Deck 21: Evaluation of Portfolio Performance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Evaluation of Portfolio Performance
1
The portfolios identified below are being considered for investment. During the period under consideration Rf = 0.03. 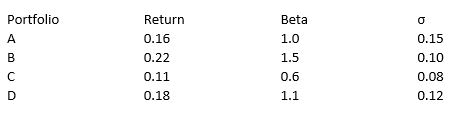
Using the Sharpe Measure, which portfolio performed best?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Two portfolios are tied

Using the Sharpe Measure, which portfolio performed best?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Two portfolios are tied
B
2
Information ratio portfolio performance measures
A) adjust portfolio risk to match benchmark risk.
B) compare portfolio returns to expected returns under CAPM.
C) evaluate portfolio performance on the basis of return per unit of risk.
D) indicate historic average differential return per unit of historic variability of differential return.
E) none of the above.
A) adjust portfolio risk to match benchmark risk.
B) compare portfolio returns to expected returns under CAPM.
C) evaluate portfolio performance on the basis of return per unit of risk.
D) indicate historic average differential return per unit of historic variability of differential return.
E) none of the above.
D
3
Portfolio managers who anticipate an increase in interest rates should
A) Act to keep the duration constant.
B) Decrease the portfolio duration.
C) Increase the portfolio duration.
D) Assume higher risk in the market.
E) Invest in junk bonds.
A) Act to keep the duration constant.
B) Decrease the portfolio duration.
C) Increase the portfolio duration.
D) Assume higher risk in the market.
E) Invest in junk bonds.
B
4
In the Characteristic Selectivity (CS) performance measure,
A) portfolio performance is measured by assessing the quality of services provided by money managers by looking at adjustments made to the content of their portfolios.
B) portfolio performance is measured by examining both unsystematic and systematic risk.
C) portfolio performance is measured by comparing the returns of each stock in the portfolio to the return of a benchmark portfolio. With the same aggregate investment characteristics as the security in question.
D) portfolio performance is measured on the basis of return per unit of risk.
E) portfolio performance is measured on the basis of historic average differential return per unit of historic variability of differential return.
A) portfolio performance is measured by assessing the quality of services provided by money managers by looking at adjustments made to the content of their portfolios.
B) portfolio performance is measured by examining both unsystematic and systematic risk.
C) portfolio performance is measured by comparing the returns of each stock in the portfolio to the return of a benchmark portfolio. With the same aggregate investment characteristics as the security in question.
D) portfolio performance is measured on the basis of return per unit of risk.
E) portfolio performance is measured on the basis of historic average differential return per unit of historic variability of differential return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The measure of performance which divides the portfolio's risk premium by the portfolio's beta is the
A) Sharpe measure.
B) Jensen measure.
C) Fama measure.
D) alternative components model (MCV).
E) Treynor measure.
A) Sharpe measure.
B) Jensen measure.
C) Fama measure.
D) alternative components model (MCV).
E) Treynor measure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
For a poorly diversified portfolio the appropriate measure of portfolio performance would be
A) the Treynor measure because it evaluates portfolio performance on the basis of return and diversification.
B) the Sharpe measure because it evaluates portfolio performance on the basis of return and diversification.
C) the Treynor measure because it uses standard deviation as the risk measure.
D) the Sharpe measure because it uses beta as the risk measure.
E) none of the above.
A) the Treynor measure because it evaluates portfolio performance on the basis of return and diversification.
B) the Sharpe measure because it evaluates portfolio performance on the basis of return and diversification.
C) the Treynor measure because it uses standard deviation as the risk measure.
D) the Sharpe measure because it uses beta as the risk measure.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A portfolio's gross selectivity is made up of
A) Manager's risk.
B) net selectivity.
C) diversification.
D) a and b.
E) b and c.
A) Manager's risk.
B) net selectivity.
C) diversification.
D) a and b.
E) b and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The cost of active management is the coefficient σER and it is sometimes referred to as
A) market timing.
B) reward for risk.
C) excess reward.
D) excess risk.
E) tracking error.
A) market timing.
B) reward for risk.
C) excess reward.
D) excess risk.
E) tracking error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the evaluation of bond portfolio performance, the policy effect refers to
A) the difference in portfolio duration and index duration.
B) the extra return attributable to acquiring bonds that are temporarily mispriced relative to risk.
C) short-run changes in the portfolio during a specific period.
D) the differential return from changing duration of the portfolio during a specific period.
E) none of the above.
A) the difference in portfolio duration and index duration.
B) the extra return attributable to acquiring bonds that are temporarily mispriced relative to risk.
C) short-run changes in the portfolio during a specific period.
D) the differential return from changing duration of the portfolio during a specific period.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Under the performance attribution analysis method, the ____ measures the manager's ability to form specific market segment portfolios that generate superior returns relative to the way in which the comparable market segment is defined in the benchmark portfolio weighted by the manager's actual market segment investment proportions.
A) selection effect
B) allocation effect
C) distribution effect
D) diversification effect
E) attribution effect
A) selection effect
B) allocation effect
C) distribution effect
D) diversification effect
E) attribution effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements concerning performance measures is false?
A) The Sharpe measure examines both unsystematic and systematic risk.
B) The Treynor measure examines systematic risk.
C) The Jensen measure examines systematic risk.
D) All three measures examine both unsystematic and systematic risk.
E) None of the above (that is, all statements are true).
A) The Sharpe measure examines both unsystematic and systematic risk.
B) The Treynor measure examines systematic risk.
C) The Jensen measure examines systematic risk.
D) All three measures examine both unsystematic and systematic risk.
E) None of the above (that is, all statements are true).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consider the data presented below on three mutual funds and the market. 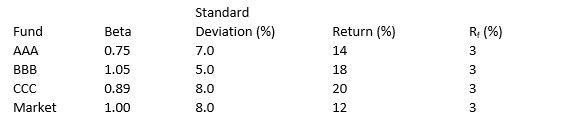 Compute the Sharpe Measure for the AAA fund.
Compute the Sharpe Measure for the AAA fund.
A) 4.49
B) 2.74
C) 1.57
D) 1.70
E) 1.27
 Compute the Sharpe Measure for the AAA fund.
Compute the Sharpe Measure for the AAA fund.A) 4.49
B) 2.74
C) 1.57
D) 1.70
E) 1.27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Sharpe's performance measure divides the portfolio's risk premium by the
A) standard deviation of the rate of return.
B) variance of the rate of return.
C) slope of the fund's characteristic line.
D) beta.
E) risk free rate.
A) standard deviation of the rate of return.
B) variance of the rate of return.
C) slope of the fund's characteristic line.
D) beta.
E) risk free rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose the expected return for the market portfolio and risk-free rate are 13% and 3% respectively. Stocks A, B, and C have Treynor measures of 0.24, 0.16, and 0.11, respectively. Based on this information an investor should
A) buy stocks A, B and C.
B) buy stocks A and B and sell stock C.
C) buy stock A and sell stocks B and C.
D) sell stocks A, B and C.
E) hold stocks A, B and C.
A) buy stocks A, B and C.
B) buy stocks A and B and sell stock C.
C) buy stock A and sell stocks B and C.
D) sell stocks A, B and C.
E) hold stocks A, B and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Portfolio managers are often evaluated using a boxplot of returns for a universe of investors over a specific period of time which is known as a(n)
A) return adjusted comparison
B) efficient frontier comparison
C) time plot comparison
D) peer group comparison
E) none of the above
A) return adjusted comparison
B) efficient frontier comparison
C) time plot comparison
D) peer group comparison
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



