Deck 12: Growth Theory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/149
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Growth Theory
1
A restaurant's production function would show the relationship between:
A) the number of workers hired and the number of meals served.
B) the number of workers hired and the level of profit.
C) the level of profit and the number of meals served.
D) the level of profit and the cost of producing the meals.
E) the number of workers hired and the cost of producing the meals.
A) the number of workers hired and the number of meals served.
B) the number of workers hired and the level of profit.
C) the level of profit and the number of meals served.
D) the level of profit and the cost of producing the meals.
E) the number of workers hired and the cost of producing the meals.
the number of workers hired and the number of meals served.
2
The aggregate production function describes the relationship between the total output in the economy and:
A) physical capital, human capital, and natural resources.
B) total spending in the economy.
C) total income earned in the economy.
D) the inflation rate.
E) the unemployment rate.
A) physical capital, human capital, and natural resources.
B) total spending in the economy.
C) total income earned in the economy.
D) the inflation rate.
E) the unemployment rate.
physical capital, human capital, and natural resources.
3
Which of the following is true?
A) Economists formulate theory and then sometimes try to verify the theory with real-world observations.
B) Real-world observations are used to formulate economic theory, but this is of little use to policymakers.
C) Once an economic theory is developed, it is rarely tested against real-world observations.
D) When a policymaker has an idea about how to advance economic growth, she will ask an economist to formulate a theory, and then this will be compared to real-world observations.
E) Real-world observations motivate economists to formulate theories about how economic growth evolves, and these theories are then used and reevaluated as new data become available.
A) Economists formulate theory and then sometimes try to verify the theory with real-world observations.
B) Real-world observations are used to formulate economic theory, but this is of little use to policymakers.
C) Once an economic theory is developed, it is rarely tested against real-world observations.
D) When a policymaker has an idea about how to advance economic growth, she will ask an economist to formulate a theory, and then this will be compared to real-world observations.
E) Real-world observations motivate economists to formulate theories about how economic growth evolves, and these theories are then used and reevaluated as new data become available.
Real-world observations motivate economists to formulate theories about how economic growth evolves, and these theories are then used and reevaluated as new data become available.
4
Which best explains the relationship between physical capital and the level of wealth in a country?
A) As countries become wealthier, they acquire more physical capital.
B) As countries acquire more physical capital, they become wealthier.
C) Wealthier countries invest less in physical capital.
D) Poor countries can only become wealthier if they acquire more physical capital.
E) A country does not need physical capital to increase wealth.
A) As countries become wealthier, they acquire more physical capital.
B) As countries acquire more physical capital, they become wealthier.
C) Wealthier countries invest less in physical capital.
D) Poor countries can only become wealthier if they acquire more physical capital.
E) A country does not need physical capital to increase wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
According to modern growth theory, the key to economic growth is:
A) paved roads.
B) modern buildings.
C) skilled labor.
D) a large pool of unskilled labor.
E) institutions.
A) paved roads.
B) modern buildings.
C) skilled labor.
D) a large pool of unskilled labor.
E) institutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The relationship between the growth rate of real gross domestic product (GDP) and the growth rate of real investment is:
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) unpredictable.
D) nonexistent.
E) positive at low levels of real GDP and then negative at higher levels of GDP.
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) unpredictable.
D) nonexistent.
E) positive at low levels of real GDP and then negative at higher levels of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the production function in the Solow growth model is given by q = f(human capital, physical capital), then in this model:
A) there is no investment.
B) there is no labor.
C) labor is represented by the human capital variable.
D) there is no depreciation.
E) there is no economic growth.
A) there is no investment.
B) there is no labor.
C) labor is represented by the human capital variable.
D) there is no depreciation.
E) there is no economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The graphical relationship between real gross domestic product (GDP) and capital is called the:
A) steady state.
B) capital function.
C) production function.
D) investment function.
E) marginal product curve.
A) steady state.
B) capital function.
C) production function.
D) investment function.
E) marginal product curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to modern growth theory, a country that wants to foster long-run economic growth and the accumulation of wealth should focus on:
A) its institutions.
B) acquiring physical capital.
C) its supply of unskilled labor.
D) its educated workforce.
E) acquiring modern buildings.
A) its institutions.
B) acquiring physical capital.
C) its supply of unskilled labor.
D) its educated workforce.
E) acquiring modern buildings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Economic models are:
A) complex representations of reality.
B) not related to real-world observations.
C) used by teachers but not policymakers.
D) updated as new real-world data become available.
E) rarely reevaluated.
A) complex representations of reality.
B) not related to real-world observations.
