Deck 12: The Government Budget, the Public Debt, and Social Security
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/106
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: The Government Budget, the Public Debt, and Social Security
1
The return to government deficit after 2001 was due to:
A) drop in the government revenues
B) both revenue drop and expenditure rise
C) rise in the government expenditure
D) after 2001, US government did not experience budget deficit
A) drop in the government revenues
B) both revenue drop and expenditure rise
C) rise in the government expenditure
D) after 2001, US government did not experience budget deficit
drop in the government revenues
2
Savings in the United States is "too low" if
A) the rate of return on investment exceeds the rate of time preference.
B) the rate of return on investment is less than the rate of time preference.
C) per capita capital is growing faster than population growth.
D) None of the above.
A) the rate of return on investment exceeds the rate of time preference.
B) the rate of return on investment is less than the rate of time preference.
C) per capita capital is growing faster than population growth.
D) None of the above.
the rate of return on investment exceeds the rate of time preference.
3
A cut in income taxes tends to
A) temporarily shift the short-run Phillips Curve and to permanently increase aggregate demand.
B) permanently shift the short-run Phillips Curve and to temporarily increase aggregate demand.
C) temporarily shift both the short-run Phillips Curve and aggregate nominal demand.
D) permanently shift both the short-run Phillips Curve and aggregate demand.
A) temporarily shift the short-run Phillips Curve and to permanently increase aggregate demand.
B) permanently shift the short-run Phillips Curve and to temporarily increase aggregate demand.
C) temporarily shift both the short-run Phillips Curve and aggregate nominal demand.
D) permanently shift both the short-run Phillips Curve and aggregate demand.
temporarily shift both the short-run Phillips Curve and aggregate nominal demand.
4
The tax cuts in 1981 and 1982 did not lead to growth in GDP as did the tax cuts in 1964. One reason for this difference was that
A) the 1981-82 tax cuts concentrated on personal tax cuts, but the 1964 cuts were for both personal and corporate taxpayers.
B) the saving rate increased in 1981-82, but it decreased in 1964.
C) expansionary monetary policy accompanied the 1964 tax cuts, but the 1981-82 cuts were accompanied by restrictive monetary policy.
D) tax indexation was built into the 1981-82 tax-cut program, but in 1964 there was no indexation.
A) the 1981-82 tax cuts concentrated on personal tax cuts, but the 1964 cuts were for both personal and corporate taxpayers.
B) the saving rate increased in 1981-82, but it decreased in 1964.
C) expansionary monetary policy accompanied the 1964 tax cuts, but the 1981-82 cuts were accompanied by restrictive monetary policy.
D) tax indexation was built into the 1981-82 tax-cut program, but in 1964 there was no indexation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Supply siders argue that policies pursued by the Reagan administration after 1981 undermined the effect of the 1981 tax cuts. Which of the following policies has been cited by supply siders?
A) Some of the incentives to business investment were reversed.
B) The minimum wage was increased.
C) Government expenditures decreased along with the decrease in revenues.
D) Trade protectionist legislation was passed.
A) Some of the incentives to business investment were reversed.
B) The minimum wage was increased.
C) Government expenditures decreased along with the decrease in revenues.
D) Trade protectionist legislation was passed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Private savings and thus investment could be increased by which of the following government policies, ceteris paribus?
A) elimination of the corporate income tax
B) allowing corporations to use "replacement cost accounting"
C) exemption of interest earnings from income taxation
D) All of the above.
A) elimination of the corporate income tax
B) allowing corporations to use "replacement cost accounting"
C) exemption of interest earnings from income taxation
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If monetary policy is used to control real GDP then fiscal policy is a major determinant of
A) interest rates and economic growth.
B) interest rates and the foreign trade deficit.
C) unemployment and the foreign exchange rate.
D) None of the above.
A) interest rates and economic growth.
B) interest rates and the foreign trade deficit.
C) unemployment and the foreign exchange rate.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following policies would NOT affect the natural unemployment rate?
A) a reduction in minimum wages
B) an increase in public-service employment
C) an increase in subsidized private employment
D) a reduction sales taxes
A) a reduction in minimum wages
B) an increase in public-service employment
C) an increase in subsidized private employment
D) a reduction sales taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements is NOT part of supply-side theory?
A) Income taxes reduce the after-tax reward to work and saving.
