Deck 28: Nervous Systems
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Nervous Systems
1
Which statement regarding the nervous system is true?
A) Sensory neurons convey signals from the central nervous system (CNS) to sensory receptors.
B) Motor neurons convey signals from the CNS to effector cells.
C) The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is composed entirely of nerves.
D) The CNS includes the brain and peripheral nerves.
A) Sensory neurons convey signals from the central nervous system (CNS) to sensory receptors.
B) Motor neurons convey signals from the CNS to effector cells.
C) The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is composed entirely of nerves.
D) The CNS includes the brain and peripheral nerves.
B
2
Multiple sclerosis results from an autoimmune disease that primarily involves
A) destruction of the hippocampus.
B) destruction of myelin sheaths.
C) destruction of regions of the motor cortex.
D) deterioration of parts of the spinal cord.
A) destruction of the hippocampus.
B) destruction of myelin sheaths.
C) destruction of regions of the motor cortex.
D) deterioration of parts of the spinal cord.
B
3
The two major anatomical divisions of the nervous system are the
A) sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system.
B) central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
C) sensory nervous system and motor nervous system.
D) voluntary nervous system and involuntary nervous system.
A) sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system.
B) central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
C) sensory nervous system and motor nervous system.
D) voluntary nervous system and involuntary nervous system.
B
4
Which statement about resting potential is true?
A) A resting membrane allows much more sodium than potassium to diffuse across it.
B) The concentration of sodium is much higher inside the cell than outside.
C) The resting potential exists because of differences in glucose concentration inside and outside the cell.
D) The sodium-potassium pump contributes to the resting membrane potential.
A) A resting membrane allows much more sodium than potassium to diffuse across it.
B) The concentration of sodium is much higher inside the cell than outside.
C) The resting potential exists because of differences in glucose concentration inside and outside the cell.
D) The sodium-potassium pump contributes to the resting membrane potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The functional unit of the nervous system is the
A) cell body.
B) neuron.
C) axon.
D) synapse.
A) cell body.
B) neuron.
C) axon.
D) synapse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Once an action potential is triggered, there is a
A) reversal of the membrane polarity, with the interior of the cell becoming positively charged.
B) reversal of the membrane polarity, with the interior of the cell becoming negatively charged.
C) sudden rush of potassium into the neuron.
D) sudden impermeability of the membrane to the transport of ions.
A) reversal of the membrane polarity, with the interior of the cell becoming positively charged.
B) reversal of the membrane polarity, with the interior of the cell becoming negatively charged.
C) sudden rush of potassium into the neuron.
D) sudden impermeability of the membrane to the transport of ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Botulinum toxin (Botox) produced by certain bacteria will
A) prevent enzymatic breakdown of neurotransmitters.
B) cause continual contraction of smooth muscle.
C) initiate an increase in the strength of a transmitted signal.
D) inhibit the release of acetylcholine.
A) prevent enzymatic breakdown of neurotransmitters.
B) cause continual contraction of smooth muscle.
C) initiate an increase in the strength of a transmitted signal.
D) inhibit the release of acetylcholine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Once the threshold is reached as a cell depolarizes
A) K+ channels open.
B) Na+ channels close.
C) an action potential is triggered.
D) the interior of the cell becomes negative with respect to the outside.
A) K+ channels open.
B) Na+ channels close.
C) an action potential is triggered.
D) the interior of the cell becomes negative with respect to the outside.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The signal that crosses a synapse is stopped when the
A) receiving cell runs out of sodium and is no longer able to respond to the stimulus.
B) receiving cell runs out of potassium and is no longer able to respond to the stimulus.
C) neurotransmitters are enzymatically broken down or transported back to the signaling cell.
D) neurotransmitters are actively transported into glia cells.
A) receiving cell runs out of sodium and is no longer able to respond to the stimulus.
B) receiving cell runs out of potassium and is no longer able to respond to the stimulus.
C) neurotransmitters are enzymatically broken down or transported back to the signaling cell.
D) neurotransmitters are actively transported into glia cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
During transmission across a typical chemical synapse
A) neurotransmitter molecules are stored in the synaptic cleft.
B) action potentials trigger chemical changes that make the synaptic vesicles fuse with each other.
C) vesicles containing neurotransmitters diffuse to the receiving cell's plasma membrane.
D) neurotransmitter molecules bind to receptors in the receiving cell's plasma membrane.
A) neurotransmitter molecules are stored in the synaptic cleft.
B) action potentials trigger chemical changes that make the synaptic vesicles fuse with each other.
C) vesicles containing neurotransmitters diffuse to the receiving cell's plasma membrane.
D) neurotransmitter molecules bind to receptors in the receiving cell's plasma membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Nervous system effector cells
A) are white blood cells found in the circulatory system.
