Deck 20: Carbohydrates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/92
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Carbohydrates
1
How many acetals are present in the disaccharide shown below? 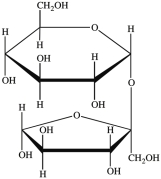
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
B
2
Which Haworth projection represents the anomer of the monosaccharide shown below? 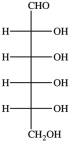
A)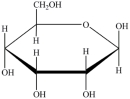
B)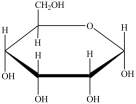
C)
D)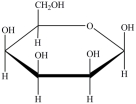

A)

B)

C)

D)


3
What product forms when the compound below is treated with Benedict's reagent? 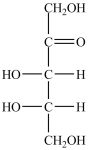
A)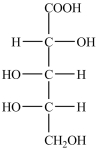
B)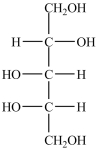
C)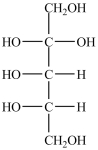
D)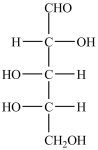
E)No reaction occurs.

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)No reaction occurs.
A
4
What product forms when the compound below is treated with Benedict's reagent? 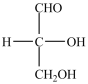
A)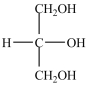
B)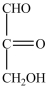
C)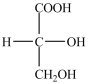
D)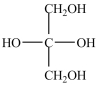

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The formation of what color in the Benedict's test indicates a reducing sugar is present in solution?
A)blue
B)brick red
C)bright yellow
D)silver
A)blue
B)brick red
C)bright yellow
D)silver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Salicin is a naturally occurring, carbohydrate-containing pain reliever. Which statement concerning the functional groups present in salicin is incorrect? 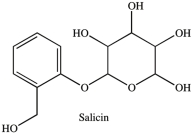
A)Salicin contains an acetal.
B)Salicin contains an alcohol.
C)Salicin contains a hemiacetal.
D)Salicin contains a phenol.

A)Salicin contains an acetal.
B)Salicin contains an alcohol.
C)Salicin contains a hemiacetal.
D)Salicin contains a phenol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What are monosaccharides with a carbonyl group at C1 called?
A)anomers
B)aldoses
C)ketoses
D)alditols
A)anomers
B)aldoses
C)ketoses
D)alditols

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which carbohydrates cannot be converted to simpler compounds by hydrolysis?
A)disaccharides
B)monosaccharides
C)polysaccharides
D)starches
A)disaccharides
B)monosaccharides
C)polysaccharides
D)starches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What product forms when the compound below is treated with H2 in the presence of a Pd catalyst? 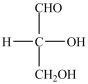
A)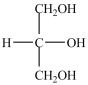
B)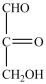
C)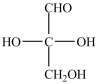
D)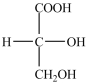

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When converting a Fischer projection to a Haworth projection, where are all of the substituents on the right side of the carbon skeleton drawn in the Haworth projection?
A)down
B)up
C)down in an anomer and up in a anomer
D)down in an anomer and up in a anomer
A)down
B)up
C)down in an anomer and up in a anomer
D)down in an anomer and up in a anomer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the classification of the compound shown below? 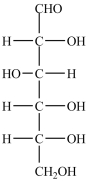
A)an aldohexose
B)a ketohexose
C)an aldopentose
D)a ketopentose

A)an aldohexose
B)a ketohexose
C)an aldopentose
D)a ketopentose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
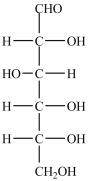
12
The structures of galactose (left)and glucose (right)are shown below. How are the two monosaccharides related? 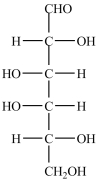
A)structural isomers
B)stereoisomers
C)enantiomers
D)anomers


