Deck 22: Transition Metals: Biological and Medical Applications
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/142
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Transition Metals: Biological and Medical Applications
1
What do you predict for the geometry of Ti(H2O)63+?
A)octahedral
B)tetrahedral
C)square planar
D)trigonal bipyramidal
E)square pyramidal
A)octahedral
B)tetrahedral
C)square planar
D)trigonal bipyramidal
E)square pyramidal
octahedral
2
For the coordination compound K3[Fe(CN)6], identify, in order, the charge on the complex ion, the oxidation state of the metal, and the coordination number of the metal.
A)3+, 3-, 6+
B)0, 0, 6+
C)3-, 3+, 3+
D)3-, 3+, 6+
E)None of these choices is correct.
A)3+, 3-, 6+
B)0, 0, 6+
C)3-, 3+, 3+
D)3-, 3+, 6+
E)None of these choices is correct.
3-, 3+, 6+
3
What is the shape of the complex ion CoF63-?
A)square pyramidal
B)octahedral
C)tetrahedral
D)trigonal bipyramidal
E)square planar
A)square pyramidal
B)octahedral
C)tetrahedral
D)trigonal bipyramidal
E)square planar
octahedral
4
The coordination number around the Ni ion in [Co(NH3)6][Ni(CN)5] is ________
A)2.
B)1
C)6.
D)5.
E)7.
A)2.
B)1
C)6.
D)5.
E)7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
For the coordination compound [Co(NH3)4Cl2]NO3, identify, in order, the charge on the complex ion, the oxidation state of the metal, and the coordination number of the metal.
A)1+, 1+, 6
B)0, 0, 4
C)3+, 3+, 4
D)1+, 3+, 6
E)None of these choices is correct.
A)1+, 1+, 6
B)0, 0, 4
C)3+, 3+, 4
D)1+, 3+, 6
E)None of these choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What do you predict for the geometry of [Fe(CO)4(CN)]-?
A)octahedral
B)tetrahedral
C)square planar
D)trigonal bipyramidal
E)square pyramidal
A)octahedral
B)tetrahedral
C)square planar
D)trigonal bipyramidal
E)square pyramidal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The coordination number around the Co ion in [Co(NH3)6][CrF6] is ________
A)3.
B)4.
C)6.
D)2.
E)5.
A)3.
B)4.
C)6.
D)2.
E)5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How many ions are formed when [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 dissolves in water?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the oxidation state of the nickel atom in the Ni(CN)53-complex ion?
A)(+0)
B)(+1)
C)(+2)
D)(+3)
E)(+4)
A)(+0)
B)(+1)
C)(+2)
D)(+3)
E)(+4)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
For the coordination compound [Cr(NH3)3(H2O)3]Cl3, identify, in order, the charge on the complex ion, the oxidation state of the metal, and the coordination number of the metal.
A)3+, 1+, 6
B)0, 0, 6
C)3+, 3+, 4
D)1+, 3+, 6
E)3+, 3+, 6
A)3+, 1+, 6
B)0, 0, 6
C)3+, 3+, 4
D)1+, 3+, 6
E)3+, 3+, 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The coordination number for nickel in the compound Na3[Ni(CN)5] is ________
A)2.
B)3.
C)6.
D)4.
E)5.
A)2.
B)3.
C)6.
D)4.
E)5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the oxidation state of the gold atom in the AuCl4-complex ion?
A)(+0)
B)(+1)
C)(+2)
D)(+3)
E)(+4)
A)(+0)
B)(+1)
C)(+2)
D)(+3)
E)(+4)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In Na2[Zn(CN)4], the counter ion is ________, and in [Co(NH3)4Cl2]NO3, the counter ion is ________.
A)CN-; NO3-
B)Na+; NO3-
C)CN-; Cl-
D)Na+; Cl-
E)Zn2+; Co3+
A)CN-; NO3-
B)Na+; NO3-
C)CN-; Cl-
D)Na+; Cl-
E)Zn2+; Co3+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which orbital hybridization in a metal atom would be appropriate for octahedral complexes?