B) consist of sensory cells.
C) include muscle cells and gland cells.
D) provide automatic responses to stimuli.
A) are white blood cells found in the circulatory system.
B) consist of sensory cells.
C) include muscle cells and gland cells.
D) provide automatic responses to stimuli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Action potentials normally travel along an axon
A) toward the cell body.
B) away from the cell body.
C) either toward or away from the cell body.
A) toward the cell body.
B) away from the cell body.
C) either toward or away from the cell body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Neurotransmitters that open Na+ channels and trigger action potentials in receiving cells are called
A) inhibitory.
B) excitatory.
C) sympathetic.
D) parasympathetic.
A) inhibitory.
B) excitatory.
C) sympathetic.
D) parasympathetic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The speed of impulse conduction along an axon may be increased by
A) myelin sheaths.
B) graded potentials.
C) neurotransmitters.
D) effector cells.
A) myelin sheaths.
B) graded potentials.
C) neurotransmitters.
D) effector cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
One neurotransmitter associated with sleep, mood, attention, and learning is
A) acetylcholine.
B) nitric oxide.
C) epinephrine.
D) serotonin.
A) acetylcholine.
B) nitric oxide.
C) epinephrine.
D) serotonin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What part of a neuron carries signals toward the part of the cell that houses the nucleus?
A) node of Ranvier
B) axon
C) cell body
D) dendrite
A) node of Ranvier
B) axon
C) cell body
D) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Action potentials relay different intensities of information due to the
A) amplitude of action potentials relative to the strength of the stimulus.
B) frequency of action potentials relative to the strength of the stimulus.
C) duration of action potentials relative to the strength of the stimulus.
A) amplitude of action potentials relative to the strength of the stimulus.
B) frequency of action potentials relative to the strength of the stimulus.
C) duration of action potentials relative to the strength of the stimulus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The gap between the transmitting and receiving neurons in a chemical synapse is known as the
A) node of Ranvier.
B) ion channel.
C) gap junction.
D) synaptic cleft.
A) node of Ranvier.
B) ion channel.
C) gap junction.
D) synaptic cleft.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The central communication conduit between the brain and the rest of the body is the
A) brainstem.
B) nerve bundle.
C) spinal cord.
D) nervous system.
A) brainstem.
B) nerve bundle.
C) spinal cord.
D) nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The effect of a sending neuron on a receiving neuron is typically greater when ________ neurotransmitters bind to the receiving neuron and the synapse is ________ the base of the receiving cell's axon.
A) more; close to
B) fewer; close to
C) more; far from
D) fewer; far from
A) more; close to
B) fewer; close to
C) more; far from
D) fewer; far from

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
You start to fall but then catch yourself, regaining your balance. Which of the following brain regions is responsible for the rapid coordination of muscle activity that kept you from falling?
A) motor cortex
B) thalamus
C) cerebellum
D) pons
A) motor cortex
B) thalamus
C) cerebellum
D) pons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When you are very nervous, perhaps before you must speak in front of your class, you notice that your mouth is dry and your heart is racing. This is most likely due to stimulation by the
A) enteric division of your autonomic nervous system.
B) sympathetic division of your autonomic nervous system.
C) parasympathetic division of your autonomic nervous system.
A) enteric division of your autonomic nervous system.
B) sympathetic division of your autonomic nervous system.
C) parasympathetic division of your autonomic nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which statement regarding the brain is true?
A) Ventricles in the brain are filled with interstitial fluid.
B) The blood-brain barrier helps to maintain a stable chemical environment for the brain.
C) Layers of connective tissue, called epithelium, surround and protect the brain and spinal cord.
D) White matter is composed of mainly dendrites.
A) Ventricles in the brain are filled with interstitial fluid.
B) The blood-brain barrier helps to maintain a stable chemical environment for the brain.
C) Layers of connective tissue, called epithelium, surround and protect the brain and spinal cord.
D) White matter is composed of mainly dendrites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The autonomic nervous system
A) integrates sensory inputs to the brain.
B) carries signals to and from skeletal muscles.
C) regulates the internal environment of the body.
D) is part of the central nervous system.
A) integrates sensory inputs to the brain.
B) carries signals to and from skeletal muscles.
C) regulates the internal environment of the body.
D) is part of the central nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which results from stimulation by the sympathetic nervous system?
A) release of glucose from the liver
B) decreased heart rate
C) stimulation of the digestive organs
D) constriction of the bronchi
A) release of glucose from the liver
B) decreased heart rate
C) stimulation of the digestive organs
D) constriction of the bronchi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Parkinson's disease is associated with a deficiency in
A) dopamine.
B) serotonin.
C) acetylcholine.
D) endorphins.