B) Capital gains should be indexed so that only real gains, and not nominal gains, are taxed.
C) An increase in the after-tax reward to work and saving would create a significant increase in the amount of work and saving.
D) After cutting taxes, the federal government would collect more revenue than before the tax cuts.
A) Income taxes reduce the after-tax reward to work and saving.
B) Capital gains should be indexed so that only real gains, and not nominal gains, are taxed.
C) An increase in the after-tax reward to work and saving would create a significant increase in the amount of work and saving.
D) After cutting taxes, the federal government would collect more revenue than before the tax cuts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A falling natural-employment deficit indicates that
A) the growth rate in the economy has increased.
B) the government is following a restrictive fiscal policy.
C) the government is following an expansionary fiscal policy.
D) the actual surplus is rising.
A) the growth rate in the economy has increased.
B) the government is following a restrictive fiscal policy.
C) the government is following an expansionary fiscal policy.
D) the actual surplus is rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A decrease in deficit spending or an increase in the government surplus will lead to
A) accelerated economic growth if the money supply is increased to stabilize the output ratio.
B) accelerated economic growth if the money supply is decreased to stabilize the output ratio.
C) a recession if the money supply is increased to stabilize the output ratio.
D) a recession if the money supply grows at a fixed rate.
A) accelerated economic growth if the money supply is increased to stabilize the output ratio.
B) accelerated economic growth if the money supply is decreased to stabilize the output ratio.
C) a recession if the money supply is increased to stabilize the output ratio.
D) a recession if the money supply grows at a fixed rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Supply side economists believe that decreases in marginal tax rates will lead to revenue increases because
A) after tax incomes will increase as will work effort and saving.
B) a rightward shift in SAS will force people into higher tax brackets.
C) a leftward shift of LAS will mean more revenue per unit of output.
D) None of the above
A) after tax incomes will increase as will work effort and saving.
B) a rightward shift in SAS will force people into higher tax brackets.
C) a leftward shift of LAS will mean more revenue per unit of output.
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A major side-effect of a stimulative fiscal policy is that it will
A) discriminate in favor of housing.
B) crowd out private expenditures.
C) increase the natural rate of unemployment.
D) permanently raise the rate of inflation.
A) discriminate in favor of housing.
B) crowd out private expenditures.
C) increase the natural rate of unemployment.
D) permanently raise the rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a society's rate of time preference increases, as may have occurred in the United States during the 1970s, then, ceteris paribus, per capita
A) current consumption increases, future consumption decreases and economic growth accelerates in the long run.
B) current consumption decreases, future consumption increases and economic growth decelerates in the short run.
C) current consumption increases, future consumption decreases and economic growth decelerates in the long run.
D) current consumption increases, future consumption decreases and economic growth stabilizes in the long run.
A) current consumption increases, future consumption decreases and economic growth accelerates in the long run.
B) current consumption decreases, future consumption increases and economic growth decelerates in the short run.
C) current consumption increases, future consumption decreases and economic growth decelerates in the long run.
D) current consumption increases, future consumption decreases and economic growth stabilizes in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following beliefs is not part of supply-side economics?
A) A sharp reduction in personal income taxes would bring forth higher labor-force participation.
B) A sharp reduction in personal income taxes would bring forth a higher capital stock through greater saving and investment.
C) A reduction in tax rates would lead to increased output and actually allow tax revenues to rise.
D) A sharp reduction in corporate income taxes would discourage U.S. corporations from shifting their production facilities to other countries, thus leading to a decrease in the unemployment rate.
A) A sharp reduction in personal income taxes would bring forth higher labor-force participation.
B) A sharp reduction in personal income taxes would bring forth a higher capital stock through greater saving and investment.
C) A reduction in tax rates would lead to increased output and actually allow tax revenues to rise.
D) A sharp reduction in corporate income taxes would discourage U.S. corporations from shifting their production facilities to other countries, thus leading to a decrease in the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A greater reduction in the government's deficit spending would stimulate investment if it were achieved by which of the following changes, ceteris paribus?
A) an increase in the income tax rate on interest payments
B) a decrease in the income tax rate on transfer payments
C) an increase in sales taxes on consumption goods
D) a decrease in sales taxes on consumption goods
A) an increase in the income tax rate on interest payments
B) a decrease in the income tax rate on transfer payments
C) an increase in sales taxes on consumption goods
D) a decrease in sales taxes on consumption goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
"Economists have generally come to agree that monetary policy is better suited than fiscal policy for controlling GDP" because
A) money is neutral and therefore changes affect real income but not prices.
