Deck 19: Electrochemistry and the Quest for Clean Energy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/103
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Electrochemistry and the Quest for Clean Energy
1
You have a job as a summer intern in an orange juice processing plant. Part of your job is to determine the amount of vitamin C in a given quantity of orange juice. To make this determination, you titrate the orange juice with I3-, the triiodide ion. To make sure you know what you are doing, your supervisor asks you how many electrons are transferred in the reaction. The reaction describing the titration is given below. What is your response? ascorbate + H2O + I3- dehydroascorbate + 2H+ + 3I-
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 0
E) It is impossible to tell.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 0
E) It is impossible to tell.
2
2
In the smelting of iron from iron oxide according to the equation Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) + 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
What is the change in oxidation number for iron?
A) +3
B) -3
C) +2
D) -2
E) 0
What is the change in oxidation number for iron?
A) +3
B) -3
C) +2
D) -2
E) 0
-3
3
Proteins containing a certain functional group (identified as RSH) can be titrated with triiodide ion to produce another functional group (identified as RSSR). The reaction equation is given below. What is oxidized and what is reduced in this reaction? 2RSH + I3- 3I- + RSSR + 2H+
A) RSH is oxidized, I3- is reduced.
B) RSH is reduced, I is oxidized.
C) Both RSH and I are oxidized.
D) Both RSH and I are reduced.
E) This reaction is not oxidation-reduction.
A) RSH is oxidized, I3- is reduced.
B) RSH is reduced, I is oxidized.
C) Both RSH and I are oxidized.
D) Both RSH and I are reduced.
E) This reaction is not oxidation-reduction.
RSH is oxidized, I3- is reduced.
4
This is a true story; can you explain what happened? Prior to a really important dinner party, the hostess discovered that her silverware was very tarnished. She needed a quick fix. She remembered reading that the tarnish (Ag2S) would be removed if you immersed the silverware in a hot solution of baking soda (NaHCO3) in a pan lined with aluminum foil. So she did, and so it was, but she noticed a bit of a rotten egg smell (H2S) being produced. Which one of the following statements cannot represent what might have been happening? Metal/Metal ion
E silver/silver(I)0.799
silver/silver(I)0.799
Aluminum/aluminum(III)-1.677
A) Al Al3+ + 3e-
B) Ag+ + e- Ag
C) 2HCO3- +S2- H2S + 2CO32-
D) HCO3- +S2- HS- + CO32-
E) 2HCO3- +Ag2S H2S + 2CO32- + 2Ag
E
 silver/silver(I)0.799
silver/silver(I)0.799Aluminum/aluminum(III)-1.677
A) Al Al3+ + 3e-
B) Ag+ + e- Ag
C) 2HCO3- +S2- H2S + 2CO32-
D) HCO3- +S2- HS- + CO32-
E) 2HCO3- +Ag2S H2S + 2CO32- + 2Ag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
This is a true story; can you explain what happened? Prior to a really important dinner party, the hostess discovered that her silverware was very tarnished. She needed a quick fix. She remembered reading that the tarnish (Ag2S) would be removed if you immersed the silverware in a hot solution of backing soda (NaHCO3) in a pan lined with aluminum foil. So she did, and so it was, but she noticed a bit of a rotten egg smell (H2S) being produced. Metal/Metal ion
E silver/silver(I)0.799
silver/silver(I)0.799
Aluminum/aluminum(III)-1.677
A) Aluminum ions react with S2-, form an aluminum sulfide precipitate, and gaseous carbon dioxide is released.
B) Silver ions in the presence of the baking soda, (NaHCO3), oxidize the sulfide to elemental sulfur that attacks the aluminum foil, which produces the smelly aluminum sulfide.
C) The aluminum acts as a reducing agent for the silver(I) in the silver sulfide; then the bicarbonate ion protonates the sulfide ion that is released.
D) Aluminum is plated onto the silver surface, making it shiny again, and then the reaction of the bicarbonate with the aluminum oxide releases CO2.
E) Silver in Ag2S reduces the aluminum, becomes metallic silver in the process, and releases hydrogen sulfide, H2S.
E
 silver/silver(I)0.799
silver/silver(I)0.799Aluminum/aluminum(III)-1.677
A) Aluminum ions react with S2-, form an aluminum sulfide precipitate, and gaseous carbon dioxide is released.
B) Silver ions in the presence of the baking soda, (NaHCO3), oxidize the sulfide to elemental sulfur that attacks the aluminum foil, which produces the smelly aluminum sulfide.
C) The aluminum acts as a reducing agent for the silver(I) in the silver sulfide; then the bicarbonate ion protonates the sulfide ion that is released.
D) Aluminum is plated onto the silver surface, making it shiny again, and then the reaction of the bicarbonate with the aluminum oxide releases CO2.
E) Silver in Ag2S reduces the aluminum, becomes metallic silver in the process, and releases hydrogen sulfide, H2S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Reduction is the __________
A) gain of electrons.
B) loss of electrons.
C) gain of protons.
D) loss of protons.
E) loss of mass.
A) gain of electrons.
B) loss of electrons.
C) gain of protons.
D) loss of protons.
E) loss of mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The standard hydrogen electrode is __________
A) used to calibrate voltmeters.
B) used to produce a set of standard reduction potentials.
C) needed to activate electrochemical cells.
D) often overlooked in measuring standard reduction potentials.
E) used to produce a standard cell potential of exactly 1 V.
A) used to calibrate voltmeters.
B) used to produce a set of standard reduction potentials.
C) needed to activate electrochemical cells.
D) often overlooked in measuring standard reduction potentials.
