontrollably.
C) The animal's muscles would not be able to contract.
D) The animal's muscle cells would show shrinkage in mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
After reading the paragraph below, answer the questions that follow.
The "Ironman" is a version of the triathlon, a race that includes three events: swimming, bicycling, and running. In an Ironman, an athlete must swim 2.4 miles, bike 112 miles, and run 26.2 miles, in that order, without a break. The annual Ironman World Championship is held in Hawaii every year. The men's course record was set in 2011 by Australia's Craig Alexander with a time of 8 hours, 18 minutes, and 37 seconds, and the women's course record was set in 2009 by England's Chrissie Wellington with a time of 8 hours, 54 minutes, and 2 seconds.
Which event of the Ironman would likely contribute the most to bone development and growth?
A) swimming
B) bicycling
C) running
The "Ironman" is a version of the triathlon, a race that includes three events: swimming, bicycling, and running. In an Ironman, an athlete must swim 2.4 miles, bike 112 miles, and run 26.2 miles, in that order, without a break. The annual Ironman World Championship is held in Hawaii every year. The men's course record was set in 2011 by Australia's Craig Alexander with a time of 8 hours, 18 minutes, and 37 seconds, and the women's course record was set in 2009 by England's Chrissie Wellington with a time of 8 hours, 54 minutes, and 2 seconds.
Which event of the Ironman would likely contribute the most to bone development and growth?
A) swimming
B) bicycling
C) running

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
After reading the paragraph below, answer the questions that follow.
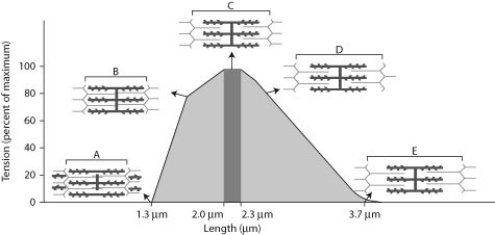 When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
What portion of the graph would involve myosin forming cross-bridges and going through power strokes?
A) from A to B
B) from D to B
C) from B to E
D) from A to E
 When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.What portion of the graph would involve myosin forming cross-bridges and going through power strokes?
A) from A to B
B) from D to B
C) from B to E
D) from A to E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
After reading the paragraph below, answer the questions that follow.
 When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
At what point on the graph is the most tension generated?
A) point A
B) point B
C) point C
D) point E
 When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.At what point on the graph is the most tension generated?
A) point A
B) point B
C) point C
D) point E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the year 2000, it was estimated that the number of new osteoporotic fractures in men and women ages 50 and older was 9.0 million: 1.6 million were at the hip, 1.7 million were at the forearm, and 1.4 million were from the spine and humerus. Consider the following data and answer the questions that follow.
Estimated Number of Fractures (in Thousands) Worldwide at the Sites Shown in Men and Women in the Year 2000
Source: Adapted from Johnell, O., & Kanis, J.A. (2006). Osteoporosis International, 17(12): 1726. doi:10.1007/s00198-006-0172-4.
-Compare the percentage of fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus in men and women combined to the percentage of fractures at other sites in men and women combined. What do you conclude?
A) There are about 50% more fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus in men and women than in fractures at other sites in men and women.
B) There are about 20% more fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus in men and women than in fractures at other sites in men and women.
C) There are about 10% fewer fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus in men and women than in fractures at other sites in men and women.
D) There are 100% fewer fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus in men and women than in fractures at other sites in men and women.
Estimated Number of Fractures (in Thousands) Worldwide at the Sites Shown in Men and Women in the Year 2000
Source: Adapted from Johnell, O., & Kanis, J.A. (2006). Osteoporosis International, 17(12): 1726. doi:10.1007/s00198-006-0172-4.
-Compare the percentage of fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus in men and women combined to the percentage of fractures at other sites in men and women combined. What do you conclude?
A) There are about 50% more fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus in men and women than in fractures at other sites in men and women.
B) There are about 20% more fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus in men and women than in fractures at other sites in men and women.
C) There are about 10% fewer fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus in men and women than in fractures at other sites in men and women.
D) There are 100% fewer fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus in men and women than in fractures at other sites in men and women.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the year 2000, it was estimated that the number of new osteoporotic fractures in men and women ages 50 and older was 9.0 million: 1.6 million were at the hip, 1.7 million were at the forearm, and 1.4 million were from the spine and humerus. Consider the following data and answer the questions that follow.
Estimated Number of Fractures (in Thousands) Worldwide at the Sites Shown in Men and Women in the Year 2000
Source: Adapted from Johnell, O., & Kanis, J.A. (2006). Osteoporosis International, 17(12): 1726. doi:10.1007/s00198-006-0172-4.
-Fractures at sites other than hip, forearm, spine, and humerus were
A) equally common in men than in women.
B) less common in men than in women.
C) more common in men than in women.
Estimated Number of Fractures (in Thousands) Worldwide at the Sites Shown in Men and Women in the Year 2000
Source: Adapted from Johnell, O., & Kanis, J.A. (2006). Osteoporosis International, 17(12): 1726. doi:10.1007/s00198-006-0172-4.
-Fractures at sites other than hip, forearm, spine, and humerus were
A) equally common in men than in women.
B) less common in men than in women.
C) more common in men than in women.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
After reading the paragraph below, answer the questions that follow.