A)structural isomers
B)stereoisomers
C)enantiomers
D)anomers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Disaccharides and polysaccharides contain monosaccharide units joined together by which of the following?
A)hydrogen bonding
B)glycosidic linkages
C)hemiacetal bonds
D)dipole-dipole forces
A)hydrogen bonding
B)glycosidic linkages
C)hemiacetal bonds
D)dipole-dipole forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Lactose is present in milk. What type of sugar is lactose?
A)a disaccharide
B)a monosaccharide
C)a polysaccharide
D)a starch
A)a disaccharide
B)a monosaccharide
C)a polysaccharide
D)a starch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which labeled carbon atom in the structure below is the anomeric carbon? 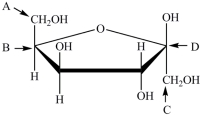
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many chirality centers are present in the compound shown below? 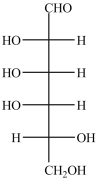
A)2
B)4
C)5
D)6

A)2
B)4
C)5
D)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the classification of the compound shown below? 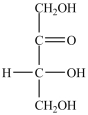
A)a tetraketose
B)a ketotriose
C)a ketotetrose
D)an aldotriose

A)a tetraketose
B)a ketotriose
C)a ketotetrose
D)an aldotriose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which monosaccharide is an aldotriose?
A)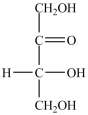
B)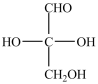
C)
D)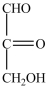
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the classification of the compound shown below? 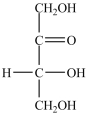
A)L
B)D
C)A sugar this small is not classified as L or D.

A)L
B)D
C)A sugar this small is not classified as L or D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which compound is the most soluble in water?
A)CH2OHCHOHCHOHCHOHCHOHCHO
B)CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH
C)CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
D)CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
A)CH2OHCHOHCHOHCHOHCHOHCHO
B)CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH
C)CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
D)CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The simplest aldose is commonly called glyceraldehyde, although its IUPAC name is 2, 3-dihydroxypropanal. What is the structure of this compound?
A)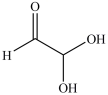
B)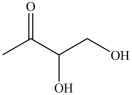
C)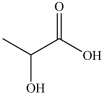
D)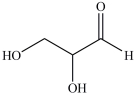
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the most common type of starch molecules?
A)cellulose
B)amylose
C)amylopectin
D)glycogen
A)cellulose
B)amylose
C)amylopectin
D)glycogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the structure of amylopectin?
A)unbranched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
B)branched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
C)unbranched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
D)branched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
A)unbranched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
B)branched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
C)unbranched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
D)branched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which is not a naturally-occurring polysaccharide?
A)starch
B)cellulose
C)maltose
D)glycogen
A)starch
B)cellulose
C)maltose
D)glycogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the difference between the disaccharides lactose and maltose?
A)Lactose contains two glucose units, while maltose contains two galactose units.
B)The two monosaccharides in lactose are joined by a 1 4- -glycoside bond, while the two monosaccharides in maltose are joined by a 1 4- -glycoside bond.
C)Lactose contains both an acetal and a hemiacetal, while maltose contains two acetals.
D)Lactose can be hydrolyzed in the body, but maltose cannot.
A)Lactose contains two glucose units, while maltose contains two galactose units.
B)The two monosaccharides in lactose are joined by a 1 4- -glycoside bond, while the two monosaccharides in maltose are joined by a 1 4- -glycoside bond.
C)Lactose contains both an acetal and a hemiacetal, while maltose contains two acetals.
D)Lactose can be hydrolyzed in the body, but maltose cannot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What monosaccharide is found in cellulose, starch, and glycogen?
A)glucose
B)galactose
C)sucrose
D)fructose
A)glucose
B)galactose
C)sucrose
D)fructose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Dihydroxyacetone, shown below, is the simplest ketose. Does the structure shown represent D-dihydroxyacetone or L-dihydroxyacetone? 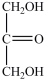
A)D-dihydroxyacetone
B)L-dihydroxyacetone
C)Neither D nor L; dihydroxyacetone is not chiral
D)It is impossible to tell from the Fischer projection alone.