E) used to produce a standard cell potential of exactly 1 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Using the following data, determine the standard cell potential 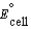 for the electrochemical cell constructed using the following reaction, where zinc is the anode and lead is the cathode. Zn(s) + Pb2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Pb(s)
for the electrochemical cell constructed using the following reaction, where zinc is the anode and lead is the cathode. Zn(s) + Pb2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Pb(s)
Half-reaction Standard Reduction Potential
Zn2+(aq) + 2e- Zn(s) -0.763
Pb2+(aq) + 2e- Pb(s) -0.126
A) +0.637 V
B) -0.637 V
C) +1.274 V
D) -0.889 V
E) +0.889 V
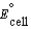 for the electrochemical cell constructed using the following reaction, where zinc is the anode and lead is the cathode. Zn(s) + Pb2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Pb(s)
for the electrochemical cell constructed using the following reaction, where zinc is the anode and lead is the cathode. Zn(s) + Pb2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Pb(s)Half-reaction Standard Reduction Potential
Zn2+(aq) + 2e- Zn(s) -0.763
Pb2+(aq) + 2e- Pb(s) -0.126
A) +0.637 V
B) -0.637 V
C) +1.274 V
D) -0.889 V
E) +0.889 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which one of the following items does not characterize a reducing agent?
A) A reducing agent loses electrons.
B) A reducing agent causes another species to be reduced.
C) The oxidation number of a reducing agent increases.
D) A good reducing agent is a metal in a high oxidation state, such as Mn7+.
E) An example of a good reducing agent is an alkali metal, such as Na.
A) A reducing agent loses electrons.
B) A reducing agent causes another species to be reduced.
C) The oxidation number of a reducing agent increases.
D) A good reducing agent is a metal in a high oxidation state, such as Mn7+.
E) An example of a good reducing agent is an alkali metal, such as Na.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which statement about a cathode in a voltaic cell is not correct?
A) Oxidation occurs at the cathode.
B) Reduction occurs at the cathode.
C) Usually the cathode is a metal strip.
D) In the external circuit, electrons flow toward the cathode.
E) Chemical species can have their oxidation number decreased at the cathode.
A) Oxidation occurs at the cathode.
B) Reduction occurs at the cathode.
C) Usually the cathode is a metal strip.
D) In the external circuit, electrons flow toward the cathode.
E) Chemical species can have their oxidation number decreased at the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Oxidation refers to __________
A) an increase in oxidation number.
B) a decrease in oxidation number.
C) a gain in the number of protons.
D) an increase in the atomic number.
E) an increase in mass.
A) an increase in oxidation number.
B) a decrease in oxidation number.
C) a gain in the number of protons.
D) an increase in the atomic number.
E) an increase in mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
This is a true story; can you explain what happened? Prior to a really important dinner party, the hostess discovered that her silverware was very tarnished. She needed a quick fix. She remembered reading that the tarnish (Ag2S) would be removed if you immersed the silverware in a hot solution of baking soda (NaHCO3) in a pan lined with aluminum foil. So she did, and so it was, but she noticed a bit of a rotten egg smell (H2S) being produced. Which one of the following statements cannot represent what might have been happening? Metal/Metal ion
E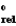 silver/silver(I) 0.799
silver/silver(I) 0.799
Aluminum/aluminum(III) -1.677
A) Al Al3+ + 3e-
B) Ag+ + e- Ag
C) 2HCO3- +S2- H2S + 2CO32-
D) 3Ag2S + 2Al +3H2O 6Ag + Al2O3 +3H2S
E) 2HCO3- +Ag2S H2S + 2CO32- + 2Ag
E
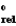 silver/silver(I) 0.799
silver/silver(I) 0.799Aluminum/aluminum(III) -1.677
A) Al Al3+ + 3e-
B) Ag+ + e- Ag
C) 2HCO3- +S2- H2S + 2CO32-
D) 3Ag2S + 2Al +3H2O 6Ag + Al2O3 +3H2S
E) 2HCO3- +Ag2S H2S + 2CO32- + 2Ag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Reduction refers to __________
A) a decrease in oxidation number.
B) an increase in oxidation number.
C) a gain in the number of protons.
D) a decrease in the atomic number.
E) loss of mass.
A) a decrease in oxidation number.
B) an increase in oxidation number.
C) a gain in the number of protons.
D) a decrease in the atomic number.
E) loss of mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which statement about a voltaic cell is not correct?
A) Electrons are produced as a product at the cathode.
B) Reduction occurs at the cathode.
C) Usually the cathode is a metal strip.
D) In the external circuit, electrons flow toward the cathode.
E) Chemical species can have their oxidation number decreased at the cathode.
A) Electrons are produced as a product at the cathode.
B) Reduction occurs at the cathode.
C) Usually the cathode is a metal strip.
D) In the external circuit, electrons flow toward the cathode.
E) Chemical species can have their oxidation number decreased at the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An electrochemical cell is constructed with a zinc metal anode in contact with a 0.052 M solution of zinc nitrate and a silver cathode in contact with a 0.0042 M solution of silver(I) nitrate. What is the value of Q to use in the Nernst equation for this cell?
A) 2900
B) 12
C) 8.1 *10-2
D) 3.4 *10-4
E) 1.00
A) 2900
B) 12
C) 8.1 *10-2
D) 3.4 *10-4
E) 1.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The Nernst equation can be used to calculate __________
A) standard cell potentials from standard reduction potentials.
B) the change in standard Gibbs free energy from standard cell potentials.
C) cell potentials from standard cell potentials when the conditions of concentration and temperature are not standard.
D) cell potentials given the temperature and reactant concentrations.
E) cell potentials from standard oxidation potentials.
A) standard cell potentials from standard reduction potentials.
B) the change in standard Gibbs free energy from standard cell potentials.
C) cell potentials from standard cell potentials when the conditions of concentration and temperature are not standard.
D) cell potentials given the temperature and reactant concentrations.
E) cell potentials from standard oxidation potentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The spontaneous redox reaction in a voltaic cell has __________
A) a negative value of Ecell and a negative value of G.
B) a positive value of Ecell and a positive value of G.
C) a negative value of Ecell and a positive value of G.
D) a positive value of Ecell and a negative value of G.
E) a positive value of Ecell and a value of zero for G.
A) a negative value of Ecell and a negative value of G.
B) a positive value of Ecell and a positive value of G.