B) fiscal spending and tax changes affect the economy less than changes in the money supply.
C) the Fed can make decisions quickly, Congress and the President more slowly.
D) Congress can make decisions quickly, the Fed more slowly.
A) money is neutral and therefore changes affect real income but not prices.
B) fiscal spending and tax changes affect the economy less than changes in the money supply.
C) the Fed can make decisions quickly, Congress and the President more slowly.
D) Congress can make decisions quickly, the Fed more slowly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Once monetary policy is dedicated to controlling the level of nominal GDP, then fiscal policy can be used to
A) choose the overall level of interest rates, with a high budget surplus implying a high level of interest rates.
B) choose the overall level of interest rates, with a high budget deficit implying a high level of interest rates.
C) control the level of inflation, with a high budget surplus implying a faster rate of inflation.
D) control the level of inflation, with a high budget deficit implying a faster rate of inflation.
A) choose the overall level of interest rates, with a high budget surplus implying a high level of interest rates.
B) choose the overall level of interest rates, with a high budget deficit implying a high level of interest rates.
C) control the level of inflation, with a high budget surplus implying a faster rate of inflation.
D) control the level of inflation, with a high budget deficit implying a faster rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a society's rate of time preference increases, as may have occurred in the United States during the 1970s, then, ceteris paribus, per capita
A) private savings increase.
B) private savings decrease.
C) personal consumption decreases.
D) B and C are both correct.
A) private savings increase.
B) private savings decrease.
C) personal consumption decreases.
D) B and C are both correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The government can meet its interest bill without having to levy taxes if it issues more bonds and if the
A) economy's real growth rate of output is greater than the real interest rate.
B) economy's real growth rate of output is equal to the nominal interest rate.
C) economy's real growth rate of output equals or exceeds its real interest rate.
D) economy's nominal growth rate of output equals or exceeds its real interest rate.
A) economy's real growth rate of output is greater than the real interest rate.
B) economy's real growth rate of output is equal to the nominal interest rate.
C) economy's real growth rate of output equals or exceeds its real interest rate.
D) economy's nominal growth rate of output equals or exceeds its real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Government debt which pays for ________ is a burden in that it yields no ________ benefits.
A) hospitals, future
B) ammunition for military target practice, current
C) Social Security benefits, future
D) public universities, current
A) hospitals, future
B) ammunition for military target practice, current
C) Social Security benefits, future
D) public universities, current

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the economy is growing 3% a year and the government increases the ratio of interest on the national debt to GDP, we may conclude that
A) the output ratio will fall.
B) additional interest payments exceed 3% of GDP.
C) tax revenues will fall.
D) the Laffer curve will be inoperable.
A) the output ratio will fall.
B) additional interest payments exceed 3% of GDP.
C) tax revenues will fall.
D) the Laffer curve will be inoperable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A true and unambiguous burden on future generations will be created whenever government deficit spending
A) increases the ratio of government expenditure to GDP.
B) pays for goods that yield no future benefits.
C) is used as part of a countercyclical fiscal expansion.
D) pays for capital expenditures.
A) increases the ratio of government expenditure to GDP.
B) pays for goods that yield no future benefits.
C) is used as part of a countercyclical fiscal expansion.
D) pays for capital expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
We may conclude if our present path in the figure above is C, that
A) from t0 to t1 policies may be adopted to lower savings.
B) from t0 to t1 policies may be adopted to raise savings.
C) prior to t0 policies may be adopted to lower savings.
D) after t1 policies may be adopted to increase savings.
A) from t0 to t1 policies may be adopted to lower savings.
B) from t0 to t1 policies may be adopted to raise savings.
C) prior to t0 policies may be adopted to lower savings.
D) after t1 policies may be adopted to increase savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A country saves too little if
A) its rate of time preference is greater than the national rate of return on investment.
B) its rate of time preference is less than the national rate of return on investment.
C) its rate of investment is less than the real interest rate.
D) its rate of investment is less than the nominal interest rate.
A) its rate of time preference is greater than the national rate of return on investment.
B) its rate of time preference is less than the national rate of return on investment.
C) its rate of investment is less than the real interest rate.
