Deck 22: Amazing Ice: Glaciers and Ice Ages
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Amazing Ice: Glaciers and Ice Ages
1
Cirques and horns are features associated with ________.
A) mountain glaciation
B) continental glaciation
C) glacial outwash deposits
D) loess deposits
A) mountain glaciation
B) continental glaciation
C) glacial outwash deposits
D) loess deposits
A
2
During the last ice age,a ________ glacier covered much of the northern United States.
A) piedmont
B) cirque
C) mountain
D) continental
A) piedmont
B) cirque
C) mountain
D) continental
D
3
What type of glacier is seen in the foreground of the following picture? 
A) a continental glacier
B) a cirque glacier
C) a piedmont glacier
D) an alpine glacier

A) a continental glacier
B) a cirque glacier
C) a piedmont glacier
D) an alpine glacier
C
4
Ice is a substance with a high albedo,which means it ________.
A) requires much heat to raise its temperature by 1°C
B) absorbs most of the light that falls on it
C) reflects most of the light that falls on it
D) strongly refracts the light that falls on it
A) requires much heat to raise its temperature by 1°C
B) absorbs most of the light that falls on it
C) reflects most of the light that falls on it
D) strongly refracts the light that falls on it

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A glacier will always advance from its source area if the rate of accumulation is greater than the rate of ________.
A) subsidence
B) erosion
C) ablation
D) uplift
A) subsidence
B) erosion
C) ablation
D) uplift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
At the present,glaciers cover about ________ of the surface of the continents.
A) 1%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 20%
A) 1%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Glacial ice cores can be used to determine the atmospheric concentration of CO2 during the Earth's history.How do scientists come up with these data?
A) They use the thickness of the ice layers to determine how much CO2 was in the atmosphere.
B) They melt the ice and measure how much carbon was trapped in the ice.
C) They record changes in the shape of ice crystals to determine the paleoclimate.
D) They break the ice apart,release the air trapped in bubbles,and then measure the gases.
A) They use the thickness of the ice layers to determine how much CO2 was in the atmosphere.
B) They melt the ice and measure how much carbon was trapped in the ice.
C) They record changes in the shape of ice crystals to determine the paleoclimate.
D) They break the ice apart,release the air trapped in bubbles,and then measure the gases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The current interglacial interval began a little more than ________ years ago.
A) 1,000
B) 10,000
C) 100,000
D) 1 million
A) 1,000
B) 10,000
C) 100,000
D) 1 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Glacial ice exhibits ________ behavior near the top but ________ behavior at a depth of more than 60 m.
A) brittle; plastic
B) plastic; brittle
C) solid; elastic
D) plastic; elastic
A) brittle; plastic
B) plastic; brittle
C) solid; elastic
D) plastic; elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Glaciers form as fresh ________ falls to the ground and accumulates.The accumulation adds pressure,which compresses the ________ until they form a packed granular material called ________.Some material melts and then ________ in the pore spaces to create a solid mass of ice.
A) snow; snowflakes; cirques; dissolves
B) snow; snowflakes; firn; refreezes
C) ice; ice; firn; refreezes
D) firn; glacier; ice; gets trapped
A) snow; snowflakes; cirques; dissolves
B) snow; snowflakes; firn; refreezes
C) ice; ice; firn; refreezes
D) firn; glacier; ice; gets trapped