A)sp
B)sp2
C)sp2d
D)sp3d
E)sp3d 2
A)sp
B)sp2
C)sp2d
D)sp3d
E)sp3d 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the shape of Zn(OH)42-?
A)triangular pyramid
B)tetrahedral
C)octahedral
D)square pyramid
E)T-shaped
A)triangular pyramid
B)tetrahedral
C)octahedral
D)square pyramid
E)T-shaped

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many ions are formed when Na[Co(CO)4] dissolves in water?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5
E)6
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5
E)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The coordination number for copper in the compound K2[CuCl4] is ________
A)2.
B)1.
C)6.
D)5.
E)7.
A)2.
B)1.
C)6.
D)5.
E)7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In K4[Fe(CN)6], the counter ion is ________, and in [Co(NH3)4Cl2]NO3, the counter ion is ________.
A)CN-; NO3-
B)K+; NO3-
C)CN-; Cl-
D)K+; Cl-
E)Fe2+; Co3+
A)CN-; NO3-
B)K+; NO3-
C)CN-; Cl-
D)K+; Cl-
E)Fe2+; Co3+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The coordination number for [Pt(NH3)4]Cl2 is ________
A)2.
B)3.
C)6.
D)4.
E)5.
A)2.
B)3.
C)6.
D)4.
E)5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which ligand below is not correctly named?
A)H2O, hydro
B)NH3, ammine
C)CN-, cyano
D)CO, carbonyl
E)OH-, hydroxo
A)H2O, hydro
B)NH3, ammine
C)CN-, cyano
D)CO, carbonyl
E)OH-, hydroxo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the chemical formula of amminetrichloroplatinate(II)?
A)[Pt2(NH3)Cl3]-
B)[Pt(NH3)3Cl]-
C)[Pt(NH3)Cl3]2-
D)[Pt(NH3)Cl3]+
E)[Pt(NH3)Cl3]-
A)[Pt2(NH3)Cl3]-
B)[Pt(NH3)3Cl]-
C)[Pt(NH3)Cl3]2-
D)[Pt(NH3)Cl3]+
E)[Pt(NH3)Cl3]-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which is the correct formula for potassium hexacyanoferrate(II)?
A)K[Fe(CN)2]
B)K2[Fe(CN)2]
C)K3[Fe(CN)6]
D)K4[Fe(CN)6]
E)K6[Fe(CN)6]
A)K[Fe(CN)2]
B)K2[Fe(CN)2]
C)K3[Fe(CN)6]
D)K4[Fe(CN)6]
E)K6[Fe(CN)6]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The correct formula for ammonium tetracyanoplatinate(II) is ________
A)(NH3)2[Pt(CN)4].
B)(NH4)2[Pt(CN)4].
C)(NH4)2Pt(CN)4.
D)(NH4)2[Pt(CN)6].
E)NH4[Pt(CN)4].
A)(NH3)2[Pt(CN)4].
B)(NH4)2[Pt(CN)4].
C)(NH4)2Pt(CN)4.
D)(NH4)2[Pt(CN)6].
E)NH4[Pt(CN)4].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the correct formula for hexamminecobalt(III) nitrite?
A)[Co(NH3)6]( NO3)3
B)Co(NH3)6( NO2)3
C)[Co(NH3)6]( NO2)3
D)[Co(NH3)6]( NO2)2
E)[Co(NH3)6]( NO3)2
A)[Co(NH3)6]( NO3)3
B)Co(NH3)6( NO2)3
C)[Co(NH3)6]( NO2)3
D)[Co(NH3)6]( NO2)2
E)[Co(NH3)6]( NO3)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
EDTA is an example of a ________ ligand.
A)tridentate
B)hexadentate
C)tetradentate
D)pentadentate
E)hydrocarbon
A)tridentate
B)hexadentate
C)tetradentate
D)pentadentate
E)hydrocarbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The correct formula for the complex ion tetrabromocuprate(II) is ________
A)[CuBr4]2-.