C) a negative value of Ecell and a positive value of G.
D) a positive value of Ecell and a negative value of G.
E) a positive value of Ecell and a value of zero for G.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An electrochemical cell with a standard hydrogen electrode and a cathode consisting of a metallic chromium electrode, Cr(s), in contact with a 1.00 M chromium solution, Cr3+(aq), was constructed. The voltage produced by this cell was measured at 25°C. Which statements describe the results of this measurement, assuming the conditions are ideal? The cell voltage with the appropriate sign equals __________
(I) the cell potential.
(II) the electromotive force.
(III) the standard cell potential.
(IV) the standard reduction potential for Cr/Cr3+.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I, II, and III
D) I, II, III, and IV
E) III only
(I) the cell potential.
(II) the electromotive force.
(III) the standard cell potential.
(IV) the standard reduction potential for Cr/Cr3+.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I, II, and III
D) I, II, III, and IV
E) III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which statement does not correctly describe a standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)?
A) The SHE is assigned a standard reduction potential of exactly 1 V.
B) 2H+(aq) + 2e- H2(g)
C) Pt|H2(g, 1atm)|H+(aq, 1 M)||
D) ||H+(aq, 1 M)|H2(g, 1atm)|Pt
E) The SHE consists of a platinum electrode immersed in an acid solution and a stream of hydrogen gas.
A) The SHE is assigned a standard reduction potential of exactly 1 V.
B) 2H+(aq) + 2e- H2(g)
C) Pt|H2(g, 1atm)|H+(aq, 1 M)||
D) ||H+(aq, 1 M)|H2(g, 1atm)|Pt
E) The SHE consists of a platinum electrode immersed in an acid solution and a stream of hydrogen gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which one of the following items does not characterize an oxidizing agent?
A) An oxidizing agent gains electrons.
B) An oxidizing agent causes another species to be oxidized.
C) The oxidation number of an oxidizing agent decreases.
D) A good oxidizing agent is a metal in a high oxidation state, such as Mn7+.
E) An example of a good oxidizing agent is an alkali metal, such as Na.
A) An oxidizing agent gains electrons.
B) An oxidizing agent causes another species to be oxidized.
C) The oxidation number of an oxidizing agent decreases.
D) A good oxidizing agent is a metal in a high oxidation state, such as Mn7+.
E) An example of a good oxidizing agent is an alkali metal, such as Na.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The magnitude of the charge on a mole of electrons is __________
A) 1 C.
B) 9.65 C.
C) 9.65 *104 C.
D) 6.02 *1023 C.
E) 9650 C.
A) 1 C.
B) 9.65 C.
C) 9.65 *104 C.
D) 6.02 *1023 C.
E) 9650 C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Does pH have an effect on the cell potential (Ecell) for the following oxidation-reduction reaction? 5Fe2+(aq) + MnO4-(aq) + 8H+(aq) 5Fe3+(aq) + Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O( 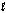 )
)
A) Yes, because Ecell values for all redox reactions depend on the pH.
B) Yes, because Ecell values for redox reactions involving the hydronium ion depend on the pH.
C) No, because Ecell values for redox reactions depend only on the major species in the reaction, in this case, Fe2+, MnO4-, Fe3+, and Mn2+.
D) No, because Ecell values for redox reactions depend on concentrations and temperatures but not on pH.
E) No, because Ecell values for redox reactions do not depend on the pH.
 )
)A) Yes, because Ecell values for all redox reactions depend on the pH.
B) Yes, because Ecell values for redox reactions involving the hydronium ion depend on the pH.
C) No, because Ecell values for redox reactions depend only on the major species in the reaction, in this case, Fe2+, MnO4-, Fe3+, and Mn2+.
D) No, because Ecell values for redox reactions depend on concentrations and temperatures but not on pH.
E) No, because Ecell values for redox reactions do not depend on the pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which statement does not correctly describe a "dead" battery with a voltage of 0?
A) The free-energy change for the reaction now is 0.
B) All the reactants have been converted into products.
C) The products and reactants now are in equilibrium.
D) Q = K
E) cell potential = 0
A) The free-energy change for the reaction now is 0.
B) All the reactants have been converted into products.
C) The products and reactants now are in equilibrium.
D) Q = K
E) cell potential = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The work involved in moving exactly 1 mol of electrons through a potential difference of exactly 1 V is __________
A) 1 J.
B) 1 kJ.
C) 96.5 J.
D) 6.02 kJ.
E) 96.5 kJ.
A) 1 J.
B) 1 kJ.
C) 96.5 J.
D) 6.02 kJ.
E) 96.5 kJ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In a classroom demonstration of a redox reaction, Professor Smith set up a voltaic cell with a copper metal anode and a silver metal cathode. The two electrodes were in contact with solutions of the corresponding metal ions, Cu2+ and Ag+. During the illuminating lecture on redox chemistry, the crystals of silver metal deposited on the silver electrode as the copper solution turned a darker blue. The added silver crystals had a mass of 2.68 g after 50.0 minutes of lecture. What was the average current that the cell produced?
A) 0.799 A
B) 2.40 A
C) 47.9 A
D) 1.60 A
E) 0.479 A
A) 0.799 A
B) 2.40 A
C) 47.9 A
D) 1.60 A
E) 0.479 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The charge supplied by a battery can be determined by __________
A) multiplying amperes by seconds.
B) dividing amperes by seconds.
C) multiplying coulombs by volts.
D) multiplying coulombs by seconds.
E) dividing coulombs by seconds.
A) multiplying amperes by seconds.
B) dividing amperes by seconds.
C) multiplying coulombs by volts.
D) multiplying coulombs by seconds.