A) dopamine.
B) serotonin.
C) acetylcholine.
D) endorphins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The enteric division of the autonomic nervous system consists of neurons in the digestive tract, the gallbladder, and the
A) heart.
B) lymphatic system.
C) pancreas.
D) thyroid gland.
A) heart.
B) lymphatic system.
C) pancreas.
D) thyroid gland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In all vertebrates, the brain consists of the
A) cerebrum, forebrain, and hindbrain.
B) cerebrum, midbrain, and hindbrain.
C) forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
D) cerebrum, cerebellum, and hindbrain.
A) cerebrum, forebrain, and hindbrain.
B) cerebrum, midbrain, and hindbrain.
C) forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
D) cerebrum, cerebellum, and hindbrain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which division of the human nervous system carries signals to skeletal muscles?
A) parasympathetic nervous system
B) sympathetic nervous system
C) motor system
A) parasympathetic nervous system
B) sympathetic nervous system
C) motor system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which results from stimulation by the parasympathetic nervous system?
A) increased heart rate
B) inhibition of the digestive organs
C) inhibition of urination
D) stimulation of saliva secretion
A) increased heart rate
B) inhibition of the digestive organs
C) inhibition of urination
D) stimulation of saliva secretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The simplest animals to display cephalization and centralization of the nervous system are
A) sponges.
B) flatworms.
C) cnidarians.
D) echinoderms.
A) sponges.
B) flatworms.
C) cnidarians.
D) echinoderms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Our biological clock, which regulates the sleep-wake cycle, is housed within the
A) cerebrum.
B) hypothalamus.
C) cerebellum.
D) brainstem.
A) cerebrum.
B) hypothalamus.
C) cerebellum.
D) brainstem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What part of the brain sorts incoming information, such as touch signals from your hand, into categories before relaying it to the cerebral cortex?
A) thalamus
B) hypothalamus
C) pons
D) hippocampus
A) thalamus
B) hypothalamus
C) pons
D) hippocampus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which brain region controls the secretion of pituitary hormones and exerts direct control over many other aspects of homeostasis?
A) thalamus
B) hypothalamus
C) hippocampus
D) cerebellum
A) thalamus
B) hypothalamus
C) hippocampus
D) cerebellum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The uniformity in the way nerve cells function within the animal kingdom
A) indicates that the peripheral nervous system (PNS) evolved before the central nervous system (CNS).
B) is evidence that the neuron was an early evolutionary adaptation.
C) is proof of neurotransmitter efficiency.
D) must have prevented the development of diversity.
A) indicates that the peripheral nervous system (PNS) evolved before the central nervous system (CNS).
B) is evidence that the neuron was an early evolutionary adaptation.
C) is proof of neurotransmitter efficiency.
D) must have prevented the development of diversity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The sophisticated behavior of mammals and birds is directly related to
A) their relatively large cerebrum.
B) the presence of a hindbrain.
C) their relatively large midbrain.
D) the presence of a forebrain.
A) their relatively large cerebrum.
B) the presence of a hindbrain.
C) their relatively large midbrain.
D) the presence of a forebrain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Natural selection tends to correlate the structures of a nervous system with an animal's function within the environment. A good example is sessile or slow-moving molluscs such as clams, which
A) have little or no cephalization and simple sense organs.
B) use chemical synapses to process complex information.
C) have a well-developed brain that functions as a master control center.
D) use their circulatory system as a mechanism for distributing nerve impulses.
A) have little or no cephalization and simple sense organs.
B) use chemical synapses to process complex information.
C) have a well-developed brain that functions as a master control center.
D) use their circulatory system as a mechanism for distributing nerve impulses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Valium, a prescription drug used to treat anxiety, works by
A) binding and activating acetylcholine receptors.
B) preventing serotonin reuptake into neurons.
C) increasing the release and availability of norepinephrine and dopamine at synapses.
D) activating receptors for GABA.
A) binding and activating acetylcholine receptors.
B) preventing serotonin reuptake into neurons.
C) increasing the release and availability of norepinephrine and dopamine at synapses.
D) activating receptors for GABA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
One of the most important branch points in the evolution of animals and their nervous systems was the appearance of
A) radial symmetry.
B) bilateral symmetry.
C) the spinal column.
D) specialized cells for transmitting signals.
A) radial symmetry.
B) bilateral symmetry.
C) the spinal column.
D) specialized cells for transmitting signals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A physician friend of yours is telling you about a patient with a head injury who suddenly stopped breathing. Your friend explains that the bony rim was pressing against the breathing center. You guess that the "bony rim" (whatever that is) must have been exerting pressure in the region of the
A) basal ganglia and hippocampus.
B) cerebellum and cerebrum.
C) thalamus and hypothalamus.