B)[CuBr4]2+.
C)CuBr4.
D)[CoBr4]2+.
E)[CoBr4]2-.
A)[CuBr4]2-.
B)[CuBr4]2+.
C)CuBr4.
D)[CoBr4]2+.
E)[CoBr4]2-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which one of the following compounds is called potassium monochloropentacyanoferrate(III)?
A)K3[FeCl(CN)5]
B)K[FeCl(CN)3]
C)K4[FeCl(CN)6]
D)K4[FeCl(CN)5]
E)K3[Fe3Cl(CN)5]
A)K3[FeCl(CN)5]
B)K[FeCl(CN)3]
C)K4[FeCl(CN)6]
D)K4[FeCl(CN)5]
E)K3[Fe3Cl(CN)5]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Terpyridine, which is shown below, is an example of a ________ ligand. 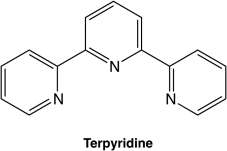
A)monodentate
B)bidentate
C)tridentate
D)hydrocarbon
E)poor

A)monodentate
B)bidentate
C)tridentate
D)hydrocarbon
E)poor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The correct name for [Fe(NH3)4(H2O)2][NiCl4] is ________
A)tetraamminodiaquoiron(II) tetrachloronickel(II).
B)tetraamminodiaquoiron(II) tetrachloronickelate(II).
C)tetraamminodiaquoiron(III) tetrachloronickelate(IV).
D)tetraamminodiaquoiron(III) tetrachloronickelate(II).
E)tetraammoniadiwateriron(II) tetrachloronickelate(II).
A)tetraamminodiaquoiron(II) tetrachloronickel(II).
B)tetraamminodiaquoiron(II) tetrachloronickelate(II).
C)tetraamminodiaquoiron(III) tetrachloronickelate(IV).
D)tetraamminodiaquoiron(III) tetrachloronickelate(II).
E)tetraammoniadiwateriron(II) tetrachloronickelate(II).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the correct formula for sodium tetracyanodihydroxovanadate(II)?
A)Na2[V(CN)4(OH)2]
B)Na3[V(CN)4(OH)2]
C)Na4[V(CN)4(OH)2]
D)Na[V(CN)4(OH)2]
E)Na3[V(CN)4(OH)]
A)Na2[V(CN)4(OH)2]
B)Na3[V(CN)4(OH)2]
C)Na4[V(CN)4(OH)2]
D)Na[V(CN)4(OH)2]
E)Na3[V(CN)4(OH)]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The correct name for K2[CuCl4] is ________
A)potassium copper chloride.
B)potassium tetrachlorocuprate(II).
C)dipotassium chlorocuprate(II).
D)potassium tetrachlorocopper(II).
E)dipotassium tetrachlorocopper(II).
A)potassium copper chloride.
B)potassium tetrachlorocuprate(II).
C)dipotassium chlorocuprate(II).
D)potassium tetrachlorocopper(II).
E)dipotassium tetrachlorocopper(II).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Dimethylphophsinoethane (DMPE), which is shown below, is an example of a ________ ligand. 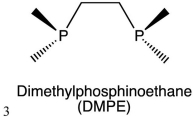
A)undentate
B)monodentate
C)bidentate
D)tridentate
E)pincer

A)undentate
B)monodentate
C)bidentate
D)tridentate
E)pincer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is a polydentate ligand?
A)NH3
B)OH-
C)H2O
D)diethylenetriamine
E)CN-
A)NH3
B)OH-
C)H2O
D)diethylenetriamine
E)CN-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The correct name for the complex ion [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]+ is ________
A)tetraaquadichlorochromium(II).
B)tetraaquadichlorochromium(III).
C)dichlorotetraaquochromium(II).
D)tetraaquadichlorochromate(III).
E)tetraaquadichlorochromium.
A)tetraaquadichlorochromium(II).
B)tetraaquadichlorochromium(III).
C)dichlorotetraaquochromium(II).
D)tetraaquadichlorochromate(III).