D) its rate of investment is less than the nominal interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The argument that households will increase savings to pay increases in future taxes which result from a tax cut financed from deficit spending
A) assumes that people do not budget bequests for their children.
B) is a new Keynesian argument.
C) is the Barro-Ricardo equivalence theorem.
D) was proved by data in the 1980s.
A) assumes that people do not budget bequests for their children.
B) is a new Keynesian argument.
C) is the Barro-Ricardo equivalence theorem.
D) was proved by data in the 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is least likely to increase the ratio of investment to real GDP? A reduction in ________.
A) transfer payments
B) subsidies to farms and corporations
C) defense outlays
D) spending on highways
A) transfer payments
B) subsidies to farms and corporations
C) defense outlays
D) spending on highways

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The conditions for joining the "Euro" single-currency block led a number of European countries to ________ and consequently reduce their debt-GDP ratios.
A) tighten monetary policy
B) loosen monetary policy
C) loosen fiscal policy
D) tighten fiscal policy
A) tighten monetary policy
B) loosen monetary policy
C) loosen fiscal policy
D) tighten fiscal policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the inflation rate is 7 percent, real GDP growth is 2 percent, and the current budget deficit is $100 billion, what must the current national debt be if the debt-GDP ratio is to remain the same?
A) $1,111 billion
B) $2,000 billion
C) $1,429 billion
D) $5,000 billion
A) $1,111 billion
B) $2,000 billion
C) $1,429 billion
D) $5,000 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Society's rate of time preference refers to
A) the preference people have for leisure compared to working.
B) the rate at which corporations can depreciate "preferred" capital goods.
C) the extra amount people would be willing to pay to have consumption now instead of in the future.
D) the preferred rate of economic growth.
A) the preference people have for leisure compared to working.
B) the rate at which corporations can depreciate "preferred" capital goods.
C) the extra amount people would be willing to pay to have consumption now instead of in the future.
D) the preferred rate of economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The national debt must eventually be paid off to
A) ourselves, which implies we collectively can expect an increase in income in the future.
B) the government, which implies additional revenue to the government in the future.
C) foreigners, which means a loss of freedom in the future.
D) no one, as long as there is confidence in the continuing viability of the government's taxing powers.
A) ourselves, which implies we collectively can expect an increase in income in the future.
B) the government, which implies additional revenue to the government in the future.
C) foreigners, which means a loss of freedom in the future.
D) no one, as long as there is confidence in the continuing viability of the government's taxing powers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Over a decade or longer, a government budget deficit
A) reduces national saving and stimulates economic growth.
B) reduces national saving and economic growth.
C) increases national saving and economic growth.
D) increases national saving and decreases economic growth.
A) reduces national saving and stimulates economic growth.
B) reduces national saving and economic growth.
C) increases national saving and economic growth.
D) increases national saving and decreases economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
"In the 1980's the pain which results from a large government deficit was deferred, placed on future taxpayers since foreigners loaned money to the government to pay the debt." Gordon suggests that this "pain" maybe deferred forever if
A) the government uses the "deficit funds" to provide taxpayers increased future benefits from which to pay the interest to foreigners.
B) monetary policy is tighter in the future.
C) fiscal policy is tighter in the future.
D) B and C are correct.
A) the government uses the "deficit funds" to provide taxpayers increased future benefits from which to pay the interest to foreigners.
B) monetary policy is tighter in the future.
C) fiscal policy is tighter in the future.
D) B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the economy is growing 5% a year and GDP is $1000 billion, the additional revenues available to meet interest payments on the government deficit would be, ceteris paribus,
A) 50.
B) 500.
C) it depends upon the amount of new debt issued.
D) there would be no additional revenues.
A) 50.
B) 500.
C) it depends upon the amount of new debt issued.
D) there would be no additional revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the country in the figure above
A) imposes a consumption tax at t1 its consumption path will be C'.
B) imposes a higher tax at to pay for Social Security, its consumption path will be C'.
C) imposes a consumption tax at to its consumption path will be C'.
D) none of the above.
A) imposes a consumption tax at t1 its consumption path will be C'.
B) imposes a higher tax at to pay for Social Security, its consumption path will be C'.
C) imposes a consumption tax at to its consumption path will be C'.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Government debt places a burden on future generations if
A) the debt is used to fund the current consumption of its citizens.
B) the debt is used to fund the production of investment goods.
