Deck 8: Portfolio Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Portfolio Analysis
1
The "optimal" portfolio will be the one where the investor's indifference curve touches the efficient set to the furthest
A) north.
B) northwest.
C) southwest.
D) southeast.
A) north.
B) northwest.
C) southwest.
D) southeast.
B
2
The efficient set theorem states that an investor will choose an optimal portfolio from the set of portfolios that offers
A) maximum expected returns for varying levels of risk
B) minimum expected returns for varying levels of risk
C) the same expected returns for varying levels of risk
D) maximum expected returns at the same levels of risk
A) maximum expected returns for varying levels of risk
B) minimum expected returns for varying levels of risk
C) the same expected returns for varying levels of risk
D) maximum expected returns at the same levels of risk
A
3
Stocks with betas less than one are less volatile than the market index and are known as _____ stocks.
A) aggressive
B) hedge
C) defensive
D) speculative
A) aggressive
B) hedge
C) defensive
D) speculative
C
4
Market risk, alternatively known as _______ risk, is that portion of a security's total risk that is related to moves in the market portfolio.
A) systematic
B) unsystematic
C) unique
D) index
A) systematic
B) unsystematic
C) unique
D) index

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Unique risk, alternatively known as _______ risk, is that portion of a security's total risk that can be diversified away.
A) systematic
B) non-market
C) market
D) index
A) systematic
B) non-market
C) market
D) index

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The ______ simply represents all portfolios that could be formed from a group of known securities.
A) market portfolio
B) efficient set
C) feasible set
D) optimal portfolio
A) market portfolio
B) efficient set
C) feasible set
D) optimal portfolio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The set of portfolios meeting the condition of maximum expected returns for varying levels of risk and minimum risk for varying levels of expected returns is known as the
A) market portfolio
B) efficient set
C) market frontier
D) feasible set
A) market portfolio
B) efficient set
C) market frontier
D) feasible set

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Portfolio "optimizers" tend to
A) provide low turnover portfolios.
B) ignore modern Portfolio Theory.
C) ignore transaction costs.
D) rely on qualitative judgment.
A) provide low turnover portfolios.
B) ignore modern Portfolio Theory.
C) ignore transaction costs.
D) rely on qualitative judgment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The active ______ is the combinations of securities that offer investors both maximum expected active return for varying levels of active risk and minimum active risk for varying levels of expected active return.
A) market portfolio
B) market set
C) feasible set
D) efficient set
A) market portfolio
B) market set
C) feasible set
D) efficient set

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When plotting the risk/return relationships for possible portfolios of two securities, the lowest standard deviation of the portfolio possibilities would occur if the correlation coefficient were
A) 0.
B) -1.
C) .5.
D) 1.
A) 0.
B) -1.
C) .5.
D) 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The efficient set of portfolios consists of portfolios that
A) maximize risk for a given level of return.
B) maximize return.
C) minimize return for a given level of risk.
D) minimize risk for a given level of risk.
A) maximize risk for a given level of return.
B) maximize return.
C) minimize return for a given level of risk.
D) minimize risk for a given level of risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
____ or the slope in a security's market model measures the sensitivity of the security's returns to the market index's returns.
A) Random error
B) Beta
C) Alpha
D) Delta
A) Random error
B) Beta
C) Alpha
D) Delta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The process of selecting securities in a manner that explicitly considers the standard deviations and correlations of the securities is known as efficient
A) allocation
B) returns
C) diversification
D) risk allocation
A) allocation
B) returns
C) diversification
D) risk allocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For the market model, each security's error term is assumed to
A) have the same standard deviation.
B) have an expected value of 100%.
C) be in a flat distribution.
D) have an expected value of 0.
A) have the same standard deviation.
B) have an expected value of 100%.
C) be in a flat distribution.
D) have an expected value of 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
To determine the composition of the portfolios in the efficient set, the analyst must solve a
A) quadratic program.
B) correlation matrix.
C) expected return vector.
D) probability distribution.
A) quadratic program.
B) correlation matrix.
C) expected return vector.
D) probability distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The market model is a simple linear model that expresses the relationship between the return on a(n) _____ and the return on a(n) ____ index.
A) market, security
B) security, price
C) bond, bond
D) security, market
A) market, security
B) security, price
C) bond, bond
D) security, market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The feasible set of portfolios consists
A) of all possible portfolios of the N securities.
B) only the inefficient portfolios.
C) of a straight line with negative slope.
D) only the efficient portfolios.
A) of all possible portfolios of the N securities.
B) only the inefficient portfolios.
C) of a straight line with negative slope.
D) only the efficient portfolios.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The more positive the slope is for a security's market model,
A) the more defensive the security.
B) the lower the risk-free return.
C) the more sensitive the security's return is to that in the market.
D) the more the market return can change without affecting the security return.
A) the more defensive the security.
B) the lower the risk-free return.
C) the more sensitive the security's return is to that in the market.
D) the more the market return can change without affecting the security return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the market model, the difference between what the return actually is and what it is expected to be, given the return on the market index, is attributed to the effect of the ________ term.
A) random error
B) slope
C) intercept
D) return on the security
A) random error
B) slope
C) intercept
D) return on the security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
According to the market model, the total risk of any security measured by its variance consists of ______ risk and _____ risk.
A) expected, unexpected
B) market, inflation
C) interest rate, human
D) market, unique
A) expected, unexpected
B) market, inflation
C) interest rate, human
D) market, unique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the total market risk equation for security i as follows: 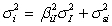 which term denotes the market risk of security i ?
which term denotes the market risk of security i ?
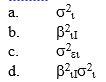
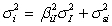 which term denotes the market risk of security i ?
which term denotes the market risk of security i ?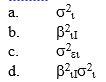