E)tetraaquadichlorochromium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The correct name for [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 is ________
A)pentaamminechlorocobalt(III) chloride.
B)pentaamminechlorocobalt(II) chloride.
C)chloropentaamminecobalt(III) chloride.
D)pentaamminechlorocobaltate(III) chloride.
E)pentaamminedichlorocobalt(III).
A)pentaamminechlorocobalt(III) chloride.
B)pentaamminechlorocobalt(II) chloride.
C)chloropentaamminecobalt(III) chloride.
D)pentaamminechlorocobaltate(III) chloride.
E)pentaamminedichlorocobalt(III).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Ethylenediamine is an example of a ________ ligand.
A)tridentate
B)hexadentate
C)bidentate
D)pentadentate
E)hydrocarbon
A)tridentate
B)hexadentate
C)bidentate
D)pentadentate
E)hydrocarbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The correct name for the complex ion [Mo(CN)6]4- is ________
A)hexacyanomolybdenum(II).
B)hexacyanomolybdenite(III).
C)hexacyanomolybdenate(II).
D)molybdenum(0) hexacyanide.
E)molybdenum(VIII) cyanide.
A)hexacyanomolybdenum(II).
B)hexacyanomolybdenite(III).
C)hexacyanomolybdenate(II).
D)molybdenum(0) hexacyanide.
E)molybdenum(VIII) cyanide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The correct name for the compound [Fe(NH3)5H2O](NO3)2 is ________
A)pentaammineaquairon(II) nitrate.
B)pentaammineaquairon(III) nitrate.
C)pentaammineaquaferrate(II) nitrate.
D)aquapentaammineiron(II) nitrate.
E)pentaammineaquadinitroiron(III).
A)pentaammineaquairon(II) nitrate.
B)pentaammineaquairon(III) nitrate.
C)pentaammineaquaferrate(II) nitrate.
D)aquapentaammineiron(II) nitrate.
E)pentaammineaquadinitroiron(III).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The correct name for [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6] is ________
A)cobaltammine chromiumcyanide.
B)hexamminecobalt(III) hexacyanochromate (II).
C)hexamminecobaltate(III) hexacyanochromium(III).
D)hexamminecobalt(III) hexacyanochromate(III).
E)hexamminecobalt(II) hexacyanochromate(II).
A)cobaltammine chromiumcyanide.
B)hexamminecobalt(III) hexacyanochromate (II).
C)hexamminecobaltate(III) hexacyanochromium(III).
D)hexamminecobalt(III) hexacyanochromate(III).
E)hexamminecobalt(II) hexacyanochromate(II).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How many chelation sites and donor groups does EDTA have?
A)2
B)10
C)6
D)4
E)5
A)2
B)10
C)6
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is a chelation agent?
A)EDTA
B)Cl-
C)NH2
D)SCN-
E)CN-
A)EDTA
B)Cl-
C)NH2
D)SCN-
E)CN-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
CoF63- absorbs light in the red region of the spectrum, while Co(NH3)63+ absorbs light in the blue region of the spectrum. This difference means that ________
A)the splitting of the d orbitals of the two complexes is nearly identical.
B)the value of the crystal field splitting is very small for both complexes.
C)the crystal field splitting is larger for the ammonia complex than for the fluoride complex.
D)the dz2 and dx2 -y2 orbitals are higher in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals in CoF63- and just the opposite splitting order for Co(NH3)63+.
E)the dz2 and dx2 - y2 orbitals are lower in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals in CoF63- and just the opposite splitting order for Co(NH3)63+.
A)the splitting of the d orbitals of the two complexes is nearly identical.
B)the value of the crystal field splitting is very small for both complexes.
C)the crystal field splitting is larger for the ammonia complex than for the fluoride complex.
D)the dz2 and dx2 -y2 orbitals are higher in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals in CoF63- and just the opposite splitting order for Co(NH3)63+.
E)the dz2 and dx2 - y2 orbitals are lower in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals in CoF63- and just the opposite splitting order for Co(NH3)63+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The greater affinity of metal ions for polydentate ligands than for monodentate ligands is known as the ________ effect.