A)D-dihydroxyacetone
B)L-dihydroxyacetone
C)Neither D nor L; dihydroxyacetone is not chiral
D)It is impossible to tell from the Fischer projection alone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is responsible for the different blood types in humans?
A)three or four proteins attached to a membrane monosaccharide on the surface of red blood cells
B)three or four monosaccharides attached to a membrane protein on the surface of red blood cells
C)three or four amino acids attached to a membrane monosaccharide on the surface of red blood cells
D)three or four lipids attached to a membrane polysaccharide on the surface of red blood cells
A)three or four proteins attached to a membrane monosaccharide on the surface of red blood cells
B)three or four monosaccharides attached to a membrane protein on the surface of red blood cells
C)three or four amino acids attached to a membrane monosaccharide on the surface of red blood cells
D)three or four lipids attached to a membrane polysaccharide on the surface of red blood cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What type of polysaccharide is depicted in the "cartoon" shown below? 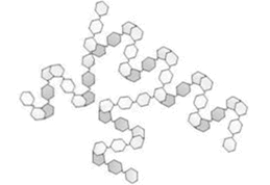
A)cellulose
B)amylose
C)amylopectin
D)chitin

A)cellulose
B)amylose
C)amylopectin
D)chitin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which is not a reducing sugar?
A)glucose
B)fructose
C)sucrose
D)galactose
E)an aldopentose
A)glucose
B)fructose
C)sucrose
D)galactose
E)an aldopentose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Chitin is identical in structure to cellulose, except that
A)the linkages are -glycoside linkages.
B)each OH group at C4 is replaced by NHCOCH3.
C)each OH group at C2 is replaced by NH3.
D)each OH group at C2 is replaced by NHCOCH3.
A)the linkages are -glycoside linkages.
B)each OH group at C4 is replaced by NHCOCH3.
C)each OH group at C2 is replaced by NH3.
D)each OH group at C2 is replaced by NHCOCH3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which naturally-occurring monosaccharide forms the Haworth structure shown? 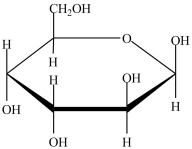
A)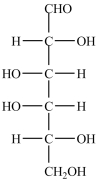
B)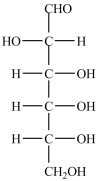
C)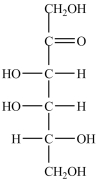
D)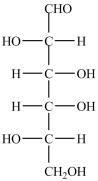

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which carbohydrate derivative forms a gel-like matrix in joints and the vitreous humor of the eye?
A)heparin
B)chondroitin
C)hyaluronate
D)chitin
A)heparin
B)chondroitin
C)hyaluronate
D)chitin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Salicin is a naturally occurring, carbohydrate-containing pain reliever. Which statement concerning the functional groups present in salicin is incorrect? 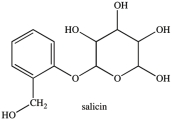
A)Salicin contains an acetal.
B)Salicin contains an alcohol.
C)Salicin contains a hemiacetal.
D)Salicin contains a phenol.