C) used by teachers but not policymakers.
D) updated as new real-world data become available.
E) rarely reevaluated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Economic theories about growth:
A) are mainly used for intellectual debate.
B) are mainly used for teaching.
C) are not based on real-world facts.
D) are used to set economic policies that impact human lives.
E) have had no influence on government policy.
A) are mainly used for intellectual debate.
B) are mainly used for teaching.
C) are not based on real-world facts.
D) are used to set economic policies that impact human lives.
E) have had no influence on government policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Economic growth theory is based on:
A) the Ricardian growth model.
B) the Solow growth model.
C) business cycle theory.
D) the theory of supply and demand.
E) the theory of investment.
A) the Ricardian growth model.
B) the Solow growth model.
C) business cycle theory.
D) the theory of supply and demand.
E) the theory of investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Economic growth theory originated about 60 years ago as a result of contributions by:
A) Robert Solow.
B) Adam Smith.
C) David Ricardo.
D) Alan Greenspan.
E) Ben Bernanke.
A) Robert Solow.
B) Adam Smith.
C) David Ricardo.
D) Alan Greenspan.
E) Ben Bernanke.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In equation form, the production function for a single firm can be expressed as:
A) q = f(human capital, physical capital).
B) q = f(price of output, price of inputs).
C) q = f(labor, price of inputs).
D) q = f(price of inputs, profit).
E) q = f(production cost, profit).
A) q = f(human capital, physical capital).
B) q = f(price of output, price of inputs).
C) q = f(labor, price of inputs).
D) q = f(price of inputs, profit).
E) q = f(production cost, profit).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An example of physical capital is:
A) a well-run government.
B) a well-developed banking system.
C) skilled labor.
D) paved roads.
E) educated teachers.
A) a well-run government.
B) a well-developed banking system.
C) skilled labor.
D) paved roads.
E) educated teachers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The main focus of the Solow growth model is:
A) physical capital.
B) human capital.
C) institutions.
D) natural resources.
E) labor.
A) physical capital.
B) human capital.
C) institutions.
D) natural resources.
E) labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The early Solow model focused on:
A) the skill level of workers.
B) the labor supply.
C) government policy.
D) the availability of capital goods.
E) institutions.
A) the skill level of workers.
B) the labor supply.
C) government policy.
D) the availability of capital goods.
E) institutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Economic growth is determined by:
A) the rate of inflation.
B) the size of the population.
C) geography.
D) cultural factors.
E) resources, technology, and institutions.
A) the rate of inflation.
B) the size of the population.
C) geography.
D) cultural factors.
E) resources, technology, and institutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The production function describes the relationship between:
A) inflation and unemployment in the economy.
B) the firm's inputs and outputs.
C) the levels of output and spending in the economy.
D) the aggregate supply and demand for goods in the economy.
E) the firm's output and the price level.
A) inflation and unemployment in the economy.
B) the firm's inputs and outputs.
C) the levels of output and spending in the economy.
D) the aggregate supply and demand for goods in the economy.
E) the firm's output and the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The growth theory we study today was formulated:
A) during the Great Depression.
B) during the 1970s.
C) during the 1950s.
D) in 1776 by the work of Adam Smith.
E) over 100 years ago.
A) during the Great Depression.
B) during the 1970s.
C) during the 1950s.
D) in 1776 by the work of Adam Smith.
E) over 100 years ago.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the Solow growth model, human capital will increase if (choose the best answer):
A) there are more workers.
B) workers are better educated.
C) there are more workers and/or existing workers become better educated and skilled.
D) real wages increase.
E) there is an increase in production.
A) there are more workers.
B) workers are better educated.
C) there are more workers and/or existing workers become better educated and skilled.
D) real wages increase.
E) there is an increase in production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When the marginal product of an input falls as the quantity of the input rises, this is known as:
A) diminishing marginal product.
B) diminishing output.
C) diminishing production.
D) decreasing returns to scale.
E) inverse marginal product.
A) diminishing marginal product.
B) diminishing output.
C) diminishing production.
D) decreasing returns to scale.
E) inverse marginal product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In a population, not all workers have a high school diploma. Suppose the size of the labor force increases but a smaller percentage of the labor force has a high school diploma. It is reasonable to expect that the larger labor force will _________ the human capital input and the smaller percentage of the labor force with a high school diploma will _________ the human capital input.
A) decrease; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease
D) increase; have no effect on
E) increase; increase
A) decrease; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease
D) increase; have no effect on
E) increase; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Use the following graph to answer the next questions. 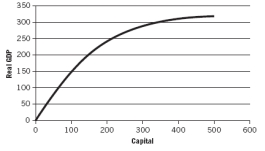
If net investment is positive, then:
A) the production function will shift upward.
B) the production function will shift downward.
C) there is an upward movement along the production function.
D) there is a downward movement along the production function.
E) there is an upward shift of the production function and an upward movement along the production function.