The "Ironman" is a version of the triathlon, a race that includes three events: swimming, bicycling, and running. In an Ironman, an athlete must swim 2.4 miles, bike 112 miles, and run 26.2 miles, in that order, without a break. The annual Ironman World Championship is held in Hawaii every year. The men's course record was set in 2011 by Australia's Craig Alexander with a time of 8 hours, 18 minutes, and 37 seconds, and the women's course record was set in 2009 by England's Chrissie Wellington with a time of 8 hours, 54 minutes, and 2 seconds.
What type of energy would the leg muscles of athletes that enter this race use during the final 26.2-mile foot race?
A) stored ATP and PCr
B) aerobic respiration
C) stored ATP and PCr plus lactic acid fermentation
D) lactic acid fermentation
The "Ironman" is a version of the triathlon, a race that includes three events: swimming, bicycling, and running. In an Ironman, an athlete must swim 2.4 miles, bike 112 miles, and run 26.2 miles, in that order, without a break. The annual Ironman World Championship is held in Hawaii every year. The men's course record was set in 2011 by Australia's Craig Alexander with a time of 8 hours, 18 minutes, and 37 seconds, and the women's course record was set in 2009 by England's Chrissie Wellington with a time of 8 hours, 54 minutes, and 2 seconds.
What type of energy would the leg muscles of athletes that enter this race use during the final 26.2-mile foot race?
A) stored ATP and PCr
B) aerobic respiration
C) stored ATP and PCr plus lactic acid fermentation
D) lactic acid fermentation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
After reading the paragraph below, answer the questions that follow.
 When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
Mammalian muscles can shorten approximately 35% of their resting length when all sarcomeres contract. If a sarcomere passes through maximal tension generation during this 35% contraction, what is the likely starting point for contraction of a sarcomere?
A) point A
B) point B
C) point D
D) point E
 When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.Mammalian muscles can shorten approximately 35% of their resting length when all sarcomeres contract. If a sarcomere passes through maximal tension generation during this 35% contraction, what is the likely starting point for contraction of a sarcomere?
A) point A
B) point B
C) point D
D) point E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
After reading the paragraph below, answer the questions that follow.
The "Ironman" is a version of the triathlon, a race that includes three events: swimming, bicycling, and running. In an Ironman, an athlete must swim 2.4 miles, bike 112 miles, and run 26.2 miles, in that order, without a break. The annual Ironman World Championship is held in Hawaii every year. The men's course record was set in 2011 by Australia's Craig Alexander with a time of 8 hours, 18 minutes, and 37 seconds, and the women's course record was set in 2009 by England's Chrissie Wellington with a time of 8 hours, 54 minutes, and 2 seconds.
What type of muscle fibers would likely be found in the legs of athletes who attempt to complete this race?
A) fast, fatigue-resistant fibers
B) fast, fatigue-susceptible fibers
C) slow, fatigue-resistant fibers
D) slow, fatigue-susceptible fibers
The "Ironman" is a version of the triathlon, a race that includes three events: swimming, bicycling, and running. In an Ironman, an athlete must swim 2.4 miles, bike 112 miles, and run 26.2 miles, in that order, without a break. The annual Ironman World Championship is held in Hawaii every year. The men's course record was set in 2011 by Australia's Craig Alexander with a time of 8 hours, 18 minutes, and 37 seconds, and the women's course record was set in 2009 by England's Chrissie Wellington with a time of 8 hours, 54 minutes, and 2 seconds.
What type of muscle fibers would likely be found in the legs of athletes who attempt to complete this race?
A) fast, fatigue-resistant fibers
B) fast, fatigue-susceptible fibers
C) slow, fatigue-resistant fibers
D) slow, fatigue-susceptible fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
After reading the paragraph below, answer the questions that follow.
 When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
At what point on the graph are thick and thin filaments most overlapped?
A) point A
B) point B
C) point D
D) point E
 When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.At what point on the graph are thick and thin filaments most overlapped?
A) point A
B) point B
C) point D
D) point E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the year 2000, it was estimated that the number of new osteoporotic fractures in men and women ages 50 and older was 9.0 million: 1.6 million were at the hip, 1.7 million were at the forearm, and 1.4 million were from the spine and humerus. Consider the following data and answer the questions that follow.
Estimated Number of Fractures (in Thousands) Worldwide at the Sites Shown in Men and Women in the Year 2000
Source: Adapted from Johnell, O., & Kanis, J.A. (2006). Osteoporosis International, 17(12): 1726. doi:10.1007/s00198-006-0172-4.
-Combined fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus were
A) greater in women than men.
B) greater in men than women.
C) equal in men and women.
Estimated Number of Fractures (in Thousands) Worldwide at the Sites Shown in Men and Women in the Year 2000
Source: Adapted from Johnell, O., & Kanis, J.A. (2006). Osteoporosis International, 17(12): 1726. doi:10.1007/s00198-006-0172-4.
-Combined fractures in the hip, forearm, spine, and humerus were
A) greater in women than men.
B) greater in men than women.
C) equal in men and women.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
After reading the paragraph below, answer the questions that follow.
 When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
At what point on the graph is the sarcomere the most extended?
A) point A
B) point B
C) point C
D) point E
 When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension). However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.At what point on the graph is the sarcomere the most extended?
A) point A
B) point B
C) point C
D) point E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In rickets, lack of calcium decreases the strength of the mineral matrix of compact bone so that it is unable to
A) resist compression.
B) complete extension.
C) complement muscle contraction.
D) bend at the joints.
A) resist compression.
B) complete extension.
C) complement muscle contraction.
D) bend at the joints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