C) the debt is used to fund schools and highways.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) the debt is used to fund the current consumption of its citizens.
B) the debt is used to fund the production of investment goods.
C) the debt is used to fund schools and highways.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 12-2, below, displays two time paths of consumption, C and 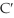 , which may characterize a country according to its growth policies.
, which may characterize a country according to its growth policies.
Figure 12-2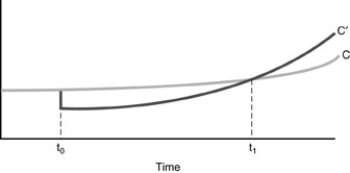
Referring to Figure above, we may conclude
A) Path C' represents the effects of a policy to lower savings from time to t1 forward.
B) Path C' represents the effects of a policy to lower savings from time t0 to t1.
C) Path C' represents the effects of a policy to lower savings from time t1 forward.
D) Path C' represents the effects of a policy to lower savings from time to t1.
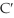 , which may characterize a country according to its growth policies.
, which may characterize a country according to its growth policies.Figure 12-2

Referring to Figure above, we may conclude
A) Path C' represents the effects of a policy to lower savings from time to t1 forward.
B) Path C' represents the effects of a policy to lower savings from time t0 to t1.
C) Path C' represents the effects of a policy to lower savings from time t1 forward.
D) Path C' represents the effects of a policy to lower savings from time to t1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following policies is likely to generate the smallest increase in national saving?
A) an increase in income taxes
B) an increase in consumption taxes
C) a cut in government transfer payments
D) None of the above policies will increase national saving.
A) an increase in income taxes
B) an increase in consumption taxes
C) a cut in government transfer payments
D) None of the above policies will increase national saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
National saving is
A) the sum of private saving and government saving.
B) reduced by government budget deficits.
C) the sum of private saving and the government budget deficit or surplus.
D) all of the above.
A) the sum of private saving and government saving.
B) reduced by government budget deficits.
C) the sum of private saving and the government budget deficit or surplus.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Gordon reports that during the Reagan administration the increase in spending as a percent of GDP, was primarily attributable to
A) increases in military spending.
B) increases in general administrative expenses.
C) increases in agricultural subsidy expenditures.
D) increases in Social Security and medicare expenditures.
A) increases in military spending.
B) increases in general administrative expenses.
C) increases in agricultural subsidy expenditures.
D) increases in Social Security and medicare expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
From 1981 till 1995 the ratio of revenue to GDP was around:
A) 19.8%.
B) 21.5%.
C) 18%.
D) 3.5%.
A) 19.8%.
B) 21.5%.
C) 18%.
D) 3.5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Between 1995 and 1998 Federal tax revenues from ________ increased sharply.
A) the personal income tax
B) the corporate profits tax
C) social insurance taxes
D) All of the above.
A) the personal income tax
B) the corporate profits tax
C) social insurance taxes
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is not an expected consequence of balancing the federal government's budget?
A) increased private investment
B) increased borrowing from foreigners
C) reduced interest payment to foreigners
D) B and C.
A) increased private investment
B) increased borrowing from foreigners
C) reduced interest payment to foreigners
D) B and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Changes in tax laws in 1993
A) reduced Federal revenues by making the tax code more regressive.
B) reduced Federal revenues by making the tax code more progressive.
C) increased Federal revenues by making the tax code more regressive.
D) increased Federal revenues by making the tax code more progressive.
A) reduced Federal revenues by making the tax code more regressive.
B) reduced Federal revenues by making the tax code more progressive.
C) increased Federal revenues by making the tax code more regressive.
D) increased Federal revenues by making the tax code more progressive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The debt-GDP ratio
A) fell sharply after 1997 due to a high output ratio and higher income tax rates.
B) rose from 1981-1992 due to large budget deficits.
C) began to decline in 1993.
D) all of the above.
A) fell sharply after 1997 due to a high output ratio and higher income tax rates.
B) rose from 1981-1992 due to large budget deficits.
C) began to decline in 1993.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The debt-GDP ratio was lower in 1997 than it was during
A) the Civil War.
B) World War I.
C) World War II.
D) all of the above.
A) the Civil War.
B) World War I.
C) World War II.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A sharp reduction in the U.S. debt-GDP ratio occurred
A) between 1998 and 2001 .
B) between 1996 and 1997.
C) between 1994 and 1995.