D) medulla oblongata and pons.
A) basal ganglia and hippocampus.
B) cerebellum and cerebrum.
C) thalamus and hypothalamus.
D) medulla oblongata and pons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
You are practicing throwing baseballs long distances with the members of your baseball team. At the same time that your partner throws the ball to you, another player across from you throws his baseball off-target, and it heads straight toward you. You hold your baseball glove up to catch your partner's ball, and you instinctively throw up your other arm to protect your face from the other incoming ball. The protective action of throwing up your arm is an example of a(n)
A) reflex.
B) synapse.
C) sympathetic response.
D) parasympathetic response.
A) reflex.
B) synapse.
C) sympathetic response.
D) parasympathetic response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which statement regarding brain activity is true?
A) Recent research has revealed that the 1848 accident involving Phineas Gage caused damage to his hindbrain.
B) People usually die following a hemispherectomy.
C) People cannot function when the communication channels between the hemispheres are cut.
D) Electrical stimulation of the cerebral cortex can cause people to experience sensations.
A) Recent research has revealed that the 1848 accident involving Phineas Gage caused damage to his hindbrain.
B) People usually die following a hemispherectomy.
C) People cannot function when the communication channels between the hemispheres are cut.
D) Electrical stimulation of the cerebral cortex can cause people to experience sensations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which statement about ion channels and voltage-gated ion channels is true?
A) Voltage-gated ion channels are always open.
B) Ion channels allow ions to flow against their concentration gradients.
C) Voltage-gated ion channels only open when a stimulus is applied.
D) Ion channels do not contribute to resting membrane potential.
A) Voltage-gated ion channels are always open.
B) Ion channels allow ions to flow against their concentration gradients.
C) Voltage-gated ion channels only open when a stimulus is applied.
D) Ion channels do not contribute to resting membrane potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
During a game, a football player got hit in the head and is now "seeing stars." What region of his brain might have been damaged?
A) occipital lobe
B) parietal lobe
C) frontal lobe
D) temporal lobe
A) occipital lobe
B) parietal lobe
C) frontal lobe
D) temporal lobe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which best describes the protective action of blinking?
A) An interneuron detects motion and sends this message to the peripheral nervous system (PNS), and the PNS sends a message back to blink.
B) A sensory receptor detects motion, a sensory neuron sends this information to the spinal cord, and the information in the central nervous system (CNS) sends a message back to blink.
C) A cell body detects motion, a sensory neuron sends this message to the peripheral nervous system (PNS), and the PNS sends a message back to blink.
D) A cell body detects motion, a sensory neuron sends this message to the spinal cord, and the information in the central nervous system (CNS) sends a message back to blink.
A) An interneuron detects motion and sends this message to the peripheral nervous system (PNS), and the PNS sends a message back to blink.
B) A sensory receptor detects motion, a sensory neuron sends this information to the spinal cord, and the information in the central nervous system (CNS) sends a message back to blink.
C) A cell body detects motion, a sensory neuron sends this message to the peripheral nervous system (PNS), and the PNS sends a message back to blink.
D) A cell body detects motion, a sensory neuron sends this message to the spinal cord, and the information in the central nervous system (CNS) sends a message back to blink.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Low levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine can lessen the ability to focus effectively on tasks. However, high levels of dopamine can result in feelings of motivation. How would you classify dopamine and why?
A) Dopamine is excitatory because it enhances motivation levels.
B) Dopamine is inhibitory because it diminishes the ability to focus.
C) Dopamine is both inhibitory and excitatory because it can enhance motivation levels but diminish the ability to focus.
A) Dopamine is excitatory because it enhances motivation levels.
B) Dopamine is inhibitory because it diminishes the ability to focus.
C) Dopamine is both inhibitory and excitatory because it can enhance motivation levels but diminish the ability to focus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Treatments for depression often include drugs that help correct imbalances in the levels of
A) serotonin.
B) acetylcholine.
C) nitric oxide.
D) epinephrine.
A) serotonin.
B) acetylcholine.
C) nitric oxide.
D) epinephrine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The network of neurons that extends through the core of the brainstem and selects information that reaches the cerebral cortex during sleep is the
A) medulla.
B) limbic system.
C) reticular formation.
D) brainstem core.
A) medulla.
B) limbic system.
C) reticular formation.
D) brainstem core.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
You are sitting with a friend in the park next to some children who are playing Frisbee. You turn to talk to your friend and out of the corner of your eye you see a Frisbee quickly approaching your face. As an innate, protective behavior, you blink your eyes. The protective action of blinking is an example of a(n)
A) reflex.
B) synapse.
C) sympathetic response.
D) parasympathetic response.
A) reflex.
B) synapse.
C) sympathetic response.