E) dividing coulombs by seconds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A concentration cell is constructed by using the same half-reaction for both the cathode and anode. What is the value of 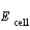 for a concentration cell that combines silver electrodes in contact with 0.10 M silver nitrate and 0.00003 M silver nitrate solutions? ( E
for a concentration cell that combines silver electrodes in contact with 0.10 M silver nitrate and 0.00003 M silver nitrate solutions? ( E  = + 0.80 V for Ag/Ag+)
= + 0.80 V for Ag/Ag+)
A) +0.21 V
B) +0.59 V
C) +0.80 V
D) -0.21 V
E) +1.01 V
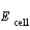 for a concentration cell that combines silver electrodes in contact with 0.10 M silver nitrate and 0.00003 M silver nitrate solutions? ( E
for a concentration cell that combines silver electrodes in contact with 0.10 M silver nitrate and 0.00003 M silver nitrate solutions? ( E 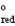 = + 0.80 V for Ag/Ag+)
= + 0.80 V for Ag/Ag+)A) +0.21 V
B) +0.59 V
C) +0.80 V
D) -0.21 V
E) +1.01 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If 15 g of aluminum from an empty soda can could be used as an anode of a battery, how long could it supply a current of 10 amps?
A) 45 hr
B) 15 hr
C) 5.4 hr
D) 4.5 hr
E) 1.5 hr
A) 45 hr
B) 15 hr
C) 5.4 hr
D) 4.5 hr
E) 1.5 hr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Energizer Bunny in the television commercial "keeps going and going." What property of the battery (voltaic cell) is being featured in this commercial?
A) The quantities of oxidizing agent and reducing agent in the battery.
B) The high voltage of the battery.
C) The low internal resistance of the battery.
D) The excellent conductivity of the battery's casing.
E) The ability of the battery to function over a wide temperature range.
A) The quantities of oxidizing agent and reducing agent in the battery.
B) The high voltage of the battery.
C) The low internal resistance of the battery.
D) The excellent conductivity of the battery's casing.
E) The ability of the battery to function over a wide temperature range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The energy supplied by a battery can be determined by __________
A) multiplying amperes supplied by seconds.
B) dividing amperes supplied by seconds.
C) multiplying coulombs supplied by volts.
D) multiplying coulombs supplied by seconds.
E) dividing coulombs supplied by seconds.
A) multiplying amperes supplied by seconds.
B) dividing amperes supplied by seconds.
C) multiplying coulombs supplied by volts.
D) multiplying coulombs supplied by seconds.
E) dividing coulombs supplied by seconds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The change in free energy for a reaction, G, depends on the stoichiometric coefficients used in writing the reaction, but cell potentials, E, do not depend on these coefficients. Which statement accounts for this difference?
A) These quantities ( G and E) are not related, so this difference is not an issue.
B) The free-energy change is defined for general reactions, and the electromotive force is defined for electrochemical reactions, so this difference is not an issue.
C) The difference is not relevant because the units differ: kJ/mol for G, and V for E.
D) The change in free energy depends on both the reaction and the amount of material reacting, while the cell potential only depends on the cell composition.
E) The statement is false. G does not depend on the stoichiometric coefficients.
A) These quantities ( G and E) are not related, so this difference is not an issue.
B) The free-energy change is defined for general reactions, and the electromotive force is defined for electrochemical reactions, so this difference is not an issue.
C) The difference is not relevant because the units differ: kJ/mol for G, and V for E.
D) The change in free energy depends on both the reaction and the amount of material reacting, while the cell potential only depends on the cell composition.
E) The statement is false. G does not depend on the stoichiometric coefficients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The average electrical current delivered if 1.0 g of zinc were oxidized to zinc(II) in 60 s is __________
A) 29.5 A.
B) 49.2 A.
C) 24.6 A.
D) 3.05 *10-2 A.
E) 1.53* 10-2 A.
A) 29.5 A.
B) 49.2 A.
C) 24.6 A.
D) 3.05 *10-2 A.
E) 1.53* 10-2 A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A concentration cell is constructed by using the same half-reaction for both the cathode and anode. What is the value of standard cell potential, E 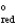 , for a concentration cell that combines a silver anode in contact with 0.10 M silver nitrate and a silver cathode in contact with 0.00003 M silver nitrate? (E
, for a concentration cell that combines a silver anode in contact with 0.10 M silver nitrate and a silver cathode in contact with 0.00003 M silver nitrate? (E 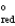 = + 0.80 V for Ag/Ag+)
= + 0.80 V for Ag/Ag+)
A) -0.21 V
B) 0.00 V
C) 0.80V
D) -0.80 V
E) +0.21 V
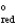 , for a concentration cell that combines a silver anode in contact with 0.10 M silver nitrate and a silver cathode in contact with 0.00003 M silver nitrate? (E
, for a concentration cell that combines a silver anode in contact with 0.10 M silver nitrate and a silver cathode in contact with 0.00003 M silver nitrate? (E 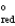 = + 0.80 V for Ag/Ag+)
= + 0.80 V for Ag/Ag+)A) -0.21 V
B) 0.00 V
C) 0.80V
D) -0.80 V
E) +0.21 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The electrodes on batteries are labeled + and -. The __________ is labeled __________, and __________ occurs there.
A) anode / positive / oxidation
B) anode / negative / reduction
C) cathode / positive / reduction
D) cathode / negative / reduction
E) cathode / positive / oxidation
A) anode / positive / oxidation
B) anode / negative / reduction
C) cathode / positive / reduction
D) cathode / negative / reduction
E) cathode / positive / oxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The unit of electrical power, watt (W), is defined as __________
A) 1 C.
B) 1 V.
C) 1 J.
D) 1 C V
E) 1 J/s
A) 1 C.
B) 1 V.
C) 1 J.
D) 1 C V
E) 1 J/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An electrochemical cell has both a silver anode and a silver cathode. The solutions of silver nitrate in contact with the electrodes have different concentrations. Which statement(s) correctly describe this cell?
(I) The cell potential is 0.
(II) The cell potential is negative.
(III) The cell potential is positive.
(IV) No electrons will flow through the external circuit.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and IV
E) II and IV
(I) The cell potential is 0.
(II) The cell potential is negative.
(III) The cell potential is positive.