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An intermediate product in the transformation of snow to glacial ice is ________.
A) firn
B) deposition
C) ablation
D) terminus
A) firn
B) deposition
C) ablation
D) terminus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Boulders left behind by glacial ice are known as __________.
A) till
B) erratics
C) piedmont
D) horns
A) till
B) erratics
C) piedmont
D) horns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Today,continental glaciers are limited to Antarctica and ________.
A) Alaska
B) Greenland
C) Canada
D) Siberia
A) Alaska
B) Greenland
C) Canada
D) Siberia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The polar ice caps on Mars are an example of what type of glacier?
A) continental glacier
B) cirque glacier
C) piedmont glacier
D) valley glacier
A) continental glacier
B) cirque glacier
C) piedmont glacier
D) valley glacier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is true of flowing water and glacial ice?
A) Both flowing water and glacial ice are capable of sorting sediments based on clast size.
B) Flowing water will sort sediment based on clast size; glacial ice will not.
C) Glacial ice will sort sediment based on clast size; flowing water will not.
D) Neither flowing water nor glacial ice will sort sediment based on clast size.
A) Both flowing water and glacial ice are capable of sorting sediments based on clast size.
B) Flowing water will sort sediment based on clast size; glacial ice will not.
C) Glacial ice will sort sediment based on clast size; flowing water will not.
D) Neither flowing water nor glacial ice will sort sediment based on clast size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
At depths of greater than 60 m,ice moves by plastic deformation.What causes this transition from brittle to ductile behavior?
A) A decrease in temperature causes the glacier to melt and slide.
B) An increase in pressure increases friction and melts the ice.
C) An increase in the pressure allows for only minute deformation.
D) A decrease in the amount of trapped sediments allows more flow.
A) A decrease in temperature causes the glacier to melt and slide.
B) An increase in pressure increases friction and melts the ice.
C) An increase in the pressure allows for only minute deformation.
D) A decrease in the amount of trapped sediments allows more flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An angular peak surrounded by three or more bowl-shaped depressions formed by a mountain glacier is termed a(n)________.
A) arête
B) cirque
C) horn
D) tarn
A) arête
B) cirque
C) horn
D) tarn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Glacial deposits consist primarily of __________.
A) very fine-grained material
B) very coarse-grained material
C) very well-sorted material
D) very poorly sorted material
A) very fine-grained material
B) very coarse-grained material
C) very well-sorted material
D) very poorly sorted material

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A bowl-shaped depression formed by a mountain glacier is termed a(n)________.
A) arête
B) cirque
C) horn
D) tarn
A) arête
B) cirque
C) horn
D) tarn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Currently,almost all the glaciers on the Earth are in a state of retreat,which means that the rate of ________ is less than the rate of ________.
A) accumulation; ablation
B) ablation; accumulation
C) formation; sublimation
D) calving; advance
A) accumulation; ablation
B) ablation; accumulation
C) formation; sublimation
D) calving; advance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
You are hiking in your favorite forest when you encounter a surface that appears to have very fine scratches in it.What are these features?
A) glacial till
B) moraines
C) striations
D) scour marks
A) glacial till
B) moraines
C) striations
D) scour marks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Identify the farthest reach of the glacier in the figure below. 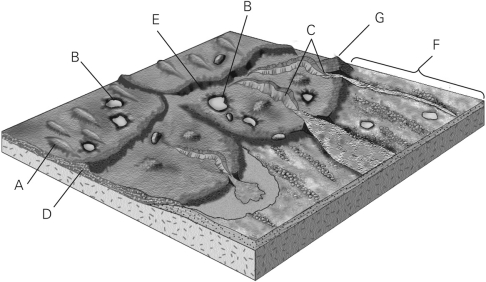
A) E
B) C
C) G
D) F

A) E
B) C
C) G
D) F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Identify the esker in the figure below. 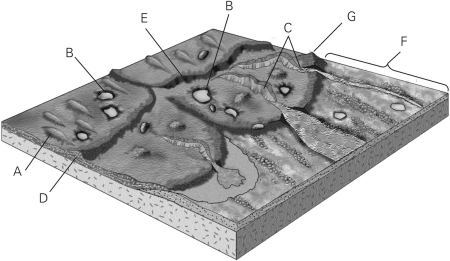
A) E
B) C
C) A
D) F

