Deck 15: Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
1
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s).
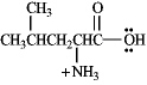
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 1.50.
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 1.50.
2
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s).
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. How many possible stereoisomers of leucine are there?
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. How many possible stereoisomers of leucine are there?
Since leucine has one chirality center, there are 21, or 2 possible leucine stereoisomers.
3
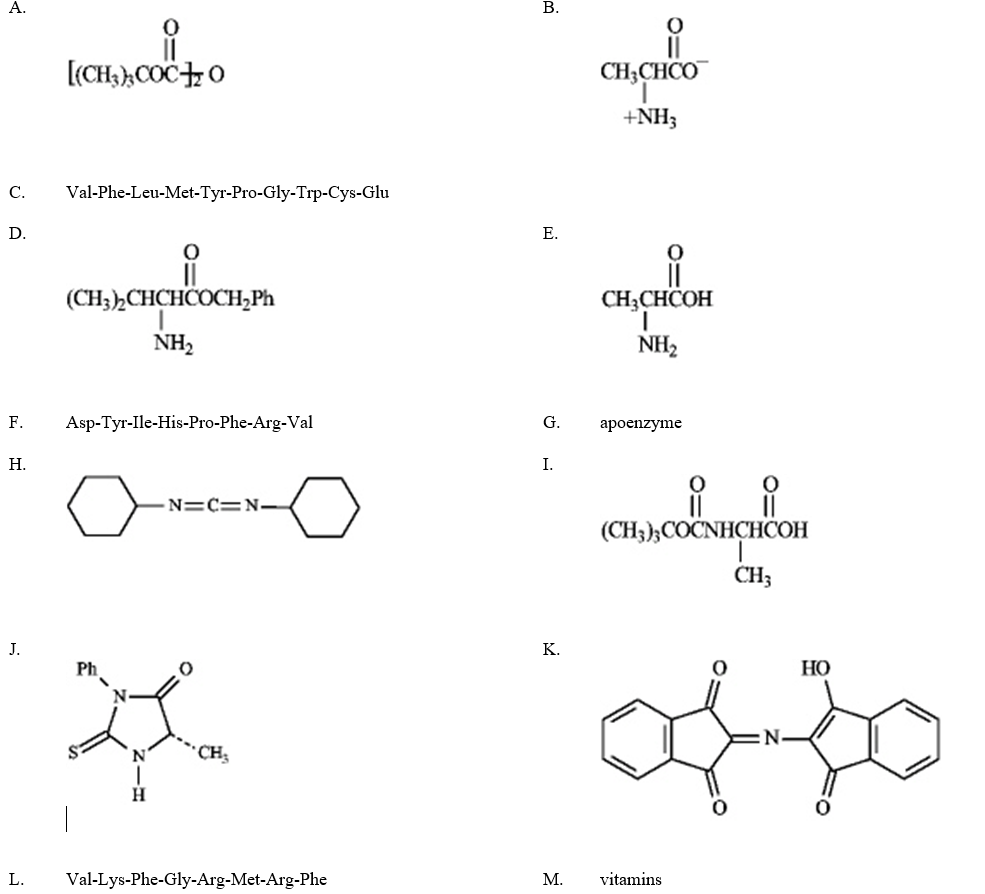
Instructions: Match a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.


4
Instructions: Consider the following structure. Based on this structure answer the following question(s). 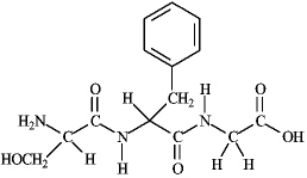 Refer to instructions. How many other peptides could be formed from this same combination of amino acids?
Refer to instructions. How many other peptides could be formed from this same combination of amino acids?
A) 3
B) 6
C) 9
D) 12
 Refer to instructions. How many other peptides could be formed from this same combination of amino acids?
Refer to instructions. How many other peptides could be formed from this same combination of amino acids?A) 3
B) 6
C) 9
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s).