A)dentate
B)ligand
C)chelate
D)Lewis base
E)Lewis acid
A)dentate
B)ligand
C)chelate
D)Lewis base
E)Lewis acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Transition metal ions often absorb visible light in promoting electrons from a ground state to an excited state. Why doesn't aluminum(III) ion have this property?
A)It does, and this fact accounts for the color of some gemstones.
B)Aluminum(III) has a noble gas configuration—that of argon.
C)Aluminum(III) has a noble gas configuration—that of neon.
D)Aluminum(III) has a filled d subshell.
E)The crystal field splitting of the d orbitals in aluminum(III) is very large.
A)It does, and this fact accounts for the color of some gemstones.
B)Aluminum(III) has a noble gas configuration—that of argon.
C)Aluminum(III) has a noble gas configuration—that of neon.
D)Aluminum(III) has a filled d subshell.
E)The crystal field splitting of the d orbitals in aluminum(III) is very large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
CoCl42-(aq) absorbs light in the orange region of the spectrum. The color of a solution containing this ion is ________
A)blue.
B)blue-violet.
C)violet.
D)yellow-orange.
E)red.
A)blue.
B)blue-violet.
C)violet.
D)yellow-orange.
E)red.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The dz2 and dx2 - y2 orbitals are higher in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals in an octahedral complex because these two orbitals ________
A)do not point directly at ligands.
B)point directly at ligands.
C)occupy larger volumes than the other three orbitals.
D)are in the same plane and repel one another.
E)occupy smaller volumes than the other three orbitals.
A)do not point directly at ligands.
B)point directly at ligands.
C)occupy larger volumes than the other three orbitals.
D)are in the same plane and repel one another.
E)occupy smaller volumes than the other three orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Co(NH3)63+(aq) absorbs light in the blue region of the spectrum. The color of a solution containing this ion is ________
A)blue.
B)blue-violet.
C)violet.
D)yellow-orange.
E)red.
A)blue.
B)blue-violet.
C)violet.
D)yellow-orange.
E)red.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A solution containing the ion CoF63- has an absorption maximum at max = 680 nm. The color of this solution is ________
A)red.
B)green.
C)blue.
D)orange.
E)violet.
A)red.
B)green.
C)blue.
D)orange.
E)violet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals are lower in energy than the dz2 and dx2 - y2 orbitals in an octahedral complex because these three orbitals ________
A)do not point directly at ligands.
B)point directly at ligands.
C)occupy larger volumes than the other two orbitals.
D)are in the same plane and repel one another.
E)occupy smaller volumes than the other two orbitals.
A)do not point directly at ligands.
B)point directly at ligands.
C)occupy larger volumes than the other two orbitals.
D)are in the same plane and repel one another.
E)occupy smaller volumes than the other two orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A solution containing an octahedral metal ion has an absorption maximum at max = 535 nm. The color of this solution is ________
A)red.
B)green.
C)blue.
D)orange.
E)violet.
A)red.
B)green.
C)blue.
D)orange.
E)violet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Oxalic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with the structure HOOCCOOH. How many coordination sites does the ion (OOCCOO)2- have?
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)1
E)5
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)1
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which 3d orbitals have a higher energy in an octahedral field?
A)dxy and dxz
B)dz2 and dyz
C)dz2 and dx2 - y2
D)dx2 - y2 and dxz
E)dxy, dxz, and dyz
A)dxy and dxz
B)dz2 and dyz
C)dz2 and dx2 - y2
D)dx2 - y2 and dxz
E)dxy, dxz, and dyz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which atoms on EDTA bond to metal ions?
A)carbon and oxygen
B)carbon and nitrogen
C)oxygen and nitrogen
D)nitrogen and hydrogen
E)oxygen and hydrogen
A)carbon and oxygen
B)carbon and nitrogen
C)oxygen and nitrogen
D)nitrogen and hydrogen
E)oxygen and hydrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When the five 3d orbitals on a metal ion experience an octahedral field in a complex, they split into ________ energy levels.