If net investment is positive, then:
A) the production function will shift upward.
B) the production function will shift downward.
C) there is an upward movement along the production function.
D) there is a downward movement along the production function.
E) there is an upward shift of the production function and an upward movement along the production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Solow model emphasizes:
A) the development of institutions.
B) capital and diminishing returns.
C) the importance of skilled labor.
D) technological change.
E) cultural factors.
A) the development of institutions.
B) capital and diminishing returns.
C) the importance of skilled labor.
D) technological change.
E) cultural factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Bob owns and manages an apple orchard. In Bob's business, an example of physical capital would be:
A) a ladder.
B) the apple trees.
C) the water he uses on the trees.
D) the number of workers he hires to pick the apples.
E) Bob's level of education.
A) a ladder.
B) the apple trees.
C) the water he uses on the trees.
D) the number of workers he hires to pick the apples.
E) Bob's level of education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Use the following graph to answer the next questions. 
Consider a country that improves its educational system such that a greater percentage of workers become college educated. It is reasonable to expect:
A) the production function will shift upward.
B) the production function will shift downward.
C) there will be an upward movement along the production function.
D) there will be a downward movement along the production function.
E) there will be no effect on the production function.

Consider a country that improves its educational system such that a greater percentage of workers become college educated. It is reasonable to expect:
A) the production function will shift upward.
B) the production function will shift downward.
C) there will be an upward movement along the production function.
D) there will be a downward movement along the production function.
E) there will be no effect on the production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the following graph to answer the next questions. 
If more natural resources are discovered, then:
A) the production function will shift upward.
B) the production function will shift downward.
C) there will be an upward movement along the production function.
D) there will be a downward movement along the production function.
E) there will be no effect on the production function.

If more natural resources are discovered, then:
A) the production function will shift upward.
B) the production function will shift downward.
C) there will be an upward movement along the production function.
D) there will be a downward movement along the production function.
E) there will be no effect on the production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the Solow growth model, human capital measures:
A) the number of workers.
B) the educational level of the workers.
C) the level of technology available to workers.
D) the labor input in terms of the physical number of workers and the knowledge and skills embodied in those workers.
E) how much firms spend to train workers.
A) the number of workers.
B) the educational level of the workers.
C) the level of technology available to workers.
D) the labor input in terms of the physical number of workers and the knowledge and skills embodied in those workers.
E) how much firms spend to train workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Use the following graph to answer the next questions. 
If capital is increasing, then:
A) the production function will shift upward.
B) the production function will shift downward.
C) there is an upward movement along the production function.
D) there is a downward movement along the production function.
E) there is an upward shift of the production function and an upward movement along the production function.