A) E
B) C
C) A
D) F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If you wander around Central Park in New York City,you will eventually encounter random,large boulders that are made of a type of rock not found in the area.How did these large boulders get to Central Park?
A) The Parks and Recreation Department placed them there for kids to play on.
B) They were carried by rivers and deposited in point bars.
C) They were carried by glaciers and dropped as glacial erratics.
D) They were placed there by a giant tsunami millions of years ago.
A) The Parks and Recreation Department placed them there for kids to play on.
B) They were carried by rivers and deposited in point bars.
C) They were carried by glaciers and dropped as glacial erratics.
D) They were placed there by a giant tsunami millions of years ago.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A(n)________ in global sea level is ultimately the result of a ________ event.
A) increase; global cooling
B) increase; local uplift
C) decrease; subsidence
D) decrease; global cooling
A) increase; global cooling
B) increase; local uplift
C) decrease; subsidence
D) decrease; global cooling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If glaciers carry a mixture of different clast sizes,why are glacial outwash deposits layered?
A) because clasts fall out of the glacier in size progression
B) because gravity pulls out only the smallest particles
C) because glacial outwash is formed from the bottom of the glacier
D) because the glacier does not deposit the sediments; the river does
A) because clasts fall out of the glacier in size progression
B) because gravity pulls out only the smallest particles
C) because glacial outwash is formed from the bottom of the glacier
D) because the glacier does not deposit the sediments; the river does

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following figures is of glacial lake-bed deposits? 
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Cirques,horns,and arêtes form due to glacial ________,whereas moraines,erratics,and till form from glacial ________.
A) erosion; deposition
B) deposition; carving
C) retreat; advance
D) erosion; sublimation
A) erosion; deposition
B) deposition; carving
C) retreat; advance
D) erosion; sublimation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When the sea level rises,causing the ocean to fill a glacially carved valley,a ________ results.
A) cirque
B) tarn
C) fjord
D) estuary
A) cirque
B) tarn
C) fjord
D) estuary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Sediments deposited directly by glaciers as they melt are characterized by ________.
A) uniformly coarse grain size
B) uniformly fine grain size
C) an absence of sorting
D) graded bedding
A) uniformly coarse grain size
B) uniformly fine grain size
C) an absence of sorting
D) graded bedding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Stratified sorted sand and gravel are deposited by ________.
A) mountain glaciers
B) continental glaciers
C) glacial outwash streams
D) windstorms
A) mountain glaciers
B) continental glaciers
C) glacial outwash streams
D) windstorms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A hanging valley is formed when a ________.
A) smaller glacially carved valley intersects with a larger glacially carved valley
B) smaller stream-cut valley intersects with a larger stream-cut valley
C) smaller stream-cut valley intersects with a larger glacially carved valley
D) stream-cut valley is on the upthrust side of a normal fault
A) smaller glacially carved valley intersects with a larger glacially carved valley
B) smaller stream-cut valley intersects with a larger stream-cut valley
C) smaller stream-cut valley intersects with a larger glacially carved valley
D) stream-cut valley is on the upthrust side of a normal fault

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Sediments deposited directly by glaciers as they melt are ________.
A) firn
B) loess
C) outwash
D) till
A) firn
B) loess
C) outwash
D) till

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Identify the area where layered sediments have been deposited in the figure below. 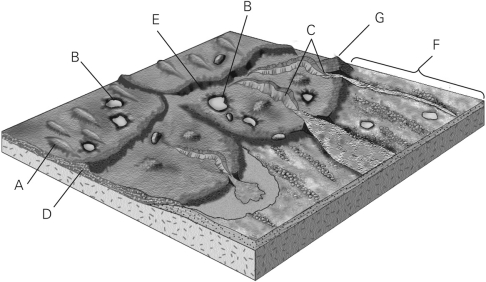
A) E
B) C
C) A
D) F