A)two
B)three
C)four
D)five
E)six
A)two
B)three
C)four
D)five
E)six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When the five 3d orbitals on a metal ion experience a square planar field in a complex, they split into ________ energy levels.
A)two
B)three
C)four
D)five
E)six
A)two
B)three
C)four
D)five
E)six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
As the value of the crystal field splitting, o, increases from one complex ion to another, ________
A)the wavelength of absorbed light increases.
B)the wavelength of absorbed light decreases.
C)the number of d electrons increases.
D)the number of d electrons decreases.
E)the color of the solution shifts from red toward blue.
A)the wavelength of absorbed light increases.
B)the wavelength of absorbed light decreases.
C)the number of d electrons increases.
D)the number of d electrons decreases.
E)the color of the solution shifts from red toward blue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Crystal field theory describes ________
A)how ligands cause the metal d orbitals to have different energies.
B)the covalent bonding in transition metal complexes.
C)how d orbitals change their shapes when ligands are present.
D)how metal s, p, and d orbitals are hybridized to bond with ligands.
E)the molecular orbitals that describe the bonding in transition metal complexes.
A)how ligands cause the metal d orbitals to have different energies.
B)the covalent bonding in transition metal complexes.
C)how d orbitals change their shapes when ligands are present.
D)how metal s, p, and d orbitals are hybridized to bond with ligands.
E)the molecular orbitals that describe the bonding in transition metal complexes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which statement describing the splitting of metal d orbitals in an octahedral complex ion is not correct?
A)The d orbitals are split into two energy levels.
B)One energy level is threefold degenerate.
C)One energy level is twofold degenerate.
D)The dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals have the lowest energy.
E)The dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals point directly at the ligands.
A)The d orbitals are split into two energy levels.
B)One energy level is threefold degenerate.
C)One energy level is twofold degenerate.
D)The dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals have the lowest energy.
E)The dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals point directly at the ligands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which statement concerning ligands in transition metal complexes is not correct?
A)The addition of ammonia to a chloro complex should generate the corresponding ammine complex because ammonia is a stronger Lewis base than chloride.
B)Ammonia is a stronger ligand than water because ammonia is a stronger Lewis base than water.
C)All ligands are Lewis bases.
D)Cyanide is a stronger ligand than water because cyanide is a stronger Lewis base than water.
E)Cyanide is a stronger ligand than fluoride because it is composed of two atoms.
A)The addition of ammonia to a chloro complex should generate the corresponding ammine complex because ammonia is a stronger Lewis base than chloride.
B)Ammonia is a stronger ligand than water because ammonia is a stronger Lewis base than water.
C)All ligands are Lewis bases.
D)Cyanide is a stronger ligand than water because cyanide is a stronger Lewis base than water.
E)Cyanide is a stronger ligand than fluoride because it is composed of two atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Complex ions with different ligands have different colors because the ligands ________
A)are different colors.
B)affect the energy levels of the lone-pair electrons on the metal.
C)have different energies for their bonding electrons.
D)affect the energy levels of the metal d orbitals.
E)have different energies for their lone-pair electrons.
A)are different colors.
B)affect the energy levels of the lone-pair electrons on the metal.
C)have different energies for their bonding electrons.
D)affect the energy levels of the metal d orbitals.
E)have different energies for their lone-pair electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following ligands will cause the smallest crystal field splitting of the d orbitals in an octahedral complex?
A)OH-
B)Br-
C)CN-
D)NO2-
E)EDTA4-
A)OH-
B)Br-
C)CN-
D)NO2-
E)EDTA4-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which statement concerning the crystal field theory of octahedral transition metal complexes is not correct?
A)The crystal field splitting ( o) increases with increasing charge of the metal ion for the same set of ligands.
B)The crystal field splitting ( o) is determined solely by the charge of the transition metal complex ion.
C)The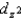 and
and 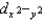 orbitals are higher in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals because these two point directly toward the ligands.
orbitals are higher in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals because these two point directly toward the ligands.