If capital is increasing, then:
A) the production function will shift upward.
B) the production function will shift downward.
C) there is an upward movement along the production function.
D) there is a downward movement along the production function.
E) there is an upward shift of the production function and an upward movement along the production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Diminishing marginal product is also known as:
A) diminishing returns.
B) net investment.
C) depreciation.
D) investment.
E) the steady state.
A) diminishing returns.
B) net investment.
C) depreciation.
D) investment.
E) the steady state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The change in output divided by the change in input is defined as:
A) marginal product.
B) average product.
C) diminishing returns.
D) labor productivity.
E) profit per unit output.
A) marginal product.
B) average product.
C) diminishing returns.
D) labor productivity.
E) profit per unit output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The marginal product of an input is defined as:
A) the change in output.
B) the change in output divided by the change in input.
C) the change in input.
D) the total output divided by the total inputs.
E) the cost of the input.
A) the change in output.
B) the change in output divided by the change in input.
C) the change in input.
D) the total output divided by the total inputs.
E) the cost of the input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Use the following graph to answer the next questions. 
If this country experiences an epidemic that reduces human capital, then:
A) the production function will shift upward.
B) the production function will shift downward.
C) there will be an upward movement along the production function.
D) there will be a downward movement along the production function.
E) there will be no effect on the production function.

If this country experiences an epidemic that reduces human capital, then:
A) the production function will shift upward.
B) the production function will shift downward.
C) there will be an upward movement along the production function.
D) there will be a downward movement along the production function.
E) there will be no effect on the production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Human capital relates to _________ and physical capital relates to _________.
A) people; buildings
B) firms; people
C) education; money
D) money; buildings
E) output; money
A) people; buildings
B) firms; people
C) education; money
D) money; buildings
E) output; money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Bob owns and manages an apple orchard. In Bob's business, an example of human capital would be:
A) a ladder.
B) the time spent by the workers picking apples.
C) the apple trees.
D) the amount of fertilizer used on the trees.
E) the boxes used to store the apples.
A) a ladder.
B) the time spent by the workers picking apples.
C) the apple trees.
D) the amount of fertilizer used on the trees.
E) the boxes used to store the apples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider the data in the following table. 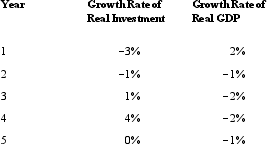 Do the data match the experience of a developed country like the United States?
Do the data match the experience of a developed country like the United States?
A) Yes, because the two growth rates are positively correlated.
B) No, because the two growth rates should be positively correlated.
C) Yes, because the two growth rates are negatively correlated.
D) No, because the two growth rates should be negatively correlated.
E) Yes, because these two growth rates are unrelated.
 Do the data match the experience of a developed country like the United States?
Do the data match the experience of a developed country like the United States?A) Yes, because the two growth rates are positively correlated.
B) No, because the two growth rates should be positively correlated.
C) Yes, because the two growth rates are negatively correlated.
D) No, because the two growth rates should be negatively correlated.
E) Yes, because these two growth rates are unrelated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In a population, the size of the labor force shrinks but a greater percentage of the labor force has a college degree. We can expect the human capital input to:
A) be unaffected.
B) increase.
C) decrease.
D) first increase and then decrease.
E) increase or decrease depending on which change has a larger impact.
A) be unaffected.
B) increase.
C) decrease.
D) first increase and then decrease.
E) increase or decrease depending on which change has a larger impact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Country X has a higher growth rate of real investment than country Y. You might expect country X to have:
A) a higher growth rate of real gross domestic product (GDP).
B) the same growth rate of real GDP.
C) a lower growth rate of real GDP.
D) a lower level of net investment.
E) a lower level of depreciation.
A) a higher growth rate of real gross domestic product (GDP).
B) the same growth rate of real GDP.
C) a lower growth rate of real GDP.
D) a lower level of net investment.
E) a lower level of depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the data in the following table.  Do the data match the experience of a developed country like the United States?
Do the data match the experience of a developed country like the United States?
A) Yes, because the two growth rates are positively correlated.
B) No, because the two growth rates should be positively correlated.
C) Yes, because the two growth rates are negatively correlated.
D) No, because the two growth rates should be negatively correlated.
E) Yes, because these two growth rates are unrelated.
 Do the data match the experience of a developed country like the United States?
Do the data match the experience of a developed country like the United States?A) Yes, because the two growth rates are positively correlated.
B) No, because the two growth rates should be positively correlated.
C) Yes, because the two growth rates are negatively correlated.
D) No, because the two growth rates should be negatively correlated.
E) Yes, because these two growth rates are unrelated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A key assumption of the Solow model is:
A) increasing returns to labor and diminishing returns to capital.
B) diminishing returns to capital only.
C) diminishing marginal product of capital and labor.
D) diminishing marginal product of capital and increasing marginal product of labor.
E) constant marginal product of capital only.
A) increasing returns to labor and diminishing returns to capital.
B) diminishing returns to capital only.
C) diminishing marginal product of capital and labor.
D) diminishing marginal product of capital and increasing marginal product of labor.
E) constant marginal product of capital only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the following production function to answer the next questions. 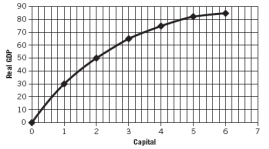
This production function exhibits:
A) diminishing marginal product.
B) constant marginal product.
C) increasing marginal product.
D) increasing returns to capital.
E) a constant rate of depreciation.