D) parasympathetic response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What would happen if a drug that acted to block all potassium channels were introduced to a neuron?
A) The neuron would hyperpolarize.
B) The neuron would depolarize.
C) The neuron would not be able to generate action potentials.
A) The neuron would hyperpolarize.
B) The neuron would depolarize.
C) The neuron would not be able to generate action potentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which statement about Alzheimer's disease is true?
A) Alzheimer's disease is suspected if a patient cannot retain his or her balance.
B) Alzheimer's disease is age-related, increasing in frequency as people age.
C) Alzheimer's disease often reverses or improves with time.
D) Alzheimer's disease frequently involves positive changes in personality.
A) Alzheimer's disease is suspected if a patient cannot retain his or her balance.
B) Alzheimer's disease is age-related, increasing in frequency as people age.
C) Alzheimer's disease often reverses or improves with time.
D) Alzheimer's disease frequently involves positive changes in personality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The human cerebral cortex accounts for what percentage of the total mass of the brain?
A) 20%
B) 40%
C) 60%
D) 80%
A) 20%
B) 40%
C) 60%
D) 80%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Excitatory neurotransmitters are most like what part of an automobile?
A) brakes
B) windshield wiper
C) accelerator
D) horn
A) brakes
B) windshield wiper
C) accelerator
D) horn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Inhibitory neurotransmitters are most like what part of an automobile?
A) brakes
B) radio
C) muffler
D) engine
A) brakes
B) radio
C) muffler
D) engine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Schizophrenia
A) can best be described as feeling a sense of worthlessness.
B) is often associated with hallucinations and paranoid delusions.
C) causes changes in body weight and sleeping patterns.
D) is best defined as a type of mental deterioration or dementia.
A) can best be described as feeling a sense of worthlessness.
B) is often associated with hallucinations and paranoid delusions.
C) causes changes in body weight and sleeping patterns.
D) is best defined as a type of mental deterioration or dementia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
During REM sleep, an EEG shows
A) a flat trace with very few waves.
B) a pattern that is similar to when a person is in deep sleep.
C) an irregular, rapidly changing pattern.
A) a flat trace with very few waves.
B) a pattern that is similar to when a person is in deep sleep.
C) an irregular, rapidly changing pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What part of the brain allows us to recognize the emotional content of facial expressions and also helps lay down emotional memories?
A) hippocampus
B) amygdala
C) prefrontal cortex
D) corpus callosum
A) hippocampus
B) amygdala
C) prefrontal cortex
D) corpus callosum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Parkinson's disease
A) can be cured with injections of serotonin.
B) results from the death of neurons in the cerebellum.
C) is a motor disorder, affecting physical movements of the body.
D) is age-related, decreasing in frequency as people age.
A) can be cured with injections of serotonin.
B) results from the death of neurons in the cerebellum.
C) is a motor disorder, affecting physical movements of the body.
D) is age-related, decreasing in frequency as people age.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Our emotions, learning, and memory depend upon the
A) limbic system.
B) parietal lobes.
C) frontal lobes.
D) occipital lobes.
A) limbic system.
B) parietal lobes.
C) frontal lobes.
D) occipital lobes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When the human brain's normal electrical activity is suddenly altered, a seizure can result. Seizures cause several behavioral and physical complications such as sudden mood changes, muscle spasms, or uncontrollable body shaking. Seizure impulses often start in one hemisphere of the brain and travel to the other. Which of the following surgical treatments would reduce the severity of seizures?
A) surgically altering the hypothalamus so that the patient's biological clock has altered circadian rhythms
B) severing the corpus callosum so that the brain has diminished ability to send messages between the two cerebral hemispheres
C) severing the parietal lobe so that speech capabilities are diminished
D) stimulating the cerebrum to allow the retention of short-term memory capabilities
A) surgically altering the hypothalamus so that the patient's biological clock has altered circadian rhythms
B) severing the corpus callosum so that the brain has diminished ability to send messages between the two cerebral hemispheres
C) severing the parietal lobe so that speech capabilities are diminished
D) stimulating the cerebrum to allow the retention of short-term memory capabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which part of this diagram of the human brain depicts the cerebellum? 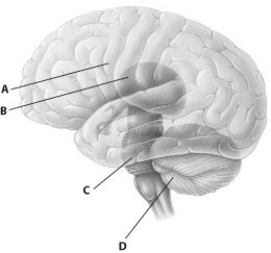
A) part A
B) part B
C) part C
D) part D

A) part A
B) part B
C) part C
D) part D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Why is there a bias towards positive results in scientific publications?