(IV) No electrons will flow through the external circuit.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and IV
E) II and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider the voltaic cell based on the following reaction: Ma(s) + Mb+(aq) Ma+(aq) + Mb(s)
Two students are assigned to measure the standard cell potential. Yvonne claims that both solutions of ions have to be at exactly 1.00 M concentration, but Zelda is sure that the measurement will be the same if the concentrations of the two solutions are equal, but not necessarily 1.00 M. What do you think? (The temperature is controlled at 25°C, so that's not an issue).
A) Yvonne is right because by definition standard cell potentials must be measured at concentrations of 1.00 M.
B) Yvonne is right because she understands the Nernst equation and what it describes.
C) Zelda is right because she understands the Nernst equation and what it describes.
D) Zelda is right because cell potentials do not depend on the concentration.
E) Both are right because cell potentials do not depend on the concentration.
Two students are assigned to measure the standard cell potential. Yvonne claims that both solutions of ions have to be at exactly 1.00 M concentration, but Zelda is sure that the measurement will be the same if the concentrations of the two solutions are equal, but not necessarily 1.00 M. What do you think? (The temperature is controlled at 25°C, so that's not an issue).
A) Yvonne is right because by definition standard cell potentials must be measured at concentrations of 1.00 M.
B) Yvonne is right because she understands the Nernst equation and what it describes.
C) Zelda is right because she understands the Nernst equation and what it describes.
D) Zelda is right because cell potentials do not depend on the concentration.
E) Both are right because cell potentials do not depend on the concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The unit of current, Ampere (A), is defined as __________
A) 1 C.
B) 1 C/s.
C) 1 mol of electrons.
D) 1 mol of electrons per second.
E) 96,500 C/s.
A) 1 C.
B) 1 C/s.
C) 1 mol of electrons.
D) 1 mol of electrons per second.
E) 96,500 C/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An electrochemical cell is constructed with a zinc metal anode in contact with a 0.052 M solution of zinc(II) nitrate and a silver cathode in contact with a 0.0042 M solution of silver(I) nitrate. What is the emf of this cell at 5°C? Metal/Metal ion
E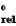 silver/silver(I)+0.799 V
silver/silver(I)+0.799 V
Zinc/zinc(II)-0.762 V
A) 1.656 V
B) 1.465 V
C) 1.561 V
D) 1.370 V
E) 1.609 V
E
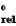 silver/silver(I)+0.799 V
silver/silver(I)+0.799 VZinc/zinc(II)-0.762 V
A) 1.656 V
B) 1.465 V
C) 1.561 V
D) 1.370 V
E) 1.609 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the potential of a voltaic cell is +1.20 V, what is the free-energy change when one mole of electrons is transferred in the oxidation-reduction reaction?
A) 116 kJ
B) 1.20 kJ
C) -1.20 kJ
D) -116 kJ
E) +602 kJ
A) 116 kJ
B) 1.20 kJ
C) -1.20 kJ
D) -116 kJ
E) +602 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
For a chemical reaction to be considered for use in a fuel cell, it is absolutely essential for the __________
A) free-energy change to be negative.
B) reactants to be solids.
C) reactants to be liquids.
D) reactants to be gases.
E) free-energy change to be positive.
A) free-energy change to be negative.
B) reactants to be solids.
C) reactants to be liquids.
D) reactants to be gases.
E) free-energy change to be positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A voltaic cell is constructed based on the oxidation of zinc metal and the reduction of silver metal. Solutions of silver nitrate and zinc nitrate also were used. Locate the silver metal on the diagram. 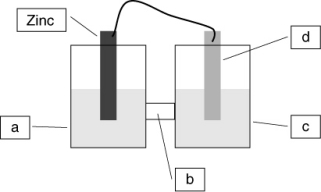
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A voltaic cell is constructed based on the oxidation of zinc metal and the reduction of silver metal. Solutions of silver nitrate and zinc nitrate also were used. Locate the silver nitrate on the diagram. 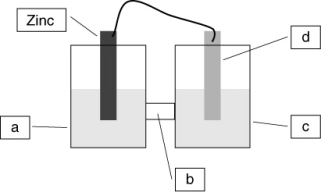
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
How do fuel cells differ from traditional electrochemical cells (batteries)?
A) The supply of reactants is continually renewed.
B) The cell potentials generally are lower.
C) The cell potentials generally are higher.
D) Fuel cells are closed systems; batteries are open systems.
E) Fuel cells do not involve oxidation-reduction reactions.
A) The supply of reactants is continually renewed.
B) The cell potentials generally are lower.
C) The cell potentials generally are higher.
D) Fuel cells are closed systems; batteries are open systems.
E) Fuel cells do not involve oxidation-reduction reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How long would it take to electroplate a flute with 28.3 g of silver at a constant current of 2.0 amps using AgNO3?
A) 211 min
B) 422 min
C) 844 min
D) 1688 min
E) 105 min
A) 211 min
B) 422 min
C) 844 min
D) 1688 min
E) 105 min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The electrodes on batteries are labeled + and -. The __________ is labeled __________, and __________ occurs there.
A) anode / positive / oxidation
B) anode / negative / oxidation
C) cathode / positive / oxidation
D) cathode / negative / reduction
E) anode / positive / reduction
A) anode / positive / oxidation
B) anode / negative / oxidation
C) cathode / positive / oxidation
D) cathode / negative / reduction
E) anode / positive / reduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The oxidation of hydrogen by oxygen is one of the most-used reactions in fuel-cell technology. The overall reaction, which is given below, has a G° value of -474 kJ/mol. What is the standard cell potential for this fuel cell? 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O( 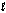 )
)
A) 2.46 V
B) 4.91 V
C) 1.23 V
D) 2.46 v
E) 1.50 V
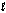 )
)A) 2.46 V
B) 4.91 V
C) 1.23 V
D) 2.46 v
E) 1.50 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The oxidation of hydrogen by oxygen is one of the most-used reactions in fuel-cell technology. The overall reaction, which is given below, has a G° value of -237 kJ/mol. What is the standard cell potential for this fuel cell? H2(g) + 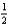 O2(g) H2O(
O2(g) H2O(  )
)
A) 2.46 V
B) 4.91 V
C) 1.23 V
D) 2.46 v
E) 1.50 V
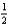 O2(g) H2O(
O2(g) H2O(  )
)A) 2.46 V
B) 4.91 V
C) 1.23 V
D) 2.46 v
E) 1.50 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Luke Skywalker found that the batteries for his light-saber were running low. A cryptic inscription on the handle translated roughly into "Four AA dark-side batteries required." The total voltage produced by the four 1.50 V batteries in series therefore was 6.00 volts. If the cell reaction transfers one electron for each mole of the reactants, what is the Gibbs free-energy change for the redox reaction in each of Luke's batteries?