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. Draw the condensed structure for leucine, and label all chirality centers with an asterisk and identify the amine as primary, secondary or tertiary.
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. Draw the condensed structure for leucine, and label all chirality centers with an asterisk and identify the amine as primary, secondary or tertiary.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Instructions: Consider the following structure. Based on this structure answer the following question(s). 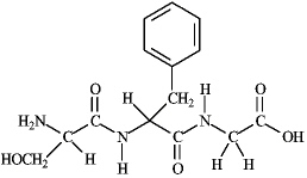 Refer to instructions. Circle the peptide bonds.
Refer to instructions. Circle the peptide bonds.
 Refer to instructions. Circle the peptide bonds.
Refer to instructions. Circle the peptide bonds.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question.
 Refer to inatructions. The most acidic amino acid is ____.
Refer to inatructions. The most acidic amino acid is ____.
 Refer to inatructions. The most acidic amino acid is ____.
Refer to inatructions. The most acidic amino acid is ____.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s).
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. What is the pI of leucine?
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. What is the pI of leucine?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s).
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. Draw a Fischer projection of L-leucine and label the chirality center(s) as R or S.
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. Draw a Fischer projection of L-leucine and label the chirality center(s) as R or S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Instructions: Consider the following structure. Based on this structure answer the following question(s). 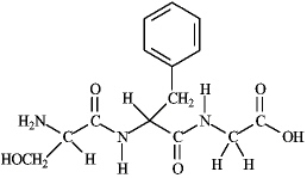 Refer to instructions. Name the peptide using both the three-letter and one-letter codes.
Refer to instructions. Name the peptide using both the three-letter and one-letter codes.
 Refer to instructions. Name the peptide using both the three-letter and one-letter codes.
Refer to instructions. Name the peptide using both the three-letter and one-letter codes.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s).
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. Leucine is described as an essential amino acid. What does this mean?
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. Leucine is described as an essential amino acid. What does this mean?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following amino acids would contain the highest concentration of zwitterions at pH 5.90?
A) aspartic acid (pI 2.77)
B) alanine (pI 6.01)
C) lysine (pI 9.74)
D) glutamic acid (pI 3.22)
E) all of these contain approximately equal concentrations of zwitterions
A) aspartic acid (pI 2.77)
B) alanine (pI 6.01)
C) lysine (pI 9.74)
D) glutamic acid (pI 3.22)
E) all of these contain approximately equal concentrations of zwitterions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s).
Porcine dynorphin is a neuropeptide having 17 amino acid residues. Its structure is shown below.
Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Ile-Arg-Pro-Lys-Leu-Lys-Trp-Asp-Asn-Gln
Refer to instructions. What fragments would result if dynorphin were cleaved by chymotropsin?
Porcine dynorphin is a neuropeptide having 17 amino acid residues. Its structure is shown below.
Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Ile-Arg-Pro-Lys-Leu-Lys-Trp-Asp-Asn-Gln
Refer to instructions. What fragments would result if dynorphin were cleaved by chymotropsin?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s).
Porcine dynorphin is a neuropeptide having 17 amino acid residues. Its structure is shown below.
Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Ile-Arg-Pro-Lys-Leu-Lys-Trp-Asp-Asn-Gln
Refer to instructions. What fragments would result if dynorphin were cleaved by trypsin?
Porcine dynorphin is a neuropeptide having 17 amino acid residues. Its structure is shown below.
Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Ile-Arg-Pro-Lys-Leu-Lys-Trp-Asp-Asn-Gln
Refer to instructions. What fragments would result if dynorphin were cleaved by trypsin?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Write the equation for the reaction, using methanol (CH3OH), that would render the carboxyl group of alanine unreactive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question.
 Refer to instructions. The most basic amino acid is __________.
Refer to instructions. The most basic amino acid is __________.
 Refer to instructions. The most basic amino acid is __________.
Refer to instructions. The most basic amino acid is __________.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Define isoelectric point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question.