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A "well-diversified" portfolio will have at least the following number of securities:
A) 30.
B) 5.
C) 100.
D) 10.
A) 30.
B) 5.
C) 100.
D) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If an analyst is considering 40 securities for inclusion in a portfolio and is using the covariance approach, she must estimate total parameters numbering
A) 860.
B) 780.
C) 80.
D) 800.
A) 860.
B) 780.
C) 80.
D) 800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
You have developed a market model with a forecasted market return of 15% and an intercept of 6%. A security with a beta of .8 would have an expected return of
A) 21%.
B) 18%.
C) 12.8%.
D) 16.8%.
A) 21%.
B) 18%.
C) 12.8%.
D) 16.8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
To use the market model with 25 securities to include in the portfolio, the number of parameters the analyst must estimate is
A) 27.
B) 300.
C) 125.
D) 77.
A) 27.
B) 300.
C) 125.
D) 77.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When using the market model for portfolio development, the analyst assumes that the correlation between each security's random error is
A) .5.
B) 0.
C) -.5.
D) -1.
A) .5.
B) 0.
C) -.5.
D) -1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
As long as the correlations between the securities are less than 1 or greater than -1, the northwest portion of their risk/return will
A) consist of one portfolio.
B) not allow an optimal solution.
C) be concave.
D) be a straight line.
A) consist of one portfolio.
B) not allow an optimal solution.
C) be concave.
D) be a straight line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Selection of the ________ portfolio involves the combination of the _____ set and the investor's ___________ .
A) feasible, efficient, indifference curves
B) optimal, efficient, feasible set
C) optimal, efficient, indifference curves
D) optimal, feasible, indifference curves
A) feasible, efficient, indifference curves
B) optimal, efficient, feasible set
C) optimal, efficient, indifference curves
D) optimal, feasible, indifference curves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Using the market model instead of the full covariance approach
A) does not require the calculation of betas.
B) requires less assumptions.
C) less individual variances need to be estimated.
D) requires less parameter estimate.
A) does not require the calculation of betas.
B) requires less assumptions.
C) less individual variances need to be estimated.
D) requires less parameter estimate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Adding a low beta security to a two-security portfolio will not reduce the
A) portfolio beta.
B) total portfolio risk.
C) market variance.
D) standard deviation of the random error.
A) portfolio beta.
B) total portfolio risk.
C) market variance.
D) standard deviation of the random error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
For the market model with 40 securities, the number of parameters the analyst must estimate for forecasting the portfolio return is
A) 41.
B) 780.
C) 81.
D) 1.
A) 41.
B) 780.
C) 81.
D) 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If an analyst has to estimate 65 parameters using covariances, the number of securities he is considering for inclusion in the portfolio is
A) 20.
B) 30.
C) 5.
D) 10.
A) 20.
B) 30.
C) 5.
D) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Plotting any possible risk/return relationships between two securities will result in a
A) triangle.
B) straight line.
C) trapezoid.
D) series of concentric lines.
A) triangle.
B) straight line.
C) trapezoid.
D) series of concentric lines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Diversification will
A) not reduce a portfolio's total risk.
B) reduce a portfolio's unique risk.
C) increase a portfolio's total risk.
D) not reduce a portfolio's unsystematic risk.
A) not reduce a portfolio's total risk.
B) reduce a portfolio's unique risk.
C) increase a portfolio's total risk.
D) not reduce a portfolio's unsystematic risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An aggressive security
A) has a large, positive beta.
B) will have a small covariance with market returns.
C) will have a small variance.
D) has a flat market line.
A) has a large, positive beta.
B) will have a small covariance with market returns.
C) will have a small variance.
D) has a flat market line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The efficient set theorem states that an investor will choose an optimal portfolio from the set of portfolios that offers the following two conditions:
A) minimum expected returns for varying levels of risk and minimum risk for varying levels of expected returns
B) maximum expected returns for varying levels of risk and minimum risk for varying levels of expected returns
C) the same expected returns for varying levels of risk
D) maximum expected returns at the same levels of risk and minimum risk for varying levels of expected returns
A) minimum expected returns for varying levels of risk and minimum risk for varying levels of expected returns
B) maximum expected returns for varying levels of risk and minimum risk for varying levels of expected returns
C) the same expected returns for varying levels of risk
D) maximum expected returns at the same levels of risk and minimum risk for varying levels of expected returns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The portfolio standard deviation will be equal to the weighted average of its components' standard deviations only if the correlation coefficient for returns among the components is
A) -1.
B) 1.
C) .5.
D) -.5.
A) -1.
B) 1.
C) .5.
D) -.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The feature that leads to there only being one tangency point between the indifference curve and the efficient set is the
A) efficient set is convex.
B) indifference curve has a negative slope.
C) efficient set has only N feasible choices.
D) efficient set is concave.
A) efficient set is convex.
B) indifference curve has a negative slope.
C) efficient set has only N feasible choices.
D) efficient set is concave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
To find the efficient set for 20 securities that may be included in a portfolio, the analyst must calculate covariances numbering
A) 400.
B) 190.
C) 380.
D) 20.
A) 400.
B) 190.
C) 380.
D) 20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
From the market model, the unique risk is the
A) market risk.
B) unsystematic risk.
C) beta risk.
D) market variance.
A) market risk.
B) unsystematic risk.
C) beta risk.
D) market variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A portfolio consists of Securities X and Y in the proportions of .4 and .6. Security X has a random error standard deviation of 15%; Security Y at 4%. The market standard deviation is 12%; the beta for X is .6; the beta for Y is 1.5. The total portfolio variance is
A) 173.
B) 129.
C) 148.5.
D) 229.
A) 173.
B) 129.
C) 148.5.
D) 229.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Your market model has a intercept of 4%, and you forecast a market return of 10%. If your security has a beta of 1.3 and has an actual return of 12%, the error term is
A) -8.3%.
B) -5%.
C) 3.2%.
D) 4.6%.
A) -8.3%.
B) -5%.
C) 3.2%.
D) 4.6%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Security X has a standard deviation of its error term of 7% and a beta of 1.4. If the standard deviation of the market is 12%, the total variance for Security X is
A) 118.
B) 331.
C) 80.6.
D) 213.
A) 118.
B) 331.
C) 80.6.
D) 213.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The optimal portfolio is designated by
A) the point of tangency between the efficient set and the investor's indifference curve
B) the point of highest indifference curve and its tangency to the feasible set
C) the point of tangency with the opportunity set and the security market line
D) the point of tangency between the efficient and the feasible set
A) the point of tangency between the efficient set and the investor's indifference curve
B) the point of highest indifference curve and its tangency to the feasible set
C) the point of tangency with the opportunity set and the security market line
D) the point of tangency between the efficient and the feasible set