This production function exhibits:
A) diminishing marginal product.
B) constant marginal product.
C) increasing marginal product.
D) increasing returns to capital.
E) a constant rate of depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider the following table that shows the total number of acres plowed per hour as a function of the number of tractors used is increased. Use this table to answer the next questions. 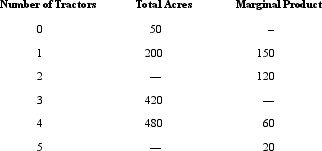
The total acres plowed when five tractors are used is:
A) 500.
B) 540.
C) 520.
D) 480.
E) 460.

The total acres plowed when five tractors are used is:
A) 500.
B) 540.
C) 520.
D) 480.
E) 460.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider the following table that shows the number of trucks owned by a delivery firm and the corresponding number of deliveries made. Use the table to answer the next questions. 
The marginal product of the third truck is:
A) 12 deliveries.
B) 6 deliveries.
C) 36 deliveries.
D) 15 deliveries.
E) 2 deliveries.

The marginal product of the third truck is:
A) 12 deliveries.
B) 6 deliveries.
C) 36 deliveries.
D) 15 deliveries.
E) 2 deliveries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the following production function to answer the next questions. 
This production function exhibits diminishing returns to capital for:
A) all units of capital after the first.
B) no units of capital.
C) all units of capital after the second.
D) all units of capital after the third.
E) all units of capital except the sixth.

This production function exhibits diminishing returns to capital for:
A) all units of capital after the first.
B) no units of capital.
C) all units of capital after the second.
D) all units of capital after the third.
E) all units of capital except the sixth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the following graph to answer the next questions. 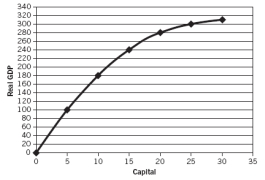
The marginal product of the 15th unit of capital is:
A) negative.
B) greater than the 10th unit.
C) the same as the 10th unit.
D) less than the 10th unit.
E) zero.