A) because only studies that yield positive results are accepted by scientific journals
B) because studies that yield positive results are better designed than those that yield negative results
C) because studies always yield positive results
D) because studies that yield positive results are more likely to be submitted for publication than studies that yield negative results
A) because only studies that yield positive results are accepted by scientific journals
B) because studies that yield positive results are better designed than those that yield negative results
C) because studies always yield positive results
D) because studies that yield positive results are more likely to be submitted for publication than studies that yield negative results

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the figure below to answer the questions that follow.
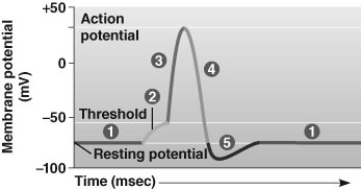
In what stage(s) is(are) voltage-gated potassium channels opening?
A) stage 3 only
B) stage 4 only
C) stages 3 and 4
D) stages 4 and 5
E) stages 3, 4, and 5

In what stage(s) is(are) voltage-gated potassium channels opening?
A) stage 3 only
B) stage 4 only
C) stages 3 and 4
D) stages 4 and 5
E) stages 3, 4, and 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
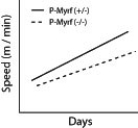
Oligodendrocytes are cells in the brain that produce myelin in the central nervous system. Myelin regulatory factor (MyRF) is a transcription factor that is required by oligodendrocytes in order to produce myelin. Researchers investigated the importance of MyRF by having mice learn how to run on complex wheels (there were many gaps in the wheel thus making it difficult to run on-see graph below).
Researchers created a genetic strain of mice that were lacking both genes for MyRF. What is the most likely effect that this would have on the mice?
A) decreased rate of signal propagation via axons
B) increased flow of ions through voltage-gated sodium channels
C) decreased flow of ions through voltage-gated potassium channels
D) increased number of dendrites on neuron cell bodies
Oligodendrocytes are cells in the brain that produce myelin in the central nervous system. Myelin regulatory factor (MyRF) is a transcription factor that is required by oligodendrocytes in order to produce myelin. Researchers investigated the importance of MyRF by having mice learn how to run on complex wheels (there were many gaps in the wheel thus making it difficult to run on-see graph below).

Researchers created a genetic strain of mice that were lacking both genes for MyRF. What is the most likely effect that this would have on the mice?
A) decreased rate of signal propagation via axons
B) increased flow of ions through voltage-gated sodium channels
C) decreased flow of ions through voltage-gated potassium channels
D) increased number of dendrites on neuron cell bodies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which statement about this figure is true? 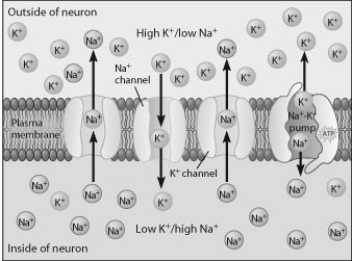
A) The outside of the cell is negatively charged.
B) Sodium ions are moving against their concentration gradient.
C) There are fewer positive charges on the inside of the neuron, so it is more negative.
D) The concentration of potassium ions is higher inside the cell.

A) The outside of the cell is negatively charged.
B) Sodium ions are moving against their concentration gradient.
C) There are fewer positive charges on the inside of the neuron, so it is more negative.
D) The concentration of potassium ions is higher inside the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Oligodendrocytes are cells in the brain that produce myelin in the central nervous system. Myelin regulatory factor (MyRF) is a transcription factor that is required by oligodendrocytes in order to produce myelin. Researchers investigated the importance of MyRF by having mice learn how to run on complex wheels (there were many gaps in the wheel thus making it difficult to run on-see graph below).

When mice are learning to run on these complex wheels, what part of the brain are they primarily using?
A) cerebellum
B) cerebrum
C) diencephalon
D) brainstem
Oligodendrocytes are cells in the brain that produce myelin in the central nervous system. Myelin regulatory factor (MyRF) is a transcription factor that is required by oligodendrocytes in order to produce myelin. Researchers investigated the importance of MyRF by having mice learn how to run on complex wheels (there were many gaps in the wheel thus making it difficult to run on-see graph below).

When mice are learning to run on these complex wheels, what part of the brain are they primarily using?
A) cerebellum
B) cerebrum
C) diencephalon
D) brainstem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
During practice, a soccer player got hit in the head. After a few minutes, she was able to get up and went to the sidelines to get a bottle of water. As she was walking she felt extremely dizzy and fell over. What part of her brain may have been damaged?
A) cerebrum
B) cerebellum
C) midbrain
D) hypothalamus
A) cerebrum
B) cerebellum
C) midbrain
D) hypothalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Curare is a potent neurotoxin extracted from the Strychnos toxifera plant in Central and South America. Indigenous peoples of South America applied curare to arrows, which they used to hunt and kill animals. Curare acts at synapses between motor neurons and skeletal muscle cells. When a motor neuron synapses with a skeletal muscle cell, the skeletal muscle cell may be stimulated or inhibited just like postsynaptic neurons are. Curare acts by binding temporarily to acetylcholine receptors on the postsynaptic cell and prevents acetylcholine from binding.