D) between 1993 and 1995.
A) between 1998 and 2001 .
B) between 1996 and 1997.
C) between 1994 and 1995.
D) between 1993 and 1995.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
From 1968 till 1980, budget deficit was on average around ________ percent of natural GDP; and from 1981 till 1995 it was ________ percent of natural GDP.
A) 19.8; 21.5
B) 21.5; 19.8
C) 1.5; 3.5
D) 3.5; 1.5
A) 19.8; 21.5
B) 21.5; 19.8
C) 1.5; 3.5
D) 3.5; 1.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the debate over U.S. federal budget deficits, the "pussycats" believe that
A) increased domestic private investment requires a cut in the deficit.
B) borrowing form foreigners in the 1980s was a sign of economic strength.
C) deficits create political pressure to slow the growth of government spending programs.
D) a sizeable deficit cannot be tolerated.
A) increased domestic private investment requires a cut in the deficit.
B) borrowing form foreigners in the 1980s was a sign of economic strength.
C) deficits create political pressure to slow the growth of government spending programs.
D) a sizeable deficit cannot be tolerated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
During 1998-2001 the government budget
A) moved deeper into deficit and caused a substantial increase in borrowing from foreign investors.
B) moved into surplus but the beneficial effect was largely offset by a drop in household saving.
C) was balanced and the inflow of capital from foreign lenders was finally stopped.
D) moved into surplus and resulted in large capital outflows from the United States.
A) moved deeper into deficit and caused a substantial increase in borrowing from foreign investors.
B) moved into surplus but the beneficial effect was largely offset by a drop in household saving.
C) was balanced and the inflow of capital from foreign lenders was finally stopped.
D) moved into surplus and resulted in large capital outflows from the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Return to deficit after 2001 was due to:
A) a drop in the revenue share
B) an increase in the expenditure share
C) both a drop in the revenue share and an increase in the expenditure share
D) due to recession
A) a drop in the revenue share
B) an increase in the expenditure share
C) both a drop in the revenue share and an increase in the expenditure share
D) due to recession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Society's rate of time preference is
A) the extra amount people would be willing to pay to have consumption goods in the future instead of now.
B) the value that people place on the time saved by purchasing capital goods rather than consumer goods.
C) the extra amount people would be willing to pay to have consumption goods now instead of the future.
D) is negative if people prefer present consumption to future consumption.
A) the extra amount people would be willing to pay to have consumption goods in the future instead of now.
B) the value that people place on the time saved by purchasing capital goods rather than consumer goods.
C) the extra amount people would be willing to pay to have consumption goods now instead of the future.
D) is negative if people prefer present consumption to future consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the period from 1990 to 1994, which of the following countries experienced a drop in national debt as percentage of GDP?
A) Italy
B) United States
C) Germany
D) none of the above
A) Italy
B) United States
C) Germany
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the IS-LM model, we can be at natural real GDP with a low interest rate given the combination of ________ fiscal policy and ________ monetary policy.
A) tight, tight
B) tight, easy
C) easy, tight
D) easy, easy
A) tight, tight
B) tight, easy
C) easy, tight
D) easy, easy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following contributed to the sharp increase in Federal tax revenues between 1995 and 2001?
A) An increase in income tax rates.
B) A sustained economic expansion.
C) Increased income inequality.
D) All of the above.
A) An increase in income tax rates.
B) A sustained economic expansion.
C) Increased income inequality.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The gap between Federal expenditures and Federal revenues after 1980 was caused primarily by
A) the recessions which occurred in the 1980s.
B) a substantial decrease in Federal revenues.
C) a substantial increase in Federal expenditures.
D) rising interest rates which made caused investment and growth to collapse.
A) the recessions which occurred in the 1980s.
B) a substantial decrease in Federal revenues.
C) a substantial increase in Federal expenditures.
D) rising interest rates which made caused investment and growth to collapse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
As it is currently calculated, Gordon thinks that national saving is
A) overstated.
B) understated.
C) accurately measured.
D) so ambiguous that it is impossible to say in what direction its inaccuracies lie.
A) overstated.
B) understated.
C) accurately measured.
D) so ambiguous that it is impossible to say in what direction its inaccuracies lie.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The IS-LM model tells us that output remains constant when a tax cut is combined with ________ in the money supply, with the interest rate ________ its initial level.