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Security B has a total variance of 300 and a random error variance of 121. If the market variance is 100, its beta is
A) 1.34.
B) 1.22.
C) 1.07.
D) 1.00.
A) 1.34.
B) 1.22.
C) 1.07.
D) 1.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A portfolio consists of Securities A, B, and C in the respective proportions of .3, .2, .5. If the securities' respective betas are .8, 1.4, 1.1, the beta for the portfolio is
A) .98.
B) 1.12.
C) 1.07.
D) 1.23.
A) .98.
B) 1.12.
C) 1.07.
D) 1.23.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements is true regarding a portfolio's diversification?
A) proper diversification can reduce or eliminate systematic risk
B) the risk-reducing benefits of diversification do not occur meaningfully until at least 16 or more securities have been added to the portfolio
C) because diversification reduces a portfolio's total risk, it must reduce the portfolio's expected return
D) as more securities are added to a portfolio, total risk would be expected to fall at a decreasing rate under normal conditions
A) proper diversification can reduce or eliminate systematic risk
B) the risk-reducing benefits of diversification do not occur meaningfully until at least 16 or more securities have been added to the portfolio
C) because diversification reduces a portfolio's total risk, it must reduce the portfolio's expected return
D) as more securities are added to a portfolio, total risk would be expected to fall at a decreasing rate under normal conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which one of the following statements is true regarding the variance of risky portfolios?
A) the higher the correlation coefficient between securities, the greater will be the reduction in the portfolio variance
B) there is a direct relationship between the securities correlation coefficient and the portfolio variance
C) the degree to which the portfolio variance is reduced depends on the degree of correlation between securities
D) proper diversification can reduce or eliminate all of a portfolio's risk
A) the higher the correlation coefficient between securities, the greater will be the reduction in the portfolio variance
B) there is a direct relationship between the securities correlation coefficient and the portfolio variance
C) the degree to which the portfolio variance is reduced depends on the degree of correlation between securities
D) proper diversification can reduce or eliminate all of a portfolio's risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Given the efficient set, risk seeking investors would tend to prefer portfolios in the ______ region
A) southern
B) northeastern
C) northwestern
D) southeastern
A) southern
B) northeastern
C) northwestern
D) southeastern