A) E
B) C
C) A
D) F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Using the figure below,identify which way the glacier advanced. 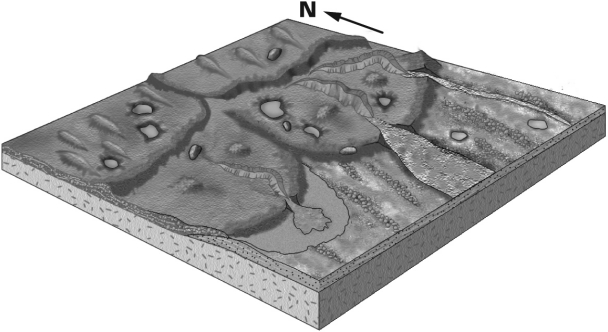
A) north
B) south
C) east
D) west

A) north
B) south
C) east
D) west

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Valleys carved by glaciers tend to be shaped like the letter ________,whereas valleys carved by water tend to be shaped like the letter ________.
A) V; U
B) V; C
C) U; V
D) I; V
A) V; U
B) V; C
C) U; V
D) I; V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Moraines are composed of jumbled piles of very poorly sorted rock fragments ranging in size from boulder to clay that fall out near the edges of glaciers.Why are the larger particles (boulders,etc.)not broken down during transport in the glacier?
A) because the ice is not strong enough to break up rock
B) because sediments are picked up and carried along with the ice as it moves
C) because the sediments are not carried for very long distances
D) because the ice stops the chemical weathering processes
A) because the ice is not strong enough to break up rock
B) because sediments are picked up and carried along with the ice as it moves
C) because the sediments are not carried for very long distances
D) because the ice stops the chemical weathering processes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What types of moraines are shown prominently in the figure below? 
A) medial moraines
B) terminal moraines
C) lateral moraines
D) recessional moraines

A) medial moraines
B) terminal moraines
C) lateral moraines
D) recessional moraines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Wind blows finer particles long distances from glacial environments,where they settle out to form ________.
A) firn
B) loess
C) outwash
D) till
A) firn
B) loess
C) outwash
D) till

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which types of features would you find in a glacially eroded landscape?
A) eskers,drumlins,cirques,and kettles
B) cirques,arêtes,horns,and moraines
C) cirques,arêtes,kettles,and tarns
D) drumlins,ground moraines,and arêtes
A) eskers,drumlins,cirques,and kettles
B) cirques,arêtes,horns,and moraines
C) cirques,arêtes,kettles,and tarns
D) drumlins,ground moraines,and arêtes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
List and describe one short-term cause for glaciations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Label the glaciers in the image below using words from the word bank included.(Hint: not all the names will be used.)

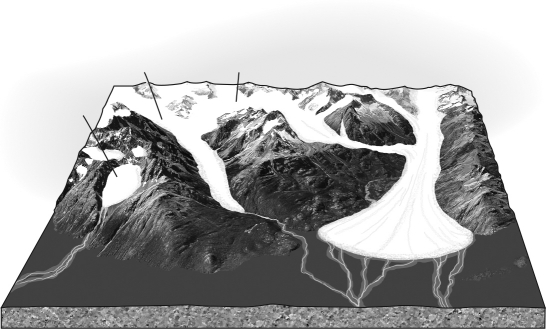



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Examine the graph below.There have been ________ to ________ ice ages in the Earth's history,with the latest one occurring in the ________. 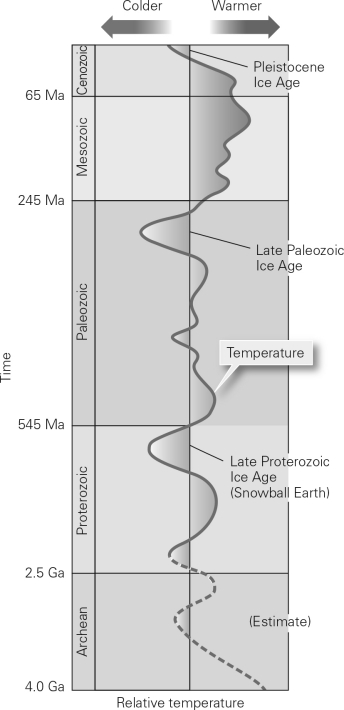
A) four; five; Pleistocene Period
B) five; six; Pleistocene Period
C) four; five; Proterozoic Era
D) five; six; Cenozoic Era