A) an increase, rising above
B) an increase, falling below
C) a decrease, rising above
D) a decrease, falling below
A) an increase, rising above
B) an increase, falling below
C) a decrease, rising above
D) a decrease, falling below

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Persistent deficit after 1980 was almost entirely due to:
A) higher share of expenditures in GDP.
B) lower tax revenue.
C) lower share of expenditures in GDP.
D) Higher tax revenue.
A) higher share of expenditures in GDP.
B) lower tax revenue.
C) lower share of expenditures in GDP.
D) Higher tax revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Suppose the economy is at the natural real GDP. Changing macroeconomic policy to lower the interest rate while not affecting output means shifting the IS curve to the ________ and the LM curve to the ________.
A) right, right
B) right, left
C) left, right
D) left, left
A) right, right
B) right, left
C) left, right
D) left, left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
To raise economic growth, a tighter fiscal policy should be accompanied by a ________ money supply in order to keep the ________ from falling.
A) larger, output ratio
B) larger, real interest rate
C) smaller, output ratio
D) smaller, real interest rate
A) larger, output ratio
B) larger, real interest rate
C) smaller, output ratio
D) smaller, real interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the United States it is clear that if a dollar were diverted from present consumption to present investment, the return on that investment would be ________ to reward the deferral of consumption, meaning that overall economic welfare would rise with ________ in national saving.
A) insufficient, an increase
B) insufficient, a decrease
C) more than sufficient, an increase
D) more than sufficient, a decrease
A) insufficient, an increase
B) insufficient, a decrease
C) more than sufficient, an increase
D) more than sufficient, a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The government deficit does not place a burden on future generations when
A) taxes are eventually raised to pay interest on the additional debt.
B) the borrowed funds are used for productive government investment.
C) borrowing from foreigners offsets the deficit, so that private investment is not crowded-out.
D) the borrowed funds are transferred to the purchase of nondurable consumer goods.
A) taxes are eventually raised to pay interest on the additional debt.
B) the borrowed funds are used for productive government investment.
C) borrowing from foreigners offsets the deficit, so that private investment is not crowded-out.
D) the borrowed funds are transferred to the purchase of nondurable consumer goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
With inflation of 5 percent, real GDP growth of 3 percent, and an outstanding national debt of $3400 billion, the "allowable deficit" that holds the debt-GDP ratio constant is
A) $272 billion.
B) $68 billion.
C) $170 billion.
D) $175.1 billion.
E) $510 billion.
A) $272 billion.
B) $68 billion.
C) $170 billion.
D) $175.1 billion.
E) $510 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Evidence shows that the rate of return on private investment in the United States is ________ the rate of time preference, meaning that there is too ________ saving and too ________ current consumption.
A) above, much, little
B) above, little, much
C) below, much, little
D) below, much, much
E) below, little, little
A) above, much, little
B) above, little, much
C) below, much, little
D) below, much, much
E) below, little, little

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A change in corporate tax law such that depreciation is based on current replacement cost would ________ government saving and probably ________ private business saving.
A) increase, increase
B) increase, decrease
C) decrease, increase
D) decrease, decrease
A) increase, increase
B) increase, decrease
C) decrease, increase
D) decrease, decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the U.S. government sells bonds to fund improvements in infrastructure, and the bonds are bought by foreigners, the burden on future U.S. taxpayers
A) is not increased so long as the return on the improvements is at or above the borrowing cost.
B) is not increased so long as the return on the improvements is below the borrowing cost.
C) is not increased so long as the return on the improvements is above zero.
D) is increased regardless of the borrowing cost and the return on the improvements.
A) is not increased so long as the return on the improvements is at or above the borrowing cost.
B) is not increased so long as the return on the improvements is below the borrowing cost.
C) is not increased so long as the return on the improvements is above zero.
D) is increased regardless of the borrowing cost and the return on the improvements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose that interest income is exempted from taxation, which costs the Treasury $100 billion in tax revenues, while at the same time transfer payments are reduced by $100 billion. Together, these two changes in fiscal policy ________ national saving while moving the distribution of income toward greater ________ .
A) reduce, equality
B) reduce, inequality
C) increase, equality
D) increase, inequality
E) do not affect, equality
A) reduce, equality
B) reduce, inequality
C) increase, equality
D) increase, inequality
E) do not affect, equality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A fiscal policy designed for maximum stimulus of economic growth must discourage current ________ and thus makes for, at least in the short run, a ________ even income distribution.