A)Salicin contains an acetal.
B)Salicin contains an alcohol.
C)Salicin contains a hemiacetal.
D)Salicin contains a phenol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the polysaccharide form in which glucose is stored in animals?
A)cellulose
B)amylose
C)amylopectin
D)glycogen
A)cellulose
B)amylose
C)amylopectin
D)glycogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the structure of cellulose?
A)unbranched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
B)branched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
C)unbranched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
D)branched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
A)unbranched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
B)branched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
C)unbranched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages
D)branched skeleton of glucose molecules joined by 1 4- -glycoside linkages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Why are humans not able to digest cellulose?
A)Humans cannot digest glucose.
B)Humans do not possess the enzyme necessary to hydrolyze the 1 4- -glycoside linkages found in cellulose.
C)Humans do not possess the enzyme necessary to unwind the helical shape of the cellulose molecule.
D)Humans do not possess the enzyme necessary to hydrolyze the 1 4- -glycoside linkages found in cellulose.
A)Humans cannot digest glucose.
B)Humans do not possess the enzyme necessary to hydrolyze the 1 4- -glycoside linkages found in cellulose.
C)Humans do not possess the enzyme necessary to unwind the helical shape of the cellulose molecule.
D)Humans do not possess the enzyme necessary to hydrolyze the 1 4- -glycoside linkages found in cellulose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The simplest aldose is commonly called glyceraldehyde, although its IUPAC name is 2, 3-dihydroxypropanal. What is the structure of this compound?
A)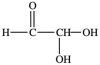
B)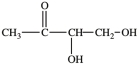
C)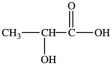
D)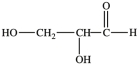
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which structure is a three-carbon alditol?
A)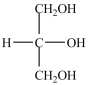
B)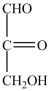
C)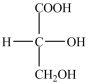
D)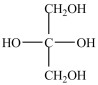
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which is not a glycosaminoglycan?
A)hyaluronate
B)chitin
C)heparin
D)chondroitin
A)hyaluronate
B)chitin
C)heparin
D)chondroitin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The monosaccharide shown below is an anomer. 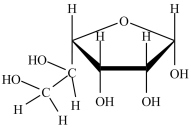


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Gentobiose, a rare disaccharide found in saffron, produces two identical monosaccharides when it undergoes hydrolysis. What is the identity of the hydrolysis product? 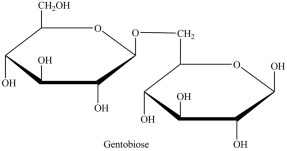
A)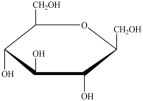
B)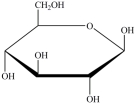
C)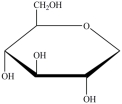
D)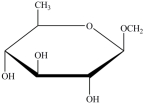

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Fischer projections of two monosaccharides are shown below. Which term best describes the relationship between the two? 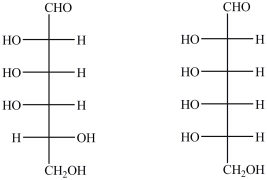
A)enantiomers
B)anomers
C)constitutional isomers
D)diastereomers

A)enantiomers
B)anomers
C)constitutional isomers
D)diastereomers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which statement concerning carbohydrates is incorrect?
A)Carbohydrates serve important energy and structural roles for both plants and animals.
B)Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and are known as simple sugars.
C)Humans store excess glucose for short term energy requirements in the polysaccharide cellulose.
D)Carbohydrates that can be oxidized by Benedict's reagent are called reducing sugars.
A)Carbohydrates serve important energy and structural roles for both plants and animals.
B)Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and are known as simple sugars.
C)Humans store excess glucose for short term energy requirements in the polysaccharide cellulose.
D)Carbohydrates that can be oxidized by Benedict's reagent are called reducing sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The monosaccharide shown below is an anomer. 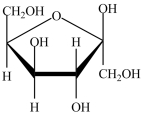


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The anomer of a cyclic monosaccharide has the -OH group drawn down, below the ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
At equilibrium, a solution of glucose in water is an equal mixture of the anomer, the anomer, and the acyclic aldehyde.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A hemiacetal is a compound that contains a hydroxyl group (-OH)and an alkoxy group (-OR)on adjacent carbon atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Carbohydrates that are oxidized with Benedict's reagent are called reducing sugars, because they reduce the Cu2+ in Benedict's reagent to Cu+ during the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An glycoside has the glycosidic linkage oriented down, below the plane of the ring that contains the acetal joining the monosaccharides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An alditol contains an -OH group on every carbon atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The carbonyl group of an aldose is reduced to a secondary alcohol using hydrogen (H2)in the presence of palladium (Pd)metal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When a monosaccharide forms a cyclic hemiacetal, the carbon atom that is part of the hemiacetal is a new chirality center, called the anomeric carbon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
All disaccharides contain at least one acetal that joins the rings together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Certain monosaccharides-notably aldopentoses and ketohexoses-form five-membered rings, not six-membered rings, in solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Melibiose is a carbohydrate found in some plant juices. Which statement concerning melibiose is incorrect? 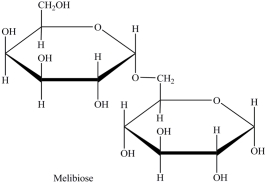
A)It is a disaccharide.
B)It is composed of two different monosaccharides.
C)It contains both an acetal and a hemiacetal.
D)It contains a 1 5- -glycosidic linkage.