A) -145 kJ/mol
B) +145 kJ/mol
C) 869 kJ/mol
D) -869 kJ/mol
E) +579 kJ/mol
A) -145 kJ/mol
B) +145 kJ/mol
C) 869 kJ/mol
D) -869 kJ/mol
E) +579 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A NiMH battery uses __________ as the reducing agent.
A) nickel
B) a metal hydride
C) hydroxide
D) hydronium ion
E) nickel oxide
A) nickel
B) a metal hydride
C) hydroxide
D) hydronium ion
E) nickel oxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Applying a current to a rechargeable battery converts it from __________ cell to __________ cell.
A) a voltaic / an electrolytic
B) an electrolytic / a voltaic
C) a Leclanché / a Nernst
D) a Nernst / a Leclanché
E) a Born cell / a Haber
A) a voltaic / an electrolytic
B) an electrolytic / a voltaic
C) a Leclanché / a Nernst
D) a Nernst / a Leclanché
E) a Born cell / a Haber

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which one of the following is not an advantage of lithium batteries?
A) the extremely negative standard reduction potential of lithium
B) the small molar mass of lithium
C) the high mobility of lithium in solids
D) the small cell potentials produced by these batteries
E) a high battery capacity
A) the extremely negative standard reduction potential of lithium
B) the small molar mass of lithium
C) the high mobility of lithium in solids
D) the small cell potentials produced by these batteries
E) a high battery capacity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Copper metal is purified by electrolysis. How much copper metal could be produced from copper(II) oxide by applying a current of 10.0 amps at the appropriate negative potential for 12.0 hours?
A) 284 g
B) 142 g
C) 28.4 g
D) 14.2 g
E) 4.48 g
A) 284 g
B) 142 g
C) 28.4 g
D) 14.2 g
E) 4.48 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A voltaic cell is constructed based on the oxidation of zinc metal and the reduction of silver metal. Solutions of silver nitrate and zinc nitrate also were used. Locate the zinc nitrate on the diagram. 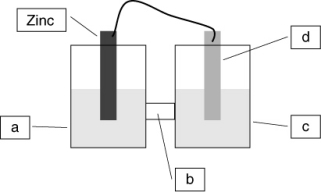
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Aluminum metal is refined in a very energy-intensive process from bauxite ore using the Hall process, which requires electrolysis of aluminum oxide, Al2O3, in molten cryolyte at more than 1012°C. In an industrial electrolysis cell, 1900 kg of aluminum oxide was reduced with a current of 1500 amps. How long did it take to reduce all the reactant to aluminum metal?
A) 1000 hr
B) 2000 hr
C) 330 hr
D) 4000 hr
E) 660 hr
A) 1000 hr
B) 2000 hr
C) 330 hr
D) 4000 hr
E) 660 hr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is not an advantage in using hydrogen fuel cells rather than gasoline engines in vehicles?
A) It is a more efficient use of chemical energy.
B) Only water is emitted as a reactant product.
C) Imported petroleum is replaced as the source of energy.
D) Storage is less dangerous than the gasoline tank.
E) Hydrogen is an abundant element.
A) It is a more efficient use of chemical energy.
B) Only water is emitted as a reactant product.
C) Imported petroleum is replaced as the source of energy.
D) Storage is less dangerous than the gasoline tank.
E) Hydrogen is an abundant element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which statement regarding battery-powered electric cars is not correct? Currently battery-powered electric cars __________.
A) are more efficient than internal combustion engines.
B) have a limited range due to battery capacity.
C) use energy produced primarily by the combustion of coal and natural gas.
D) show promise in shifting the energy needs of our transportation system from petroleum to nuclear and solar sources.
E) do not contribute to pollution of the atmosphere by producing carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other gases.
A) are more efficient than internal combustion engines.
B) have a limited range due to battery capacity.
C) use energy produced primarily by the combustion of coal and natural gas.
D) show promise in shifting the energy needs of our transportation system from petroleum to nuclear and solar sources.
E) do not contribute to pollution of the atmosphere by producing carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other gases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When a voltaic cell reaches equilibrium, __________
A) E = 0
= 0
B) Ecell = 0
C) Ecell = K
D) E = K
= K
E) Ecell = Q
A) E
 = 0
= 0B) Ecell = 0
C) Ecell = K
D) E
 = K
= KE) Ecell = Q

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A NiMH battery uses __________ as the oxidizing agent.
A) Ni
B) MH
C) hydroxide
D) hydronium ion
E) NiO(OH)
A) Ni
B) MH
C) hydroxide
D) hydronium ion
E) NiO(OH)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is true when a battery (voltaic cell) is dead?
A) E = 0 and Q = K
= 0 and Q = K
B) Ecell = 0 and Q = K
C) Ecell = 0 and Q = 0
D) E = 0 and Q = 0
= 0 and Q = 0
E) Ecell = 0 and K = 0
A) E
 = 0 and Q = K
= 0 and Q = KB) Ecell = 0 and Q = K
C) Ecell = 0 and Q = 0
D) E
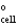 = 0 and Q = 0
= 0 and Q = 0E) Ecell = 0 and K = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the oxidation number of chromium in the ionic compound ammonium dichromate, (NH4)2Cr2O7?