A) consumption, less
B) consumption, more
C) private saving, less
D) private saving, more
A) consumption, less
B) consumption, more
C) private saving, less
D) private saving, more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose the government borrows to purchase military ammunition which is immediately used up in target practice. The rate of return on this investment is ________, and in this case the government debt ________ a burden on future taxpayers.
A) r, is not
B) r, is
C) 0, is not
D) -r, is not
E) -r, is
A) r, is not
B) r, is
C) 0, is not
D) -r, is not
E) -r, is

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Elimination of the corporate income tax would ________ government saving and probably ________ private business saving.
A) increase, increase
B) increase, decrease
C) decrease, increase
D) decrease, decrease
A) increase, increase
B) increase, decrease
C) decrease, increase
D) decrease, decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When the rate of return on the last dollar of investment is below the rate of time preference, an economy is currently investing too ________ and consuming too ________.
A) much, much
B) much, little
C) little, much
D) little, little
A) much, much
B) much, little
C) little, much
D) little, little

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the federal government borrows to build a new dam in North Dakota with a rate of return above the borrowing rate, and later raises federal income taxes to pay the interest, future welfare in the United States is
A) redistributed and lowered overall.
B) redistributed but not lowered overall.
C) not redistributed but lowered overall.
D) not redistributed and not lowered overall.
A) redistributed and lowered overall.
B) redistributed but not lowered overall.
C) not redistributed but lowered overall.
D) not redistributed and not lowered overall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Government spending and taxation determine the position of the ________ curve and, where that curve intersects the vertical line at YN, the ________ target of monetary policy.
A) IS, inflation rate
B) IS, real interest rate
C) LM, inflation rate
D) LM, real interest rate
A) IS, inflation rate
B) IS, real interest rate
C) LM, inflation rate
D) LM, real interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose that a change in the fiscal/monetary policy mix shifts the IS and LM curves downward by exactly the same amount. The ________ in national saving is accompanied by ________ domestic investment due to the ________ in the interest rate.
A) fall, equally lower, lower
B) fall, unchanged, unchanged
C) rise, unchanged, unchanged
D) rise, equally higher, lower
E) rise, equally lower, higher
A) fall, equally lower, lower
B) fall, unchanged, unchanged
C) rise, unchanged, unchanged
D) rise, equally higher, lower
E) rise, equally lower, higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If a teenager is willing to pay up to $208 to get a bicycle today rather than waiting a year for it and paying $200, her "rate of time preference" must be
A) $8.
B) 8 percent.
C) 4 percent.
D) -4 percent.
E) -8 percent.
A) $8.
B) 8 percent.
C) 4 percent.
D) -4 percent.
E) -8 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The "allowable deficit" that causes no change in the debt-GDP ratio is equal to the ________ times ________.
A) interest rate, outstanding national debt
B) interest rate, nominal GDP
C) rate of nominal GDP growth, outstanding national debt
D) rate of nominal GDP growth, nominal GDP
A) interest rate, outstanding national debt
B) interest rate, nominal GDP
C) rate of nominal GDP growth, outstanding national debt
D) rate of nominal GDP growth, nominal GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Borrowing to fund investment projects until the marginal rate of return falls to ________ is optimizing investment strategy for ________.
A) the borrowing rate, businesses and governments
B) the borrowing rate, businesses but not governments
C) the borrowing rate, governments but not businesses
D) zero, businesses and governments
E) zero, governments but not businesses
A) the borrowing rate, businesses and governments
B) the borrowing rate, businesses but not governments
C) the borrowing rate, governments but not businesses
D) zero, businesses and governments
E) zero, governments but not businesses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When the rate of return on the last dollar of investment is above the rate of time preference, an economy is currently investing too ________ and saving too ________.
A) much, much
B) much, little
C) little, much
D) little, little
A) much, much
B) much, little
C) little, much
D) little, little

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A growing consensus among economists is that ________ policy is better suited for controlling GDP because of the promptness of ________ in making policy decisions.
A) monetary, the Federal Reserve
B) monetary, Congress
C) fiscal, the Federal Reserve
D) fiscal, Congress
A) monetary, the Federal Reserve
B) monetary, Congress
C) fiscal, the Federal Reserve
D) fiscal, Congress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