 Refer to instructions. At what pH would you carry out an electrophoresis experiment if you wanted to separate a mixture of lysine, aspartic acid and phenylalanine? Explain.
Refer to instructions. At what pH would you carry out an electrophoresis experiment if you wanted to separate a mixture of lysine, aspartic acid and phenylalanine? Explain.
 Refer to instructions. At what pH would you carry out an electrophoresis experiment if you wanted to separate a mixture of lysine, aspartic acid and phenylalanine? Explain.
Refer to instructions. At what pH would you carry out an electrophoresis experiment if you wanted to separate a mixture of lysine, aspartic acid and phenylalanine? Explain.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Instructions: Consider the following structure. Based on this structure answer the following question(s). 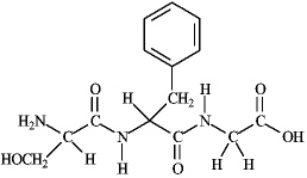 Refer to instructions. Identify the C-terminal amino acid and the N-terminal amino acid.
Refer to instructions. Identify the C-terminal amino acid and the N-terminal amino acid.
 Refer to instructions. Identify the C-terminal amino acid and the N-terminal amino acid.
Refer to instructions. Identify the C-terminal amino acid and the N-terminal amino acid.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Instructions: Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s).
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 10.00.
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to instructions. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 10.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following reagents can be used to cleave a tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) protecting group from a peptide?
A) H2/Pd
B) CF3CO2H
C) Na2CO3, H2O
D) LiAlH4
A) H2/Pd
B) CF3CO2H
C) Na2CO3, H2O
D) LiAlH4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What are the R/S designations of the two stereocenters of L-threonine? 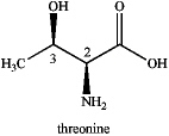
A) 2R,3R
B) 2R,3S
C) 2S,3R
D) 2S,3S

A) 2R,3R
B) 2R,3S
C) 2S,3R
D) 2S,3S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Show the steps involved in a synthesis of F-G-I using the Merrifield procedure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
BOC protecting groups are generally removed by treatment with trifluoroacetic acid. 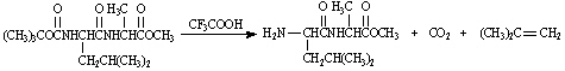 On the structures provided below, draw arrows consistent with electron flow in the mechanism of this reaction.
On the structures provided below, draw arrows consistent with electron flow in the mechanism of this reaction. 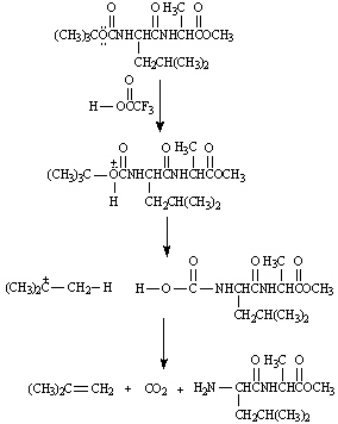
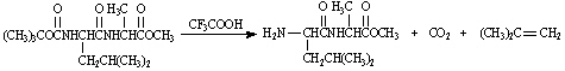 On the structures provided below, draw arrows consistent with electron flow in the mechanism of this reaction.
On the structures provided below, draw arrows consistent with electron flow in the mechanism of this reaction. 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
To what structural feature does the term "tertiary structure" refer?
A) the sequence of amino acids in proteins
B) the overall folding pattern of proteins
C) the aggregation of polypeptides
D) the conformation of local regions of polypeptides
A) the sequence of amino acids in proteins
B) the overall folding pattern of proteins
C) the aggregation of polypeptides
D) the conformation of local regions of polypeptides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following amino acids is a secondary amine?
A) proline
B) glutamine
C) histidine
D) aspargine
A) proline
B) glutamine
C) histidine
D) aspargine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following amino acids has a non-polar side chain?
A) histidine
B) arginine
C) glutamine
D) valine
A) histidine
B) arginine
C) glutamine
D) valine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
To what structural feature does the term "secondary structure" refer?