A) +3
B) +4
C) +5
D) +6
E) +7
A) +3
B) +4
C) +5
D) +6
E) +7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If in using a lead-acid battery to start a car, 1.00 gram of Pb is consumed on the anode, how long will it take to recharge the battery, using a current of 0.500 amperes, and turn the PbSO4 that was produced back into Pb?
A) 15.5 min
B) 1864 min
C) 31.1 min
D) 21.2 min
E) 42.4 min
A) 15.5 min
B) 1864 min
C) 31.1 min
D) 21.2 min
E) 42.4 min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
How many kilograms of aluminum metal can be produced by the electrolysis of Al2O3 using a current of 100 amperes for 24 hours?
A) 0.76
B) 2.4
C) 810
D) 2.2 *1013
E) 7.5 *1012
A) 0.76
B) 2.4
C) 810
D) 2.2 *1013
E) 7.5 *1012

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When hydrogen reacts with a metal to form a hydride (e.g., CaH2) what are the oxidation numbers of the calcium, in this case, and hydrogen, respectively, in the product?
A) -2 and +1
B) +1 and -2
C) +2 and -1
D) 0 and 0
E) +2 and -2
A) -2 and +1
B) +1 and -2
C) +2 and -1
D) 0 and 0
E) +2 and -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The following reaction occurs in basic solution. Identify the oxidizing agent. Note the reaction equation is not balanced. H2O( 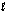 ) + Zn(s) + NO3-(aq) + OH-(aq) Zn(OH)42-(aq) + NH3(aq)
) + Zn(s) + NO3-(aq) + OH-(aq) Zn(OH)42-(aq) + NH3(aq)
A) Zn(s)
B) NO3-(aq)
C) OH-(aq)
D) H2O(l)
E) NH3(aq)
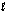 ) + Zn(s) + NO3-(aq) + OH-(aq) Zn(OH)42-(aq) + NH3(aq)
) + Zn(s) + NO3-(aq) + OH-(aq) Zn(OH)42-(aq) + NH3(aq)A) Zn(s)
B) NO3-(aq)
C) OH-(aq)
D) H2O(l)
E) NH3(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Methanol fuel cells depend on the following reaction. How many electrons are transferred in this redox reaction per mole of methanol consumed? 2CH3OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 3H2O
A) 3
B) 6
C) 8
D) 12
E) 2
A) 3
B) 6
C) 8
D) 12
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Neuron cells generate electrical signals by concentration gradients across membranes. Assuming a potassium ion concentration of 0.003 M inside the cell, and a concentration of 0.135 M outside the cell, what is the electrical potential across the cell membrane? Body temperature is 310 K. The sign identifies the change in the electrical potential across the membrane and which way the ions flow.
A) +204 mV
B) +102 mV
C) +10.0 mV
D) -204 mV
E) -136 mV
A) +204 mV
B) +102 mV
C) +10.0 mV
D) -204 mV
E) -136 mV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A pH meter uses an electrode arrangement that provides a voltage that depends on [H+], in accord with the Nernst equation. The following plot illustrates this dependence. What effect would changing temperature have on the measurement and this plot? ![<strong>A pH meter uses an electrode arrangement that provides a voltage that depends on [H<sup>+</sup>], in accord with the Nernst equation. The following plot illustrates this dependence. What effect would changing temperature have on the measurement and this plot? </strong> A) A change of temperature would have no effect. B) An increase in temperature would increase the slope. C) An increase in temperature would decrease the slope. D) An increase in temperature would increase the y intercept. E) An increase in temperature would decrease the y intercept.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0882_3562_95d8_f3cee004c3d8_TB3833_00.jpg)
A) A change of temperature would have no effect.
B) An increase in temperature would increase the slope.
C) An increase in temperature would decrease the slope.
D) An increase in temperature would increase the y intercept.
E) An increase in temperature would decrease the y intercept.
![<strong>A pH meter uses an electrode arrangement that provides a voltage that depends on [H<sup>+</sup>], in accord with the Nernst equation. The following plot illustrates this dependence. What effect would changing temperature have on the measurement and this plot? </strong> A) A change of temperature would have no effect. B) An increase in temperature would increase the slope. C) An increase in temperature would decrease the slope. D) An increase in temperature would increase the y intercept. E) An increase in temperature would decrease the y intercept.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0882_3562_95d8_f3cee004c3d8_TB3833_00.jpg)
A) A change of temperature would have no effect.
B) An increase in temperature would increase the slope.
C) An increase in temperature would decrease the slope.
D) An increase in temperature would increase the y intercept.
E) An increase in temperature would decrease the y intercept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Chromium often is electroplated on other metals and even plastics to produce a shiny metallic appearance. How many grams of chromium would plate out from a solution of Cr(NO3)3 when 10 amps of current are passed through the electrolytic cell for 5.36 hours?
A) 17.3 g
B) 34.7 g
C) 52.0 g
D) 104 g
E) 11.6 g
A) 17.3 g
B) 34.7 g
C) 52.0 g
D) 104 g
E) 11.6 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Bubbles will form on wires attached to a 9 V battery placed in water. What is happening here?
A) The wires are being oxidized.
B) The water is being reduced on the wire attached to the (-) battery electrode and oxidized on the wire attached to the (+) battery electrode.
C) The water is being oxidized on the wire attached to the (-) battery electrode and reduced on the wire attached to the (+) battery electrode.
D) Air is being forced out of the water by the electric current.
E) One wire is being oxidized; the other wire is being reduced.
A) The wires are being oxidized.
B) The water is being reduced on the wire attached to the (-) battery electrode and oxidized on the wire attached to the (+) battery electrode.
C) The water is being oxidized on the wire attached to the (-) battery electrode and reduced on the wire attached to the (+) battery electrode.
D) Air is being forced out of the water by the electric current.
E) One wire is being oxidized; the other wire is being reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Bubbles will form on wires attached to a 9 V battery placed in water. Which statements correctly describe what is happening?
