Deck 19: Option Contracts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Option Contracts
1
A foreign currency option contract traded on US exchanges allows for the sale or purchase of a set amount of
A) US currency at a floating exchange rate.
B) US currency at a fixed exchange rate.
C) foreign currency at a floating exchange rate.
D) foreign currency at a fixed exchange rate.
E) none of the above.
A) US currency at a floating exchange rate.
B) US currency at a fixed exchange rate.
C) foreign currency at a floating exchange rate.
D) foreign currency at a fixed exchange rate.
E) none of the above.
D
2
The value of a call option is positively related to
A) underlying stock price.
B) time to expiration
C) exercise price.
D) a and b
E) b and c
A) underlying stock price.
B) time to expiration
C) exercise price.
D) a and b
E) b and c
D
3
Consider the following information on put and call options for Abel Group 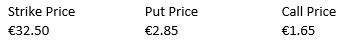 Calculate the net value of a protective put position at a stock price at expiration of €20, and a stock price at expiration of €45.
Calculate the net value of a protective put position at a stock price at expiration of €20, and a stock price at expiration of €45.
A) €6.35, €18.85
B) €29.65, €42.15
C) €21.65, €34.15
D) €8, €8
E) −€8, −€8
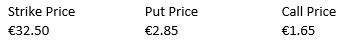 Calculate the net value of a protective put position at a stock price at expiration of €20, and a stock price at expiration of €45.
Calculate the net value of a protective put position at a stock price at expiration of €20, and a stock price at expiration of €45.A) €6.35, €18.85
B) €29.65, €42.15
C) €21.65, €34.15
D) €8, €8
E) −€8, −€8
B
4
A vertical spread involves buying and selling call options in the same stock with
A) a different time period but same price.
B) a different time period and different price.
C) the same time period and price.
D) the same time period but different price.
E) options in different markets.
A) a different time period but same price.
B) a different time period and different price.
C) the same time period and price.
D) the same time period but different price.
E) options in different markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Refer to the previous question. Calculate the price of the put option.
A) €1.086
B) €0.862
C) €6.234
D) €0.623
E) €2.317
A) €1.086
B) €0.862
C) €6.234
D) €0.623
E) €2.317

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the Black-Scholes model N(d1) represents the
A) hedge ratio.
B) partial derivative of the call's value with respect to the stock price.
C) change in the option's value given a one dollar change in the underlying security's price.
D) Option's delta.
E) all of the above.
A) hedge ratio.
B) partial derivative of the call's value with respect to the stock price.
C) change in the option's value given a one dollar change in the underlying security's price.
D) Option's delta.
E) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the Black-Scholes option pricing model, an increase in security price (S) will cause
A) an increase in call value and an increase in put value.
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.
A) an increase in call value and an increase in put value.
B) an increase in call value and a decrease in put value.
C) a decrease in call value and an increase in put value.
D) a decrease in call value and a decrease in put value.
E) an increase in call value and an increase or decrease in put value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A stock currently trades for €130 per share. Options on the stock are available with a strike price of €125. The options expire in 10 days. The risk free rate is 3% over this time period, and the expected volatility is 0.35. Use the Black-Scholes option pricing model to calculate the price of a call option.
A) €5.19
B) €4.35
C) €3.93
D) €6.19
E) €8.17
A) €5.19
B) €4.35
C) €3.93
D) €6.19
E) €8.17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a money spread, an investor would
A) Buy two out-of-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
B) Buy two in-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
C) Sell two out-of-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
D) Sell two in-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
E) Sell an out-of-the-money call and purchase an in-the-money call on the same stock with the same exercise date.
A) Buy two out-of-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
B) Buy two in-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
C) Sell two out-of-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
D) Sell two in-the-money call options on the same stock with different exercise dates.
E) Sell an out-of-the-money call and purchase an in-the-money call on the same stock with the same exercise date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Assume that you have just sold a stock for a loss at a price of £75, for tax purposes. You still wish to maintain exposure to the sold stock. Suppose that you buy a call with a strike price of £70 and a price of £6.75. Calculate the effective price paid to repurchase the stock if the price after 35 days is £65.
A) £71.75
B) £76.75
C) £58.25
D) £81.75
E) None of the above
A) £71.75
B) £76.75
C) £58.25
D) £81.75
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If you were to purchase an October option with an exercise price of 50 for 8 and simultaneously sell an October option with an exercise price of 60 for 2, you would be
A) bullish and taking a high risk.
B) bullish and conservative.
C) bearish and taking a high risk.
D) bearish and conservative.
E) neutral.
A) bullish and taking a high risk.
B) bullish and conservative.
C) bearish and taking a high risk.
D) bearish and conservative.
E) neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Black-Scholes model assumes that stock price movements can be described by
A) geometric moving averages.
B) arithmetic moving averages.
C) regression towards the mean.
D) geometric Brownian motion.
E) stochastic time lags.
A) geometric moving averages.
B) arithmetic moving averages.
C) regression towards the mean.
D) geometric Brownian motion.
E) stochastic time lags.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the hedge ratio is 0.50, this indicates that the portfolio should hold
A) two shares of stock for every call option written.
B) one share of stock for every two call options written.
C) two shares of stock for every call option purchased.
D) one share of stock for every two call options purchased.
E) two call options for every put option written.
A) two shares of stock for every call option written.
B) one share of stock for every two call options written.
C) two shares of stock for every call option purchased.
D) one share of stock for every two call options purchased.
E) two call options for every put option written.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A calendar spread requires the purchase and sale of two calls or two puts in the same stock with
A) the same expiration date but different exercise prices.
B) the same exercise price but different expiration dates.
C) different exercise prices and different expiration dates.
D) the same exercise price and the same expiration month.
E) traded in different markets.
A) the same expiration date but different exercise prices.
B) the same exercise price but different expiration dates.
C) different exercise prices and different expiration dates.
D) the same exercise price and the same expiration month.
E) traded in different markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Options on futures contracts are very popular because
A) they require the holder to purchase at a future date.
B) of their ability to create leverage.
C) the seller of the futures contract is under no obligation.
D) the amount of the underlying commodity is negotiable.
E) none of the above.
A) they require the holder to purchase at a future date.
B) of their ability to create leverage.
C) the seller of the futures contract is under no obligation.
D) the amount of the underlying commodity is negotiable.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