The marginal product of the 15th unit of capital is:
A) negative.
B) greater than the 10th unit.
C) the same as the 10th unit.
D) less than the 10th unit.
E) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider the following table that shows the number of trucks owned by a delivery firm and the corresponding number of deliveries made. Use the table to answer the next questions. 
When the firm bought their last truck, they found that the number of deliveries increased by 10. In this case, they must have just bought truck number:
A) five.
B) four.
C) three.
D) one.
E) two.

When the firm bought their last truck, they found that the number of deliveries increased by 10. In this case, they must have just bought truck number:
A) five.
B) four.
C) three.
D) one.
E) two.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When moving up along the production function, the marginal product of capital will:
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) first decrease and then increase.
D) first increase and then remain constant.
E) remain constant.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) first decrease and then increase.
D) first increase and then remain constant.
E) remain constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
There are diminishing returns to:
A) only human capital.
B) only physical capital.
C) only natural resources.
D) only human capital and physical capital.
E) human capital, physical capital, and natural resources.
A) only human capital.
B) only physical capital.
C) only natural resources.
D) only human capital and physical capital.
E) human capital, physical capital, and natural resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When the amount of physical capital is increased, then all else the same, the marginal product of capital will:
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) eventually decrease.
E) eventually increase.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) eventually decrease.
E) eventually increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the following graph to answer the next questions. 
The marginal product of the 5th unit of capital is ________ and the marginal product of the 10th unit is ________.
A) 100; 180
B) 100; 80
C) 10; 8
D) 20; 18
E) 20; 16

The marginal product of the 5th unit of capital is ________ and the marginal product of the 10th unit is ________.
A) 100; 180
B) 100; 80
C) 10; 8
D) 20; 18
E) 20; 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Use the following production function to answer the next questions. 
When the second unit of capital is hired, the marginal product is equal to:
A) 30.
B) 50.
C) 20.
D) 40.
E) 15.

When the second unit of capital is hired, the marginal product is equal to:
A) 30.
B) 50.
C) 20.
D) 40.
E) 15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The marginal product of an input is:
A) always positive.
B) never positive.
C) usually positive.
D) always decreasing.
E) always increasing.
A) always positive.
B) never positive.
C) usually positive.
D) always decreasing.
E) always increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Consider the following table that shows the number of trucks owned by a delivery firm and the corresponding number of deliveries made. Use the table to answer the next questions. 
Diminishing returns set in after the _________ truck is purchased.
A) first
B) second
C) third
D) fourth
E) fifth

Diminishing returns set in after the _________ truck is purchased.
A) first
B) second
C) third
D) fourth
E) fifth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
As additional units of an input are employed, the marginal product of the input is:
A) always increasing.
B) always decreasing.
C) constant.
D) eventually increasing.
E) eventually decreasing.
A) always increasing.
B) always decreasing.
C) constant.
D) eventually increasing.
E) eventually decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When firms buy new capital, it is called:
A) investment.
B) net investment.
C) depreciation.
D) a steady state.
E) an unstable state.
A) investment.
B) net investment.
C) depreciation.
D) a steady state.
E) an unstable state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
It is reasonable to expect that as the amount of physical capital is increased, the amount of output produced will:
A) increase at a constant rate.
B) increase at a diminishing rate.
C) increase at an increasing rate.
D) decrease.
E) be unaffected.
A) increase at a constant rate.
B) increase at a diminishing rate.
C) increase at an increasing rate.
D) decrease.
E) be unaffected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider the following table that shows the total number of acres plowed per hour as a function of the number of tractors used is increased. Use this table to answer the next questions. 
The total acres plowed when two tractors are used is:
A) 470.
B) 300.
C) 310.
D) 320.
E) 350.