(I) The wire attached to the (-) battery electrode becomes the cathode, and water is being reduced there to produce hydrogen gas.
(II) The wire attached to the (+) battery electrode becomes the anode, and water is being oxidized there to produce oxygen gas.
(III) The wire attached to the (-) battery electrode becomes the cathode, and water is being oxidized there to produce oxygen gas.
(IV) The wire attached to the (+) battery electrode becomes the anode, and water is being reduced there to produce hydrogen gas.
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) I and III
D) II and IV
E) I and IV
(I) The wire attached to the (-) battery electrode becomes the cathode, and water is being reduced there to produce hydrogen gas.
(II) The wire attached to the (+) battery electrode becomes the anode, and water is being oxidized there to produce oxygen gas.
(III) The wire attached to the (-) battery electrode becomes the cathode, and water is being oxidized there to produce oxygen gas.
(IV) The wire attached to the (+) battery electrode becomes the anode, and water is being reduced there to produce hydrogen gas.
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) I and III
D) II and IV
E) I and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Glancing at a periodic table, where do you expect to find elements that are good reducing agents?
A) in groups 16 and 17
B) on the left
C) in the middle
D) at the bottom
E) in group 17
A) in groups 16 and 17
B) on the left
C) in the middle
D) at the bottom
E) in group 17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of A-D is a disadvantage in using hydrogen fuel cells instead of gasoline engines in vehicles? If all are valid disadvantages, respond E.
A) It is difficult to store hydrogen safely.
B) No distribution network of hydrogen fuel is in place.
C) Hydrogen fuel must be produced, most likely from water, by using another energy source.
D) Hydrogen fuel is not really a source of energy, but rather is a way to store energy.
E) All the above.
A) It is difficult to store hydrogen safely.
B) No distribution network of hydrogen fuel is in place.
C) Hydrogen fuel must be produced, most likely from water, by using another energy source.
D) Hydrogen fuel is not really a source of energy, but rather is a way to store energy.
E) All the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The standard cell potential for the nickel-cadmium battery is 1.35 V, and the cell reaction can be written as 2NiO(OH)(s) + 2H2O( 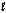 ) + Cd(s) 2Ni(OH)2(s) + Cd(OH)2(s)
) + Cd(s) 2Ni(OH)2(s) + Cd(OH)2(s)
Which one of the following statements do you expect to be true based on the Nernst equation? Note Q = reaction quotient, and K = equilibrium constant for the cell reaction.
A) As the battery is used, the cell voltage approaches zero because Q approaches K, in value.
B) When the battery no longer works, the cell voltage is zero because Q = K.
C) As the battery is used, the cell voltage does not change because Q equals 1.
D) When the battery is fully charged, Q > K.
E) When the battery is fully charged, Q < K.
 ) + Cd(s) 2Ni(OH)2(s) + Cd(OH)2(s)
) + Cd(s) 2Ni(OH)2(s) + Cd(OH)2(s)Which one of the following statements do you expect to be true based on the Nernst equation? Note Q = reaction quotient, and K = equilibrium constant for the cell reaction.
A) As the battery is used, the cell voltage approaches zero because Q approaches K, in value.
B) When the battery no longer works, the cell voltage is zero because Q = K.
C) As the battery is used, the cell voltage does not change because Q equals 1.
D) When the battery is fully charged, Q > K.
E) When the battery is fully charged, Q < K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The oxidation of methanol, as described by the equation below, has a G° value of -937.9 kJ/mol. What is the standard cell potential for a methanol fuel cell? 2CH3OH + 3O2 2 CO2 + 3H2O
A) 0.405 V
B) 9.72 V
C) 0.810 V
D) -2.43 V
E) -9.72 V
A) 0.405 V
B) 9.72 V
C) 0.810 V
D) -2.43 V
E) -9.72 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A hydrogen fuel cell depends on __________
A) fusion of hydrogen to produce deuterium.
B) the acid-base chemistry of hydrogen.
C) the redox chemistry of hydrogen.
D) the kinetic energy of hydrogen gas.
E) the enthalpy of vaporization of hydrogen.
A) fusion of hydrogen to produce deuterium.
B) the acid-base chemistry of hydrogen.
C) the redox chemistry of hydrogen.
D) the kinetic energy of hydrogen gas.
E) the enthalpy of vaporization of hydrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Glancing at a periodic table, where do you expect to find elements that are good oxidizing agents?
A) on the right (except for the last group)
B) in the middle left
C) in the top left
D) at the bottom
E) in the transition metals
A) on the right (except for the last group)
B) in the middle left
C) in the top left
D) at the bottom
E) in the transition metals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
For the following reaction, which statement, A-D, is not correct? If more than one is not correct, respond E. 2Au + 4Cl2 2AuCl4-
A) Au is the reducing agent.
B) Cl2 is the oxidizing agent
C) Au is oxidized.
D) The equation is balanced.
E) More than one statement is not correct.
A) Au is the reducing agent.
B) Cl2 is the oxidizing agent
C) Au is oxidized.
D) The equation is balanced.
E) More than one statement is not correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Electrochemical cell potentials can be used to determine equilibrium constants that would be otherwise difficult to determine because concentrations are small. Calculate the value of Ksp for CdS from the following data. CdS(s) + 2e- Cd(s) + S2-(aq)
E° = -1.21 V
Cd2+(aq) + 2e- Cd(s)
E° = -0.40 V
A) 3 *10-55
B) 4 * 10-28
C) 2 * 10-14
D) 3 * 10+27
E) 1 *10-36
E° = -1.21 V
Cd2+(aq) + 2e- Cd(s)
E° = -0.40 V
A) 3 *10-55
B) 4 * 10-28
C) 2 * 10-14
D) 3 * 10+27
E) 1 *10-36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Methanol fuel cells depend on the following reaction. How many electrons are transferred in this redox reaction as written? 2CH3OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 3H2O
A) 3
B) 6
C) 8
D) 12
E) 2
A) 3
B) 6
C) 8
D) 12
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