A)It is a disaccharide.
B)It is composed of two different monosaccharides.
C)It contains both an acetal and a hemiacetal.
D)It contains a 1 5- -glycosidic linkage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
All aldoses and ketoses are reducing sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Modern glucose meters are electronic devices that measure the amount of oxidizing agent that reacts with the glucose in a known amount of blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is not a term that would properly describe glucose as it is shown below? 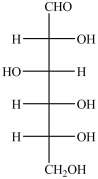
A)monosaccharide
B)aldohexose
C)reducing sugar
D) -D-glucose

A)monosaccharide
B)aldohexose
C)reducing sugar
D) -D-glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Test strips that contain the enzyme lactase are used to measure glucose concentration in urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The conversion of D-ribose to L-ribose is an example of mutarotation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
-D-galactose and -D-galactose are enantiomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In aldohexoses, it is the -OH group on C5 that reacts with the aldehyde carbonyl to form two cyclic hemiacetals called anomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Monosaccharides are polar compounds with low melting points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Carbohydrates are chiral biomolecules. The term chiral indicates that carbohydrates can be both synthesized and digested by the human body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Carbohydrates serve important energy and structural roles for both plants and animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the disaccharide structure shown, the anomeric carbons are properly labeled. 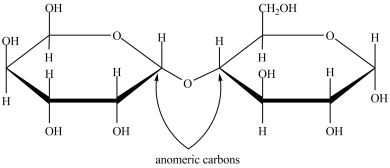


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Monosaccharides with a carbonyl group at C2 are called ketoses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The two compounds N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine are a set of constitutional isomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Cellulose is a highly branched polymer composed of repeating glucose units joined in a 1 4- -glycosidic linkage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In addition to the three monosaccharides that occur in all blood types, type A blood contains the monosaccharide N-acetyl-D-galactosamine, and type B blood contains an additional D-galactose unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Carbohydrates are structurally defined as polyhydroxyaldehydes and polyhydroxyketones, or compounds that can be hydrolyzed to them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The disaccharide shown below has an -glycosidic linkage. 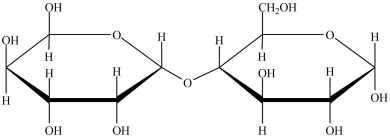


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Disaccharides contain two carbonyl groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Glucose and other naturally occurring sugars are D sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Maltose is a reducing sugar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Individuals with type AB blood are called universal recipients because their blood contains no antibodies to blood types A, B, or O. Individuals with type AB blood can receive blood of any type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The structure shown has four (4)chirality centers and is a D monosaccharide. 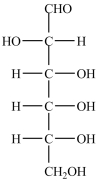


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Hydrolysis of the disaccharide below yields the indicated products. 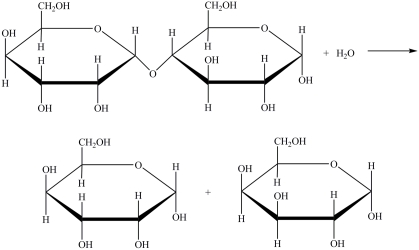


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When the monosaccharide below is oxidized by Benedict's reagent, the indicated product results. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