The total acres plowed when two tractors are used is:
A) 470.
B) 300.
C) 310.
D) 320.
E) 350.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Consider the following table, which shows the total number of customers served per hour as the number of cash registers is increased. 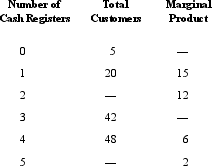 The marginal product of the third cash register is:
The marginal product of the third cash register is:
A) 42.
B) 6.
C) 12.
D) 9.
E) 10.
 The marginal product of the third cash register is:
The marginal product of the third cash register is:A) 42.
B) 6.
C) 12.
D) 9.
E) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Use the following production function to answer the next questions. 
How many units of capital should be produced in order to achieve the steady state?
A) 6
B) 5
C) 4
D) 3
E) There is not enough information to answer this question.

How many units of capital should be produced in order to achieve the steady state?
A) 6
B) 5
C) 4
D) 3
E) There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
As a nation approaches its steady state, the returns to capital _________ and the growth of real gross domestic product (GDP) _________.
A) increase; increases
B) decrease; slows down
C) increase; slows down
D) decrease; increases
E) remain unchanged; remains unchanged
A) increase; increases
B) decrease; slows down
C) increase; slows down
D) decrease; increases
E) remain unchanged; remains unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose a major hurricane hits the eastern coast of Florida and only destroys significant amounts of physical capital. All else the same, in the short run, real gross domestic product (GDP) will _________, and in the long run, real GDP will _________.
A) decline; be permanently lower
B) decline; return to the steady state level
C) be unchanged; decline
D) increase; decrease
E) decline; end up higher than the original level
A) decline; be permanently lower
B) decline; return to the steady state level
C) be unchanged; decline
D) increase; decrease
E) decline; end up higher than the original level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If an economy is in the steady state, then:
A) net investment is zero.
B) depreciation is zero.
C) investment is zero.
D) the marginal product of capital is zero.
E) there are no diminishing returns.
A) net investment is zero.
B) depreciation is zero.
C) investment is zero.
D) the marginal product of capital is zero.
E) there are no diminishing returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Suppose a major hurricane hits the eastern coast of Florida and only destroys significant amounts of physical capital. In the long run, you would expect that:
A) the production function will have shifted upward.
B) the production function will have shifted downward.
C) the production function will have shifted back to its original position after having shifted downward in the short run.
D) there has been a permanent downward movement along the production function.
E) there has been no effect on the production function and real gross domestic product (GDP) returns to the steady state level.
A) the production function will have shifted upward.
B) the production function will have shifted downward.
C) the production function will have shifted back to its original position after having shifted downward in the short run.
D) there has been a permanent downward movement along the production function.
E) there has been no effect on the production function and real gross domestic product (GDP) returns to the steady state level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
An economy is in a steady state if:
A) depreciation is zero.
B) investment is zero.
C) net investment is positive.
D) capital and output are not changing.
E) there are diminishing returns.
A) depreciation is zero.
B) investment is zero.
C) net investment is positive.
D) capital and output are not changing.
E) there are diminishing returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A firm has 100 computers, and each year 5 of them become obsolete and must be recycled. This firm is in a steady state if investment each year is equal to:
A) 0.
B) 5.
C) 1.
D) 100.
E) 95.
A) 0.
B) 5.
C) 1.
D) 100.
E) 95.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose that in the economy the level of capital is 500 units, the depreciation rate is 4%, and the level of investment is 20 units. In this case:
A) net investment is negative.
B) net investment is positive.
C) the level of output will decrease.
D) the level of capital will increase.
E) the economy is in a steady state.
A) net investment is negative.
B) net investment is positive.
C) the level of output will decrease.
D) the level of capital will increase.
E) the economy is in a steady state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Depreciation is:
A) the wearing out of capital over time.
B) the reduction of investment over time.
C) the decline of output over time.
D) the tendency of economies to converge to the same output level.
E) what happens when technology does not advance.
A) the wearing out of capital over time.
B) the reduction of investment over time.
C) the decline of output over time.