A) the sequence of amino acids in proteins
B) the overall folding pattern of proteins
C) the aggregation of polypeptides
D) the conformation of local regions of polypeptides
A) the sequence of amino acids in proteins
B) the overall folding pattern of proteins
C) the aggregation of polypeptides
D) the conformation of local regions of polypeptides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following tripeptides is not hydrolysed by chymotrypsin?
A) Phe-Lys-Glu
B) Lys-Tyr-Phe
C) Gln-Ser-Phe
D) Gln-Tyr-Ser
A) Phe-Lys-Glu
B) Lys-Tyr-Phe
C) Gln-Ser-Phe
D) Gln-Tyr-Ser

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Instructions: Match a term from the list below to each definition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following tripeptides is not hydrolysed by trypsin?
A) Glu-Arg-Ser
B) Arg-Glu-Thr
C) Glu-Ser-Arg
D) Lys-Ser-Arg
A) Glu-Arg-Ser
B) Arg-Glu-Thr
C) Glu-Ser-Arg
D) Lys-Ser-Arg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following amino acids migrates to the negative electrode on paper electrophoresis at a pH of 7.0?
A) lysine
B) aspartic acid
C) asparagine
D) glutamic acid
A) lysine
B) aspartic acid
C) asparagine
D) glutamic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Refer to the data below to answer the following questions:
The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids:
Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val2
Refer to instructions. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments:
Tyr-Val-His
Sar-Arg-Val
His-Pro-Ala
Val-Tyr-Val
Arg-Val-Tyr
What is the structure of saralasin?
Sar-Arg-Val
Arg-Val-Tyr
Val-Tyr-Val
Tyr-Val-His
His-Pro-Ala
The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids:
Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val2
Refer to instructions. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments:
Tyr-Val-His
Sar-Arg-Val
His-Pro-Ala
Val-Tyr-Val
Arg-Val-Tyr
What is the structure of saralasin?
Sar-Arg-Val
Arg-Val-Tyr
Val-Tyr-Val
Tyr-Val-His
His-Pro-Ala

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An enzyme classified as a ligase would be associated with a reaction than involves the:
A) introduction of a double bond.
B) loss of water.
C) loss of carbon dioxide.
D) transfer of an amino group.
E) hydrolysis of an ester.
A) introduction of a double bond.
B) loss of water.
C) loss of carbon dioxide.
D) transfer of an amino group.
E) hydrolysis of an ester.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
To what structural feature does the term "primary structure" refer?
A) the sequence of amino acids in proteins
B) the overall folding pattern of proteins
C) the aggregation of polypeptides
D) the conformation of local regions of polypeptides
A) the sequence of amino acids in proteins
B) the overall folding pattern of proteins
C) the aggregation of polypeptides
D) the conformation of local regions of polypeptides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following amino acids has an aromatic side chain?
A) isoleucine
B) valine
C) tyrosine
D) threonine
A) isoleucine
B) valine
C) tyrosine
D) threonine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the data below to answer the following questions:
The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids:
Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val2
Refer to instructions. Sar is the mnemonic for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine.
The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids:
Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val2
Refer to instructions. Sar is the mnemonic for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following amino acids migrates to the positive electrode on paper electrophoresis at a pH of 7.0?
A) glutamic acid
B) arginine
C) lysine
D) histadine
A) glutamic acid
B) arginine
C) lysine
D) histadine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following amino acids has a sulfur-containing side chain?
A) serine
B) cysteine
C) lysine
D) methionine
E) both b and d
A) serine
B) cysteine
C) lysine
D) methionine
E) both b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
To what structural feature does the term "quaternary structure" refer?
A) the sequence of amino acids in proteins
B) the overall folding pattern of proteins
C) the aggregation of polypeptides
D) the conformation of local regions of polypeptides
A) the sequence of amino acids in proteins
B) the overall folding pattern of proteins
C) the aggregation of polypeptides
D) the conformation of local regions of polypeptides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