Which could be an effective treatment for curare poisoning?
A) a drug that promotes acetylcholine reuptake into the presynaptic cells
B) a drug that removes acetylcholine receptors from the postsynaptic cell
C) a drug that inhibits acetylcholinesterase (an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine)
Curare is a potent neurotoxin extracted from the Strychnos toxifera plant in Central and South America. Indigenous peoples of South America applied curare to arrows, which they used to hunt and kill animals. Curare acts at synapses between motor neurons and skeletal muscle cells. When a motor neuron synapses with a skeletal muscle cell, the skeletal muscle cell may be stimulated or inhibited just like postsynaptic neurons are. Curare acts by binding temporarily to acetylcholine receptors on the postsynaptic cell and prevents acetylcholine from binding.
Which could be an effective treatment for curare poisoning?
A) a drug that promotes acetylcholine reuptake into the presynaptic cells
B) a drug that removes acetylcholine receptors from the postsynaptic cell
C) a drug that inhibits acetylcholinesterase (an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Oligodendrocytes are cells in the brain that produce myelin in the central nervous system. Myelin regulatory factor (MyRF) is a transcription factor that is required by oligodendrocytes in order to produce myelin. Researchers investigated the importance of MyRF by having mice learn how to run on complex wheels (there were many gaps in the wheel thus making it difficult to run on-see graph below).

Mice that lacked the MyRF genes (P-MyRF (−/−)) and mice that had functional MyRF genes (P-MyRF (+/−)) ran on the complex wheel and their speed was recorded (see accompanying figure). What group of mice learned how to run on the complex wheel more easily?
A) mice with nonmyelinated axons
B) mice with myelinated axons
Oligodendrocytes are cells in the brain that produce myelin in the central nervous system. Myelin regulatory factor (MyRF) is a transcription factor that is required by oligodendrocytes in order to produce myelin. Researchers investigated the importance of MyRF by having mice learn how to run on complex wheels (there were many gaps in the wheel thus making it difficult to run on-see graph below).

Mice that lacked the MyRF genes (P-MyRF (−/−)) and mice that had functional MyRF genes (P-MyRF (+/−)) ran on the complex wheel and their speed was recorded (see accompanying figure). What group of mice learned how to run on the complex wheel more easily?
A) mice with nonmyelinated axons
B) mice with myelinated axons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
You recently sprayed your apartment with insecticide to remove an infestation of cockroaches. In your kitchen, you noticed some roaches lying on their backs twitching after being exposed to the insecticide. This aroused your curiosity, so you decided to investigate exactly how the insecticide works on the nervous system.
In your research, you discover that the insecticide you used contains a permanent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle to contract (including insect muscles). Acetylcholinesterase removes acetylcholine from the synapse after the signal is received. Exposure to high pesticide concentrations has a similar effect on humans, which can also be caused by exposure to the nerve gas Sarin and other chemical agents.
Why did the insecticide cause uncontrollable twitching in the roaches?
A) Acetylcholine was released, but the insecticide prevented it from diffusing across the synapse.
B) Acetylcholine was released, but the insecticide prevented it from binding to the receptor sites of the postsynaptic neurons.
C) The insecticide caused continuous stimulation of the muscles.
D) The insecticide prevented acetylcholinesterase from being removed from the synapse.
You recently sprayed your apartment with insecticide to remove an infestation of cockroaches. In your kitchen, you noticed some roaches lying on their backs twitching after being exposed to the insecticide. This aroused your curiosity, so you decided to investigate exactly how the insecticide works on the nervous system.
In your research, you discover that the insecticide you used contains a permanent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle to contract (including insect muscles). Acetylcholinesterase removes acetylcholine from the synapse after the signal is received. Exposure to high pesticide concentrations has a similar effect on humans, which can also be caused by exposure to the nerve gas Sarin and other chemical agents.
Why did the insecticide cause uncontrollable twitching in the roaches?
A) Acetylcholine was released, but the insecticide prevented it from diffusing across the synapse.
B) Acetylcholine was released, but the insecticide prevented it from binding to the receptor sites of the postsynaptic neurons.
C) The insecticide caused continuous stimulation of the muscles.
D) The insecticide prevented acetylcholinesterase from being removed from the synapse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
You recently sprayed your apartment with insecticide to remove an infestation of cockroaches. In your kitchen, you noticed some roaches lying on their backs twitching after being exposed to the insecticide. This aroused your curiosity, so you decided to investigate exactly how the insecticide works on the nervous system.