D) the tendency of economies to converge to the same output level.
E) what happens when technology does not advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A firm has 50 computers. Every year, they buy 3 new ones and get rid of 3 old ones. In this case, investment is equal to _________ and net investment is equal to _________.
A) 3; 3
B) 3; 0
C) 3; −3
D) 6; 3
E) 3; 6
A) 3; 3
B) 3; 0
C) 3; −3
D) 6; 3
E) 3; 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose that the level of capital in the economy is 100 units, the depreciation rate is 5%, and investment is equal to 10 units. In this case:
A) the level of capital will increase.
B) the economy is in a steady state.
C) the level of capital will decrease.
D) the level of output will decrease.
E) investment is less than net investment.
A) the level of capital will increase.
B) the economy is in a steady state.
C) the level of capital will decrease.
D) the level of output will decrease.
E) investment is less than net investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The economy tends to approach a steady state because:
A) there is a shortage of skilled workers.
B) people run out of new ideas.
C) there are diminishing returns.
D) government policies inhibit further growth.
E) there is depreciation.
A) there is a shortage of skilled workers.
B) people run out of new ideas.
C) there are diminishing returns.
D) government policies inhibit further growth.
E) there is depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A lawn service company has 20 lawn mowers. This year they buy 3 new ones and get rid of 2 old ones. In this case, investment is equal to _________ and net investment is equal to _________.
A) 3; 3
B) 3; 1
C) 3; 2
D) 5; 3
E) 3; 5
A) 3; 3
B) 3; 1
C) 3; 2
D) 5; 3
E) 3; 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A firm has a total of 25 workstations in four different office buildings. This year they build 3 new workstations and get rid of 5 old ones. In this case, investment is equal to _________ and net investment is equal to _________.
A) 3; 5
B) 3; −2
C) 3; 2
D) 5; 3
E) 2; −2
A) 3; 5
B) 3; −2
C) 3; 2
D) 5; 3
E) 2; −2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When the value of a resource declines over time, this is known as:
A) depreciation.
B) the steady state.
C) diminishing returns.
D) diminishing marginal product.
E) net loss.
A) depreciation.
B) the steady state.
C) diminishing returns.
D) diminishing marginal product.
E) net loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
As a country approaches the steady state, the returns to capital _________.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) turn negative.
D) become equal to zero.
E) are unaffected.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) turn negative.
D) become equal to zero.
E) are unaffected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A company has three delivery trucks. Each month the trucks require repairs to keep them in good working order. Which of the following is true?
A) Investment is equal to zero.
B) Net investment is equal to zero.
C) The company is not in a steady state.
D) Capital is increasing.
E) Capital is decreasing.
A) Investment is equal to zero.
B) Net investment is equal to zero.
C) The company is not in a steady state.
D) Capital is increasing.
E) Capital is decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
According to the Solow growth model, advanced economies with large stocks of capital will:
A) eventually stop growing.
B) continue to grow at a constant rate.
C) always have levels of real gross domestic product (GDP) that are higher than the less advanced economies.
D) all converge to the same level of real GDP.
E) never reach a steady state.
A) eventually stop growing.
B) continue to grow at a constant rate.
C) always have levels of real gross domestic product (GDP) that are higher than the less advanced economies.
D) all converge to the same level of real GDP.
E) never reach a steady state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
An economy is in the steady state if:
A) investment equals depreciation.
B) investment equals zero.
C) net investment equals depreciation.
D) capital grows at a constant rate.
E) there are no diminishing returns.
A) investment equals depreciation.
B) investment equals zero.
C) net investment equals depreciation.
D) capital grows at a constant rate.
E) there are no diminishing returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When _________ units of capital are purchased, the marginal product will _________.
A) more; increase
B) more; not change
C) more; decrease
D) fewer; decrease
E) fewer; not change
A) more; increase
B) more; not change
C) more; decrease
D) fewer; decrease
E) fewer; not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When a firm buys a new computer _________ increases, and when the firm gets rid of old computers _________ decreases.
A) investment; investment
B) net investment; net investment
C) capital; capital
D) investment; depreciation
E) depreciation; investment
A) investment; investment
B) net investment; net investment
C) capital; capital
D) investment; depreciation
E) depreciation; investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