D)All ligands contribute to the strength of the crystal field.
E)The ordering of the orbitals,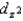 and
and 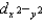 are higher in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals, is independent of the strength of the crystal field.
are higher in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals, is independent of the strength of the crystal field.
A)The crystal field splitting ( o) increases with increasing charge of the metal ion for the same set of ligands.
B)The crystal field splitting ( o) is determined solely by the charge of the transition metal complex ion.
C)The
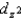 and
and 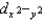 orbitals are higher in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals because these two point directly toward the ligands.
orbitals are higher in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals because these two point directly toward the ligands.D)All ligands contribute to the strength of the crystal field.
E)The ordering of the orbitals,
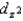 and
and 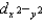 are higher in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals, is independent of the strength of the crystal field.
are higher in energy than the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals, is independent of the strength of the crystal field.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following ligands will cause the largest crystal field splitting of the d orbitals in an octahedral complex?
A)H2O
B)Br -
C)NH3
D)CN-
E)I-
A)H2O
B)Br -
C)NH3
D)CN-
E)I-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How many d electrons are there in the chromium(III) ion?
A)0
B)3
C)4
D)5
E)2
A)0
B)3
C)4
D)5
E)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How many unpaired spins are there in the tetrahedral complex ion, NiCl42-?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which d orbital(s) is/are highest in energy in a tetrahedral complex?
A)dz2
B)dxy, dxz, and dyz
C)dz2 and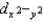
D)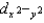
E)dxy and dxz
A)dz2
B)dxy, dxz, and dyz
C)dz2 and
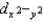
D)
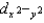
E)dxy and dxz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which d orbital(s) is/are lowest in energy in a tetrahedral complex?
A)dz2
B)dxy, dxz, and dyz
C)dz2 and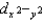
D)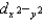
E)dxy and dxz
A)dz2
B)dxy, dxz, and dyz
C)dz2 and
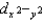
D)
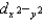
E)dxy and dxz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following complexes has the smallest crystal field splitting of the d orbitals?
A)CoF63
B)Co(CN)63-
C)CoBr63--
D)Co(H2O)63+
E)CoI63-
A)CoF63
B)Co(CN)63-
C)CoBr63--
D)Co(H2O)63+
E)CoI63-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
How many unpaired spins are there in the square planar complex ion, AuCl4-?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which statement A— D concerning the crystal field theory of tetrahedral transition metal complexes is not correct?
A)The crystal field splitting ( o) increases with increasing charge of the metal ion for the same set of ligands.
B)The dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals are higher in energy than the dz2 and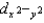 orbitals.
orbitals.
C)The crystal field splitting ( o) depends on the nature of the ligands and their positions in the spectrochemical series.
D)The lobes of the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals are closer to the ligands at the four corners of the tetrahedron than are the lobes of the dz2 and dx2 - y2 orbitals.
E)Statements A-D all are correct.
A)The crystal field splitting ( o) increases with increasing charge of the metal ion for the same set of ligands.
B)The dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals are higher in energy than the dz2 and
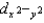 orbitals.
orbitals.C)The crystal field splitting ( o) depends on the nature of the ligands and their positions in the spectrochemical series.
D)The lobes of the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals are closer to the ligands at the four corners of the tetrahedron than are the lobes of the dz2 and dx2 - y2 orbitals.
E)Statements A-D all are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A strong crystal field produces a large value for the crystal field splitting, o, while a weak crystal field produces a small crystal field splitting. Which would be more likely to put a metal ion in a low-spin configuration?
A)strong field
B)weak field
C)left field
D)right field
E)center field
A)strong field
B)weak field
C)left field
D)right field
E)center field

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Given that the observed absorption maximum for the complex ion CoF63- in solution is max = 700 nm, what is the value of the crystal field splitting, o?
A)2.8 10-19 J
B)2.8 10-28 J
C)7.2 1030 J
D)3.2 10-36 J
E)7.2 10-19 J
A)2.8 10-19 J
B)2.8 10-28 J
C)7.2 1030 J
D)3.2 10-36 J
E)7.2 10-19 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Transition metals with ________ tend to form square planar complexes.