A) four; five; Pleistocene Period
B) five; six; Pleistocene Period
C) four; five; Proterozoic Era
D) five; six; Cenozoic Era

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Notice the boulders in the center of this picture of a glacially formed landscape.What are they? How did they get there? 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What happens to global sea level during times of increased glaciation? During interglacial periods? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What are the circumstances that lead to glacial advance versus glacial retreat? Most glaciers today are in retreat.What does this imply about the glaciers and their environment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe what you would expect to see in glacial till deposit.Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Contrast a glacially carved valley with one carved by a river.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The loss of rainforests would ________ the greenhouse gases,thereby ________ global warming.
A) increase; increasing
B) increase; decreasing
C) decrease; increasing
D) decrease; decreasing
A) increase; increasing
B) increase; decreasing
C) decrease; increasing
D) decrease; decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
You and some friends are going on a road trip and one of your goals is to see a glacier.Where could you go in the continental United States to do this? What type of glacier will you most likely be visiting?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the movie Ice Age: The Meltdown,there is a large wall of ice that begins to melt and finally breaks,causing a large flood.What real-life geologic event was this part of the movie based on?
A) the destruction of Glacial Lake Missoula
B) the formation of the Great Salt Lake
C) the breakup of the Ross Ice Shelf
D) the draining of Lake Bonneville
A) the destruction of Glacial Lake Missoula
B) the formation of the Great Salt Lake
C) the breakup of the Ross Ice Shelf
D) the draining of Lake Bonneville

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Explain why the deposits made by glacial outwash are stratified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Imagine that you live in a desert.Installing a roof that is a light tan color would help ________ your house by ________ the albedo.
A) warm; increasing
B) warm; decreasing
C) cool; increasing
D) cool; decreasing
A) warm; increasing
B) warm; decreasing
C) cool; increasing
D) cool; decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The effect of periodic changes in the Earth's orbital eccentricity and magnitude and direction (precession)of its axial tilt on the advance and retreat of ice sheets was first proposed by ________.
A) Richter
B) Milankovitch
C) Mohorivic
D) Lyell
A) Richter
B) Milankovitch
C) Mohorivic
D) Lyell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
By increasing the albedo of the Earth,global ice sheets produce conditions that are ________ to their further advance,thus providing an example of ________ feedback.
A) detrimental; positive
B) detrimental; negative
C) favorable; positive
D) favorable; negative
A) detrimental; positive
B) detrimental; negative
C) favorable; positive
D) favorable; negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Imagine you are living in your current home but during the Pleistocene Ice Age.Contrast the present climate with that of your new climate in the Pleistocene.In one sentence,summarize how the climate is different now.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
During the Pleistocene Ice Age,all the climate belts of the northern hemisphere shifted to the __________.
A) north
B) south
C) east
D) west
A) north
B) south
C) east
D) west

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An important long-term factor that determines whether glacial ice will form on a continent has likely been the proportion of which gas in the atmosphere?
A) oxygen
B) nitrogen
C) carbon dioxide
D) carbon monoxide
A) oxygen
B) nitrogen
C) carbon dioxide
D) carbon monoxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The formation of continental glaciers ____________ the weight of the lithosphere causing it to __________.
A) increases; subside
B) increases; uplift
C) decreases; subside
D) decreases; uplift
A) increases; subside
B) increases; uplift
C) decreases; subside
D) decreases; uplift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Milankovitch cycles describe the change in ________ because of changes in the ________ of the Earth relative to the Sun.
A) greenhouse gases; tilt
B) eccentricity; orientation
C) albedo; precession
D) solar insolation; orientation
A) greenhouse gases; tilt
B) eccentricity; orientation
C) albedo; precession
D) solar insolation; orientation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