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The greatest shortcoming of standard deviation as a measure of volatility is
A) it discriminates in favor of investments with volatility on the "downside"
B) it discriminates in favor of investments with volatility on the "upside"
C) it is normally distributed meaning the possibility of an "upside" outcome is just as likely as a "downside" outcome
D) volatility is averaged rather than incremental
A) it discriminates in favor of investments with volatility on the "downside"
B) it discriminates in favor of investments with volatility on the "upside"
C) it is normally distributed meaning the possibility of an "upside" outcome is just as likely as a "downside" outcome
D) volatility is averaged rather than incremental

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The unsystematic risk of a risky security
A) is likely to be higher in a bull market
B) results from the international market forces
C) cannot be diversified by ordinary methods
D) results from its own unique factors
A) is likely to be higher in a bull market
B) results from the international market forces
C) cannot be diversified by ordinary methods
D) results from its own unique factors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A portfolio consists of Securities A and B in the proportions of .7 and .3. Security A has a random error standard deviation of 7%; Security B at 11%. The portfolio beta is 1.2, and the market standard deviation is 10%. The total portfolio variance is
A) 158.
B) 204.
C) 265.
D) 179.
A) 158.
B) 204.
C) 265.
D) 179.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Security Y has a total variance of 225. Its beta is 1.2 and the market variance is 100. The standard deviation of its random error term is
A) 6%.
B) 14%.
C) 3%.
D) 9%.
A) 6%.
B) 14%.
C) 3%.
D) 9%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Security A has a beta of .9 and a standard deviation of its error term of 8%. If the standard deviation of the market is 10%, the total variance for Security A is
A) 17.2.
B) 73.
C) 145.
D) 154.
A) 17.2.
B) 73.
C) 145.
D) 154.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