A)d 8 and d 9 configurations
B)d 1 and d 2 configurations
C)half-filled d orbitals
D)high spin
E)no d electrons
A)d 8 and d 9 configurations
B)d 1 and d 2 configurations
C)half-filled d orbitals
D)high spin
E)no d electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which d orbital is indicated by the arrow in the crystal field splitting diagram for a square planar field?
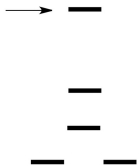
A)dz2
B)dyz
C)dxz
D)dx2 - y2
E)dxy
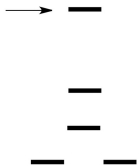
A)dz2
B)dyz
C)dxz
D)dx2 - y2
E)dxy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following complexes has the largest crystal field splitting of the d orbitals?
A)CoF63-
B)Co(CN)63-
C)CoBr63-
D)Co(H2O)63+
E)CoI63-
A)CoF63-
B)Co(CN)63-
C)CoBr63-
D)Co(H2O)63+
E)CoI63-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following cations would possess, the largest crystal field splitting ( o), assuming an identical ligand set for all ions?
A)Ti3+
B)Fe3+
C)Co2+
D)Cr4+
E)Cu+
A)Ti3+
B)Fe3+
C)Co2+
D)Cr4+
E)Cu+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which d orbitals are indicated by the arrow in the crystal field splitting diagram for a square planar field? 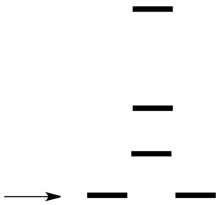
A)dz2 and dx2 - y2
B)dyz and dxz
C)dz2 and dxz
D)dxy and dx2 - y2
E)dx2 - y2 and dyz

A)dz2 and dx2 - y2
B)dyz and dxz
C)dz2 and dxz
D)dxy and dx2 - y2
E)dx2 - y2 and dyz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A transition metal complex ion with octahedral geometry has a value of 4.4 10-19 J for the crystal field splitting, o. What is the wavelength for the absorption maximum, max, for this complex ion?
A)5.0 10-15 nm
B)452 nm
C)4.5 10-16 nm
D)524 nm
E)637 nm
A)5.0 10-15 nm
B)452 nm
C)4.5 10-16 nm
D)524 nm
E)637 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A strong crystal field produces a large value for the crystal field splitting, o, while a weak crystal field produces a small crystal field splitting. Which would be more likely to put a metal ion in a high-spin configuration?
A)strong field
B)weak field
C)left field
D)right field
E)center field
A)strong field
B)weak field
C)left field
D)right field
E)center field

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In a tetrahedral crystal field, ________
A)dxy, dxz, and dyz are lower in energy than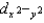 and dz2.
and dz2.
B)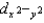 and dz2 are lower in energy than dxy, dxz, and dyz.
and dz2 are lower in energy than dxy, dxz, and dyz.
C)dxy, dxz, dyz,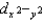 , and dz2 all have different energies.
, and dz2 all have different energies.
D)dxy, dxz, dyz,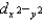 , and dz2 all have the same energy.
, and dz2 all have the same energy.
E)dxy, dxz, and dyz have the same energy, and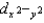 and dz2 have different energies.
and dz2 have different energies.
A)dxy, dxz, and dyz are lower in energy than
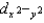 and dz2.
and dz2.B)
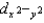 and dz2 are lower in energy than dxy, dxz, and dyz.
and dz2 are lower in energy than dxy, dxz, and dyz.C)dxy, dxz, dyz,
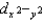 , and dz2 all have different energies.
, and dz2 all have different energies.D)dxy, dxz, dyz,
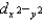 , and dz2 all have the same energy.
, and dz2 all have the same energy.E)dxy, dxz, and dyz have the same energy, and
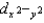 and dz2 have different energies.
and dz2 have different energies.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