In your research, you discover that the insecticide you used contains a permanent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle to contract (including insect muscles). Acetylcholinesterase removes acetylcholine from the synapse after the signal is received. Exposure to high pesticide concentrations has a similar effect on humans, which can also be caused by exposure to the nerve gas Sarin and other chemical agents.
Since pesticides affect humans in a manner similar to that of roaches, it would be valid to conclude that
A) acetylcholinesterase affects the DNA of all animals.
B) the mechanism of stimulating skeletal muscle contraction must be similar in humans and roaches.
C) pesticides are more harmful to roaches than humans.
D) the terminal end of the axon releases acetylcholine in roaches, but not in humans.
You recently sprayed your apartment with insecticide to remove an infestation of cockroaches. In your kitchen, you noticed some roaches lying on their backs twitching after being exposed to the insecticide. This aroused your curiosity, so you decided to investigate exactly how the insecticide works on the nervous system.
In your research, you discover that the insecticide you used contains a permanent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle to contract (including insect muscles). Acetylcholinesterase removes acetylcholine from the synapse after the signal is received. Exposure to high pesticide concentrations has a similar effect on humans, which can also be caused by exposure to the nerve gas Sarin and other chemical agents.
Since pesticides affect humans in a manner similar to that of roaches, it would be valid to conclude that
A) acetylcholinesterase affects the DNA of all animals.
B) the mechanism of stimulating skeletal muscle contraction must be similar in humans and roaches.
C) pesticides are more harmful to roaches than humans.
D) the terminal end of the axon releases acetylcholine in roaches, but not in humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the figure below to answer the questions that follow.

In what stage(s) is(are) voltage-gated sodium channels opening?
A) stage 2 only
B) stage 3 only
C) stages 2 and 3
D) stages 3 and 4
E) stages 2, 3, and 4

In what stage(s) is(are) voltage-gated sodium channels opening?
A) stage 2 only
B) stage 3 only
C) stages 2 and 3
D) stages 3 and 4
E) stages 2, 3, and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What does the concept of neuronal plasticity imply?
A) that the nervous system is composed of a fixed and static group of structures
B) that the nervous system can be reorganized or remodeled
C) that the nervous system loses functionality as animals age
D) that the nervous system of humans is more advanced than those of other animals
A) that the nervous system is composed of a fixed and static group of structures
B) that the nervous system can be reorganized or remodeled
C) that the nervous system loses functionality as animals age
D) that the nervous system of humans is more advanced than those of other animals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Curare is a potent neurotoxin extracted from the Strychnos toxifera plant in Central and South America. Indigenous peoples of South America applied curare to arrows, which they used to hunt and kill animals. Curare acts at synapses between motor neurons and skeletal muscle cells. When a motor neuron synapses with a skeletal muscle cell, the skeletal muscle cell may be stimulated or inhibited just like postsynaptic neurons are. Curare acts by binding temporarily to acetylcholine receptors on the postsynaptic cell and prevents acetylcholine from binding.
What effect does curare likely have on the postsynaptic cell?
A) prevents voltage-gated channels from opening
B) hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic cell
C) stimulates muscle contraction
Curare is a potent neurotoxin extracted from the Strychnos toxifera plant in Central and South America. Indigenous peoples of South America applied curare to arrows, which they used to hunt and kill animals. Curare acts at synapses between motor neurons and skeletal muscle cells. When a motor neuron synapses with a skeletal muscle cell, the skeletal muscle cell may be stimulated or inhibited just like postsynaptic neurons are. Curare acts by binding temporarily to acetylcholine receptors on the postsynaptic cell and prevents acetylcholine from binding.
What effect does curare likely have on the postsynaptic cell?
A) prevents voltage-gated channels from opening
B) hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic cell
C) stimulates muscle contraction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which part of this diagram of a neuron depicts the axon? 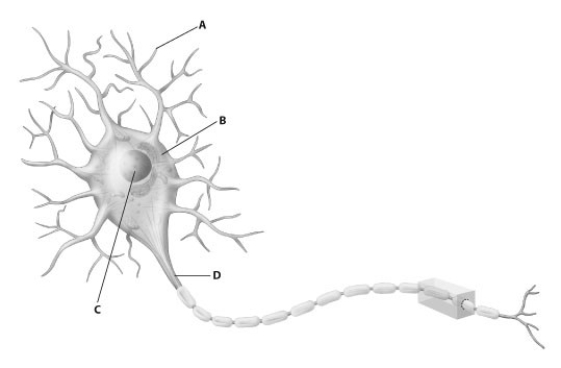
A) part A
B) part B
C) part C
D) part D

A) part A
B) part B
C) part C
D) part D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



